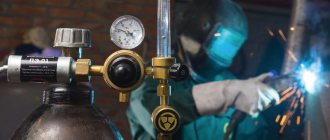
Welding metal parts has been known to mankind for a long time. However, with the development of metallurgy, the emergence of new alloys and compounds, technology began to improve in order to meet all the requirements of emerging realities. Any novice welder needs to learn more information about TIG welding: what it is, how to use the equipment, what strengths and weaknesses it has.
TIG welding
What it is?
People started welding metals quite a long time ago. However, old and modern welding are very different. TIG welding is one of the most modern methods of joining metal workpieces. Its main principle is the use of a tungsten electrode introduced into the atmosphere of a chemically inactive gas. A rod of this kind itself is usually classified as a “non-melting” category.
The welder has to sharpen the electrode tool, otherwise it is impossible to achieve a constant stable existence of the electric arc. The official definition of the term TIG is argon arc welding using an infusible electrode tool. Of course, even tungsten can melt - but only at a temperature not lower than 3500 degrees. Sometimes the scheme involves supplying not argon, but another neutral gas. It is worth noting that in technical documentation this method may have other names. For example, in German-language literature the term WIG is used. There is also the name GTA, which does not indicate the chemical properties of the gas used.
Tungsten gas welding came into commercial use in the 1940s. It became a real salvation for the aviation industry, and later for rocketry, where other connection methods were no longer satisfactory. Quite soon, engineers from other industries also appreciated the advantages of TIG. The main characteristics of this method:
- maximum uniformity of the seam (the appearance of pores and abnormal cavities is excluded);
- reduction of internal mechanical stresses;
- no melting spatter;
- Suitable for virtually any pure metal or alloy;
- no need to further process the workpieces after joining;
- the opportunity to generally master the equipment and working methods in 2-3 sessions;
- low efficiency of work in the open air (without insulation from the wind);
- the need for careful surface preparation;
- complication of work due to the unacceptability of an acute angle of burner placement;
- the need to clean out marks left by the electric arc.
Crucible welding is suitable for working with almost all types of steel. When the electrode tool is located in the collet, it is rigidly fixed in the torch. Excess length is hidden by an additional cap, which eliminates the risk of short circuit. The final part of the burner is a special ceramic nozzle. In its middle there is an electrode surrounded by an insulating gas.
When the plates are separated by a gap, or the goal is to obtain a weld with high resistance to tearing and fracture, filler wire must be used. The cross-section of this wire is determined by the required thickness of the product and specifically the seam. In some cases, a pulsed version of TIG welding is used. This option implies that the current parameters change from maximum to minimum in a relatively short time. Both direct and alternating current can be used for operation. Both the type and thickness of metal blanks are taken into account. It is imperative to understand the differences between TIG and MMA.
The second option - MMA involves the use of a coated electrode. This approach eliminates the use of insulating gas. Melting electrodes leave a reinforced seam. You can work with steel confidently using MMA equipment. The TIG technique allows you to effectively manipulate aluminum and other non-ferrous metals.
History of appearance
Welding has been known to mankind for decades. The idea that it was possible to join metal parts under intense heat first appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. Charles L. Coffin, an American engineer, thought about creating such equipment. However, the first samples of equipment did not allow the device to be used in industrial conditions or to weld metal alloys.
A non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas (inert helium) were first tested in the 1940s. Using this technology, it was possible to combine aluminum, magnesium, and nickel. The method became popular in aircraft and rocket engineering, and then gained popularity among other areas of industry.
Operating principle
In order to understand what it is - TIG argon arc welding, you must have at least basic knowledge in the field of welding. TIG welding process technology was developed in 1841. The progress was that this made it possible to weld materials that had not previously been connected by this method.
The essence of the method is the burning of an electric arc in argon. This gas has a number of remarkable properties. Heavier than air, it penetrates the weld pool and protects it from other atmospheric gases. As a result, the seam is obtained without an oxide film. This contributes to good quality of metal joining. Argon is the most inexpensive welding shielding gas.
The main element is a tungsten electrode. Its melting point is almost 4000°C. This makes it possible to work with almost all types of steel. The tungsten electrode does not melt. It only requires periodic sharpening to ensure a precise and neat weld. The electrode located in the collet is fixed in the burner. Its excess length, inactive in operation, is located in a special cap, which prevents the possibility of short-circuiting.
