The process of joining two metal workpieces ceased to be a problem after the advent of the welding machine. Some difficulties still remain. For example, it is not easy for beginners to do the job of welding two thin metal sheets in good quality. The article examines in detail the question of how to properly weld thin metal using electric welding. Looking ahead a little, it is worth saying that to perform such operations, technologies and equipment are used that allow the work to be completed without deforming the welding sheet and burning out the working area.
How to carry out the procedure with thin-walled objects
Let's assume that the thickness of the workpiece is 1-1.5 mm. It is quite difficult to select an electrode for it, because it must have an even smaller cross-section (according to unspoken rules). Is it really 0.7-0.9 mm? You won’t be able to find such consumables on sale; they simply don’t exist; standard rulers start at 2–3 mm. Yes, one and a half ones are also available, you can buy them, but they are also uncomfortable for beginners to work with.
To solve the problem, you need to use special equipment that generates direct current under high voltage. It is easy to adjust, and with its help it is quite possible to ensure excellent seam quality.
Stainless steel welding methods
There are several methods for welding stainless steels. Each method involves the use of specific equipment and consumables. How to properly cook stainless steel with electrodes will be analyzed further.
Manual electrode
Manual welding of stainless steels with a coated electrode is universal and can be used in almost any industry. This method provides acceptable connection quality, so it is used by home and professional performers. Another important advantage of MMA technology is the simplicity and ease of the welding process. In addition, welding stainless steel with arc welding has several more advantages:
- affordability of electrodes and equipment;
- the devices can work throughout the working day;
- the units have compact dimensions and low weight, which allows you to quickly move around the work site;
- high speed of work with skillful handling of equipment and consumables;
- strength of welds;
- There is an opportunity to independently study this welding method and apply it in practice.
In order for a weld to be highly reliable, it is necessary to select the right welding materials. The following brands are suitable for manual welding:
OZL-8 are designed to weld products exposed to aggressive environments. At the same time, increased requirements for resistance to MCC are not imposed on the deposited metal. Performers use OZL-8 electrodes to process critical structures.
NZh-13 electrodes create a reliable connection and prevent the formation of ICC. A thin layer of slag crust disappears spontaneously after cooling and compression of the working area. This significantly speeds up the process when a large number of seams need to be completed.
TsL-11 electrodes are characterized by good insulation of the weld pool from external factors. This brand provides a strong connection.
When using this technology, direct current is used to weld stainless steel, the polarity is reversed.
After analyzing this information, a performer of any level will be able to learn how to weld stainless steel using arc welding.
Manual argon
Manual welding of stainless steel in an argon environment is carried out using tungsten electrodes. This technology guarantees high-quality and reliable seams. Moreover, the connections meet all the requirements, even if they are made at home. Consequently, argon arc welding is used when the performer needs an aesthetic result. The seams do not need to be cleaned of slag. There are no sparks during welding. This is the cleanest connection method. This method is also intended for working with parts with very thin walls.
Welding is carried out with alternating or direct current of straight polarity.
The type of stress depends on the thickness of the metal:
- if the thickness of the sheets being welded is 1 mm, then a direct current of 30-60 A is used, the diameter of the electrodes is 2 mm.
- Welding stainless steel with alternating current is also possible when working with elements 1 mm thick: voltage – 35-75 A, electrode Ø – 2 mm.
- data for processed products with a thickness of 1.5 mm: direct current of direct polarity, 40-75 A, Ø welding rod - 2 mm;
- alternating current, 45-85 A, Ø – 2 mm.
Features of this method:
- the arc should be ignited in a non-contact manner so that tungsten from the electrodes does not get into the molten metal;
- welding must be carried out without oscillatory movements of the rod. Violation of this rule may lead to a violation of the protection of the working area, which will lead to oxidation of the seam.
Advice! Using this method, you can reduce the consumption of welding materials. To do this, it is necessary not to turn off the argon supply for 10-15 seconds after welding is completed. This procedure allows you to protect the hot electrode from active oxidation.
Technology for welding thin metal with an inverter for beginners
To achieve a decent result while maintaining occupational safety, you must adhere to a few simple rules:
- Clean the joints from dirt and possible rust (even if you see that there is no corrosion, just in case).
- Securely secure the workpieces so that they do not move out during the process.
- Preliminarily outline the connection line, so as not to get lost later and not to disturb the desired geometry - with dots every 5–7 cm.
- Complete the work as quickly as possible - without delays in any areas, in one pass.
- Set the minimum current strength - if the device has a smooth adjustment function, this will not be difficult.
