A common problem with processing non-ferrous metals (and their alloys) at high temperatures is that under such conditions they are easily deformed.
The specificity of welding brass (copper + zinc) also lies in the fact that, firstly, the element “Zn” included in its composition (30th position in the periodic table) begins to evaporate already when heated to +420 ºС. Secondly, this process is accompanied by the release of a toxic component - the oxide of this metal. The technology of welding brass using argon is the most promising technique, as it eliminates many difficulties and ensures high speed of operations. What it consists of, what are the features of this work is the topic of this article.
Features of brass welding
Brass is a difficult to weld alloy of copper and zinc. Elements such as nickel, tin and lead can be added to the alloy. During welding, zinc is actively released, which causes the appearance of pores and reduces the strength of the joint. The thermal conductivity of the alloy exceeds even steel. Therefore, it is recommended to use a high-power torch for processing brass products.
To eliminate negative processes, it is recommended to adjust the burner so that the excess oxygen is at least 25%. This will reduce the porosity of the seam and increase its strength. However, if this indicator of excess oxygen is excessive, the process of zinc oxidation may begin. In this case, a brass filler welding wire with a powerful deoxidizer is used. For this, it is advisable to use silicon, which can then be removed into slag using fluxes.
Features of preparing parts for welding
Preparing brass parts for welding is similar to preparing copper. A distinctive feature is that brass products are thin and therefore do not require preheating. However, thick elements of products should be heated in those places where they will be welded. Preparatory work helps improve the quality of the seam joint, so the finished product will be durable.
During preparation, special attention should be paid to processing the working edges. If the edge thickness is less than 1.5 mm, additional beading should be performed to increase this figure. This increases the strength of the welded joint. If the edge thickness is within the normal range, flanging is not required. However, it is necessary to maintain a gap between the elements of about 2 mm. To increase this indicator, you can use linings.
To connect products where high strength is required, it is recommended to use double-sided welding. If it is possible to achieve a significant thickness of the seam, this moment guarantees a strong and reliable connection.
Preparing parts for joining is a mandatory and very important stage of work. If you incorrectly estimate the thickness of the material or the length of the seam, the structure may become deformed. This occurs due to increased metal stress. Therefore, to connect thick sheets or to work with high-strength structures, it is better to use the services of specialists.
Advantages of argon arc welding of brass parts
It is no coincidence that argon arc welding of brass products, carried out with non-consumable electrodes, is so popular. The advantages of this technological process are as follows.
- To weld brass in an argon environment, neither specially coated electrodes, which are quite expensive, nor flux are required.
- This technology for connecting parts made of brass is one of the cleanest from an environmental point of view.
- Argon welding is characterized by high speed of execution.
- Welds obtained by argon welding are distinguished by high aesthetic characteristics.
- There is no slag crust on welds made using this technique, which must be cleaned.
- The edges of the connected brass parts are reliably protected from the formation of oxide and nitride crusts through the use of inert gas.
- A jet of argon supplied to the welding zone blows out all waste from the technological process.
- This welding method is universal: it can be used to connect both small and large brass products and restore them using the surfacing method.
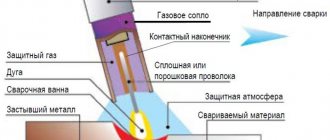
Argon welding
For welding bronze and brass, it is recommended to use direct current of straight polarity. Therefore, welding brass with argon is an extremely convenient way to manufacture products from this metal.
The first stage of welding is preparing the surfaces of the parts to be welded. To do this, they are protected with an iron brush, after which they are treated with a solvent. An important step is choosing the right brass wire for welding. It must contain silver, silicon, nickel, aluminum or other powerful deoxidizing agents. This welding method increases the anti-corrosion properties of the seam.
The technology of argon welding of brass consists of joining parts not with a single seam, but in small sections. To avoid burning through parts, it is recommended to weld with a long arc in order to reduce the current in the area that is currently being welded. At the final stage, the burner must be moved to the side.
This method is optimal for products where high strength is required. However, welding of brass at home is most often not carried out. This is because the process releases hazardous chemicals, so it must be carried out in open areas with good ventilation. For example, welding of brass and stainless steel, which is performed only by experienced welders, is carried out only with the help of argon.
