The process of joining two metal workpieces ceased to be a problem after the advent of the welding machine. Some difficulties still remain. For example, it is not easy for beginners to do the job of welding two thin metal sheets in good quality. The article examines in detail the question of how to properly weld thin metal using electric welding. Looking ahead a little, it is worth saying that to perform such operations, technologies and equipment are used that allow the work to be completed without deforming the welding sheet and burning out the working area.
Features of the technology
To avoid burning the metal, you need to draw an electric arc along the joint as quickly as possible. The consumable must be carried evenly, without stopping in any place. The operating current for performing such operations is reduced to a minimum, below which the operation is simply impossible.
To weld thin sheets of metal, you need a welding machine with continuously adjustable output current. To get rid of possible problems with ignition of the welding arc, devices with an open circuit voltage of at least 70V are used. When welding sheet materials, you should carefully monitor the geometry of the edges. It can become deformed when exposed to high temperatures. To prevent this, you should follow a few simple rules.
First of all, it is important to carefully prepare the workpieces for the upcoming operation. The edges are cleaned and freed from rust, paint, industrial fats and other things. If required, the workpieces are aligned and secured. A good and durable connection can only be obtained if the edges of the workpieces being welded are smooth and clean. Upon completion of the preparatory work, the edges are tacked every 7-10 cm. And only after this can one begin to form a continuous seam.
If you plan to weld two thin sheets overlapping, then you can set a slightly higher current than with a butt joint. Double sheets of blanks significantly reduce the negative impact of high temperature on the surface of the blanks. The probability of burning through the surface is reduced several times, and deformation is practically not observed.
Experienced welders advise resorting to a little trick when welding thin metal with an electrode. The effect of high temperature can be minimized by placing copper sheets under the workpieces. Non-ferrous metal has excellent thermal conductivity and effectively removes excess heat from the work area. This reduces the likelihood of sheet deformation or metal burning. If there is no copper sheet, then you can use wire, which is laid at the welding site.
Let's sum it up
Welding thin-walled metal structures has a number of features that are important for an inexperienced welder to understand: you need to know which electrodes should be used, and also understand how to properly weld metal with an inverter.
Electrodes used for welding thin metal must be moved along the weld quite quickly so as not to allow the surface to cool. But at the same time, the movements should not be overly rapid, otherwise failures in penetration, which reduce the strength of the connection, cannot be avoided.
How to weld thin metal with an inverter
When it is necessary to weld thin sheets of iron using an inverter, specialists resort to the reverse polarity method. It consists in the fact that the “ground” is attached to the workpiece, and the positive pole is connected to the holder. With this connection method, the electrode heats up more, and the metal heats up less. This minimizes the likelihood of the workpiece burning through or edge deformation. Welding work is carried out faster, and the seam is of high quality.
Another feature that allows you to improve the quality of welding of thin-walled materials is the use of small-diameter consumables. In our case, electrodes with a diameter of up to 2 mm are used. It is advisable to choose brands of electrodes with a high melting coefficient. This allows you to reduce the current during operation, which has a positive effect on the quality of the welded joint.
| Metal thickness, mm | 0.5 mm | 1.0 mm | 1.5 mm | 2.0 mm |
| Electrode diameter, mm | 1.0 mm | 1.6 mm - 2 mm | 2 mm | 2.0 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Current strength, A | 10-20 amps | 30-35 amps | 35-45 amps | 50-65 amps |
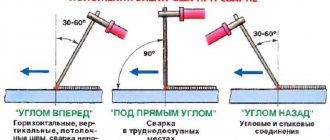
The movement of the electrode along the joint should be smooth, and it should be positioned at an angle forward to the metal surface (45-90 degrees).
Technological process
Welding thin metal with an inverter.
Step-by-step instructions for the welding process will allow you to cope with the work without much difficulty. To begin with, it is necessary to ensure safety measures when carrying out work, which include the use of protective clothing - a welding mask, gloves, clothing made of thick, coarse fabric. Do not use rubber gloves.
You can then follow the following instructions:
- First, the current is adjusted and an electrical conductor is selected to work with the inverter. The current indicator is taken based on the characteristics of metal parts. The required diameter of the electrode is selected and inserted into the holder. The ground terminal is connected to the part; the electrical conductor should not be brought too sharply to avoid sticking.
- Ignition of the electric arc starts the operation of the inverter apparatus. To activate the arc, point the electrode at a slight angle to the welding line. The electrode should be held until a small red spot appears on the surface - this means that a drop of hot metal is located underneath it, which will facilitate further welding along the entire length of the seam.
The electrode is held from the welding site at a distance corresponding to its diameter.
- By following these steps and choosing a specific welding method, there is a great chance of getting a high-quality and even seam. Scale and scale formed at the welding site are removed with a small hammer.
Advantages of welding thin-walled workpieces with an inverter
Thanks to the use of modern equipment, the quality of the weld has significantly improved. If the work was carried out by a specialist with sufficiently extensive experience, then we can safely say that the metal is heated normally, and there are no burns or thermal deformation. The fact is that direct current allows you to select the minimum power. The possibility of metal burning is minimized and is allowed only by inexperienced users.
