Quite often there is a need to calculate the weight of rolled steel pipes, which actually involves calculating the weight of one linear meter of pipe.
In this article we will help you make these calculations and find out the weight of the pipe depending on its characteristics.
To calculate the weight of a pipe, you can use several options, one of them is a special table for the weight of steel pipes, another is GOST for the weight of pipes, as well as calculation using special formulas.
Today we will look at the last option, namely calculating the weight of the pipe using the formulas .
These formulas practically do not differ in their results, and are quite suitable for calculating the weight of rolled steel pipes.
It’s worth saying right away that the two available formulas for calculating the mass of a pipe are not limited to some types of steel pipes, it can be gas and electric welding pipes, the calculation of their weight is unchanged and the result will be correct (within these formulas).
Knowing the formulas and the need to calculate the weight of rolled steel, depending on its characteristics, you can use one of the proposed formulas.
Now let's move directly to the formulas.
The first formula for calculating the weight of rolled steel:
Mn = ((Dn – Ts)/40.5)*Ts.
DN is the actual diameter of the steel pipe, which is measured in millimeters;
Tc is the wall thickness of a steel pipe, measured in millimeters;
MP is the weight of a linear meter of pipe.
Now let's move on to the second formula for calculating the weight of steel pipes:
Here is our second formula: Mn = (Dy – Tc)*Tc*0.0246615 ,
DN – diameter of a steel pipe, measured in millimeters;
Тс – wall thickness of a steel pipe, units of measurement are millimeters;
MP - the final result, as in the previous formula, is the weight of one linear meter of steel pipe.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in these formulas; using them and calculating the weight of pipes does not require special knowledge and skills; it is enough to know the formulas and have a calculator nearby.
Source: www.junona-2.ru
Formula for calculating the theoretical weight of a pipe
You can also calculate the weight of the pipe using special formulas, which we will consider below. The data in such formulas are the dimensions of the pipes, which can be taken from the factory markings. So, in all calculation formulas we will find the weight of 1 linear meter.
For hollow round pipes:
Weight 1 p/m [kg] = (L - T) * T * 0.025
D – outer diameter of the pipe [mm]; T – wall thickness [mm]; 0.025 is a constant coefficient for a round pipe.
For square hollow tubes:
Weight 1 p/m [kg] = (W - T) * T * 0.0316
W – size of one of the sides [mm]; T – wall thickness [mm]; 0.0316 is a constant coefficient for a square pipe.
For rectangular hollow pipes:
Weight 1 p/m [kg] = (W1 + W2 - 2T) * T * 0.0158
Ш1 – size of one side [mm]; Ш2 – size of the second side [mm]; T – wall thickness [mm]; 0.0158 is a constant coefficient for a rectangular pipe.
Methods for calculating pipeline capacity
Hydraulic calculations are carried out in order to select system elements with optimal characteristics to ensure uninterrupted operation, reduce operating costs and reduce equipment wear.
Hydraulic calculation of the pipeline
Calculations are carried out using Shevelev tables according to the following algorithm:
- The required flow rate Q and the optimal speed of the medium in each section are set.
- The diameter of the pipe is selected, and the pressure loss along the length is determined.
- The procedure is repeated for all sections.
- The specific value of pressure loss per 1 linear line is found. m.
- All other losses from suction, local resistance, etc. are summed up. The resulting value must be less than or equal to the pump power.
- Based on the technical characteristics of the equipment, the flow rate Q of the pump is determined.
- Q and Qpump are compared. If the values are approximately equal, the pump is selected correctly. If not, you need to set new parameters and calculate again.
Calculation of sewer pipe capacity
The diameter and angle of inclination are set at which wastewater flows randomly, and the system constantly cleans itself (from 0.005 to 0.035 depending on the cross-section):
The degree of filling of the pipe according to the standard is 0.6-0.8 and also depends on the diameter:
Dependence of filling on pipe diameter
Using the Lukin tables, it is clarified whether the selected diameter corresponds to the specified parameters. If there are deviations, the cross section needs to be changed up/down. For more accurate calculations, graphs, formulas and correction factors are used.
Calculation of gas pipeline capacity
In accordance with the parameters of the designed network, the diameters of the pipes at the inlet and outlet of the gas distribution system are set. Then, comparing the values in the tables, they find a ratio in which the conditions are maximally met.
Gas pressure in a gas pipeline: classification, types and categories of pipes Natural gas is used in everyday life and in industrial enterprises. Pipelines are used to deliver it to its destination. The most important indicator for them is the gas pressure in the gas pipeline. This…
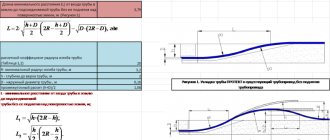
How to calculate chimney parameters
The main characteristics that are determined during the calculations are the length of the chimney pipe and its working cross-section. If the parameters are incorrectly selected, toxic substances are not removed from the combustion chamber and penetrate into the room.
When designing, the standards SP 7.13130.2013 and SNiP III-G.11-62 are used. Although the latest regulation is considered ineffective, it contains recommendations specifically related to chimneys.
Complex industrial devices are calculated in professional bureaus; for home ovens, a simpler method is used.
Example:
- The speed of smoke movement is set to U=2 m/s.
- In an hour, approximately B = 6 kg of wood with a humidity of 20-25% burns in the firebox.
- Temperature of heated smoke T=140°.
The volume of emanating smoke is determined by the formula:
Vgas = (B x Vfuelx (1+T/273))/3600, m3/s, where Vfuel is the volume of air required to burn 1 kg of wood. In this case it is 10 m³, for a brown corner 12 m³, for a stone corner 17 m³.
Vgas=6x10x(1+140/273))/3600=0.025 m³/s.
