Types of drills
The ideal drilling result depends not only on the professionalism and experience of the master, but also on the correct selection of the drill. The right tool will make the job much easier. Types of drills for metal surfaces differ in the type of configuration and the material from which they are made.
1. Twist drills are standard cylindrical products. They reach 80 mm in diameter. Made from high quality steel. Their design is such that the working surfaces are sharpened at an angle of 118 degrees. They are needed for almost all basic drilling work in metal. This is a versatile, durable tool.
2. Conical (or stepped) drills - are made in the form of cones with a stepped surface (spiral). They can easily drill a two-millimeter hole. They are also used to correct small defective holes that were formed as a result of poor performance of another tool.
3. Core drills are serrated hollow bits. They are also called annular cutters. The craftsman needs them to work with thin metal to make neat holes up to 30 mm. This tool can drill to great depths, due to the fact that the chips pass into the cavity of the crown.
4. Feather (flat) drills consist of replaceable working plates. They are designed to drill perfect deep holes in metal of any strength. The peculiarity of this type is that the flat drill practically does not distort during drilling. In addition, they are the cheapest, so they attract the attention of craftsmen.
Depending on the production material, drills are divided into cobalt and carbide. The first ones are made of cobalt. The second ones are made of high-strength alloys. — Cobalt drills are used at high temperatures, as they do not lose their qualities. Cobalt alloyed high speed steel tools allow you to work with very tough materials and highly tough metal products. Cobalt drills have an average price, but their quality and performance fully justify it. — Carbide drills have high cutting edge hardness. The equipment itself is usually made of simple steel for metalworking tools. And the plates are made of carbide alloy. Such models are needed for drilling products made of particularly strong materials of great thickness. The peculiarity of a carbide drill is that it can self-sharpen during operation.
Typical drill sets for various materials
Initially, when developing the design and materials, leading manufacturers adopted an approach in which a set of drilling tools of different diameters was oriented towards use for drilling a specific material. Therefore, all microdrills in the set differ only in diameter. The sharpening angle of the edge, the inclination of the spiral grooves for chip removal and the cutting speed are exactly the same for all elements of the set.
Sets of microdrills for drilling steel and alloys are distinguished by the tool material used:
- Drills made of HSS-E steel, alloyed with cobalt up to 5%, for processing alloyed, carbon, hardened high-strength steels;
- Sets of microdrills made of HSS-G steel for processing lighter materials - graphite, copper, aluminum, all types of cast iron. The drill is subjected to particularly precise multi-pass grinding, so the resulting hole has an accuracy class of A, with a tolerance of h8;
- Ordinary microdrills made from high-speed steel HSS-R are produced both in single versions and in the form of a set, with a range of diameters from 0.1 to 3 mm. This tool can be used for drilling wood, soft polymers and composites.
Micro drills cannot be classified as ordinary metal-cutting tools; most often, sets of small diameter drills, up to 1 mm, are used by engravers and repairmen. Such a kit is not cheap, so the best option would be to buy a high-quality tool from a well-known brand, for example, Bosch or Heller.
High quality German drills
is rightfully considered the world's first manufacturer of drilling tools, both for domestic purposes and in industrial production. The quality of Heller set drills is determined by the very precisely selected characteristics of the cutting edge and the HSS high-speed steel used.
The standard form of sale of the kit is a case, a metal box with a folding tripod in which the drills are located. For household purposes, the tool can be sold in plastic packaging with mandatory marking of the material and a number of drill diameters included.
For professional activities, the Heller HSS Cobalt and Heller Prefix HSS-Super kits are used. In addition to a large selection of tool diameters, the drills presented in the Perfix set are made using triple center grinding technology.
Russian drilling tools
Among the numerous products of machine-building plants that produce metal-cutting tools, both of their own design and of licensed type, we can note the products of young and dynamically developing ones. You can evaluate the quality of manufactured drills for a wide range of applications using a set for drilling steels and alloys, with a tensile strength of up to 800 MPa.
The set is called “Technician” and contains 370 units of tools, assembled in 19 sections of a metal case. The drills are made of steel R4M2 in accordance with the requirements of GOST 10902-77 for accuracy class B1. This set of drills for metal “Bison” costs 49 thousand rubles for one set. According to the manufacturer, the set is designed for use in repair shops, service stations and small mechanical assembly areas.