Welding machines have microprocessor control, which allows you to avoid equipment malfunctions and obtain the ideal current for this type of work at the output. The disadvantages of the inverter include its unstable operation at low temperatures. Even branded models fail at sub-zero temperatures.
Alternative Methods
A reliable alternative to an inverter is the use of semi-automatic devices for connecting thin metal elements . The use of wire allows you to increase productivity due to the absence of pauses for replacing electrodes. The range of consumables allows you to choose the ideal option for a particular case.
The disadvantage of a semi-automatic machine is the increased requirements for the qualifications of the worker - a novice welder is not able to master all the skills of working with this equipment in a short period of time.
Features of welding thin galvanized sheets
To weld galvanized steel, you will have to completely remove zinc from the edges being joined. To do this, you can use a sander or hand abrasives.
You can get rid of the galvanized layer by burning it out using a welding machine. But the welder needs to be especially careful. Zinc vapor is toxic to humans and can cause severe poisoning if ingested. You can only work in an open area or indoors, provided there is a powerful exhaust hood at the workplace.
Basic connection methods
The technique for performing the work depends on the welding equipment and consumables used . Let us consider the features of the connection depending on the technology, with the exception of welding with consumable electrodes, which was discussed above.
Non-consumable graphite electrodes
This method has become especially widespread when working with thin-walled products by professional welders. There are two ways to achieve the goal:
- Use of filler wire;
- Melting method followed by joining.
The second method is used more often, since reflow eliminates the use of additional filler materials, which affects the cost of work. The essence of the method is to heat treat the edges being joined until the aggregate state of the surface changes. This creates conditions for joining the material. With certain skills, you can create a tight connection without burning out individual sections.
Wire is used as a filler for various cavities and voids. The size of the cross-section of the manufacturing material must correspond to the characteristics of the workpiece.
Very thin metal
This problem is most often encountered by service station workers when repairing car body parts. Modern transport manufacturers use sheets whose thickness does not exceed 0.8 mm. Thus, the use of inverter welding machines is not possible, except in emergency cases.
The main way to solve the problem is to use overlays made of thicker material, which plays the role of a frame for the future connection..
Features of working with galvanized steel
When working with galvanization, we recommend removing the protective coating manually or mechanically . Otherwise, the zinc will burn out during the joining process, which can lead to worker poisoning from its fumes.
In industrial enterprises, a directed flame is used to prepare the product, burning out the zinc layer.
Due to the insignificant thickness, experts recommend using the point connection method.
Selecting a welding helmet
As we mentioned at the beginning, when welding at low currents, the light from the arc is less bright, so the joining line is difficult to see. Due to insufficient lighting, you can even put a stitch bypass. It is more convenient to weld thin metal with coated electrodes in chameleon masks with a darkening range of 4-8 DIN or 9-13 DIN.
Unlike a mask with a conventional light filter, in a chameleon you can precisely point the tip of the electrode at the junction. This reduces the number of “bunnies” and helps keep the front surface of the product clean. Adjustable darkening power from 4 to 8 DIN makes it easy to adjust to different low welding currents.
We recommend buying a BARSVELD MS 307 mask with ASF-707 with a range of 5-8 and 9-13 DIN, which has a large viewing window of 98x87 mm. Thanks to this, a good overview is maintained in all spatial positions. Full Color technology conveys everything in natural colors and it will be easier for a beginner to distinguish the molten slag of the electrode coating from the liquid metal. The price of the mask is a little more than 5,000 rubles, which makes it quite affordable even for household welding in a garage or country house.
Which electrodes should you use?
You can cook with direct current using any electrodes, it is important to choose the diameter. It is recommended to use 2 mm, and if metals of different thicknesses are joined, then welding with 2.5-3 mm electrodes is allowed.
The choice of brand depends on the preferences of the welder. Most people use electrodes of the ANO-4 type, which are easier to ignite, but they often use UONI 13/55 or similar.
Approximate cost of UONI 13/55 electrodes on Yandex.market
You can also use welding materials from Kobelco. These are Lb-52U electrodes, their diameter differs from Russian standards - 2.6 and 3.2 mm. They are much more expensive than domestic ones, but due to the use of high-quality coating by the manufacturer, it is easier to cook with them than with similar SSSIs.
Approximate cost of Kobelco electrodes on Yandex.market
It is better to choose electrodes with graphite tips. This technology facilitates the initial ignition of the arc.
Practical advice
Before the process, experienced welders recommend familiarizing yourself with useful tips:
- Initially, you should train on excess residues and defective products.
- With the inverter method, a small power is selected, because it is forbidden to break the work between the electrode and the iron sheet.
- For any operation, it is necessary to wear protective clothing and additional accessories, for example, heat-resistant gloves, a flame retardant jacket, a durable helmet, and goggles.
- A special lining reduces the likelihood of burning holes, making it easier to weld thin metal.
- A smaller arc prevents overheating of the treated area.
High-quality welding of thin sheet metal is carried out using specialized equipment. The main thing is to prepare the products, remove excess temperature, and set the current.