- Monitor the open circuit voltage - it is important that it remains at least 70 V.
Welding thin steel with an inverter - plus or minus electrode
It is recommended to cook thin steel with an inverter in reverse polarity. To do this, the holder with the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the device. At the same time, the welding technology remains the same. It is also important to take into account the speed of movement of the electrode, the time it takes for the metal to cool, the welding current, etc.
What does reverse polarity do? Everything is simple, since the main concentration of temperature falls not on the metal being welded, but on the tip of the electrode. Welding with reverse polarity makes it possible not to burn through thin-walled metal, and also to prevent the occurrence of deformations during welding.
The main difficulties of welding thin sheet metal
There are certain processing specifics that beginners should take into account:
- The progress and result of the process are extremely dependent on the parameters of the electrode. It is necessary, firstly, to correctly select it in size, and secondly, to drive it smoothly, at the same speed, with zigzag movements (more on this below). Otherwise, burns cannot be avoided.
- The bath should not be very large so that it does not load the seam with its weight and does not push it through. Otherwise, you risk seeing roller-like sagging on the reverse side of the product (although the front side will look quite aesthetically pleasing).
- When talking about how to properly weld thin metal with an electrode, we must not forget that due to inexperience, the material is very easy to overheat, and then it becomes deformed. In the zone of excessive thermal influence, stretching occurs and waves are formed; if the product is faulty, it is permissible to straighten it with a rubber hammer; if not, the only option for correcting the defect is to apply a new seam overlapping the one already made.
- The passage must be done quickly, but at the same time it is important not to rush, because haste is fraught with insufficient penetration, violating the tightness of the finished product (up to its complete unsuitability), which is especially critical in the production of various containers for filling liquids.
Electrodes used
Electrodes for welding thin metal must be selected with extreme care. This is due to the fact that even the slightest deviation from established standards leads to the appearance of serious defects. When considering which electrode to weld 2 mm metal, we note the following points:
- When choosing low current values, the most suitable electrodes are those with a diameter of 2 to 3 mm. This is due to the fact that too high an indicator leads to arc attenuation.
- The optimal temperature in the welding zone is 170 degrees Celsius. This is quite enough to pierce steel, but its structure is not transformed. Due to this effect, the coating begins to melt evenly, and the welder can change the shape of the seam.
- In most cases, an electrode that has a high-quality coating is used. Often the technology used involves the use of a burst arc, due to which the weld pool is small in size.
Electrodes for welding 2 mm
Welding thin metal with an inverter can only take place when using special electrodes that can stabilize the arc.
Selection of modes and conductors: polarity
Considering how to weld thin sheets of metal with an inverter, it should be said that it is better suited for this work than a transformer. Why? Because with its help it is easier to set the desired characteristics and, more importantly, adjust them in the process of creating seams.
So what amperage should you choose? This directly depends on the walls of the workpiece, as well as on the cross-section of the filler rod. We present the current ratio in the table below.
| Part thickness | Electrode diameter | Current strength |
| mm | A | |
| 0,5 | 1 | 10–20 |
| 1 | 1–1,6 | 30–35 |
| 1,5 | 2 | 35–45 |
| 2 | 2,5 | 50–65 |
| 2,5 | 2–3 | 65 |
Here it is worth clarifying which metal is considered thin in principle. We answer, up to 5 mm - this is an official, but too vague definition. After all, even the table hints that problems arise when processing parts that are no thicker than 2-2.5 mm.
If a beginner clearly needs to focus on the above dependence, then an experienced specialist will often select the optimal mode “by eye”. Although he also needs to remember about one pass at a time, because modern additives are distinguished by the fact that they melt relatively quickly, which means you need to be careful with them.
Welding with consumable electrodes
In order to successfully weld metal products with small thickness, it is necessary to use electrodes whose diameter does not exceed 2 mm. When working with steel sheets with a thickness of 1-1.5 mm, you need to use an electrode with a diameter of 1.6 mm.
Consumable electrode welding.
The consumable electrode welding technique involves careful control to prevent overheating and subsequent burning of the metal. The electrode is guided along the seam of the surfaces being welded at an average speed; if a tendency for the steel to burn is visible, the speed is increased. The current strength is selected empirically, but should not exceed 40A. If it is possible to carry out an experimental seam, this will make the task easier. Welding is carried out on the test material at different current values, taking into account the speed of movement of the electrode
At the time of welding, it is important to ensure complete penetration of the steel edges, but not to burn through it. The peculiarity here is that the melting of thin edges occurs almost instantly, and there is no way to control the weld pool
That is, it is necessary to experimentally achieve thorough welding and absence of burning of the steel, since the slightest delay leads to burnout.