The burner ends in a ceramic nozzle. An electrode runs along the center line of the nozzle, and there is an inert gas around it. When TIG welding, argon acts as an inert gas. Its presence prevents air from entering the weld pool, which would cause porosity in the weld during solidification. The start of argon is controlled by a button on the torch.
The electrode ignites an arc, and it melts the edges of the metals being welded. If there is a gap between the metal plates or the task is to create a seam with high tensile and fracture resistance, then filler wire is used. Its diameter is selected depending on the thickness of the product and the weld. In manual welding, the welder feeds the wire into the melting zone.
A high-quality seam is ensured by argon-assisted welding. This is accomplished by supplying shielding gas to the other side of the seam.
Argon arc welding with blowing has the following modes:
- auto;
- semi-automatic;
- manual.
In the first case, argon welding with blowing is carried out fully automatically. Laying out the trajectories along which the electrode and filler wire move is the function of the apparatus. In semi-automatic mode, the operator controls the welding using the machine, and the wire feeds automatically. In manual mode, the author of the process is the welder.
In manual argon arc welding, coated electrodes are not used, since the protection is an inert gas. The high temperature is provided by an electric arc. A coated electrode would not provide the required level of protection. In addition, hydrogen can accumulate in damp electrodes, which damages the quality of the seam.
Automatic argon arc welding works on the same principle as manual welding. The difference is that control occurs using automatic machines. The operator installs the necessary program, and the technical equipment begins to work according to the specified parameters. The automatic system also feeds the wire at the set speed.
Argon arc welding with a consumable electrode assumes that the arc is ignited when the electrode comes into contact with the metal. When non-consumable electrodes are used, this method is not applicable, since argon has a high ionization value and will require a strong spark for ignition. When using a tungsten electrode for ignition, you need an additional device - an oscillator. It produces a high frequency current for the ignition pulse. During the welding process, the oscillator generates pulses that stabilize the arc.
A high voltage with a high pulse frequency is applied to the electrode. This ensures ionization and ignition of the arc. The use of an oscillator allows the welder to safely carry out welding, both with alternating and direct currents.
The equipment can operate in different modes. Let's figure out what this is - TIG welding mode. For welding, two methods are used depending on the type of current: alternating or direct.
In TIG welding with alternating current, after ignition, the role of a stabilizing element that supplies pulses when changing the polarity of TIG welding is played by the oscillator. This guarantees the constancy of the arc.
During DC TIG welding, the heat generated at the anode and cathode is not the same. For better heating of the metal, a direct type of polarity is used, in which the plus is on the part and the minus is on the electrode. This TIG welding polarity is suitable for all alloys except aluminum. They require AC welding to remove surface oxide more effectively.
DC operation has the following advantages:
- Economical process.
- Possibility of welding at great depths. As a result, the seam becomes deep but narrow.
- Increasing the speed of the process.
When TIG welding with alternating current, pole change occurs automatically. Modes are selected depending on the metals being welded.
Technological process
Despite the fact that argon arc TIG welding requires skill and professional knowledge, it can be done with your own hands. Before this, you need to understand what TIG welding is in principle, what equipment is needed, and the sequence of actions.
Stages of assembling the welding machine:
- Connection of the oscillator to the inverter.
- Attaching the wire responsible for ground to the terminal with a plus sign.
- Attaching the wire connected to the burner to the terminal with a minus sign.
- Attaching the burner to the sleeve through which the gas passes.
- Preparing an argon cylinder. Gearbox winding.
- Attaching the gas supply hose to the reducer.
- Connecting the inverter to a 220 V network. The oscillator is powered by a 6 V unit.
Do-it-yourself argon arc welding in manual mode has the following algorithm:
- Cleaning the surface where welding will be done.
- Preparing the burner for operation.
- Argon supply.
- Ignition of the arc.
- Start of welding.
For cleaning, you can use mechanical or chemical methods. Cleaning must be completed by degreasing. Gas should be supplied a few seconds before connecting the power source. This will ensure the appearance of a protective layer.
Important! In order for a small welding arc to be created, the electrode must be located at a distance of at least 2 mm from the surface to be welded.
After igniting the arc, you can begin the welding process. With the torch in his left hand, the welder draws an arc along the seam, and with his right hand he moves the wire towards the movement of the torch. The electrode and wire should form an angle of approximately 90°. Sharp wire feeding is unacceptable, as this can lead to splashes of hot metal and the formation of an uneven seam.