Knowing the volume of outgoing gas and its speed, you can find the cross-sectional area of the chimney pipe:
S=Vgas/U=0.025/2=0.0126 m².
The diameter is determined by the geometric formula:
D=2√(S/p)=2√(0.0126/3.14)=0.126 m = 126 mm.
The nearest pipe diameter, rounded up, is 150 mm.
The length of the chimney to ensure normal draft is selected according to SP 7.13130.2013, which standardizes the height from the head to the stove grate, the roof ridge, as well as the distance to surrounding large objects.
Pipe calculator
How is the mass of pipes calculated?
To calculate the mass of round pipes, use the formula
m = Pi * ro * S * (D - S) * L
- Pi = 3.1415926,
- ro is the density of the pipe material,
- S - wall,
- D - outer diameter,
- L is the length of the pipe.
The following densities are used (kg/m3):
- 7850 - carbon steel
- 7900 - 04Х18Н10
- 7960 - 06XH28MDT
- 7700 - 08X13
- 7700 - 08X17T
- 7700 - 08X20H14C2
- 7900 - 08X18H10
- 7900 - 08X18H10T
- 7950 - 08X18H12T
- 8100 - 08X17H15M3T
- 7600 - 08X22H6T
- 7900 - 08X18H12B
- 8000 – 10X17H13M2T
- 7950 - 10X23H18
- 7700 - 12X13
- 7700 - 12X17
- 7950 - 12X18H10T
- 7900 – 12X18H12T
- 7900 - 12X18H9
- 7600 – 15X25T
- 7900 - 17X18H9
- 2850 - duralumin
- 4540 - titanium
- 8960 - copper
- 8600 - brass
- 11340 - lead
- 19300 - gold
Density values are taken from the book: Enochovich A.S. "A Brief Guide to Physics." M.: Higher School, 1976.
Weight of rectangular pipes
The mass is calculated using an interpolation formula, with the masses of the pipes taken as the nodal points in accordance with GOST 8645-68 “Rectangular steel pipes” and GOST 8639-82 “Square steel pipes”. That. the masses of pipes with standard dimensions exactly correspond to GOST.
For intermediate sizes (not according to GOST), calculation according to the formula from the book: Rozov N.V. "Directory. The mass of one meter of pipes.” M.: Metallurgy, 1966.:
m = Kp * 0.0157 * S * (A + B - 2.86 * S) * L
- Kp - density coefficient (1 for carbon steel, ro/7850 - for other materials)
- m—mass, kg
- S—wall, mm
- A - large side, mm
- B—smaller side, mm
- L—length, m.
Source: www.trubnik.by
Calculation methods in industry
At large and large-scale facilities under construction or renovation, the process of determining parameters begins with incoming inspection. Engineers and installers check the accompanying documentation, certificates and company markings applied to the pipe rolling by the manufacturer.
A thorough inspection of a batch of pipe material at the time of delivery allows us to identify potential inconsistencies and, if detected, to reasonably refuse the supplier to accept substandard products
From this data, one finds out the nominal dimensions of the resulting material, the grade of metal or type of plastic, the batch number of the goods, the results of X-ray flaw detection carried out by the manufacturer and the chemical analysis of the smelting, the type of heat treatment and the date of specifications.
In production conditions, the actual length of the pipe is measured using a measuring wire or tape measure. Deviation from the figures stated in the factory documentation, up or down, for first class products is considered acceptable if it does not exceed 15 millimeters, for second class – 100 millimeters.
Basic data about the pipe can be obtained from the markings. It is usually applied to the outer or inner part of the product at a short distance from one of the ends. There they indicate the name of the manufacturer, heat number, equivalent carbon content (for metals), production date, number and nominal dimensional parameters
The outer diameter of pipes used in industry is checked using the formula:
D = L:π-2Δр-0.2 mm
It takes into account such parameters as:
- D – required diameter;
- L – length of the outer circumference of the pipe;
- Δр – thickness of the material from which the tape measure is made;
- 0.2 millimeters is the permissible allowance for contact with the surface of the measuring tool.
Errors and deviations of the actual diameter from those declared by the manufacturer for products with a cross-section of up to 200 millimeters are allowed within 1.5 millimeters. For pipes with a large cross-section, this figure is considered normal if it does not exceed 0.7% of the diameter specified in the documentation.
Steel pipe weight: calculation calculator and formulas
Reading time: 3 minutes No time?
We will send the material to you by e-mail
Pipes, both round and profile, are sold at retail by the meter. However, when calculating future building structures, as well as when hiring a carrier, it is necessary to know the exact weight of the product. The steel pipe calculator calculates the weight of a pipe based on theoretical principles and allows you to calculate the mass of all existing types of pipes made from different grades of steel.
Round steel pipes
Remembering geometry
Calculation of the mass of a round pipe
- Calculate the circumference of the pipe . It is equal to the product of the outer diameter of the pipe and the number pi.
- We calculate the surface area of a linear meter of pipe . It is equal to the product of the circumference by... that same one meter.
- We calculate the volume of the substance per linear meter of pipe . With sufficient accuracy, it can be considered equal to the product of the area and the wall thickness.
- We calculate the mass of a linear meter of pipe . Steel has a density of 7850 kg/m3. The mass of a linear meter will be equal to the product of this number and the volume of pipe material we have calculated.
- We multiply the resulting mass per linear meter by the length of the pipeline . In meters, of course. Let's celebrate the victory.
As an example, let’s calculate the mass of those same thousand two hundred meters of pipe with a diameter of 100 mm and walls 4 mm thick.
- 0.1*3.14159265=0.314159265 m.
- 0.314159265*1=0.314159265 m2. To be honest, this operation could have been skipped.