When welding very thin metal, an intermittent or spot welding method is used. The essence of this method is that points (tacks) are created by briefly creating an arc, then the arc is extinguished and the same process is carried out at a short distance (2-3) of the electrode diameter. It is advisable to reduce the pauses between tacks to a minimum, without allowing the metal to cool completely. To create leaky connections from thin steel, this method is chosen. Thanks to point heating centers, it is possible to avoid significant warping of the metal.
Argon welding with consumable electrode.
In some cases, changing the polarity of the current allows you to get better results, so when the polarity is reversed (plus on the electrode), the tip of the electrode heats up, as the electrons move from minus to plus.
It is much easier to weld thick metal to thin metal. In this case, the electrode focuses on the thick steel, that is, the main temperature center is created on the thick metal.
Particular care must be taken when creating vertical seams. To do this, you need to use the spot method and weld from top to bottom, without allowing additional heating of adjacent areas from upward heat
The right technology: how to weld thin metal using electric welding
According to the recommendations, this problem needs to be solved in 3 stages:
- Take preliminary measures.
- Connect the parts.
- Clean the seams.
The selection of equipment is carried out mainly for the first two steps, which is why they deserve the closest attention and detailed consideration.
Preparatory work
They boil down to cleaning all contact surfaces of the joint from any possible types of contamination. Particular attention must be paid to the installation point of the supporting part of the apparatus.
Corrosion stains should be carefully removed with sandpaper. It is also better to remove the zinc coating (if any) using a grinder, although if time is pressing, you can leave it in the expectation that it will melt when heated. But it is still recommended to remove it so as not to create unnecessary irregularities.
Working with galvanized steel
Welding thin-walled galvanized steel, or galvanized steel as it is called, causes welding difficulties. What is galvanized steel? Ordinary steel, as a rule, is sheet, with a zinc coating, which creates difficulties during welding.
The zinc coating does not allow making a high-quality seam, so it must first be removed from the edges.
This is done using sandpaper, a grinder, an angle grinder, or a metal brush.
An important condition for such work is that cleaning must be done outdoors or in a well-ventilated room. During stripping, zinc can evaporate and its fumes are toxic.
Fulfillment of all the listed conditions - the correct selection of equipment and components, an optimally configured machine, a successful choice of welding method, compliance with the rules of safe welding - all this will help you achieve the desired result.
Do-it-yourself welding of thin metal with an inverter
It is necessary to adhere to the following algorithm:
- Clear the end of the electrode (approximately 5 mm) from the coating - for the fastest possible ignition.
- Make a short-term fire and pinpoint the material along the entire seam line, at intervals of 5–7 cm - this will help prevent possible deformation.
- To ignite an arc for continuous use, simply strike the filler rod against the metal or tap it. Maintain a flame length of 2–3 mm and a distance corresponding to the cross-section of the consumable (see table).
- Make a bath of melt, trying to keep it an elongated oval shape, and start making a seam - then it will most likely turn out to be of high quality.
- Carry out the passage smoothly and quickly, without bringing the conductor closer to the part to avoid drops.
When discussing how to weld thin metal (iron) with an inverter for beginners, we always advise using a machine with arc forcing and anti-stick functions. It is more convenient than usual, because it regulates the process and automatically adds tension when the flame stretches excessively or releases it when the filler rod gets dangerously close to the workpiece.
In addition, to ensure a high-quality result, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Position the holder so that it is at a 60-degree angle to the surface and does not block the view of the seam and the bath. If you tilt it too much, the joint will be bulging and uneven.
- Monitor the speed of movement, trying to maintain a uniform and progressive motion.
- Move the electrode from bottom to top (for vertical joints) or from left to right (for horizontal joints); the trajectory should be zigzag.
Knowing how to properly weld thin metal using inverter welding, do not forget that after the operation is completed, the joint should be carefully inspected: clean off the slag and make sure there are no burns or lack of penetration.
Welding technique
Welding thin-sheet iron requires proper approach of the edges of the plates to each other. Butt joints often result in burn-throughs and are only suitable for experienced welders. If possible, it is worth placing the plates overlapping. This will create some basis for the deposited metal, and will not allow burning through the entire product. In this case, the electrode is directed primarily to the bottom plate, since a different position will lead to undercuts on the top side.
When joining into a butt, the edges are not cut. There is no need for a gap either. It is necessary to bring the ends of the parts together as tightly as possible and tack. Low current strength and thin electrodes make the work much easier. You can then cook it in several ways:
- Set the current to low and quickly sew the seam without oscillating movements, strictly along the connection line.