Gas
Gas welding of brass is used in exceptional cases. Basically, it is carried out in the absence of electricity or when it is impossible to conduct electric arc welding. The formed seam is quite strong and of high quality, but this method is accompanied by intense evaporation of zinc. This process can only be hindered by an oxidizing flame. As a result of the reaction of the compound with oxygen, a film is formed on the surface, which prevents the gas from escaping.
In gas welding, combustible gas is burned in a special burner. Its role is played by acetylene, hydrogen, natural gas, gasoline or kerosene vapor. The most popular is a mixture of acetylene and oxygen, as it has a high calorific value. The power of the flame directly affects the quality of the seam, so before performing work it is necessary to adjust the welding parameters. Gas welding technology involves heating the filler material in a flame. The rod with the additive should always be in a high temperature zone, and the seam itself should be applied at maximum speed.
The wire, which plays the role of filler material, does not require the use of additional flux. Silicon brass wire is usually used and produces a tight and durable weld. Excess waste must be washed off with water. The seam is then forged, annealed and slowly cooled. When working on a vertical surface, you should remember the fluidity of the metal.
Electric arc method
Welding of brass can also be done using the electric arc method. It is produced using a rod brand LK 80-3. The welding process is performed using direct current of reverse polarity. A short arc is used to reduce the likelihood of zinc catching fire.
Before welding parts, the workpieces must be preheated to a temperature of 300 degrees. Another important preparatory step is forging the weld seam. Welding of brass, which has a low copper content, is carried out so that the parts are hot. Therefore, it requires annealing first. This will change the structure of the seam, reducing its graininess, which will make the connection strong and durable.
Features of the technology
The essence of the process is the formation of a seam in one layer. After its completion, the connection is forged. Repeated passage along the seam is not allowed, since when performing welding work, slag is deposited on the connecting section, forming a crust that is simply impossible to break through.
- If the thickness of the metal of the structural elements being welded is more than 5 mm, then this technology is not recommended.
- It is better to treat the edges of the workpieces being joined before welding with a specialized flux, which will prevent the evaporation of zinc.
- Welding work is recommended to be carried out using brass multicomponent wire.
- Recommended temperature conditions for annealing: 750 degrees - preheating of the joined parts of the product; 625 degrees - the annealing temperature; 100 degrees/hour - the rate of change from heating to cooling.
- The recommended burner power is 120 l/h of combustible composition per 1 mm of material.
To distinguish brass from other alloys, you need to pay attention to the behavior of the melted material during the welding process. When argon arc welding, brass will spit and hiss.
Techniques for welding brass using automatic and semi-automatic machines
Welding brass with a semi-automatic machine is practically no different from welding copper parts. Automatic and semi-automatic welding of brass is performed with thin wire. In this case, welding must be carried out without transverse vibrations in order to prevent porosity of the seam.
Semi-automatic welding with brass wire provides a more even seam. In addition, such a device makes it possible to work in any position. Welding using a semi-automatic machine ensures that the process of fastening parts is carried out in a protective carbon dioxide environment. The quality of work depends on the source materials, the speed of gas and wire supply, as well as the qualifications of the craftsman.
Thus, there are many ways in which brass is welded. Each technology has certain advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to choose the optimal method based on the characteristics of the alloy, the initial quality of the parts, the required strength of the finished product, as well as technological capabilities.
However, due to the release of hazardous chemicals during the heating of metal, the procedure must be carried out only if you have experience in welding, as well as a room with high-quality ventilation.
Welding technologies for brass products
As you know, brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. In some cases, when it is necessary to obtain a metal with special characteristics, other chemical elements can be added to it - tin, nickel, lead.
Zinc, which is contained in a significant amount in brass, begins to evaporate when heated strongly, which leads to porosity in the welded joint. In addition, by reacting with oxygen contained in the surrounding air, zinc vapor is converted into the oxide of this metal, which forms a white coating on the surface of the parts being connected. Possessing refractoriness and thereby complicating the welding process, this coating poses a great danger to human health, as it is very poisonous.
Mechanical properties and chemical composition of brass
Taking into account all the above factors, experts have developed several technologies that can effectively weld brass. These include:
- gas and electric arc welding;
- joining brass parts under a layer of flux;
- welding performed in a shielding gas environment, which is most often used argon.
Of all the listed technologies, it is brass argon welding that has become most widespread due to its high efficiency and the ability to obtain high-quality welded joints in any conditions.