In addition to general-purpose tools, it offers the 429625H20P set under the trade names “Expert” and “Met-Sh”. It includes ten and twenty drills, respectively, with a diameter of 0.33 mm to 1 mm. The tool is made from inexpensive high-speed steel R6M5. According to the manufacturers, the microdrills included in the set provide high positioning accuracy due to the presence of a cross-shaped reverse sharpening of the cutting edge.
The cost of the kit does not exceed 500 rubles; it is designed for use in repairing printed circuit boards of small household appliances.
Drill set made in China
Most often, to repair household appliances, small appliances and tools, you buy a simple and relatively inexpensive drilling kit made in China from an unknown company, as in the photo.
A set of 150 units of drills of various diameters, from 0.4 mm to 3.2 mm, is placed in a gray plastic case. The top cover is made of transparent plastic, with size and diameter markings on the surface. There are no markings on the tool itself, so if the lid is slightly opened, or the box is shaken vigorously, most of the drills will fly out of their cells, and it will be very difficult to sort them by size.
The drills are made and sharpened according to the old Soviet pattern with a centering belt on the edge. The quality of sharpening can be seen from the photo. The tool life will be a maximum of 4-5 drills. The cost of the set is 560 rubles.
Marking features
Markings on drills depend on their technical properties and country of manufacture. Russian GOST requires markings on all drills with a diameter of two centimeters and above. It usually contains basic information about the product: the grade of steel and the diameter of the drill. The marking is located on the shank of the cutting tool. On domestically produced instruments you can see markings of this type: “Р6М5К”. This is a formula in which each symbol is detailed information about the drill. This marking, for example, means that the product is made of high-speed steel (P), the tungsten content in it is six percent (6), molybdenum - five percent (M5) and five percent cobalt (K5). Foreign-made drills bear the HSS marking and additional designations, which, just like those of domestic manufacturers, indicate the characteristics of the product. For example, "HSS-4241" means that this model is suitable for working with aluminum.
Metal drills: varieties of diameters depending on the shape and task
The need to make a hole in a metal product arises not only among builders or metal craftsmen. Quite often, such a need may arise at home. But to make a hole you will need suitable tools and drills of the required diameter.
At the same time, the question arises: what types of metal drills exist? Surely each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. The answers to this and many other questions are in this article.
Selection Criteria
Choosing a drill for metal is a very important step. After all, the quality of work largely depends on this product. By purchasing a low-quality model or a drill of the wrong diameter , you can not only ruin your mood, but also damage the metal product in which you needed to make a hole.
Therefore, when choosing, you should rely on the following characteristics:
- Required diameter.
- Symmetrical sharpening.
- Hardness and strength of the product.
- The type of metal from which the drill is made.
- Manufacturer.
- And, of course, the price.
In order not to make a mistake with the choice, experts recommend purchasing such devices in a set. Usually in one package there are 6-8 drills of different diameters. However, products can be purchased individually. True, this will require certain knowledge.
Variety of shapes and diameters
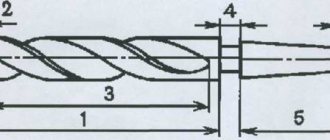
A standard drill has a cylindrical shape and consists of a cutting part and a shank. At the same time, each product has special recesses (so-called working surfaces) that remove chips from the hole. Based on these parameters, a wide variety of products are distinguished, each of which has its own diameter ranges:
- Screw model with tapered shank . Most often, such modifications can be found on special two-handed drills or drilling machines. In this case, the drill is mounted on a conical shank, and not on a chuck, as usual. Such products are used for drilling large holes, and therefore have a wide diameter.
- Crown varieties . The cutting part of such models is much wider than the shank, so it is shaped like a crown. As a rule, such modifications are used to drill holes in several metal sheets. Therefore, there are frequent teeth on the working surface.
- Products with a stepped shape . They appeared relatively recently, so they have a less wide selection of products. Nevertheless, they are gaining popularity by leaps and bounds due to their versatility. The fact is that with the same drill you can make holes with a width of 4 to 36 mm. Accordingly, the more “steps”, the higher the cost. However, this innovation can only be used on sheet metal.