Areas of application
TIG technology is used in:
- shipbuilding;
- production of cars and aircraft;
- obtaining parts of various machines and mechanisms;
- manufacturing of medical equipment;
- production of household and professional power tools.
This technique allows you to successfully weld products made of ferrous metal - cast iron and steel. You can perfectly weld, say, carbon and stainless steel workpieces. There is no need to carefully select the filler material - almost any option will do. Along with pure tungsten tools, tungsten-containing structures can also be used. Cast iron has to be preheated. Working with alloyed steels and steels containing a lot of carbon is possible if they do not experience strong mechanical loads; in addition, it is necessary to protect the metal from excessive heat.
TIG welding of aluminum with direct current has almost fallen out of use in recent years. The method itself is characterized by increased cost. Therefore, it is used mainly where high demands are placed on the products themselves and their connections. Full-fledged work can only be performed in industrial production conditions. In a private home or small workshop, serious problems usually arise.
The TIG method can also cook copper products relatively well. This option allows you to get a very beautiful seam. It is imperative to take into account the fluidity of the copper melt and the increased thermal conductivity of this metal. Strong heating of copper leads to the appearance of refractory components that are characterized by increased fragility. It is impossible to create vertical or ceiling seams - all because of the same special fluidity of the metal.
Modes
TIG equipment operates using unipolar or alternating current. Each of the individual TIG welding modes is used for different materials.
TIG welding mode
D.C
Equipment operating on direct current has certain advantages. These include:
- The efficiency of the work process increases.
- You can weld parts to great depth. The seam is narrow, but deep.
- The speed of the welding process increases.
The minus is fed to the tungsten electrode, the plus goes to the workpiece. Equipment operating on direct current is suitable for joining alloy steels and stainless steel.
Alternating current
Equipment during operation of which there is an automatic change of minus and plus. As the reverse polarity increases, the surface is more effectively cleaned of the oxide film.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The main advantages include:
- Displacement of air by argon from the area where welding occurs. Thanks to this, the seam is obtained without defects.
- Possibility of welding different metals.
- High quality seam.
- Low heating of parts, which eliminates their deformation.
- Working with metals that are difficult to weld.
- Ability to work with structures of different sizes.
- Fire safety.
- No waste.
- Isolation from the influence of the external environment.
- Electric arc stability.
- Versatility.
- Ability to work with thin metal sheets.
- Small heating zone of the product.
- Learning what TIG welding is is not difficult.
- Protecting the surface from oxide film.
- No need for additional processing after welding.
- Good control over the condition of the weld pool.
- Possibility of surfacing during restoration and restoration work.
- Possibility of using direct and reverse polarities.
- The compactness of the inverter with this function.
- Various TIG welding modes.
Disadvantages of the method:
- Low performance.
- Slow process speed.
- High cost of the equipment used.
- Availability of professional skills.
- Ineffective work in drafts or strong winds. It is necessary to install special shields and increase the supply of argon, which leads to its overconsumption.
- The need for preliminary surface preparation.
- Difficulty working in hard-to-reach places.
Provided that the shortcomings are not too significant, the use of this method is justified.
Devices (devices) for welding
For tig welding, an inexperienced welder is best suited to an MMA inverter machine with a tig function equipped with an oscillator. With this inverter, a beginner will be able to learn tig welding on stainless steel, low-alloy steel, etc., which do not require much skill from beginners.
To work with aluminum, magnesium, etc., you need a more serious inverter that switches to alternating current.
Professional inverters are equipped with additional functions:
- arc stabilization;
- welding current modulation;
- accelerated ignition;
- crater filling.
Only qualified welders can use and adjust them correctly.
Oscillator
For non-contact ignition of the arc at the beginning of welding and its stability during operation, a high-voltage high-frequency generator is used - an oscillator. It can be either a separate device or integrated into a welding machine.
Using the device, the arc is ignited without the electrode coming into contact with the metal. This is very convenient for beginners. During the welding process, the arc is constant with respect to the changing gap between the electrode and the metal surface. As a result of the operation of the oscillator, a uniform seam is obtained.
Non-consumable electrodes
The melting point of tungsten is more than 3400 degrees, so the electrode does not burn or melt under high temperature. There are electrodes made of pure tungsten or with alloying additives. The tips are painted in different colors, depending on their purpose.
