- Home >>
- GOST >>
- GOST sheet >>
Sheet and coil cold-rolled steel, hot-dip galvanized in continuous galvanizing units, intended for cold profiling, for painting, for the manufacture of stamped parts, dishes, containers and other metal products, is produced in accordance with GOST 14918-80.
Galvanized thin sheet steel (GTS) is divided into:
- by assignment to groups:
- ХШ - for cold stamping,
- HP - for cold profiling,
- PC - for painting (trained),
- OH - general purpose;
- N - normal hood,
- G - deep drawing,
- VG - very deep drawing;
- Hli - with normal thickness variation,
- UR - with reduced thickness variation.
By agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer, galvanized steel can be produced:
- KR - with a crystallization pattern,
- MT - without crystallization pattern.
Galvanized steel is produced:
- width from 710 to 1800 mm inclusive;
- thickness from 0.5 to 2.5 mm inclusive.
Depending on the thickness of the coating, galvanized steel is divided into three classes in accordance with those indicated in the table.
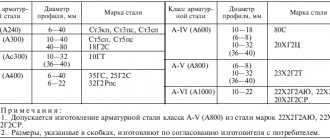
ASSORTMENT
2.1. Galvanized steel is manufactured with a width from 710 to 1800 mm inclusive, and a thickness from 0.5 to 2.5 mm inclusive.
2.2. Dimensions, maximum deviations and other requirements for the assortment must comply with the requirements of GOST 19904-90. Galvanized steel of the highest quality category is produced: with a crescent shape of rolled steel of no more than 6 mm per 3 m of length; with flatness PV and PU and permissible thickness deviations according to the standards of increased rolling accuracy; with telescopic rolls with a steel width of up to 1000 mm no more than 30 mm.
Examples of symbols
Galvanized steel 0.8 thick, 1000 wide, 2000 mm long, normal rolling accuracy B, normal flatness PN, with unedged edge NO group OH, with crystallization pattern KR, first class zinc coating according to GOST 14918-80:
Galvanized rolled steel 1.2 thick, 1000 mm wide, increased rolling accuracy A, with cut edge O, grade 08kp, very deep drawing VG, without MT crystallization pattern, with reduced thickness variation UR, second class coating according to GOST 14918-80:
Galvanized rolled steel with a differentiated coating 0.5 thick, 710 mm wide, increased rolling accuracy A, with a cut edge O, grade BSt3kp, for PC painting, without a crystallization pattern MT with a reduced thickness difference UR, with a coating on one side of the first, and on the other other second class according to GOST 14918-80:
Note. The steel category XSh is not indicated in the order, and the drawing ability index (N, G or VG) is indicated in the symbols. Section 2. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
CLASSIFICATION
1. CLASSIFICATION
1.1. Galvanized thin sheet steel (GTS) is divided into:
by appointment to groups
for cold stamping - KhSh, for cold profiling - KhP, for painting (trained) - PK, for general purpose - OH;
by drawing ability (steel group XSh) into category
normal drawing - N, deep drawing - G, very deep drawing - VG;
by uniformity of zinc coating thickness
with normal thickness variation - HP, with reduced thickness variation - UR. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
1.2. By agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer, galvanized steel can be produced: with a crystallization pattern - KR, without a crystallization pattern - MT.
1.3. Depending on the thickness of the coating, galvanized steel is divided into three classes in accordance with those indicated in Table 1.
Table 1
| Thickness class | Weight of 1 m of coating layer applied on both sides, g | Coating thickness, microns |
| P (increased) | up to 855 incl. | Over 40 to 60 inclusive. |
| 1 | » 258 » 570 » | » 18 » 40 » |
| 2 | 142,5 » 258 » | » 18 » |
When producing steel with a differentiated coating, its thickness on one side of the sheet must correspond to class 2, and on the other side to class P (for sheets) or class 1. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
ACCEPTANCE RULES
4.1. Galvanized steel is accepted in batches. The batch must consist of sheets or rolls of one group of galvanized steel, one size, one type and class of coating thickness, type of preservation, one grade and melt (steel of groups XSh, XP and PK) and drawing category (steel of group XSh), must be registered and be accompanied by a quality document in accordance with GOST 7566-94 with the addition of values of optional quality indicators.
The batch weight should not exceed the shift production of the unit.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
4.2. In the quality document, test results and chemical composition data are indicated at the request of the consumer.
For galvanized steel that has been awarded the state Quality Mark, the designation of the state Quality Mark is affixed to the quality document.
