An indispensable piece of equipment in the manufacture of plastic products is the extruder.
Inside this apparatus, the polymer base melts, which, having acquired the desired consistency, passes through nozzles (dies) that form products of a given shape. In this way, both profiles and a wide variety of parts are manufactured.
Applications of extruders
Technologies for processing materials by extrusion are actively used in a variety of fields:
- Agriculture (production of animal feed, greenhouse films).
- Food industry (confectionery, pasta, baby food, chewing gum, corn flakes).
- Production of packaging materials, multilayer bags, shrink films.
- Stationery, printing, lamination, printing, production of hydrogels for 3D printing.
- Construction materials (extrusion of foam blocks, insulation, PVC profiles, polystyrene, polypropylene).
- Production of plastic pipelines.
- Chemical industry (production of fertilizers, silicone products, rubber).
- Metalworking (aluminum profile).
- Extrusion of cable coverings, heat-shrinkable tubes.
- Alternative energy (solid biofuels).
The shape of the finished product depends on the type of cross-section of the hole in the calibrating device. If the extrudate passes through the slot-shaped section, the output will be a sheet product. If the cross-section of the channel has the shape of a ring, pipes (pasta) are obtained.
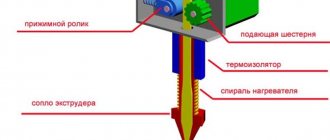
Operating principle of extruders
Diagram of the extruder structure
Structurally, the machine is divided into three compartments:
- Loading area.
- Melting.
- Dosing.
In the first compartment of the extruder - the feeding zone - granulated raw materials, polymer powder, or waste secondary raw materials are poured into a hopper and fed to the blades of a screw rotating from an electric drive. Loading of granules occurs by gravity or forced under the influence of compressed air supplied from the compressor. As more and more new portions arrive, the polymer gradually moves to the hot sections and ends up in the melting zone. In this place, the depth of the screw thread and the distance between the turns of the auger are much smaller than in other areas. Under the influence of increased pressure, the polymer plug is pressed against the hot walls and intensively compacted.
Next, in the dosing zone of the extruder, the molten mass is forced through mesh filters with small and large holes located in front of the head. The main task of the mesh package is to improve the homogenization of the melt and remove the smallest contaminant particles. This is especially important in the production of the thinnest super transparent films, which, in the presence of foreign particles, are prone to destruction of the structure and the formation of holes in the film.
At the final stage, the extruded material comes out through a forming nozzle with a hole of a certain cross-section, depending on the configuration of the product being produced.
The melting of polymer granules mainly occurs due to powerful shear deformations of the compacted raw material. The heating elements of the extruder only speed up the melting process. If internal friction of the mass releases such a large amount of heat that it becomes sufficient for stable melting of the polymer, then the electric heaters are automatically turned off and the system enters a thermodynamic adiabatic mode.
The design and principle of operation of an extruder, what is it?
Just by the fact that the words “extruder” and “extrusion” are the same root, it becomes clear that the extruder is the main working body of the extrusion line.
Along the length, the polymer extruder is conventionally divided into three zones: loading, melt compression and dosing.
Extruder for film
Diagram of an extruder for polyethylene
- Loading Zone. Granules (powder, secondary raw materials) are fed into the hopper by gravity or under the pressure of air compressed by a compressor. The screw, which is driven by the drive, rotates and compacts the polymer into a plug and moves it to the hot sections of the extruder.
- Melting zone. Here the pitch between turns begins to decrease. As a consequence, the same volume of polymer tries to fit into a reduced space. The plug is pressed against the heated walls of the extruder pipe, melts, and the melt is mixed. We would like to clarify that melting occurs mainly not due to heaters (they only intensify the process), but due to enormous shear deformations in the compacting polymer.
- Dosing area. At the exit from the extruder, the polymer is forced through a system of filter meshes and passes through a molding hole, the profile of which depends on the shape of the product being manufactured.
Important! Extruders can vary in type and number of screws. Available: single-screw, twin-screw and multi-screw, disk and multi-disc extruders.
About the design of a single screw extruder.
Inside the thick-walled housing (pipe), a screw rotates - a metal rod with a screw winding. The screw moves the granules towards the extrusion head. The body is surrounded by sections of clamp heaters, which heat the metal and melt the polymer, which is pressed by a screw to the inner surface of the pipe. The “hot” part of the equipment is placed in a water-cooled casing, and the top is insulated with a thermal cover.
