Home / Devices
Back
Reading time: 4 min
0
2083
Welding technology using argon gives the master many possibilities. The argon arc method will help connect steels, alloys and carbon metals of any thickness.
But a welder who works for himself may not have the opportunity to buy a production machine for such welding: some doubt the manufacturers, others will not find a machine at the right price.
This problem can be solved in the same way as many other technological problems in welding - by making a device for the argon arc technique yourself from an inverter. It can replace simple factory models without being inferior to them in functionality and ease of use.
We will tell you the basics of assembling an argon apparatus.
- general information
- Assembling a homemade argon apparatus What to assemble from?
- About the current source
- About the oscillator and protection unit
- About the burner and gas
- About the reducer and hose
Operating principle
In order to understand what it is - TIG argon arc welding, you must have at least basic knowledge in the field of welding. TIG welding process technology was developed in 1841. The progress was that this made it possible to weld materials that had not previously been connected by this method.
The essence of the method is the burning of an electric arc in argon. This gas has a number of remarkable properties. Heavier than air, it penetrates the weld pool and protects it from other atmospheric gases. As a result, the seam is obtained without an oxide film. This contributes to good quality of metal joining. Argon is the most inexpensive welding shielding gas.
The main element is a tungsten electrode. Its melting point is almost 4000°C. This makes it possible to work with almost all types of steel. The tungsten electrode does not melt. It only requires periodic sharpening to ensure a precise and neat weld. The electrode located in the collet is fixed in the burner. Its excess length, inactive in operation, is located in a special cap, which prevents the possibility of short-circuiting.
The burner ends in a ceramic nozzle. An electrode runs along the center line of the nozzle, and there is an inert gas around it. When TIG welding, argon acts as an inert gas. Its presence prevents air from entering the weld pool, which would cause porosity in the weld during solidification. The start of argon is controlled by a button on the torch.
The electrode ignites an arc, and it melts the edges of the metals being welded. If there is a gap between the metal plates or the task is to create a seam with high tensile and fracture resistance, then filler wire is used. Its diameter is selected depending on the thickness of the product and the weld. In manual welding, the welder feeds the wire into the melting zone.
A high-quality seam is ensured by argon-assisted welding. This is accomplished by supplying shielding gas to the other side of the seam.
Argon arc welding with blowing has the following modes:
- auto;
- semi-automatic;
- manual.
In the first case, argon welding with blowing is carried out fully automatically. Laying out the trajectories along which the electrode and filler wire move is the function of the apparatus. In semi-automatic mode, the operator controls the welding using the machine, and the wire feeds automatically. In manual mode, the author of the process is the welder.
In manual argon arc welding, coated electrodes are not used, since the protection is an inert gas. The high temperature is provided by an electric arc. A coated electrode would not provide the required level of protection. In addition, hydrogen can accumulate in damp electrodes, which damages the quality of the seam.
Automatic argon arc welding works on the same principle as manual welding. The difference is that control occurs using automatic machines. The operator installs the necessary program, and the technical equipment begins to work according to the specified parameters. The automatic system also feeds the wire at the set speed.
Argon arc welding with a consumable electrode assumes that the arc is ignited when the electrode comes into contact with the metal. When non-consumable electrodes are used, this method is not applicable, since argon has a high ionization value and will require a strong spark for ignition. When using a tungsten electrode for ignition, you need an additional device - an oscillator. It produces a high frequency current for the ignition pulse. During the welding process, the oscillator generates pulses that stabilize the arc.
A high voltage with a high pulse frequency is applied to the electrode. This ensures ionization and ignition of the arc. The use of an oscillator allows the welder to safely carry out welding, both with alternating and direct currents.
The equipment can operate in different modes. Let's figure out what this is - TIG welding mode. For welding, two methods are used depending on the type of current: alternating or direct.
In TIG welding with alternating current, after ignition, the role of a stabilizing element that supplies pulses when changing the polarity of TIG welding is played by the oscillator. This guarantees the constancy of the arc.
During DC TIG welding, the heat generated at the anode and cathode is not the same. For better heating of the metal, a direct type of polarity is used, in which the plus is on the part and the minus is on the electrode. This TIG welding polarity is suitable for all alloys except aluminum. They require AC welding to remove surface oxide more effectively.
DC operation has the following advantages:
- Economical process.
- Possibility of welding at great depths. As a result, the seam becomes deep but narrow.
- Increasing the speed of the process.
When TIG welding with alternating current, pole change occurs automatically. Modes are selected depending on the metals being welded.
