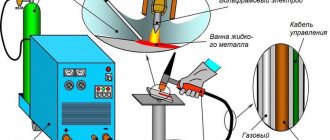
Tig welding of steel is a simple way to obtain a strong connection. This technology is often used to create seams in complex structures. When welding ferrous metal, you do not need to use expensive consumables. Standard electrodes without special coating are suitable.
Safety rules for welding at home
Regardless of work experience, the welder must take care to reduce the likelihood of injuries and other negative phenomena in the process of joining steel parts.
Safety precautions imply compliance with the following rules:
- There should be no flammable objects or liquids near the workplace. An accidental spark may start a fire. Remove everything from the working surface that could interfere with welding.
- During the process of joining parts, toxic fumes can be released, so an exhaust hood is installed above the welding table.
- Before starting welding, check the main elements of the unit. Do not use equipment with a damaged cable or gas supply hose. Make sure that the operating mode of the device is selected correctly.
- Do not use tees or other means of connecting multiple burners at the same time. The devices are connected to separate sockets.
- Suits and masks are used to protect the welder's skin and eyes. Fireproof gloves are put on your hands.
Technological aspect of the welding process
Before welding thin iron with an electrode, it is important to carry out preparatory work, namely, clean the future connecting point. It is assumed that the oil film will be removed using a solvent or other chemical substance. Then you should place the flux on the surface of the metal being processed and set the necessary parameters.
During welding work, safety rules must be observed. At the end of the process, it is recommended to evaluate the quality of the welding performed.
What modes to use for welding ferrous metal
By correctly choosing the main indicators of the functioning of the device, you can get a high-quality weld. The current strength is set in accordance with the thickness of the part. If the latter is 1 mm, the parameter should be 95-100 A. The filler material feed rate is 25-30 cm per minute. Shielding gas consumption when welding ferrous metal is 8 liters per minute.
We recommend reading: How to cook cast iron in an argon environment
Welding low carbon steels
Due to the low carbon concentrate, this type has the following properties :
- high elasticity and plasticity;
- significant impact strength;
- Can be processed well by welding.
Low-carbon steels are widely used in construction and in the production of parts using cold stamping.
Welding technology for low carbon steels
Low carbon steels are best welded. Their connection can be carried out using manual arc welding using coated electrodes. When using this method, it is important to choose the right brand of electrodes, which will ensure a uniform structure of the deposited metal. Welding must be done quickly and accurately. Before starting work, you need to prepare the parts to be connected.
Gas welding is carried out without the use of additional fluxes. Metal wires with a low carbon content are used as filler material. This will help prevent pores from forming.
Gas welding in an argon environment is used to process critical structures.
After welding, the finished structure must be subjected to heat treatment through a normalization operation: the product should be heated to a temperature of approximately 400°C; stand and cool in air. This procedure helps ensure that the steel structure becomes uniform.
Features of welding low-carbon steels
Good weldability of such steels ensures equal strength of the weld with the base metal, as well as the absence of defects.
The weld metal has a reduced carbon content, the proportion of silicon and manganese is increased.
During manual arc welding, the heat-affected area is overheated, which contributes to its slight strengthening.
A weld deposited using multilayer welding is characterized by an increased level of fragility .
The compounds are highly resistant to MCC due to their low carbon concentration.
Types of welding of low-carbon steels
1. The first method for joining low-carbon steels is manual arc welding with coated electrodes. To select the optimal type and brand of consumables, the following requirements must be taken into account:
- weld seam without defects: pores, undercuts, uncooked areas;
- equal strength connection with the main product;
- optimal chemical composition of the weld metal;
- stability of seams under shock and vibration loads, as well as high and low temperatures.
The performer receives the lowest level of stress and deformation when welding in a lower spatial position .
The following types of electrodes are used for welding ordinary structures:
Welding electrodes ANO-6
- ANO-3.
- ANO-4.
- ANO-5.
- ANO-6.
- OZS-3.
- OMM-5.
- TsM-7.
The following grades of welding materials are used for welding critical structures:
- AN-7.
- ANO-1.
- VSP-1.
- WCC-2.
- DSK-50.
- K-5A.
- KPZ-32R.
- MR-1.
- MP-3.
- OZS-2.
- OZS-4.
- OZS-6.
- OMA-2.
- RBU-5.
- SM-5.