Single screw extruder, diagram
Why is degassing carried out during extrusion?
The quality of the finished product depends on the chemical composition and condition of the raw materials loaded into the extruder. Thermal treatment and evaporation of polymers in vacuum chambers is called degassing. After degassing, the amount of air in the granules is significantly reduced, the percentage of moisture is reduced, and the raw material gets rid of harmful impurities as much as possible.
Extruder machines equipped with screw pairs with degassing systems have special compression and expansion zones. Gaseous components in the expansion zone are removed through holes in the screw or cylinder itself using vacuum pumps. The use of such screws allows you to combine extrusion stages with simultaneous removal of gases without interrupting the entire technological process.
The sequence of operations is as follows:
- loading;
- plasticization (bringing to a homogeneous state);
- melting;
- compression;
- loosening;
- removal of volatile compounds;
- recompression;
- squeezing out the finished mass without containing gases.
If degassing is incomplete, air bubbles will remain in the molten mass. As a result, cavities, voids, and cavities are formed in finished products. Such products are defective.
Features of polymer extrusion
Extrusion technology follows the following algorithm:
- The granules are poured into the machine's hopper.
- The heating turns on.
- The particles melt and form a homogeneous viscous mass, which is the prototype of the future PE film.
For melting, different types of polymers are used, differing in melting temperature. In particular, polyethylene melts at 100-125 °C. Polypropylene - at 80-170°C. Such a wide melting temperature range is due to the presence of various additives in its composition.
What is polymer extrusion?
The extrusion process occurs when polymers are heated to a maximum of 250 0C. Production takes place at speeds of up to 120 meters/minute. About 30% of the total volume of polymers is processed using extrusion technology using extruders. Let's try to understand the intricacies of this process.
Polymer extrusion is a technology for producing molded products from thermoplastics and their compositions on screw presses. It is carried out by pressing (under pressure) a homogeneous melt through the slot of the extruder molding head.
The gap has a certain shape, which determines the geometry of the product - siding, film, PVC window profile. Granules of LDPE and HDPE polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, polystyrene and other polymers are used as raw materials.
Extrusion includes the following steps:
- obtaining a homogeneous melt in the extruder;
- molding;
- product cooling;
- tension and winding (films), cutting (profile, pipe).
How does sleeve inflation occur?
To obtain a tubular film, the mass is forced through a ring-shaped hole, resulting in a narrow tube of a certain diameter. The extruder has a pipe expansion function: compressed air is supplied through hoses from the blower into the workpiece at a pressure of 0.13 MPa. The hollow pipe stretches upward, expands in volume, and becomes like a huge vertical bubble of the required size.
Scheme of the process of producing tubular films by blowing in the vertical direction:
1. Sleeve film. 2. Cutting device. 3. Guide shaft. 4. Pulling rollers. 5. Guide cheeks. 7. Extrusion head. 8. Cylindrical tube blank. 10. Control valve. 11. Hose. 12. Receiving coils. 13. Blower. 14. Receiver. 15. Extruder.
In the upper part the sleeve is cooled by air currents. The walls of the sleeve become flat, the opposite sides are connected using guide cheeks, fed to a receiving and winding device, smoothed by rollers and wound onto receiving reels. This technological process continues continuously.
Ring gap is one of the most popular polyethylene extrusion methods. This technology is most often used in the manufacture of sleeve-type polyethylene products, which are widely used in everyday life, construction, manufacturing enterprises, etc.
In order for the resulting film to have uniform thicknesses over the entire surface with a minimum number of folds, the outer and inner cylinders of the extruder ring head must constantly rotate.
Advantages of blown film technology:
- mechanical strength of the canvas;
- minimal losses when cutting films;
- relatively low production cost;
- ease of use (to turn a sleeve into a bag, just weld one edge).
Flat slot extrusion
This method is used when working with crystallizing polymers that form melts of low viscosity. Compared to tubular films, the structure of flat films is less durable and dense, but they are transparent and elastic. Extrusion by the flat-slit method occurs at high temperatures, due to which such films have much fewer defects.