GENERAL INFORMATION
So, TIG (or argon arc) welding is a type of manual arc welding performed using an inert gas (which protects the welded area from oxidation) and a non-consumable electrode (mostly tungsten).
To perform the TIG welding process, you need a special welding machine. Typically, the manufacturer indicates information about the purposes for which the device is suitable in the product characteristics.
Simply put, the “TIG” mark on the equipment indicates that it is suitable for TIG welding.
The TIG machine allows the use of inert gas and tungsten electrodes to perform the work.
The principle of its operation is similar to an inverter for MMA welding (manual arc welding with a coated electrode) - the arc is also formed between the electrode and the metal. The only difference is the ability to supply gas to the welding zone.
In this case, the gas protects the metal from oxidation. The technology can use helium, a mixture of helium with argon, or pure argon. The last option is the most common (hence the name - argon arc welding).
Since with TIG the electrode does not form a weld, but only melts the edges and does not mix with the base metal, in some cases it is necessary to add a metal rod to the welding zone to form a seam.
TIG devices are common and budget-friendly. This facilitates their use in everyday life, for machine and body work. In addition, the devices are widely used in large-scale projects - in the assembly of ships, aircraft, missiles, etc.
Application
The advantages of TIG welding of metals find its application in the following industries:
- mechanical and instrument engineering;
- food production;
- oil industry;
- chemical industry;
- drilling rigs;
- construction of metal structures for high-rise buildings;
- steel frame structures;
- pipelines;
- aviation;
- astronautics;
- aircraft manufacturing;
- shipbuilding.
Argon TIG welding is also used for less global solutions. It is often used in domestic conditions. An example is installing an air conditioner in a car or repairing cracks in a car radiator. In all homes there are kitchen utensils and metal towel rails made using this method.
TIG argon welding has become so widespread due to the fact that it can be used to weld both carbon steel and non-ferrous metals, while maintaining excellent weld quality.
Shielding gas for TIG welding
Shielding gas protects the welding area from air. Argon/Ar and Helium/He can be used. Argon is most often used. Since these gases are inert, they do not change the characteristics of the weld. Three types of gas mixtures are less commonly used. The first is Argon and Hydrogen, the second is Argon and Nitrogen, the third is Argon and Helium. Argon mixed with Helium is used when welding thick metals for better penetration of the seam. Pure Argon works well for most welding applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The main advantages include:
- Displacement of air by argon from the area where welding occurs. Thanks to this, the seam is obtained without defects.
- Possibility of welding different metals.
- High quality seam.
- Low heating of parts, which eliminates their deformation.
- Working with metals that are difficult to weld.
- Ability to work with structures of different sizes.
- Fire safety.
- No waste.
- Isolation from the influence of the external environment.
- Electric arc stability.
- Versatility.
- Ability to work with thin metal sheets.
- Small heating zone of the product.
- Learning what TIG welding is is not difficult.
- Protecting the surface from oxide film.
- No need for additional processing after welding.
- Good control over the condition of the weld pool.
- Possibility of surfacing during restoration and restoration work.
- Possibility of using direct and reverse polarities.
- The compactness of the inverter with this function.
- Various TIG welding modes.
Disadvantages of the method:
- Low performance.
- Slow process speed.
- High cost of the equipment used.
- Availability of professional skills.
- Ineffective work in drafts or strong winds. It is necessary to install special shields and increase the supply of argon, which leads to its overconsumption.
- The need for preliminary surface preparation.
- Difficulty working in hard-to-reach places.
Provided that the shortcomings are not too significant, the use of this method is justified.
Basics of argon welding of stainless steel
Stainless steels differ from ordinary steels in their anti-corrosion properties, which they obtained by adding chromium (up to 20%), nickel, manganese, molybdenum and other components. These impurities give the metal different properties and performance qualities. As a result, this leads to difficulties in argon welding of stainless steel.
The main properties of stainless steels are:
- Thermal conductivity is two times less than that of low-carbon steels. The outflow of heat from the argon welding site occurs very slowly, as a result of which the working area can overheat and burnout is possible. Therefore, the welding current should be 20% less than when working with other steels.
- The coefficient of linear expansion of stainless steel is high.
Accordingly, the change in the length of the product during heating will be significant, which can lead to its deformation or the appearance of cracks. To prevent this, it is necessary to make sufficiently large gaps between the parts being connected, especially large ones. - High specific electrical resistance - as a result of which the electrode rod heats up. To obtain a high-quality connection, you must follow the rule - to create short seams, use long electrodes with a higher resistance. When argon welding large areas, it is necessary to take electrodes measuring 35 cm.