- SM-11.
- UONI-13/45.
- UONI-13/55.
- UP-1/45.
- UP-2/45.
- UP-1/55.
- UP-2/55.
- E-138/45N.
- E-138/50N.
- ERS-1.
- ERS-2.
2. Gas welding is carried out in a protective environment of argon, without the use of flux, using metal wire as a filler material.
3. Electroslag welding is carried out using fluxes. Wire and plate electrodes are selected taking into account the composition of the base alloy.
4. Automatic and semi-automatic welding is carried out in a protective environment; pure argon or helium is used, carbon dioxide is often used. CO2 must be of high quality. If the combination of oxygen and carbon is oversaturated with hydrogen or nitrogen, this will lead to pore formation.
5. Automatic submerged arc welding is performed with electrode wire with a diameter of 3-5 mm; semi-automatic – 1.2-2 mm. Welding is performed with direct current of reverse polarity. The welding mode varies significantly.
6. The most optimal method is welding with flux-cored wires . The current strength ranges from 200 to 600 A. Welding is recommended to be carried out in the lower position.
7. For gas shielded , carbon dioxide is used, as well as mixtures of inert gas with oxygen or CO2.
Connecting products less than 2 mm thick. carried out in an atmosphere of inert gases with a tungsten electrode.
To increase arc stability, improve weld formation and reduce the sensitivity of the deposited metal to porosity, mixtures of gases should be used.
Welding in a carbon dioxide atmosphere is intended for working with alloys with a thickness of more than 0.8 mm. and less than 2.0 mm. In the first case, a consumable electrode is used, in the second - graphite or carbon. The type of current is constant, the polarity is reversed. It should be noted that this method is characterized by an increased level of spattering. [ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
Selecting a device
To connect steel workpieces in an argon environment, the following types of welding units are used:
- Manual. The welder who chooses this tool will have to hold the filler wire and torch himself. All parameters are also set manually.
- Semi-automatic. Gas and wire are fed by a special mechanism into the torch, which the welder guides along the joint.
- Automatic. Direct operator participation in the work process is not required. It controls devices remotely.
- Robotic. The operator includes the program, the CNC system follows it. The choice of this method is advisable when welding complex structures that cannot be connected by other methods.
Disadvantages of the Welding Process
As with any process and activity, welding iron with argon has inherent disadvantages. Some of these uncomfortable aspects include:
- the presence of an increased cost of the process compared to other types of welding work;
- high probability of transition of the category of work performed to the group of risky activities due to the presence and direct use of the gas component;
- the presence of boiling situations in the area of the weld pool, which is accompanied by the phenomenon of splashing of the metal component in different directions from the place of welding work, which results in a connection of poor quality with the immediate formation of life-threatening conditions;
- insufficient representation and availability of certain devices necessary for organizing the welding process.
Possible problems when working with steels
Argon welding of ferrous metal pipes can cause problems due to surface cracking.
This is explained by the following properties of steel:
- Low thermal conductivity. The treated area quickly overheats. In this case, through holes appear in the seam and the structure becomes unreliable. If this problem occurs, the current is reduced by 20%.
- Some types of steel expand greatly when heated. Subsequent shrinkage leads to deformation of the welded joint. Cracks appear in the seam and its quality deteriorates. Increasing the width of the joint helps to cope with this problem. The thicker the workpieces, the greater the distance between them should be.
- When TIG welding steel, the likelihood of consumables boiling increases, causing large amounts of spatter.
- The metal has high resistance, due to which the electrode quickly overheats. Using short rods helps eliminate this problem.
- Violation of the temperature regime worsens the properties of some types of steel, for example, stainless steel.
Recommended readingWelding carbon steels with different carbon contents.
Features of argon welding
The peculiarities of argon welding include the fact that any metals, not only non-ferrous ones, can be welded in a gas environment. Ordinary steel is not critical to oxidation, but in an inert gas environment the weld is of better quality.
Basically the process is identical as in the case of a conventional arc or semi-automatic with wire feed. The difference is technology. To obtain an ideal result, apply the melt intermittently, grabbing a centimeter at a time. This makes the molten metal flow better.
Argon-arc welding, depending on the method and speed of the process of joining two parts made of non-ferrous metals, is divided into 2 types:
- automatic;
- manual.