Schematic diagram of the production of polyethylene films using the flat-slot method:
1 – extruder; 2 – slot head, 3 – cooling drums, 4 – edge trimming mechanism, 5 and 6 – pulling rollers, 7 – guide rollers, 8 – winding unit.
The polymer melt is extruded through the slot-shaped opening of the sheet extruder head. The thickness of the gap is adjusted using forming jaws, one of which is fixedly fixed, and the second is set to the required distance depending on the given size.
The output is a continuous web, which is fed onto the smooth surface of the drum for cooling. The extruder cooling drum is made of chromium steel. Polished surfaces with incoming PE film are irrigated with water and cooled to 40 - 70 degrees. Next, the film is pulled between pulling rollers, cut and, using a winding device, wound into rolls. In order for the web to have the same thickness over the entire area, the same value of extrudate viscosity is ensured along the entire length of the forming slot.
In modern production, collector-type extruder heads have become widespread. Here the extruded melt comes out simultaneously from several points, due to which it spreads more evenly. The distribution channel is made in the form of an elongated cylinder, inside of which a distribution screw is placed, ensuring uniform spreading of the melt over the entire width of the slot die and preventing stagnation inside the channel.
In this case, the plane of the cooling drum must also have the same temperature. The difference t throughout the entire volume should not be more than two degrees. To produce super shiny and clear polyethylene films, the molten extrudate extruded through the slit is directed into an ice water bath for more rapid cooling.
Advantages of the flat-slot method:
- High process productivity.
- Polyethylene films have excellent optical properties.
- There are practically no areas of different thicknesses.
Types of extruders
Modern extrusion plants differ both in the design of the working body and in their intended purpose.
Single and twin screw extruders
Screw (worm) extruders are the most common , as they almost fully meet all the requirements of the technological process. The working body is the extruder screw (Archimedes screw, known to everyone at least from home meat grinders).
The extruder screw blade grabs the raw material in the loading area and moves it sequentially along the entire length of the housing cylinder, through the heating, homogenizing and molding zone. Depending on the technological map and the type of source material, screws can be normal or high-speed, cylindrical or conical in shape, tapering towards the exit. One of the main parameters is the ratio of the working diameter of the screw to its length. Augers also differ in the pitch of the turns and their depth.
However, single screw extruders are not always applicable. For example, if a semi-finished powder product is used as a raw material, one screw will not be able to thoroughly mix it during melting and homogenization.
In such cases, twin-screw extruders are used, the screws of which can be in mutual engagement, perform parallel or counter rotational movement, and have a straight or conical shape.
As a result, the processes of heating, mixing and homogenization are carried out more thoroughly, and a completely homogeneous and degassed mass arrives at the head.
It should be noted that in some technological processes extruders are used with a large number of screws - up to four, and in addition, there are planetary machines, when up to 12 satellites rotate around a central screw.
This may be necessary when working with certain types of plastics, which, when exposed to high temperatures, tend to undergo destruction—loss of physical properties. Thus, their heating in such extruders is carried out due to the friction force and the high pressure created.
Extruder for PVC profile
The production of plastic or composite profiles in most cases is carried out using the extrusion method. For this, depending on the material and complexity of the product shape, single- or twin-screw machines with corresponding forming heads are used.
The range is very extensive - from thin threads or strips to sheets, large panels and profiles with complex geometries. The now familiar plastic window and door systems are assembled from PVC profiles made in exactly this way.
The addition of special components to the polymer makes it possible to produce complex composites, for example, wood-plastic structures, which are also often used in the manufacture of various building structures.
Extruder for pipe production
When producing pipe products, a very important condition is the absence of gas bubbles in the homogenized mixture , therefore pipe extruders are necessarily equipped with a degassing system. Typically these are twin-screw installations in which, among other things, so-called barrier screws are used, which reliably separate the still solid semi-finished product from the completely molten one. This ensures complete homogeneity of the composition, which is very important for the performance of the produced pipe.
Extruders for polyethylene
All polymer films are produced exclusively by extrusion. A blow extruder is used to produce films. The forming unit of the extruder for stretch film can be made in the form of a narrow slot - the output is a single-layer film of the required thickness and width.
Some models use round slotted dies of large diameter - the film is produced in the form of a sleeve.
Mini film extruders produce polyethylene with a sleeve width of up to 300 mm and a thickness of up to 600 microns. The small size of the device allows it to be installed even in an ordinary room.