An important feature of stainless steel is the loss of anti-corrosion properties at the joint when heated to temperatures above +500 °C. The reason is the formation of carbides at the grain boundaries, which take on the role of anodes. They lead to an increase in the rate of intergranular corrosion of alloys.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
To protect stainless steel from overheating during welding, the argon cooling method is used. And for chromium-nickel alloys - technology for rapid cooling of the weld.
Sharpening electrodes
The main element in welding is the tungsten electrode. TIG welding electrodes require constant care. It consists of regularly sharpening its tip. This ensures a good weld.
There is a rule - when welding with direct current, the tip of the electrode is sharpened cone-shaped, and with alternating current - spherically. The length of the cone can be calculated by doubling the diameter of the electrode. For stability, the end of the cone should be slightly blunted.
Electrode sharpening angle values for TIG welding:
- at a small current value - 10-20°;
- average - 20-30°;
- for high current - 60-120°.
If the sharpening angle is less than 20°, then the capabilities of the electrode are reduced, and at an angle of more than 90°, arc burning may lose stability. It is also negatively affected by the risks that arise on the surface during sharpening.
To make them minimal, TIG electrodes must be sharpened lengthwise. Turning occurs with the help of a grinder, a fine-grained abrasive wheel, emery, rotating the electrode in the hand. To make sharpening uniform, the rod is secured in a screwdriver or electric drill. In this case, it is necessary to set small rotation speed values. To protect against dust, you should wear a mask.
History of appearance
Welding is the joining of metals at high (hundreds and thousands of degrees) temperatures. In such conditions, oxidative processes, saturation and alloying of metals with harmful impurities occur intensively.
The idea of carrying out high-temperature docking in a gas cloud arose at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries from the American engineer Charles L. Coffin. But existing technologies did not allow this method to be applied on an industrial scale. This was especially true for active metals (aluminum, magnesium, titanium).
The first practical experiments were carried out in the 40s of the last century. Using a tungsten non-consumable electrode and inert helium, Northrop Corporation specialists have developed a method for joining aluminum, magnesium and nickel. This discovery made it possible to make a technical breakthrough in the aviation industry.
The modern name of the method is TIG welding (from the German Tungsten Insert Gas), literally: welding with a non-consumable tungsten rod in a cloud of inert gas.
There is often confusion with ADS in shielding gas. This process is carried out with a consumable electrode - welding wire. Designated MIG/MAG.
Inverter for welding
The concept of inverter includes a device whose function is to convert direct current into alternating current. It can also change the frequency of alternating current.
Advantages of using welding inverters:
- Increases efficiency when working with a welding machine.
- The design of welded parts becomes more reliable.
- The seams become reliable and durable.
- Compactness allows you to easily carry the device to your work site.
- High efficiency increases process productivity.
- Electricity consumption is moderate.
- Possibility of regulating smooth current supply.
- Ease of control.
Argon welding with an inverter requires a special type of this device. It must have a function for connecting a burner, which has hoses through which gas is supplied. Argon welding with an inverter makes it possible to weld steel using direct current and aluminum using alternating current.
How to set up argon welding on stainless steel: preparation nuances
An important stage that influences the final result is the process of preparing stainless steel for subsequent argon welding:
- Carefully process the edges of the parts with a wire brush, sandpaper, or perform automatic grinding.
- Degrease with acetone, alcohol or gasoline.
- Position the parts to be welded with clearance for expansion.
- Heat the edges of the parts to +200…+300 °C when working on thin stainless steel. This will help reduce the tension in the metal and avoid cracks.
The next stage is the selection of filler material or wire. There should be more alloying additives in it than in stainless steel intended for welding. The cross-section of the wire is selected based on the thickness of the parts being connected.
Technological process
Despite the fact that argon arc TIG welding requires skill and professional knowledge, it can be done with your own hands. Before this, you need to understand what TIG welding is in principle, what equipment is needed, and the sequence of actions.
Stages of assembling the welding machine:
- Connection of the oscillator to the inverter.
- Attaching the wire responsible for ground to the terminal with a plus sign.
- Attaching the wire connected to the burner to the terminal with a minus sign.
- Attaching the burner to the sleeve through which the gas passes.
- Preparing an argon cylinder. Gearbox winding.
- Attaching the gas supply hose to the reducer.
- Connecting the inverter to a 220 V network. The oscillator is powered by a 6 V unit.
Do-it-yourself argon arc welding in manual mode has the following algorithm:
- Cleaning the surface where welding will be done.