Both types are made with consumable or non-consumable electrodes. In the second case, filler wire or rod is also used, depending on the thickness of the parts being welded.
At modern enterprises, automatic argon-arc welding is actively used, because it allows you to obtain high-quality seams in a fairly short time with a thickness of no more than 1 cm and strictly in accordance with GOST. A wire made of a similar alloy is used as an electrode, which is automatically fed to the welding site. At the same time, argon is supplied, which protects the welding site from oxidation and the formation of shells. This method is convenient because you do not have to change the electrode every time.
Argon-arc welding is also performed using special consumable electrodes. They are made from tungsten. When choosing them, you need to pay attention to the percentage of additional components, since there are no universal ones. There are different types of them on sale depending on the type of materials being welded.
Argon-arc welding with non-consumable electrodes is also used, as shown in the photo. They are made of tungsten, a metal that has a high melting point, so it does not melt in the spark zone. It is used to heat the filler material supplied to the joint.
The table below shows the main types of such electrodes designed to work with various metals.
| Designation | Compound | Materials to be welded |
| WP (green) | 99.5% tungsten | Aluminum, magnesium |
| WY (dark blue) | Ytriated, up to 2.2% oxide additive | Niobium, tantalum, molybdenum, titanium, nickel, copper, bronze |
| WL-20, WL-50 (blue, green) | Added lanthanum oxide | High alloy steels, copper, aluminum, bronze |
| WZ-8 (white) | Contains zirconium oxide | Aluminum, bronze, magnesium, nickel |
| WT-20 (red) | Contains thorium oxide | Stainless steels, molybdenum, tantalum, copper, silicon bronze, nickel, titanium |
Instructions for welding steel with argon
The process of connecting steel pipeline elements is simple. If you have good manual or semi-automatic equipment, welding can be easily done at home.
We recommend reading: How to cook brass in an argon environment
The instructions require compliance with the following recommendations:
- The seam begins to be formed in the direction of the processed edges. Zigzag movements increase the width of the joint, reducing the strength of the seam.
- It is necessary to maintain the average speed of the burner. If the indicator is too high, it will not be possible to boil the parts to the full thickness. If the speed is low, through defects will form.
- The wire must be fed evenly. This will eliminate the formation of sagging and other imperfections. The best option is to use a mechanical supply device for consumables.
- The electrode is held perpendicular to the surfaces being processed or with a slight slope. The filler material is fed at an angle of 45° to the rod.
- The gas start-up begins 10 seconds before the initiation of the electric arc, and stops after 5-7 seconds. Argon protects the seam from oxygen penetration, increasing strength.
- The iron welding is completed by gradually reducing the arc force using a rheostat.
Advantages of the welding process
In the course of welding work, it is considered possible to highlight specific positive aspects, among which there are such points as:
- ease of implementation of the process of welding metal of increased thinness;
- reducing the likelihood of defects and defects in the workpiece;
- the possibility of using welding seams of this nature everywhere in numerous areas;
- relative ease of implementing the welding process in practice;
- eliminating the possibility of failure at the moment of arc ignition;
- creation of continuous welding seams by using wire of the required length;
- the possibility of heating the metal being processed using burner gas;
- minimal need for preparatory work in relation to the metal being welded.
Quality checking
The method for assessing the strength and uniformity of the seam is chosen taking into account the purpose of the structure being welded. Visual inspection is the easiest way to identify defects.
During the procedure, the width and height of the joint are measured, which must be the same throughout the entire connection. Upon inspection, lack of penetration, sagging, and folds are detected.
To identify small defects, the capillary method is used, which uses a penetrating contrast agent. Ultrasonic testing is intended to evaluate welded seams in structures experiencing increased loads. This is an inexpensive and effective method for identifying defects that does not require determining the composition and other properties of steel.
Welding tool
The degree of quality obtained as a result of welding work significantly depends on the materials used, as well as the tool that will directly carry out the process. In order to find the answer to the question of how to qualitatively weld iron, it is important to understand the importance of studying the technology of work, but also the dependence of the welding result on the composition of the metal involved in the welding process.
At times it is quite difficult to determine the exact structure of the material being welded, as a result of which it is considered acceptable to use common brands of constituent elements of the welding process.
It should be remembered that the basis for the success of the work depends on how the specialist will weld the iron with a welding machine, taking into account compliance with the set modes, which will take into account the thickness of the material used.