To obtain a reliable seam and stabilize the arc, the working tip of the electrode must be periodically sharpened. When working with alternating current it should be round, with direct current it should be cone-shaped.
The sharpening length is approximately 2-3 times the diameter of the electrode. For the stability of the arc, the marks from the sharpening tool should be located along the tip, and not across. It is unacceptable to overheat the electrode when sharpening, because tungsten becomes more brittle.
Electrodes are selected depending on the current welding modes.
| Electrode diameter, mm | Metal thickness, mm | Current strength, A |
| 1,5 | 1 | 45 – 55 |
| 2 | 2 | 80 – 90 |
| 3,5 | 3 | 120 – 150 |
| 5 | 4 | 170 – 190 |
Beginners most often work with electrodes of 1.6 and 2.4 mm in diameter.
Welding torch
When working with low currents - 50-150A, the burner has time to cool down naturally - gas cooling. The burner with water cooling built into the handle is designed for an operating current of 200-600A. Water circulates through the entire cable channel from the apparatus to the burner.
The burner is assembled as follows:
- Install the collet holder;
- insert a collet into it;
- screw the cap on (not to the edge) - to prevent short circuits to ground;
- insert a non-consumable electrode;
- screw a ceramic nozzle onto the collet;
- adjust the electrode extension to the minimum possible;
- tighten the cap tightly.
The electrode is inserted in the center of the nozzle, and argon is supplied around the circumference.
The torch handle is attached to the cable hose statically or by means of a flexible neck, which allows for fine and long-lasting work in any plane. The button on the handle activates the supply of current to the electrode and gas.
Collet holders are available with or without a lens. The gas lens is like a filter mesh that provides an even flow of gas and a wider area of protection. This is especially useful for working with stainless steel and active metals. Without a gas lens, you can work with aluminum and black steel. For beginners, it is better to learn on black steel and not use a gas lens.
Necessary equipment
Argon arc welding of copper and other metals requires special equipment. Minimum technical equipment includes:
- Current sources.
- Oscillator.
- Inverter.
- Argon cylinder.
- Gearbox.
- Burner.
- Connecting cables.
- Tungsten electrodes.
- Filler wire.
For full TIG welding, the machine requires constant ignition. The simplest sources for TIG welding produce direct current. They can weld metals - stainless steel, ferrous metal, brass, copper, bronze. But you cannot weld metals that have an oxide film - aluminum and magnesium. They require the source to have an AC function. These are more complex sources that have the function of both direct and alternating current. For AC there are settings such as current balance.
In modern models, there are sources with modes for different material thicknesses and different spatial positions. The most common function is pulse mode. One of the characteristics is heart rate. There are sources with pulse frequencies up to 15 thousand Hz. The higher the frequency, the higher the functionality.
When choosing a machine for TIG welding, you need to decide where it will be used and for what purposes. This will determine whether the required functions are available:
- power supply voltage;
- availability of modes with direct and alternating current;
- possibility of changing polarity;
- the presence of a mode for steel with high viscosity;
- the ability to weld thick metal for a long time;
- inclusion of a water-cooled burner in the kit;
- presence of stationary type cooling;
- the ability to control operation using the display;
- Ability to work on production lines.
The advantages include additional functions:
- the possibility of contactless ignition of the arc;
- DOWN POST GAS - allows you to smoothly turn off the arc;
- BALANCE - the ability to change the polarity balance when welding with alternating current.
There are many models of welding machines for TIG welding. The TIGER 170 DC model is ahead of its competitors in terms of the ratio of device weight and performance. The device has a wide range of applications - from steel sheets with a thickness of 0.2 mm to 6 mm. The additional function of adjusting the current value allows you to weld thin sheets without burns. The device has microprocessor control and a large amount of memory. A simple and convenient interface allows you to set the necessary parameters and modes.
The HAMER TIG-200DC device can operate in two modes. This is an option for welding ferrous metals and stainless steel. The main advantage is the low price combined with the presence of all the necessary functions.
The ELAND TORS-200 welding machine has similar characteristics. There are a large number of additional functions available. A distinctive feature is that it is equipped with devices and consumables for work both for TIG and MMA welding.
GOST 5.917-71 sets out the requirements for manual torches for argon arc welding. According to this regulatory document, burners of the RGA type must be used. The most common models are RGA-150 and RGA-400. The choice of electrode diameter and thickness for TIG welding depends on the type of metal being welded.
