In traumatology, a burn is understood as acute injury to the outer shells of the body by aggressive environments: high or low temperature, acid or alkali, solar or other wave radiation, etc.
Of all ophthalmic injuries, corneal burns occur in 15% of patients.
. Most of them are obtained in production, and only a third - in everyday life. By their specificity, they belong to the category of severe injuries requiring urgent assistance. In addition to the danger of irreversible changes in the tissue of the eyeball, burns are fraught with intense pain shock, which negatively affects the functions of vital organs.
Causes
The most common causes of burns to the outer shell of the eye, adjacent skin of the eyelids, tear ducts and glands, as well as deep-seated structures, are contacts with chemicals. Such an effect in ophthalmology refers to chemical burns of the cornea and is divided into several subtypes depending on what substance got on the cornea:
- Alkali burn. Occurs when a solution or dust of caustic soda, slaked lime or fluffed lime, a solution or vapor of ammonia, ethyl alcohol and drugs based on it, or household chlorine-based bleaches come into contact with the cornea. With this type of damage, liquefaction necrosis of the eye shell occurs, the area of which is much larger than the size of the contact spot: if a drop of the reagent gets on the eye, the burn itself will be 3-7 times larger than the diameter of this drop.
- Acid burn. Occurs when the membranes of the eye come into contact with vapors or solutions of vinegar, sulfuric or hydrochloric acid. This type of damage is accompanied by the formation of a scab - a focus of coagulative tissue necrosis, the boundaries of which rarely extend beyond the diameter of the contact spot.
- Thermal burn. It can occur when the eye comes into contact with hot liquid, hot steam, metal, grease, open flame, etc. In modern realities, thermal burns are often a consequence of improper use of electrical appliances, playing with firecrackers, etc. The nature of this type of damage is the same as as in contact with acids.
- Radiation burn. Occurs due to exposure of the cornea to ionizing, infrared or ultraviolet radiation. They are similar in nature to regular thermal burns, but can be deeper.
According to statistics, the basis of any corneal burn is non-compliance with standard safety measures when using household or professional chemicals or working with potentially hazardous objects.
Antibacterial drops
If you receive a burn as a result of exposure to welding, then most likely inflammation has begun. This means the use of antibiotics will be required. But they must be in shape. Which will allow you to apply them topically, directly to the affected area.
The most famous drops with an antibacterial effect:
- Tobrex;
- Oftaquix;
- Gentamicin;
- Dexamethasone;
- Taufon or Taurine.
The mechanism of action of antibacterial drugs is to block the formation of bacterial proteins by binding to bacterial ribosomes.
Method of application: by introducing drops onto the conjunctival sac. The dose of use always depends on the severity of the condition, but the usual dosage is:
- For infections with moderate symptoms, antibacterial eye drops after welding are used in the amount of 1-2 drops with an interval of 4 days;
- For infections with symptoms of high severity, it is recommended to reduce the interval of drug administration - 1-2 drops every hour;
- Antibacterial drops can be used for a course of no more than 2 weeks.
Contraindications for use:
- Intolerance to components;
- Infancy (less than 1 year);
- Severe kidney pathologies;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- Myasthenia;
- Acoustic neuritis.
Important: long-term use of antibacterial eye medications beyond 2 weeks can lead to fungal or secondary bacterial infection.
Side effects:
- Reaction to light in the form of a spasm;
- lacrimation;
- Burning and itching;
- Development of bleeding of mucous membranes;
- Hallucinations.
Important: before using eye drops after welding, contact lenses must be removed.
Varieties
The classification of thermal, radiation and chemical burns of the cornea of the eye divides the injury according to the degree of tissue damage, localization of the lesion and stage of the pathological process. In accordance with this, there are 4 degrees of burns of the cornea of the eye:
- Mild, or I degree
- superficial damage, accompanied by slight redness of the conjunctiva and skin of the eyelids, slight erosion of the surface of the cornea, which is noticeable only after treating the eye with fluorescein. Does not require intensive therapy; as it heals, it disappears without a trace. Does not threaten vision loss.