Welding high carbon steels
Demonstration welding of steel from springs with Zeller 655 electrode
The high carbon content in steels of this type makes them, as a rule , unsuitable for the manufacture of welded structures. They are characterized by low ductility and therefore have limited use.
The need for high-carbon steels arises when carrying out repair work, in the production of springs, cutting, drilling, woodworking and other tools, high-strength wire, as well as in those products that must have high wear resistance and strength.
Welding technology for high carbon steels
Welding is possible, as a rule, with preliminary and concomitant heating to 150-400°C, as well as subsequent heat treatment . This is due to the tendency of this type of alloy to become brittle, sensitive to hot and cold cracks, and chemical heterogeneity of the weld.
For your information! Exceptions are possible if you use specialized electrodes for dissimilar steels. See photo and caption below.
- After heating, it is necessary to perform annealing , which must be carried out until the product cools down to a temperature of 20°C.
- An important condition is the inadmissibility of welding in drafts and at ambient temperatures below 5°C.
- To increase the strength of the connection, it is necessary to create smooth transitions from one to another metal being welded.
- Good results are achieved when welding with narrow beads , with cooling of each deposited layer.
- The contractor should also follow the rules provided for joining medium-carbon alloys.
This is a demonstration sample (spring, files, bearing and food-grade stainless steel are welded together). If you do not pay attention to the quality of the seams, the welds were not made by professional welders, the photo confirms that welding of “non-weldable” steels is quite possible.
Video
Features of welding high-carbon steels
The working surface must be cleaned of various types of contaminants: rust, scale, mechanical irregularities and dirt. The presence of contaminants can lead to the formation of pores.
Structures made of high-carbon steels need to be cooled slowly , in air, to normalize the structure.
Preheating critical products to 400°C allows one to achieve the required strength.
Types of welding of high-carbon steels
1. The optimal option for the welding process is manual arc welding using coated electrodes. Working with high-carbon steels has a large number of specific characteristics. Therefore, welding of high-carbon steel is carried out with specially designed electrodes, for example, NR-70. Welding is carried out with direct current of reverse polarity.
2. Submerged arc welding is also used to join this type of alloys. It is quite difficult to evenly coat the work area with flux manually. Therefore, in most cases, automatic technology is used. The molten flux forms a dense shell and prevents the influence of harmful atmospheric factors on the weld pool. For submerged arc welding, transformers are used that produce alternating current. These devices allow you to create a stable arc. The main advantage of this method is the small loss of metal due to small spattering.
It is important to note that the gas welding method is not recommended . The process is characterized by the burning of a large amount of carbon, resulting in the formation of hardening structures that negatively affect the quality of the weld.
However, if ordinary structures are welded, then the use of this method is possible. The connection is made on a normal or low flame, the power of which does not exceed 90 m3 of acetylene per hour. The product must be heated to 300°C. Welding is carried out using the left-hand method , which makes it possible to reduce the time the metal is in the molten state and the duration of its overheating.
TIG welding technology
Welding is carried out with a tungsten or tungsten-containing electrode, which is fixed in the contact tube of the welding head. In addition to electrical contact with the welding transformer, the head is connected by a flexible hose to a gas injection system containing inert gas. The welding process begins with the supply of gas, followed by ignition of the arc and the flow of filler wire into the weld pool.
Before you begin selecting consumables and calculating welding parameters, you need to understand what kind of metal you are going to weld. The four most common options are:
- Low-carbon steels (up to 0.25%) are easily weldable materials. To prevent weld fragility, it is recommended to preheat the workpieces in an oven to 150-200℃.
- Medium carbon steels (0.25-0.45%) are difficult to weld. They require mandatory heating to 150-400℃ (depending on the specific grade of steel), as well as subsequent heat treatment in the form of annealing or tempering.
- Alloy and high-carbon steels (more than 0.45%) are weldable to a limited extent. These metals are structural and therefore not recommended for welding. It is allowed to connect workpieces that do not bear significant loads, provided they are protected from sudden temperature changes.
- Cast irons (more than 2.41%) require a special welding mode with preheating; it is preferable to work with a consumable rather than a tungsten electrode. Connections made using the TIG method should not experience significant mechanical stress.
To reduce the temperature impact on heat-affected zones, cooling radiators made of copper or other heat-conducting metals are used.