- Raise the current a little higher, but conduct the seam with an intermittent arc, giving the metal time to cool before the next “portion” of the additive.
- Cook using the methods described above, but using a special substrate to maintain a heated area and avoid sagging. A metal table will not work here, since the product may be partially welded to it. A good alternative would be a graphite backing.
- To prevent severe deformation, apply stitches in a checkerboard pattern, or in small sections (100 mm each). With the latter method, it is necessary to finish the next seam at the beginning of the previous one. This will allow the product to be heated evenly along its entire length and minimize deformation.
Welding is carried out with a short arc, which allows you to quickly form a seam and avoid overheating of the area. Increasing the distance between the end of the electrode and the surface visually prevents burning of the plates, but does not contribute to the formation of a welding bead. The electrode is held towards itself at an angle of 45 degrees, or tilted to the side. Right angles should be avoided as this leads to burns.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P2CzIuF_VhQ
Converter operation
This is a device with reverse polarity, that is, it is connected to the workpiece with a minus, and to the conductor with a plus. This eliminates the very possibility of defects occurring. The rod heats up stronger and faster than the material at the point of contact, especially if this consumable is of good quality (from a foreign company, with known properties, proven in practice). It is also important that it has high buoyancy and its diameter does not exceed 2 mm.
There are many videos showing how to perform passes. Check out some of them and you'll avoid making common mistakes.
Advantages of thin-walled blanks
Welded strictly according to technology, using modern equipment, with neat seams, they:
- They have an aesthetic and even attractive appearance, because there is no scale on their surfaces.
- Exactly correspond to the design dimensions, not deformed, since during their production the material was not subject to temperature changes.
- They are completely ready for painting or other coatings because there is no slag on them.
- They can boast of a strictly planned shape, without holes, depressions or tubercles, if the stress during their manufacture was constant.
The parts have all the described advantages because they are manufactured using advanced equipment, the only drawback of which is possible interruptions when working in conditions of very sub-zero temperatures. But this is, in principle, typical for any technology of this kind.
Features of connecting thin metal with an inverter
When working, the welder focuses on the polarity of the electrodes. Their size affects the durability of the weld and the strength of the entire connection.
Electrodes with reverse polarity form a deep seam. During operation, they determine which charge to use and how to connect it. The positive charge heats up more strongly. A high-quality seam will be formed if you watch it while welding. By creating a working angle for the electrode within 30°, the electrode is brought close to the metal and a red spot is formed until a molten metal drop appears. The welding seam is formed after all the drops on the worksheet are connected to each other.
How to arc weld thin galvanized metal
The secret is to completely remove the coating from the edges before making the joint. This can be done either manually or with a grinding machine. With proper experience, the second option is preferable, as it will require less time and physical effort.
You can also burn out the ends of the parts, but this is not the best option. Remember that when heated, zinc vapors begin to be released, and they are poisonous and can provoke quite severe poisoning. Therefore, processing of workpieces must be carried out either in the fresh air or in a room with good ventilation, and always in special clothing.
Galvanized welding
Galvanized steel is the same thin sheet, only coated with a layer of zinc. If you need to weld it, you will have to completely remove this coating on the edges for welding, until you get clean steel. There are several ways. The first is to remove it mechanically: with an abrasive wheel on a grinder or grinder, sandpaper and a metal brush. There is another way - burn it out by welding. In this case, they pass the electrode twice along the seam. In this case, zinc evaporates (it evaporates at 900°C), and its vapors are very toxic. So this work can be carried out either on the street, or if there is an exhaust hood at the workplace. After each pass, you need to knock off the flux.
It is better to weld galvanization outdoors: evaporating zinc is very harmful
After complete removal of zinc, the actual welding begins. When welding galvanized pipes, to obtain a good seam, two passes with different electrodes will be needed. The first seam is welded with rutile-coated electrodes, for example, MR-3, ANO-4, OZS-4. In this case, the vibrations have a very small amplitude. Make the top seam wider. It is approximately equal to three electrode diameters
Here it is important not to rush and cook well. This passage is used by electrodes with a basic coating (for example, UONI-13/55, UONI-13/45, DSK-50)
Possible problems when welding sheet metal with an electrode
During the process, defects may arise that are similar to ordinary defects, but are caused precisely by the small thickness of the products. Among them:
- Sticking - observed if you bring the tip of the rod too close to the surface being treated; Another common cause is low amperage, and either of these will result in an uneven weld.