- Preparing the burner for operation.
- Argon supply.
- Ignition of the arc.
- Start of welding.
For cleaning, you can use mechanical or chemical methods. Cleaning must be completed by degreasing. Gas should be supplied a few seconds before connecting the power source. This will ensure the appearance of a protective layer.
Important! In order for a small welding arc to be created, the electrode must be located at a distance of at least 2 mm from the surface to be welded.
After igniting the arc, you can begin the welding process. With the torch in his left hand, the welder draws an arc along the seam, and with his right hand he moves the wire towards the movement of the torch. The electrode and wire should form an angle of approximately 90°. Sharp wire feeding is unacceptable, as this can lead to splashes of hot metal and the formation of an uneven seam.
Semi-automatic argon welding of stainless steel
Semi-automatic argon welding greatly simplifies the process, increases its speed, and also improves the quality of the weld. Most often, semi-automatic machines are used to connect parts of large thickness.
There are several features of argon welding of stainless steel using a semi-automatic machine:
- use of nickel-containing wire;
- consumption of carbon dioxide together with argon when joining thick parts - the edges of the seam are wetted with gas, reducing heating, which leads to a softening of the entire process;
- the use of three connection methods: with a short arc, with jet transfer technology or a pulse method.
It is believed that the greatest control of the process occurs during pulse welding, when the wire is fed into the work area in jerks. At the same time, its consumption is reduced, which is important due to its high cost. The heating area of the metal is reduced. Spattering is reduced.
This results in reduced post-finishing time for surfaces close to the weld because there is no molten metal splash.
Safety regulations
When welding, we must not forget about safety rules. It is necessary to use protective equipment for the welder: a mask or shield, gloves or leggings, special clothing and shoes.
All masks can be divided into active and passive. The sight glass of passive masks is permanently darkened. In active ones, darkening occurs only as a reaction to a light flash from the arc. The advantage of this option is that while the welding process is stopped, the glass becomes transparent and the welder can clearly see the object. There is no need to lift the glass, which is quite convenient.
Main types of welding gaiters:
- Canvas . They are not in demand because they do not perform well the main function of protecting hands from high temperatures and sparks. They easily burn when exposed to sparks.
- Split fibers . Made from specially treated leather from pigs or cows. Resistant to flying sparks. Durable, elastic, hygienic. Does not restrict hand movements. If there is a cotton layer inside, it keeps your hands warm.
- Felt . Convenient for welding work.
There are combined models that use different types of materials. Welding gaiters come in length up to the elbow and cover only the hand. The possibility of tightening the edge of the glove provides additional safety.
A welder's suit must be made of high quality materials. It must be resistant to splashes of molten metal. The requirements for a welder's suit are specified in GOST 12.4.250. The main parts of the suit are the jacket and trousers. The material from which they are made must have great heat resistance. According to the regulatory material, the jacket must cover the trousers by more than 20 cm. The fasteners are closed with flaps. The maximum distance between them on the jacket is 15 cm.
Safety regulations include electrical safety. The argon cylinder must be located at a distance of at least 5 meters from possible sources of fire. The cylinder must be placed vertically and secured to prevent it from falling. Before work, it is necessary to check the condition of the hoses.
Gas used
The main gas for TIG mode is argon. It is heavier than oxygen, so it displaces it from the torch zone, providing protection. Another gas is helium. The second largest substance by mass, after hydrogen. Despite the high cost, helium provides an increase in arc power by 1.5-2 times. The result is deeper metal penetration and increased productivity.
Due to its technical properties, helium is used for working with refractory materials. Responsible operations are carried out on a mixture of gases: Ar about 35-40%, He about 60-65%. This gives the following combination of advantages: light gas provides deeper penetration, and heavy gas stabilizes arc performance.
Necessary equipment
Argon arc welding of copper and other metals requires special equipment. Minimum technical equipment includes:
- Current sources.
- Oscillator.
- Inverter.
- Argon cylinder.
- Gearbox.
- Burner.
- Connecting cables.
- Tungsten electrodes.
- Filler wire.
For full TIG welding, the machine requires constant ignition. The simplest sources for TIG welding produce direct current. They can weld metals - stainless steel, ferrous metal, brass, copper, bronze. But you cannot weld metals that have an oxide film - aluminum and magnesium. They require the source to have an AC function. These are more complex sources that have the function of both direct and alternating current. For AC there are settings such as current balance.