- Average, or II degree
- is expressed by superficial necrosis of the mucous membranes of the eye and conjunctiva, their swelling, damage to the stroma and epithelial layer of the cornea. Grayish-turbid lesions on the surface of the eye and blisters on the skin of the eyelids are visually recorded. With this degree of damage, scarring is likely to form on the surface of the cornea, which leads to a partial decrease in visual acuity. - Severe, or grade III
, necrotic changes are observed throughout the conjunctiva and its underlying layers, including the sclera and cartilage of the eyelids. Its surface acquires a grayish-yellow color and a matte texture. With such a degree of burn, the cornea loses its transparency and dries out. Changes are observed on 50% or less of the surface of the eyeball. After the scab is rejected, scar defects form on the cornea, which significantly reduce visual acuity. - Particularly severe, or grade IV
, is the deepest necrosis with charring of the conjunctiva and sclera of the eye. With this degree of damage, the cornea becomes completely opaque, holes appear on it, and the internal structures of the eye also undergo changes. With this degree, the likelihood of complete loss of vision is very high.
Based on the localization and extent of the process, three types of corneal burns are distinguished:
- with damage to the conjunctival sac;
- with destruction of the eyeball;
- damage to the adnexal structures of the eye.
Depending on the stage of the pathological process, eye burns are divided into:
- early
- lasts up to 2 days and is accompanied by an increase in necrobiosis, that is, the spread of tissue necrosis due to the breakdown of proteins and polysaccharides; - medium
- lasts up to 3 weeks, accompanied by a violation of tissue trophism; - late
- last up to 3 months and are accompanied by multiple trophic disorders with a lack of oxygen in the cornea, however, against this background, restoration of nutrition of the cornea is planned; - scarring
- lasts from six months to several years, accompanied by increased synthesis of collagen and protein, restoration of corneal functions.
Important! The most favorable prognosis is for mild superficial injuries. Full restoration of visual acuity after them occurs after 12-24 months. Severe damage often results in permanent vision loss.
Vasoconstrictor drops
After pain relief, a drug is used that will effectively treat pathological symptoms: relieve swelling, remove redness and inflammation, relieve itching.
These drugs are based on adrenergic agonists that act on the receptors of the vascular walls. They cause the blood vessels to constrict, resulting in relief of the symptoms of the disease.
Vasoconstrictor eye drops are very effective, but they cannot be used for a long time. Otherwise, they will cause the opposite effect.
Eye drops after welding with a vasoconstrictor effect are used for no longer than 5 days. Otherwise, addiction to the drug develops and then the symptoms that needed to be eliminated intensify.
And, of course, local exposure to drops only relieves symptoms that cause discomfort, but does not cure the disease itself.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Childhood;
- Glaucoma;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Dry eye syndrome;
- Intolerance to naphazoline and tetrizoline.
The most effective means:
- Visine;
- Okumetil;
- Polynadim;
- Octilia;
- Naphthyzin;
- Alomide.
Vasoconstrictor eye drops are used after welding by instillation onto the conjunctiva. Dosage: 1-2 drops, 2 to 4 times a day.
Before using the drug, you need to remove contact lenses and reinsert them only after 30 minutes.
Important: the maximum period of use of such drops is 4 days. If after 2 days there is no improvement, then it is better to discontinue use.
Side effects:
- Arrhythmia;
- Increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- Decrease in temperature;
- Cold sweat;
- Pulmonary edema;
- With prolonged use, the symptoms of the disease intensify.
With the correct dosage and use of eye drops after welding, side effects are unlikely.
Symptoms
Clinically, a corneal burn always manifests itself clearly and unambiguously: even without special knowledge, it is difficult to mistake it for another injury. The most striking symptoms of chemical and thermal burns are:
- acute, almost unbearable pain localized in the damaged eye and eyelid;
- reflex closure of the eyelids, photophobia;
- intense lacrimation (if the tear ducts are damaged, the sign may be absent);
- hyperemia of the skin, mucous membranes, conjunctiva;
- clouding of the cornea (noticeable with a severe burn).
Radiation damage may not be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms immediately after receiving it. Burning sensation, lacrimation, photophobia, hyperemia and photophobia appear after a few hours.
The use of folk remedies
When considering what you can drop into your eyes after welding, do not forget about folk remedies. They can be used independently, but you should still consult your doctor first. It is better to use for mild damage, because they certainly will not help for moderate and severe damage, and sometimes they can even cause complications.
So what should you put in your eyes after welding? At home you can use homemade drops and lotions:
- Potato . You can make a mask from the tubers; it will relieve pain and relieve swelling. Raw potatoes should be rubbed through a fine grater. The resulting pulp should be placed in gauze, wrapped and applied to closed eyelids. You need to keep it for 30 minutes.