Consumables
Welding with a non-consumable electrode does not imply that it is not consumed in the process. Let's say moreover, a tungsten electrode is considered one of the types of consumables, the condition of which must be constantly monitored. It is indeed 99 percent tungsten. This material was not chosen by chance, since tungsten has a high melting point. Components such as tantalum, yttrium, thorium, and lanthanum are used as impurities. The concentration of the additive is indicated by conventional colors: white, green, blue.
The setup procedure includes work on sharpening the electrode. The shape of the end of the rod affects the shape of the arc; it should be different under different conditions. When welding with direct current, it is necessary that the arc resembles a cone. If the current is alternating, then a rounding at the point of contact is characteristic. The surface of the rod is additionally polished.
Another consumable is gas. In TIG welding, its role is played by argon. Argon is heavier than air, so it displaces oxygen from the torch. In some cases, it is necessary to protect the combustion zone from hydrogen. Here it is more advisable to use helium (the lightest gas, with the exception of hydrogen).
Helium welding increases arc power and, as a result, productivity. After weighing all factors, including the cost of the process, helium is used only when working with refractory metals. If it is necessary to carry out complex work, a mixture consisting of argon and helium is used. The share of argon is 40%. Argon provides stable welding parameters, and helium allows metal to be penetrated to a great depth.
Sharpening electrodes
The main element in welding is the tungsten electrode. TIG welding electrodes require constant care. It consists of regularly sharpening its tip. This ensures a good weld.
There is a rule - when welding with direct current, the tip of the electrode is sharpened cone-shaped, and with alternating current - spherically. The length of the cone can be calculated by doubling the diameter of the electrode. For stability, the end of the cone should be slightly blunted.
Electrode sharpening angle values for TIG welding:
- at a small current value - 10-20°;
- average - 20-30°;
- for high current - 60-120°.
If the sharpening angle is less than 20°, then the capabilities of the electrode are reduced, and at an angle of more than 90°, arc burning may lose stability. It is also negatively affected by the risks that arise on the surface during sharpening.
To make them minimal, TIG electrodes must be sharpened lengthwise. Turning occurs with the help of a grinder, a fine-grained abrasive wheel, emery, rotating the electrode in the hand. To make sharpening uniform, the rod is secured in a screwdriver or electric drill. In this case, it is necessary to set small rotation speed values. To protect against dust, you should wear a mask.
Preparation for welding
Bringing it into working condition consists of assembling all flexible connections into one unit with the device:
- We fix the reducer with a rotameter on the gas cylinder;
- connect the hose to the reducer;
- insert the bayonet connector of the burner into the negative socket;
- the control cable is connected to the corresponding socket on the front panel of the inverter;
- The ground cable is connected to the positive socket on the device.
Typically, a torch cable, gas hose and ground cable with all connecting parts are supplied with the welding machine.
Impulses. AC pulses
Cost savings thanks to reliable TIG welding
Pulsed TIG welding alternates between two different welding currents - a pulse current and a pause current (main current). The time, and therefore the frequency and pulse ratio, can be adjusted according to your requirements on the machine or using a remote control. Pulsed TIG welding is possible with both direct (DC) and alternating (AC) current.
Complex welding jobs made easy
- Better melt control in awkward and PF positions
- Easily bridge between large gaps and gaps of other sizes
Impeccable weld quality
- Low heat input vPrecise heat input control
- Minimal material warping
- Reduced heat input, optimal solution for welding chromium-nickel steel and heat-sensitive materials
- Welding seam with very uniform flakes – the optimal solution for face seams
Description of TIG welding technology
To get a high-quality seam with your own hands when using TIG welding, you need to properly prepare. That is, depending on the thickness of the parts being welded, it is necessary to correctly select the electrode diameter, current strength and filler rod. If any of the above are chosen incorrectly, the welded joint will be poor.
As for the method of igniting the arc, there are also several of them. Each of them has its own characteristics, which indicates the level of the welding machine that is used for work. Let's consider three main ones:
- Strike or contact. This is exactly what inexperienced craftsmen do. After this, the tip of the electrode is deformed and a characteristic mark remains on the workpieces. You have to spend a lot of time to remove traces.