- Left-hand modifications . It is quite difficult to find this variety in a store due to the specificity of its application. The purpose of such devices is to remove a broken screw or bolt. Based on this, there are only 5–7 varieties in diameter.
- Carbide models . They are distinguished by a one-sided sharpening angle and high strength. These qualities allow the products to be used for working with strong metal. Most often, such drills are produced with a small radius, but you can always make an individual order.
- High precision products . As the name implies, such devices are designed for high-precision work, so the size error is minimized. Because of this, high-precision drills are significantly higher in cost than standard models. As a rule, they are used in special enterprises, and not at home.
- Threaded _ They are used only in cases where it is necessary to make a thread in the hole. However, despite their narrow specialization, they have a huge variety in diameter.
Diameter and marking
The presence and volume of information on the drill depends on the size of the product. That is, the larger the diameter, the more data is indicated. Typically, manufacturers adhere to the following sizes:
- Drills with a cross-section of up to 2 mm are not marked.
- Products with a diameter of 2 to 3 mm contain information about the steel grade and cross-section.
- On models from 3 mm, data on the manufacturer, cross-section and alloy composition are entered.
However, this applies only to domestic producers. Foreign companies try to provide as much information as possible about the product . This especially applies to large brands, which usually indicate:
- The country in which the drill was made.
- Company `s logo.
- Composition (usually the grade of alloy or steel).
- Product size and cross-section.
- Accuracy class.
- And even brief recommendations for use (for which metal a particular drill is best suited).
To decipher the markings you do not need any specific skills. The manufacturer made sure that everything was intuitive. For example, the letter “P” is used to mark high-speed steel, and numbers with letters indicate the proportions of a particular element. For example, the larger the number next to the letter (for example, K - cobalt), the higher the concentration of this element.
In conclusion
In the modern world there are many products designed to work with metal. However, if you need to make a hole in a metal object, then nothing will cope with this task better than a special drill. Nevertheless, it is very important to choose a product of a suitable diameter, since the outcome of the work largely depends on this parameter.
Using low-quality products can harm both the metal object and yourself. Therefore, you should purchase products from well-known brands that not only produce high-quality drills, but also provide a wide variety of models.
- Vitaly Danilovich Orlov
Classification by color
By color you can determine the characteristics of the tool: strength, durability, purpose. Drills are available in three colors: gray, black and gold. Gray drills are among the simplest, cheapest and most short-lived. They do not have a protective coating, so their performance characteristics are quickly lost during operation. They are not suitable for high temperatures or heavy mechanical stress. But they are often used as a one-time use for simple work.
Black drills are treated with high temperature steam during manufacturing. Thanks to this treatment, the material is hardened and becomes durable. They wear out less and last longer than gray ones.
Golden drills can be lighter and more saturated. Light yellow very durable. They are made from high-speed steel using heat treatment technology. Bright gold cutting tools are even more durable than light gold ones. They have a titanium nitride coating. When drilling a hole, the gold drill experiences almost no friction force, which significantly extends its service life.
Standard diameters of drills for metal
The need to process metal products can arise both from professionals and from a craftsman who works at home. For processing it is impossible to do without some special tools. A very important one is a drill, as well as a metal drill.
Now in stores you can buy already assembled kits with different sizes of diameters and lengths. You can buy one drill that will suit you in all geometric parameters. You need to choose it so that you don’t have to change it or sharpen it after each use.
There are different types of metal drills, which differ from each other in functionality and design features.
The drill rod for metal work is specially designed in order to solve certain technological problems and take into account all the characteristics of the material.
Many experts advise correctly understanding the design features of such a tool. It is very important that with the help of these tools designed for metal work, it is possible to drill in various materials:
- ceramics;
- brick;
- various types of polymer materials;
- concrete.
Drills for metal processing have the following elements:
- A shank that is designed to secure the tool in the chuck.
- The cutting part, which performs the main function of drilling metal.
- The working surface, which is responsible for removing all metal shavings from the processing area.
Varieties:
- Spiral.
- Conical.
- Flat.
- Crowned.