- Linden tea . This remedy relieves swelling, redness, burning sensation, and itching. For cooking, it is better to use bags of raw materials. They should be brewed first and then applied to the eyes.
- Aloe . This plant has strong medicinal properties. The juice should be squeezed out of the leaves and mixed with natural honey. This combination must be instilled into each eye, 1 drop.
First aid
According to statistics, the degree and depth of damage to the cornea is influenced not by the type of traumatic impact, but by the duration of its contact with the surface of the eye. That is why everyone, without exception, needs to know basic first aid measures.
Important! A quick and correct reaction is especially important in cases where there is a thermal or chemical burn to the cornea of the eye.
What needs to be done to stop or reduce the influence of traumatic factors
:
- rinse the eye with a stream of cool, clean water, preferably saline, but regular tap water will do;
- remove foreign bodies from the surface of the eye, especially if they are hot metal particles (molten polymers should not be touched);
- Place a gel or ointment with an analgesic effect in the conjunctival sac to relieve pain and prevent the development of shock.
In the first hours after the patient’s admission to the hospital, doctors must rinse the lacrimal canals and remove foreign bodies embedded in the membrane of the eye. To prevent infection, chemically neutral antiseptic solutions are used to wash the eye.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to wash off chemical reagents from the surface of the eye with other chemicals, for example, acids and alkalis and vice versa, as this can lead to additional damage. Experts note that treating a combined corneal burn is many times more difficult than a specific type of burn.
What not to do
It’s not enough to know what to put on your eyes after welding; you also shouldn’t forget about prohibited activities. This will help to avoid unpleasant consequences in the future.
Basic prohibited recommendations:
- In no case should you rub your visual organs too hard;
- no need to rinse your eyes from the tap;
- immediately after receiving damage there is no need to use folk remedies;
- Is it possible to put Lidocaine and other drops into the eyes after welding? It is better not to do this; you should first consult a doctor.
If after welding there are unpleasant feelings in the eyes, pain, swelling, then you should immediately consult a doctor. However, it is not always possible to quickly visit an ophthalmologist; in this case, first aid must be provided. If severe pain is noted, you can drip Novocaine for the eyes after welding. This will alleviate the condition, but for a few hours. And you definitely need to get to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible, only he will be able to determine the extent of the damage, and then select the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Intensive treatment of any type of burn of the cornea begins immediately after the patient enters a medical facility. To begin with, instillation of scopolamine and atropine directly into the eye is prescribed. These drugs relieve pain and reduce the formation of adhesions between the cornea and conjunctiva.
On the first day, the process of tissue change under the influence of traumatic factors continues. It is impossible to stop it completely, so doctors will have to wait until the necrotic processes stabilize. At this stage, it is important to prevent infection of the eyeball and reduce the intensity of symptoms. For this use:
- ointments and drops
with tetracycline, ciprofloxacin or chloramphenicol; - local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Diclofenac or Ibuprofen; - substitutes for tear fluid
to prevent drying of the cornea.
After stabilization of the condition, rehabilitation treatment begins. In the absence of perforations of the membranes of the eye, conservative methods are limited:
- injections of antioxidant drugs (methylethylpyridinol);
- placing gel-like regenerating preparations (Solcoseryl or Deskpanthenol) behind the eyelid;
- instillation of antihypertensive solutions (Betaxolol or Dorzolamide) into the eyes.
If the corneal burn is deep, hormonal agents are prescribed, most often glucocorticoids in the form of solutions for injection into the eyeball or conjunctiva.
Surgical intervention is used for deep and widespread damage to the membranes and internal structures of the eye.
If the anterior chamber of the eye is affected, corneal paracentesis is performed, followed by chamber sanitation. In case of deep damage to the eyeball, the dead areas of the conjunctiva, cornea, and vitreous body are removed, after which plastic restoration of the removed tissue is carried out.
In the long-term period, patients may require plastic restoration of the eyelids: elimination of eversion and entropion, ptosis, trichiasis, correction of post-burn cataracts, lamellar keratoplasty, etc.
How to detect eye damage
During the welding process, safety must be observed, so many experienced specialists use special personal protective equipment - clothing made of thick fabric, a face and eye mask, and gloves. Otherwise, the sparks that are released during welding of metal products can get into your eyes and cause serious harm.