- Ignition by point touch or TIG LIFT. The most rational method, used in most devices. The arc is ignited at a short distance from the part or at the slightest touch, which is ensured by the control circuit of the power modules in the device.
- The third method is non-contact, but it is not implemented in all welding machines.
When welding parts, keep the electrode at a distance of 3 mm from the workpieces. If it is larger, then there is a high probability of sagging and, as a result, loss of seam strength.
If parts made of thin metal are welded, then cutting them is not necessary, but when working with thick metal, it is necessary to process the edges and take into account the gap so that the molten metal can completely fill it.
To perform high-quality welding of aluminum, cast iron or stainless steel using TIG welding, watch a video about the work process from a master. If you don't undergo some kind of instruction, you can make a lot of mistakes. For example, when using CuSi alloy for welding copper parts.
It is important when working with welding equipment with currents of up to 180, 200 or more Amps to use a welding mask, gloves and a fire-resistant gown. Of course, this method produces much fewer sparks than the arc method. Then you can better concentrate on the work process, and the result will be excellent.
Selecting a welding helmet
As we mentioned at the beginning, when welding at low currents, the light from the arc is less bright, so the joining line is difficult to see. Due to insufficient lighting, you can even put a stitch bypass. It is more convenient to weld thin metal with coated electrodes in chameleon masks with a darkening range of 4-8 DIN or 9-13 DIN.
Unlike a mask with a conventional light filter, in a chameleon you can precisely point the tip of the electrode at the junction. This reduces the number of “bunnies” and helps keep the front surface of the product clean. Adjustable darkening power from 4 to 8 DIN makes it easy to adjust to different low welding currents.
We recommend buying a BARSVELD MS 307 mask with ASF-707 with a range of 5-8 and 9-13 DIN, which has a large viewing window of 98x87 mm. Thanks to this, a good overview is maintained in all spatial positions. Full Color technology conveys everything in natural colors and it will be easier for a beginner to distinguish the molten slag of the electrode coating from the liquid metal. The price of the mask is a little more than 5,000 rubles, which makes it quite affordable even for household welding in a garage or country house.
Safety regulations
When welding, we must not forget about safety rules. It is necessary to use protective equipment for the welder: a mask or shield, gloves or leggings, special clothing and shoes.
All masks can be divided into active and passive. The sight glass of passive masks is permanently darkened. In active ones, darkening occurs only as a reaction to a light flash from the arc. The advantage of this option is that while the welding process is stopped, the glass becomes transparent and the welder can clearly see the object. There is no need to lift the glass, which is quite convenient.
Main types of welding gaiters:
- Canvas . They are not in demand because they do not perform well the main function of protecting hands from high temperatures and sparks. They easily burn when exposed to sparks.
- Split fibers . Made from specially treated leather from pigs or cows. Resistant to flying sparks. Durable, elastic, hygienic. Does not restrict hand movements. If there is a cotton layer inside, it keeps your hands warm.
- Felt . Convenient for welding work.
There are combined models that use different types of materials. Welding gaiters come in length up to the elbow and cover only the hand. The possibility of tightening the edge of the glove provides additional safety.
A welder's suit must be made of high quality materials. It must be resistant to splashes of molten metal. The requirements for a welder's suit are specified in GOST 12.4.250. The main parts of the suit are the jacket and trousers. The material from which they are made must have great heat resistance. According to the regulatory material, the jacket must cover the trousers by more than 20 cm. The fasteners are closed with flaps. The maximum distance between them on the jacket is 15 cm.
Safety regulations include electrical safety. The argon cylinder must be located at a distance of at least 5 meters from possible sources of fire. The cylinder must be placed vertically and secured to prevent it from falling. Before work, it is necessary to check the condition of the hoses.
Errors in TIG welding
The main mistake is rapid burning of the electrode. This can happen due to incorrect polarity of the selected mode, low gas flow, or poorly selected tungsten electrode diameter. Tungsten contamination of the weld may occur. The reason is that the electrode gets into the weld pool and begins to melt there.
A poor quality seam can result from the presence of condensation on the metal, a faulty hose or its loose fit, insufficient gas supply, or poor preliminary cleaning of the surface. Arc instability can occur due to incorrect polarity, dirty electrode, or too long electrode.
Common errors include discoloration of the seam and the appearance of yellow smoke. The reason is that the argon switches off too quickly. The gas is turned off 10 seconds after the arc goes out.