Twist and cone drills
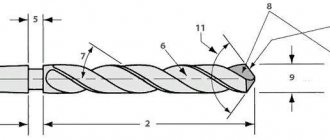
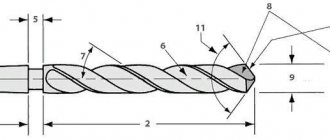
The twist drill is the most common. Used to obtain correct holes. Its design looks like a cylindrical rod, on the side of which there are spiral packings.
One or more pieces that cover the entire part of the instrument. It is these elements, which look like helical grooves , that ensure the correct removal of chips from the hole.
The diameters of the most common spiral instruments can reach up to eighty millimeters. They are actively used in factories and at home.
Left-handed spiral tools have a very small area of application , but they cannot be dispensed with in cases where a bolt with a broken head or a fastener that cannot be unscrewed in any other way needs to be drilled out of a hole. It is very easy to distinguish such a drill from a right-handed one. It is necessary to look at the spiral groove, in which direction it is twisted.
High-precision drills are usually chosen by home craftsmen who need excellent processing results. This tool can be identified by the marking A1 . Such drills allow you to make holes with a very precise diameter, maintained down to fractions of a millimeter.
Cone is a category that refers to a tool with a stepped and smooth working surface. They are used when making holes in metal products with small thickness.
They also provide easy centering of the hole during the initial drilling phase. But the main advantage of using such drills is that they can be used to produce holes of different diameters.
Flat
- they have a flat working shape, they can also be called feather ones;
- they are insensitive to distortion and cannot be damaged during processing;
- simplicity of design;
- inexpensive.
But there are also disadvantages:
- Do not drill large holes.
- There is no automatic chip removal (the geometric structure of this drill does not imply this function).
Types of drills with a special cutting edge
Core type. This type of drilling tool is made in the form of a metal cup and on the end part there are cutting teeth that are used to create large diameter holes in the metal. The teeth in them are made of carbide or they are diamond coated.
Cobalt. This is a tool created on the basis of steel (high-speed cutting), alloyed with cobalt . Cobalt gives it the highest strength, as well as resistance to deformation under mechanical and thermal stress.
Thanks to this characteristic, cobalt-type tools are successfully used for drilling holes in high-strength alloys and tough metals . The high cost of this product is fully justified by its characteristics.
Carbide. The entire carbide plate is fixed to the cutting part. The main core of the tool is made of tool steel.
For the manufacture of such plates a carbide alloy ; it is very hard and wear-resistant. When making such plates, they are sharpened. It cannot be sharpened again and is used when drilling thick metal.
How to choose the right tool
When choosing the necessary tool, you need to know for what purpose you are purchasing it and take into account the characteristics of the metal with which you are going to work. There are several parameters that you should pay attention to:
- working diameter;
- quality of sharpening;
- surface color;
- symmetry of elements;
- metal characteristics;
- functionality;
- recommendations to manufacturers;
- manufacturer's reputation.
Varieties of sizes
The diameters of metal drills that manufacturers now produce have a variety of sizes. There is a regulatory document (GOST), which provides for the division of tools into various types according to size:
- Short series - their length is 21-131 mm, diameter from 0.4-20 mm.
- Extended series - from 19-205 mm in diameter, the same as that of the short series.
- Long series - from 55-255, diameter from 1-21 mm.
Metal drills: varieties of diameters depending on the shape and task
The need to make a hole in a metal product arises not only among builders or metal craftsmen. Quite often, such a need may arise at home. But to make a hole you will need suitable tools and drills of the required diameter.
At the same time, the question arises: what types of metal drills exist? Surely each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. The answers to this and many other questions are in this article.
Classification by size
Currently, drills for working with metal are produced in different sizes to work with products of any thickness. Modern production classifies cutting tools in three working sizes:
short series drills - their minimum length is 20 mm, maximum - 130 mm; diameter ranges from 0.3 to 20 mm.
elongated - produced in lengths from 19 to 205 mm and diameters from 0.3 to 20 mm.
long series drills - reach a length of 254 mm, minimum diameter - 1 mm (maximum - 20 mm). The long model is convenient for working with products that are thick and durable. Short cutting tools are used to drill neat, uniform holes in a thin product (for example, a metal plate).