In modern models, there are sources with modes for different material thicknesses and different spatial positions. The most common function is pulse mode. One of the characteristics is heart rate. There are sources with pulse frequencies up to 15 thousand Hz. The higher the frequency, the higher the functionality.
When choosing a machine for TIG welding, you need to decide where it will be used and for what purposes. This will determine whether the required functions are available:
- power supply voltage;
- availability of modes with direct and alternating current;
- possibility of changing polarity;
- the presence of a mode for steel with high viscosity;
- the ability to weld thick metal for a long time;
- inclusion of a water-cooled burner in the kit;
- presence of stationary type cooling;
- the ability to control operation using the display;
- Ability to work on production lines.
The advantages include additional functions:
- the possibility of contactless ignition of the arc;
- DOWN POST GAS - allows you to smoothly turn off the arc;
- BALANCE - the ability to change the polarity balance when welding with alternating current.
There are many models of welding machines for TIG welding. The TIGER 170 DC model is ahead of its competitors in terms of the ratio of device weight and performance. The device has a wide range of applications - from steel sheets with a thickness of 0.2 mm to 6 mm. The additional function of adjusting the current value allows you to weld thin sheets without burns. The device has microprocessor control and a large amount of memory. A simple and convenient interface allows you to set the necessary parameters and modes.
The HAMER TIG-200DC device can operate in two modes. This is an option for welding ferrous metals and stainless steel. The main advantage is the low price combined with the presence of all the necessary functions.
The ELAND TORS-200 welding machine has similar characteristics. There are a large number of additional functions available. A distinctive feature is that it is equipped with devices and consumables for work both for TIG and MMA welding.
GOST 5.917-71 sets out the requirements for manual torches for argon arc welding. According to this regulatory document, burners of the RGA type must be used. The most common models are RGA-150 and RGA-400. The choice of electrode diameter and thickness for TIG welding depends on the type of metal being welded.
Assembling a homemade argon apparatus
What to collect from?
An argon welding machine does not require the purchase of complex components. We will tell you about the main components that will be needed for this equipment.
First, you must have a power source for welding. We will take an inverter welding device.
Next, you need an oscillator device, the purpose of which we talked about. In addition, we need a protective unit for the device. Secondary parts include gas cylinders, welding torches, reducers, gas hoses and connecting cables.
Next, we’ll talk specifically about each of them.
About the current source
Transformer and rectifier devices can be used as a source of welding current. But they are not technically new, and may not be able to handle some aspects of argon arc welding.
A functional inverter device will perform better in this role.
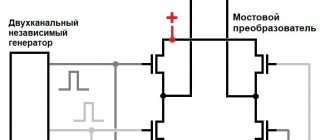
But making a machine for argon arc welding from an inverter device is somewhat more difficult. If you try to just connect an oscillator to it, the inverter may fail instead of cooking in an argon environment.
To prevent this from happening, you need to add a protective block to the device. It is assembled on the same board with the oscillator, and the board itself is equipped with an individual housing.
Errors in TIG welding
The main mistake is rapid burning of the electrode. This can happen due to incorrect polarity of the selected mode, low gas flow, or poorly selected tungsten electrode diameter. Tungsten contamination of the weld may occur. The reason is that the electrode gets into the weld pool and begins to melt there.
A poor quality seam can result from the presence of condensation on the metal, a faulty hose or its loose fit, insufficient gas supply, or poor preliminary cleaning of the surface. Arc instability can occur due to incorrect polarity, dirty electrode, or too long electrode.
Common errors include discoloration of the seam and the appearance of yellow smoke. The reason is that the argon switches off too quickly. The gas is turned off 10 seconds after the arc goes out.
Setting up a homemade device
Even a factory device must be properly configured. This also applies to homemade equipment. This way the welding will take place without problems and will produce seams of good quality. We will note what you need to consider when setting up a converted inverter.
The first stage is sharpening the electrode rod. For this you need a special sharpener. The tip of the rod should be sharp, like a pencil.
A dull electrode will destabilize the welding arc, and it will not be able to follow one straight line. Therefore, it is impossible to avoid the sharpening stage.
After sharpening, the electrode is inserted into the torch holder. The latter is turned on by turning the valve on the cylinder and pressing the ignition button. Use the gearbox to correct the flow of argon.
It should not be more than fifteen liters per minute. After the gas flow has been adjusted, turn off the burner and pause the flow.
After this, connect the oscillator device with the protective block and bring the torch to the workpiece. Before doing this, place the mass on the metal. The burner should be very close to the metal.
After switching on, an electric arc will occur. Then open the gas and at this time move the burner a little further.
Now the converted inverter can work.