- Burning - occurs when there is an excess of power, if you set too much current. As a result, the material melts and pits and depressions appear on the smooth surface.
- Lack of penetration - this is often done by beginners who hold the rod far from the part for fear of making a hole. As a result, the additive is not hot enough and spreads over the part, and when it hardens, it forms a lump that needs to be cleaned off. And, most importantly, there is no high-quality connection either.
- Deformation - appears if the temperature at the point of thermal impact is too high, causing the plane to collapse or bend.
How to avoid such problems? This is clear from their description: firstly, you need to adhere to the technique of performing the pass, and secondly, set the correct operating parameters.
Problems of welding thin-walled products
It is not recommended to carry out such work if you do not have the required skills. The most common problems are:
- Formation of a strong influx. The weld pool may blur and even collapse. Therefore, a lot of attention is paid to this point.
- Burning of thin material occurs with strong spot heating. As a rule, a similar problem arises when choosing a high current rating.
- The appearance of a low-quality roller. Controlling a short arc is quite difficult, as is the spread of molten material.
If the distance between the product and the rod is large, this can lead to the formation of a long arc. It is characterized by a higher exposure temperature in the melting zone.
In conclusion, we note that the main problems can be avoided by gaining experience, using a modern apparatus and a more suitable electrode. this is due to the fact that new inverters allow you to set optimal current values. In addition, high-quality electrodes form a stable arc even at low current. Therefore, you should not skimp on purchasing consumables, as otherwise it will be quite difficult to obtain a high-quality seam.
Necessary conditions for arc welding thin metal
Quite strict requirements are imposed on both the device and consumables.
Thus, it is recommended to use electrodes with the following parameters:
- diameter – less than the thickness of the workpiece, the optimal cross-sectional size is considered to be 1.6 mm;
- the material of manufacture is the same as the part;
- coating made of refractory materials;
- the manufacturer is a well-known company (in principle, any brand is acceptable, but it is better to choose quality, the difference in price is usually insignificant).
In addition, the equipment must be suitable:
- It’s better if the inverter is semi-automatic - it’s more convenient to use than a manual one, if only because you don’t have to spend physical effort keeping it on;
- it is more practical if it has a wide adjustment range, 10–15 A, this will allow flexible adjustment of the current supply based on the parameters of the conductor.
But any model is definitely more productive than a transformer, because the efficiency is on average 90%, and this is with modest electricity consumption.
How to choose a device
All seams made on inverter welding machines are visible. And the quality of such seams depends on what characteristics a particular device has. When choosing an inverter, you should consider the following parameters:
- resistance to unstable voltage : stability coefficient (protection coefficient) must be in the range from 20 to 25% (indicated on the device itself and in its documents);
- maximum permissible ambient temperatures at which the equipment must be operated (indicated in degrees Celsius and in the range from +40 to -40 degrees, which are optimal temperature values);
- values of the diameters of the electrodes used during welding (in particular, electrode No. 2 with a diameter of 2 mm is used for welding thin parts, for example, body metal on the fenders or doors of a car, and electrodes No. 4 with a thickness of 4 mm are used on thicker component elements of the car body) .
Approximate cost of inverters for welding on Yandex.market
You should not pay attention to the “hot start” or “anti-stick” functions, since they are initially included in all modern inverter machines in the “base” and are used by manufacturers as an advertising ploy in order to better present their product for inexperienced users.
Inverter device
Speaking of how to weld thin metal with an electrode, we note that relatively complex equipment is used for this. This is a device that must support at least several modes, each with its own frequencies and other operating parameters. To ignite the flame, it must also convert the current twice - first to direct from alternating, and then to high-frequency.
The general scheme and principle of its operation are as follows:
This shows the nature of the change in momentum. The wave passes through the bridge, the filter capacitor, the inverter itself, enters the transformer and conductor and only after that creates the necessary heating.
To make it easier for a beginner to figure out how to weld thin metal using electric welding, the body of the device must have a modern level of ergonomics. To do this, it must contain the following structural elements:
- toggle knobs - for smooth adjustment of the current strength in the required range;
- indicators - mains, overheating protection;
- connectors – for connecting cables with a cross-section of 50 sq mm or less.
In the design adopted today, its body is necessarily equipped with side ventilation grilles - for quick cooling - and, optionally, a belt for easy carrying on the shoulder.
Welding a car body with an inverter
Both the owner of a new car and the owner of a vintage car may need body repairs. With the help of welding work, a body damaged during an accident, corrosion, rotting or under the influence of time is restored. Doing the repairs yourself will save you money on auto mechanics. Timely elimination of corrosion damage and replacement of rotten parts will extend the life of the car.