Technologies for the production of plastic parts by co-extrusion
Modern technologies make it possible to produce polymers, building profiles, sheets, containers, electrical wire coatings, pipes and many other plastic products that meet a large number of requirements. They must be simultaneously:
- durable;
- lungs;
- environmentally friendly;
- durable;
- resistant to aggressive environments;
- visually attractive;
- water-, gas-tight, etc.
Coextrusion (another name for coextrusion) is the most progressive method in which polymers with different properties form multifunctional multilayer materials in which each layer retains its individual characteristics.
Vivid examples of the use of co-extrusion materials are packaging film for pharmaceuticals, vacuum sealing of perishable products with different shelf life, etc. Such multilayer films consist of several layers (from 3 to 11, and in some cases more). The minimum thickness of one layer is 2 microns, the maximum is 2-3 millimeters.
Co-extrusion technology involves the simultaneous operation of several extruders + the presence of a single molding unit. Using this method, a completely finished material is obtained in one process. This means that finished parts and molded products do not need to be sent for painting, priming, gluing and other additional processing.
Co-extrusion and co-extrusion.
Coextrusion is a technology used to produce multilayer films.
The following raw materials can be used: low and high density polyethylene, polypropylene, polyamide film and other polymers. The granules of these plastic masses are melted in different extruders, after which they are combined and passed through one molding die (head). For strong bonding, the molecular network of polymers must be similar in structure. But if you need to bind a barrier layer, for example, EVOH and linear polyethylene, then special binder copolymers are required.
Co-extruded multilayer films are used for vacuum sealing of products, such as transport packaging, agricultural film (for mulching, film with antifog effect), pharmaceutical packaging.
Using a similar technology, called co-extrusion, siding panels and PVC profiles are produced. Polyvinyl chloride is the basis of the profile, occupies about 80% of the panel thickness, the remaining 20% is acrylic. As in the case of coextrusion, the operation of two coextruders is used, where PVC and acrylic are melted separately. These melts are combined in a slot filler, from where they emerge as a ready-made soldered product.
Coronary polymer treatment
Chemically inert surfaces of polymer products produced by extrusion, as a rule, do not form strong compounds with printing inks. When inks, adhesives or dyes are applied to non-porous surfaces, the liquid is not absorbed, but collects in drops and flows off instantly.
For the production of polyethylene packages with drawings and advertising inscriptions, extrusion lines are equipped with special devices for processing the film with corona discharge in order to increase its adhesive properties. The surface energy of films that have undergone electromagnetic corona treatment increases and becomes 7-10 dynes/cm higher than the surface tension of liquid media. As a result of microetching, smooth surfaces with an activated structure are well wetted and are ready for painting, gluing, flexo printing, applying bright patterns and other types of processing.
What does an extruder operator do?
The entire process of manufacturing polymer products is under the guidance of a machinist who controls the extruder. A qualified worker must know what extrusion is, what processes occur in the machine, what parameters the manufactured product should have, etc.
Main functions of the extruder operator:
- Daily inspection of machines and mechanisms.
- Cleaning working parts and components from dirt and build-up.
- Repair, adjustment, replacement of spare parts, adjustment of programs and modes.
- Control of granule loading.
- Melting temperatures of raw materials.
- Adjusting the rotation of the auger.
- Changing the nozzle diameter and extruder head shape.
The machinist also works with the released products: he checks the finished films for compliance with standards, measures the dimensions and thickness. Monitors the quality of winding.
His responsibilities include not only monitoring the technical condition of extruder equipment, but also ensuring the safety of the workplace. Before starting a shift, the operator must check how the ventilation systems work, the serviceability of lighting sources, the operation of electrical equipment, and the presence of grounding.
Types of extruders
As mentioned above, screw extruders are sometimes called "screw extruders". This name comes from the fact that the polymer mass in the cylinder is mixed and moved using an Archimedes screw.
Most extruders have one screw and work on the same principle as a meat grinder. However, the production of some types of products requires more thorough mixing of the raw materials, and in this case, mechanisms with two (and sometimes more) screws are used. This is necessary, for example, if the raw materials are supplied in powder form. In this case, the single-screw extruder will not be able to mix it well enough and, accordingly, create the required outlet pressure.