4.3. To control the size and quality of the surface, 6% of the sheets or one roll from the batch are selected.
4.4. To control the adhesion strength of the coating, mechanical properties, and microstructure, one sheet or one roll from the batch is selected.
4.5. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, a repeat test is carried out in accordance with GOST 7566-94.
TEST METHODS
5.1. The quality of the surface of sheets and rolls is checked by external inspection without the use of magnifying devices.
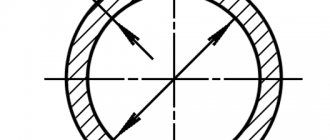
5.2. To carry out tests, samples are cut from each selected sheet or roll in accordance with the requirements of the drawing and table. 2.
Scheme of cutting samples for testing (b
- sheet width)
table 2
| Sample number | Sample dimensions, mm | Test method | |
| width | length | ||
| 1, 2 | 50 | 150 | On the adhesion strength of the zinc coating to the base metal |
| 3, 4, 5 | 50 | 50 | To determine the mass of zinc coating and thickness variations |
| 6 | 20 | 150 | To the bend |
| 7 | 90 | — | For drawing out a spherical hole (x-test location) |
| 8 | 30 | 180-300 | Tensile |
| 9, 10 | 30 | 40 | Microstructure assessment |
Note. Samples are cut with maximum size deviations of ± 3 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
5.3. To determine the mass of the zinc coating, the test sample is degreased, weighed, immersed in a solution of antimony oxide (Sb2O3) or antimony chloride (SbC13) in hydrochloric acid and kept until the violent gas evolution stops, then the sample is removed from the solution, thoroughly washed with cold and then hot water, dried with filter paper and weighed. Degreasing is carried out with synthetic technical ethyl alcohol.
A solution of antimony oxide or antimony chloride is prepared in the following way: 20 g of antimony oxide (or 32 g of antimony chloride) is dissolved in 1000 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid (GOST 3118-77) for the second and first classes or 50 g of antimony oxides of class P.
Mass of zinc coating applied on both sides of the sheet, in grams (t)
per 1 m2 calculated
according to the formula
| (1) |
where t
1
-
mass of three samples
(3, 4
and
5)
before dissolution of the zinc coating, with an error of 0.01 g, g;
m
2 - mass of three samples
(3, 4
and
5)
after dissolution of the zinc coating, with an error of 0.01 g, g;
S—
actual surface area of the samples with an error of 1·10-6 m2, m2.
To determine the mass of zinc coating, it is allowed to use other methods that provide the necessary accuracy.
The method specified in this standard is used when there is disagreement in assessment.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2).
5.4. The difference in thickness of the coating in the transverse direction of the sheet is determined as the absolute difference between the maximum and minimum values of the coating thickness on the samples 3, 4
and
5
according to the formula
| (2) |
for which purpose, first calculate the thickness of the zinc coating on each of the samples using the formula
| (3) |
where T
3—coating thickness of the corresponding sample, µm;
m
3—weight of the sample before removing zinc, g;
m
'3—weight of the sample after removal of zinc, g;
7.13—zinc density, g/cm3;
S
3—surface area of the zinc coating, cm2.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
5.4.1. The average thickness and variation in thickness of the zinc coating on the surface of a sheet with a differentiated coating are determined and calculated for each side. To do this, after degreasing the sample, one side is covered with a dense layer of rubber glue or paraffin and zinc is removed from the opposite side, as indicated above. After re-weighing, the glue or paraffin is removed mechanically or in hot water. Removal of the zinc coating on the other side of the sample is carried out in the same way.
5.5. The bend test is carried out according to GOST 13813-68.
5.6. The spherical dimple drawing test is carried out according to GOST 10510-80. Make two measurements in the test area and determine the arithmetic mean.
5.7. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 11701-84.
5.8. Determination of the grain size of ferrite is carried out according to GOST 5639-82 and structurally free cementite - according to GOST 5640-68.
5.9. Bending testing of galvanized steel with a thickness of up to 1 mm inclusive at an angle of 180° is carried out according to GOST 14019-2003. A sample of galvanized steel is tested on a mandrel equal to the thickness of the rolled product.
Galvanized steel of the highest quality category must withstand 180° bending tests without mandrel until the sides touch.
By agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer, the bending test can be replaced by a double roof lock test in accordance with OST 1411-196-86, and for galvanized steel of the PK group, by testing on the U-1A device in accordance with GOST 4765-73.
Galvanized steel with a thickness of over 1.0 mm is tested at the request of the consumer according to a method agreed upon in the prescribed manner.
5.10. To control the quality of galvanized steel, it is allowed to use non-destructive control methods.
(Changed edition, Rev. No.
2).