An inverter is a modern welding device, characterized by its small size and compactness. The current supplied from the network enters the rectifier and is converted by the device into high-frequency alternating current. Afterwards, the voltage decreases and the current increases to 200 A, necessary for welding work.
How to choose an installation
When choosing a welding machine, it is important to pay attention to several factors.
- Surge protection, this function protects the device from voltage surges. Choose a model with a protection factor of 20-30%.
- Operating temperature range. The optimal range for Russian latitudes is from -40°C to +40°C. This parameter will allow you to carry out welding work both in winter and summer. But using the device at the extreme points of the range is undesirable.
- Power. The device must be suitable for working with electrode No. 2, No. 4, then it will be possible to weld both thin body steel and metals with greater thickness.
- Device safety class.
- Protection against short circuits, overheating. The device should automatically turn off when an emergency or overheating occurs.
- Protection from moisture and dust. For use in a garage, it is better to choose an installation with automatic dust removal.
Techniques for structures with thin walls
There are several techniques that help you avoid errors with defects. So, here are the ways to weld thin metal with an electrode:
- Pointwise - you need to make a large number of local sticks, every 5-7 cm. Light the arc, make a connection in a specific place and extinguish it. This option is good for its accuracy, but its implementation takes a lot of time.
- Overlapping - it is necessary to place two workpieces on top of each other so that the edge of the upper one overlaps the end of the lower one, and process it. The main thing is to prevent burns and immediately clean off all the scale (if it appears at all). A relatively simple look, but associated with a large amount of time and material; But you don’t have to be afraid of through holes - they won’t impair the reliability of the structure.
- According to the selected electrode - here you need to quickly remove the coating over the entire surface of the rod, and then lay it in the direction of the planned seam. The passage is standard - smooth and fast - but the contact areas should still be given maximum attention.
When discussing how to properly weld thin metal using inverter welding, it is important to remember several nuances. If the parts are large, ignition should be carried out on parts with thick walls and from there the newly formed seam should be transferred to the butt section.
To remove heat, copper wire is often used - it boasts an impressive capacity. Although in practice it is a really capacious material that perfectly prevents melt leakage or burning.
How to learn to weld metal with an inverter
Begin training by igniting the arc. To do this, in addition to the apparatus, metal (5-6 mm thick) and an electrode, you will also need a welder’s mask and leggings (thick leather gloves), as well as thick clothing and boots made of thick leather to protect against sparks and scale.
Start work by connecting the welding cables. Then the selected electrode is inserted into the holder (to start, take MP 3 with a diameter of 3 mm - they light easily and cook well). After turning on the power, set the welding current (see table). For an electrode with a diameter of 3 mm, the current is set to 90-120 A. The current can be adjusted during the welding process. If you see that the result is not a roller, but just some disjointed stripes, increase it. If, on the contrary, the metal is very liquid and it is difficult to move the weld pool, reduce it. The settings greatly depend on the device and the selected electrode. So try it, change it. Having set the current, put on a welder’s mask (it will be easier for beginners to work in a chameleon mask), and you can work.
General recommendations for choosing the diameter of the electrode depending on the thickness of the metal
Welding with an inverter for beginners begins with learning how to ignite an arc. There are two methods: tap the tip of the electrode on the part several times or strike it like a match. Both methods work. Whichever is more convenient for you, use it. But for the future, keep in mind that you need to scratch along the seam line so that there are no marks left on the product. To consistently strike an arc, you will have to practice for a while and burn several electrodes.
When the arc lights up without any problems, you can move on and master the movements. This is done by laying rollers on thick metal. On a metal plate, draw a line with chalk that will replace your seam. Then you strike the arc. In the place where it rests, the metal melts and becomes covered with a film of liquid slag. This place is called the weld pool. So you will have to move it along the drawn line. Do this with one of the movements shown in the figure above.
In order for the bath to move, the electrode must be tilted slightly, approximately at an angle of 50-45°. Some have a larger angle, some have less. In general, by tilting the electrode, you change the size (width) of the weld pool. You can experiment: there are a lot of different techniques in welding and the only important thing is that the seam is of high quality, and how you achieve this is your business, especially since you will be working for yourself and for yourself.
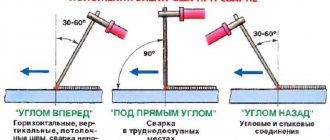
There are two main working positions of the electrode: forward and backward. When welding at an angle forward, we get less heat and the seam will be wider. This technique is used when welding thin metals . Thick ones are usually welded at an angle backwards.