It is worth noting! If the damage is not severe, the technician does not immediately experience unpleasant sensations, and they are usually not pronounced. Symptoms of eye burns often do not appear until 3-5 hours later.
Before you find out what you can put in your eyes after welding, it’s worth considering the nature of the symptoms. To begin with, it is worth studying the degree of damage, which is accompanied by certain signs:
- A superficial or mild burn occurs during brief exposure to bright ultraviolet radiation. Unpleasant signs appear within 5-7 hours. First, a slight redness of the white forms, followed by a burning sensation. When looking at the light, pain is felt, and the cornea gradually becomes cloudy. If no other signs appear in the future, treatment can be performed at home.
- In moderate cases, painful sensations in the eyes are noted. Photophobia develops, and a person experiences unpleasant sensations when looking at light. I can’t even look at the phone screen without pain, my eyes turn red, and there is severe tearing. In this case, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist. If the second degree is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe medications and send you home.
- A third degree injury is considered serious and requires immediate medical attention. To reduce discomfort, drops with an analgesic effect can be instilled into the eyes, but they will only help temporarily eliminate unpleasant feelings. Usually the same symptoms are observed as in the first two cases. Additionally, whitening of the cornea appears, nagging painful feelings that can be all over the face, they can radiate to the temple area. In addition, swelling of the eyelids will be noted.
- The fourth degree is the most severe and dangerous; you must visit a doctor very quickly, otherwise you may completely lose your vision. In this situation, damage is noted not only to the cornea, but also to the retina. The process of tissue death begins and partial necrosis develops. Often this can only be corrected by surgery. Usually there is severe pain with a cutting character, preventing you from opening your eyes.
Drug groups
Therapeutic measures for all types of burns are quite similar, only the doses and duration of the therapeutic course differ depending on the degree of damage to the eye structures.
The main groups of drugs that are used for burn injuries to the eye are shown in the table.
| Drugs | Action provided |
| Anesthetics (Lidocaine, Novocaine). | Eliminate pain syndrome. |
| Local antibiotics (Levomycetin, Lincomycin drops, Sulfacyl). | Prevent inflammation. Help minimize the risk of infection of the affected organ. |
| Artificial tear preparations (Vizin). | In case of a burn to the mucous membrane of the eye, these drops are necessary to moisturize and protect the damaged organ. |
| Antihypertensives (Ganford, Dorzolamide, Betaxol). | Reduce eye pressure. |
| Mydriatics (Atropine, Ephedrine). | Needed for normal pupil dilation and normalization of the iris. |
| Cytoplegic (Scopolamine). | Designed to relieve pain symptoms and prevent adhesions. |
| Glucocorticoids. (Dexamethasone, Betamethasone, Cortisone). | Prescribed for extensive or deep burns to eliminate redness, burning, swelling and swelling of the eyelids. |
| Anti-inflammatory (Naklof or Diklo-F). | Such drops for eye burns are necessary for the regeneration of damaged tissues. |
It is mandatory to use drops containing D-panthenol. This component significantly accelerates the regenerative processes of damaged tissues, and therefore the recovery period takes less time. Preparations that contain panthenol are Korneregel, Vitaglycan.
Conclusion
It doesn't take long to pick up bunnies; this happens even to experienced welders. It is much more difficult to provide first aid and treatment correctly. A slight burn can have a big impact in the future, don’t skimp on time, it’s better to take sick leave and have your eyes treated well. It definitely won’t be superfluous. It also wouldn’t hurt to visit a doctor; he will prescribe you the most effective course of rehabilitation.
Medicines and traditional medicine will perfectly help get rid of bunnies. But the best protection remains a good mask or glasses. Do not neglect safety rules, the consequences of this are harmful.
What happens to the eyes during welding and what are the consequences?
Welding is not only the joining of metal parts; it is also used when working with other materials.
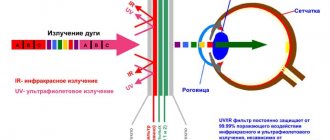
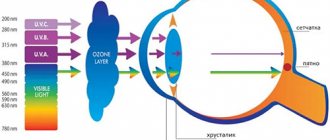
Electric current is used as a source of formation of the welding arc. So what exactly causes harm? When welding, rays of three spectra are released at once: infrared, ultraviolet and light. The intensity is too high for the human eye, it exceeds the permissible level.