Electrode positions for welding and their use
But the angle of inclination is not all the parameters that will have to be maintained. There is also the length of the arc. This is the distance from the tip of the electrode to the surface of the part. The average arc is 2-3 mm, the short one is 1 mm or even right next to each other, the long one is 5 mm or more until it comes off. Practice begins with working on the average length of the arc. Maintain 2-3 mm to metal. Then the seam will be smoother and of better quality: if the gap is too large, the arc begins to jump, the heating of the metal is insufficient, the seam turns out to be smeared, and the connection is unreliable. With a short arc, another problem arises - the seam is too convex due to the fact that the heating zone is too small. This is also not good, since undercuts remain - grooves along the seam on the part - reducing the strength of the connection.
The length of the welding arc and its effect on the quality of the seam
After practicing for some time laying beads using different movements, and when the beads are the same width and the surfacing flakes are approximately the same size, you can try welding the seams. You can read about the types of seams and joints, as well as their preparation, here, or you can watch another lesson, “Welding for Dummies.”
All the basics of welding with an inverter for beginners. All you have left is practice: you need to use more than one electrode for training. Even, maybe, more than one kilogram. When your hand makes all the movements itself, everything will seem completely uncomplicated to you.
To consolidate the acquired knowledge, first try to train your hand a little without an electrode, practicing movements while holding a pencil in your hand. This is also a good option, maybe it will seem more acceptable to you. This video tutorial on welding with an inverter for beginners explains everything very clearly, simply and easily. If there are any uncertainties, please review. You will understand how to cook using inverter welding. Lots of useful information for beginner welders.
And finally, about some features of the operation of welding inverters. They are very afraid of dust, especially metal dust. Therefore, it is advisable not to use an angle grinder near them and carry out regular cleaning with a vacuum cleaner inside (after the warranty period has expired). It is not recommended to use them in the rain or in damp areas. This is especially true for inexpensive household models. Although they have protection against electric shock, it is still better to be safe.
When choosing electrodes, pay attention to the area of their use: they must be suitable for direct current operation. When welding at the highest current or voltage, the operating mode is intermittent. It is indicated for each device in the passport.
Let's sum it up
This matter has its own specifics, there are many methods, and each of them, with its own characteristics, you just need to remember. In the process of performing a technological operation, it is important to avoid haste or delay. But the result is impressive - an aesthetically pleasing object that does not leak, without cracks or chips.
Now that you know how to weld thin metal using electric welding, you can immediately purchase consumables and start working. will help you with this - we sell bandsaw machines, to clarify the information you are interested in, contact our managers at the contact numbers listed on the page. Select conductors, set the mode, start solving the problem, armed with knowledge about this equipment. Contact Rosta LLC if you decide to buy devices for industrial use. We have manual and semi-automatic band saws in stock and on order, as well as pendulum, vertical and two-post units. To contact our specialists, call the contact numbers listed on the page.
Galvanized welding
Galvanized steel is the same thin sheet, only coated with a layer of zinc. If you need to weld it, you will have to completely remove this coating on the edges for welding, until you get clean steel. There are several ways. The first is to remove it mechanically: with an abrasive wheel on a grinder or grinder, sandpaper and a metal brush. There is another way - burn it out by welding. In this case, they pass the electrode twice along the seam. In this case, zinc evaporates (it evaporates at 900°C), and its vapors are very toxic. So this work can be carried out either on the street, or if there is an exhaust hood at the workplace. After each pass, you need to knock off the flux.
It is better to weld galvanization outdoors: evaporating zinc is very harmful
After complete removal of zinc, the actual welding begins. When welding galvanized pipes, to obtain a good seam, two passes with different electrodes will be needed. The first seam is welded with rutile-coated electrodes, for example, MR-3, ANO-4, OZS-4. In this case, the vibrations have a very small amplitude. Make the top seam wider. It is approximately equal to three electrode diameters
Here it is important not to rush and cook well. This passage is used by electrodes with a basic coating (for example, UONI-13/55, UONI-13/45, DSK-50)
Read more about choosing electrodes for inverter welding here.
Welding techniques and methods
For welding thin sheets of metal, semi-automatic models of welding machines, as well as manual arc units, are suitable. It is much easier to work with a semi-automatic machine, since some of the welding processes are automated. This allows you to overcome some of the difficulties when working with thin sheet metal.
The advantage of semi-automatic machines is also the absence of the need to change electrodes during operation, because the wire is fed stably
This speeds up the work process, which is extremely important when carrying out large-scale projects.
On a note! For domestic purposes, for non-volume operations, craftsmen often use manual arc welding due to its low cost and the ability to make the unit with their own hands.
When welding thin sheets of metal, it is important not only to have good equipment, but also to understand how to weld such material. Scheme of welding a thin sheet of metal
Scheme of welding a thin sheet of metal.
There are different welding techniques and methods that are relevant for this case:
When performing continuous welding of an entire seam, it is important to select the correct current. Optimal range - 40-60 A
It is equally important not to make a mistake with the speed of moving the electrode for welding thin metal. If you move too quickly, the root of the weld may not be welded through. And if you move too slowly, the metal surface can become covered with holes. Intermittent welding is also called spot welding. It is used more often than other technologies in the case of thin sheet metal. To implement this technology, thin electrodes are required, with one end of which dots are placed on the metal or short lines are drawn with equal spacing.
On a note! The peculiarity of intermittent welding is that even very thin metal sheets can be welded this way. The main thing is to set the welding current a little higher than usual, and to achieve rapid movements in order to prevent the material being welded from cooling down.
Experienced welders recommend adhering to the following rules when working with manual units and thin sheets of metal:
High-quality welded joints can be obtained subject to constant monitoring of the parameters of the weld from all sides during the process of electric arc welding with an inverter. When working, it is important to keep the electrical conductor as close to the metal surface as possible until a red spot appears on it. It is direct evidence that there is a metal drop under the electrical conductor, due to which the metal sheets are connected.
Advantages of welding thin workpieces with an inverter
This method allows you to make a high-quality connection of thin metal. If welding work is carried out by a professional, then temperature deformation does not occur and the product will have an aesthetic appearance. With direct current, thin products can be cooked with less current, so the likelihood of burnout is significantly reduced.
The microprocessor control of such a device allows you to eliminate “holes” and voltage failures, generating an ideal output current that is suitable for welding work.
Technology and training
Workwear for welders
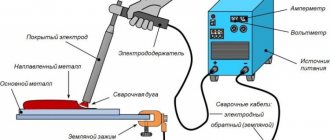
The process of welding metal, both by electric welding and by other methods, begins with the selection of work clothing and equipment. For electric welding you need:
- mask or goggles for eye protection with a special light filter;
- gloves, preferably suede;
- long sleeved clothing;
- closed shoes.
From equipment:
- welding machine;
- transformer for converting alternating current into direct current;
- electrodes included;
- hammer and other tools for knocking down slag and cleaning the seam.
Welding kit: protective mask, apparatus and electrodes
Learning how to weld metal using electric welding correctly depends on the selection of equipment, and, first of all, electrodes. The quality of welding depends on their coating or coating. Under the influence of temperature, the coating turns into a gas zone above the bath of molten metals of the base and electrode, which prevents the influence of air on the process of their fusion.
It is better to gain experience in welding work under the guidance of a professional mentor, because often the choice of equipment, its mode of operation, consumables, placement of elements to be connected, speed of arc movement, and so on occurs empirically, that is, by trial. With experience will come skills, uniformity of movement, quality of edges and seams.
Stainless steel
Alloy steel requires special electrodes for arc welding.
Welding alloy types of steel also has its own characteristics. If it contains from 12 to 20% chromium, then such steel is called stainless steel. Along with chromium, this steel contains other substances that form its specific physical and chemical properties. It is on them that its ability to weld and the way in which elements made from it can be connected depend.
Argon welding is one of the best ways to join stainless steel.
In stainless steel, thermal conductivity is reduced by 1.5 - 2 times. This is why it melts more easily, which means that when welding it is necessary to use lower currents. For the same purpose, so that electrodes with chromium-nickel rods do not overheat, they are made no more than 350 cm long. This steel, due to its high coefficient of linear expansion, can crack after welding when cooling if a sufficient gap is not maintained when connecting the edges. It must be borne in mind that after heat treatment, chromium-containing steels may lose their anti-corrosion properties. In order to avoid such an “unpleasant” effect, the heating area must be quickly cooled.
Electric welding can be used to weld stainless steel in several ways. There are three ways:
- covered electrodes;
- in a gas-argon environment;
- using stainless wire.
In any case, before welding, the edges of the surfaces planned for joining must be treated: cleaned and washed with a solvent.
The welding method is selected depending on the thickness of the metal, the requirements for the quality of the seam and the available equipment, as well as taking into account the characteristics of alloy steels.
Welding of stainless steels and ferrous metals is possible provided that special filler wire and electrodes are used.