There is a common expression among welders: “catching a bunny.” This means that the cornea of the eye has been burned. We do not perceive infrared and ultraviolet rays with our eyes, but they have a very intense effect on the eyes. Moreover, negatively. Damaging the mucous membrane, retina and lens of the eye, causing a burn.
The main eye disease that occurs under the influence of light radiation from welding is electroophthalmia.
What other causes of eye damage from welding are there?
- Negligent attitude towards work. Often welders do not use special safety glasses, which are required to be used for safety reasons. Or the use of low-quality glasses purchased in order to save money;
- Smoke effects on the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Release of gases affecting the eyes;
- Foreign body getting into the eye. Most often, these are very small pieces of metal that stick into the cornea.
Forecast and consequences
The duration and effectiveness of therapy for electroophthalmia depends on the degree of burn to the organ of vision and the timeliness of contacting a medical facility. Minor eye damage usually resolves within a few days and usually has no consequences for humans.
Grade 3–4 damage to the conjunctiva and cornea, complicated by the lack of timely specialized care and self-medication, can lead to the following consequences:
- decreased or complete loss of vision;
- development of ulcers on the membranes of the eyes;
- chronic inflammatory process on the cornea;
- a violation of the structure of the eye, causing incorrect focusing on surrounding objects - astigmatism;
- purulent inflammation of the internal membranes of the organ of vision.
Elimination of such complications is a complex and lengthy process that may require surgical intervention. Therefore, in order to avoid long-term negative consequences when receiving a burn as a result of welding work, it is important to consult a specialist and follow his recommendations for further therapy.
Stages of burns
There are 4 stages of burns of the visual system. They differ in symptoms and treatment methods.
First stage
At the first stage of the burn condition, the patient is bothered by itching, redness of the mucous membrane, burning sensation and clouding of the iris. This stage is accompanied by swelling and superficial erosions.
This stage is the easiest, so it is important to take quick measures to restore the mucous membrane and get rid of symptoms.
Second stage
The surface layers of the skin of the mobile integument are damaged. The second degree is characterized by:
- shallow necrosis of the connective membrane;
- formation of burn blisters;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- film;
- sharp pain.
In the second degree, suitable medications will help cope with the problem. These are eye drops and ointments used in combination.
Third stage
After examining the fundus, necrosis of the skin of the eyelids and conjunctiva is detected.
There are dirty gray films on the mucous membrane. Possible clouding of the cornea, infiltration. Visual perception deteriorates, the patient cannot see objects located nearby. Pain almost always accompanies the patient. There is severe swelling, it is difficult to close and open the eyes.
Fourth stage
This is the most severe stage of a burn to the visual organs. It occurs with deep necrosis of part or the entire organ, charring of the conjunctiva with the sclera.
The fourth stage of a welding burn leads to the development of inflammation of the choroid, eyesore, and secondary glaucoma. Perforation and complete blindness are possible if timely measures are not taken.
When to see a doctor
If you receive a burn while working with a welding machine, consultation with an ophthalmologist is advisable in any case, but there are situations when it is mandatory. These include the presence of the following symptoms in the victim:
- the eyes hurt continuously, even after taking anesthetic drugs;
- vision began to deteriorate;
- there is no reaction to taking medications prescribed by a doctor for three days.
Treating a burn at home is possible, but before starting it, you should consult with a specialized specialist.
List of sources
- Ophthalmology. National leadership / ed. S.E. Avetisova. M.: GEOTARMEDIA, 2008. 1017 p. [Ophthalmology. The national guideline / under the editorship of SE Avetisov. M.: GEOTARMedia, 2008. 1017 p. (in Russian)].
- Morhat M.V. Educational and methodological manual on ophthalmology for subordinate surgeons in the specialty of general medicine: educational method. allowance / M.V. Morhat. – Vitebsk: VSMU, 2022. – 124 p.
- Occupational hygiene: textbook / ed. N.F. Izmerova, V.F. Kirillova. M.: GEOTARMEDIA, 2010. 592 p.
- Puchkovskaya, N.A. Pathogenesis and treatment of eye burns and their consequences / NA. Puchkovskaya, N.S. Shulpina, V.M. Nepomyaschaya. - M., Medicine, 1973. -192 p.