Twist drills for metal: standard sizes and diameters
Tools of this type are used to perform most operations in industry and everyday life. At home, twist drills with cylindrical shanks are most often used, and in production - with conical shanks. The diameters and sizes of household and industrial metal drills differ.
Table of diameters and sizes of twist drills for metal with cylindrical shanks
Tools of this type are manufactured according to GOST 886-77. The following grades of steel are most often used.
- R6M5.
- R6M5K5.
- P18.
- H.S.S.
Photo No. 1: metal twist drills with cylindrical shanks
Standard diameters of metal drills with cylindrical shanks range from 1 to 31.5 mm. Tools with increased dimensions are manufactured according to special orders from shops and workshops.
Standard diameters and sizes of metal drills with cylindrical shanks are presented in the table below.
| Drill diameter | total length | Working length |
| 1 mm | 56 mm | 33 mm |
| 1.1 mm | 60 mm | 37 mm |
| 1.2 mm | 65 mm | 41 mm |
| 1.3 mm | ||
| 1.4 mm | 70 mm | 45 mm |
| 1.5 mm | ||
| 1.6 mm | 76 mm | 50 mm |
| 1.7 mm | ||
| 1.8 mm | 80 mm | 53 mm |
| 1.9 mm | ||
| 1.95 mm | 85 mm | 56 mm |
| 2 mm | ||
| 2.05 mm | ||
| 2.1 mm | ||
| 2.15 mm | 90 mm | 59 mm |
| 2.2 mm | ||
| 2.25 mm | ||
| 2.3 mm | ||
| 2.35 mm | ||
| 2.4 mm | 95 mm | 62 mm |
| 2.45 mm | ||
| 2.5 mm | ||
| 2.55 mm | ||
| 2.6 mm | ||
| 2.65 mm | ||
| 2.7 mm | 100 mm | 66 mm |
| 2.75 mm | ||
| 2.8 mm | ||
| 2.85 mm | ||
| 2.9 mm | ||
| 2.95 mm | ||
| 3.0 mm | ||
| 3.1 mm | 106 mm | 69 mm |
| 3.15 mm | ||
| 3.2 mm | ||
| 3.3 mm | ||
| 3.35 mm | ||
| 3.4 mm | 112 mm | 73 mm |
| 3.5 mm | ||
| 3.6 mm | ||
| 3.7 mm | ||
| 3.8 mm | 119 mm | 78 mm |
| 3.9 mm | ||
| 4.0 mm | ||
| 4.1 mm | ||
| 4.2 mm | ||
| 4.25 mm | ||
| 4.3 mm | 126 mm | 82 mm |
| 4.4 mm | ||
| 4.5 mm | ||
| 4.6 mm | ||
| 4.7 mm | ||
| 4.8 mm | 132 mm | 87 mm |
| 4.9 mm | ||
| 5.0 mm | ||
| 5.1 mm | ||
| 5.2 mm | ||
| 5.3 mm | ||
| 5.4 mm | 139 mm | 91 mm |
| 5.5 mm | ||
| 5.6 mm | ||
| 5.7 mm | ||
| 5.8 mm | ||
| 5.9 mm | ||
| 6.0 mm | ||
| 6.1 mm | 148 mm | 97 mm |
| 6.2 mm | ||
| 6.3 mm | ||
| 6.4 mm | ||
| 6.5 mm | ||
| 6.6 mm | ||
| 6.7 mm | ||
| 6.8 mm | 156 mm | 102 mm |
| 6.9 mm | ||
| 7.0 mm | ||
| 7.1 mm | ||
| 7.2 mm | ||
| 7.3 mm | ||
| 7.4 mm | ||
| 7.5 mm | ||
| 7.6 mm | 165 mm | 109 mm |
| 7.7 mm | ||
| 7.8 mm | ||
| 7.9 mm | ||
| 8.0 mm | ||
| 8.1 mm | ||
| 8.2 mm | ||
| 8.3 mm | ||
| 8.4 mm | ||
| 8.5 mm | ||
| 8.6 mm | 175 mm | 115 mm |
| 8.7 mm | ||
| 8.8 mm | ||
| 8.9 mm | ||
| 9.0 mm | ||
| 9.1 mm | ||
| 9.2 mm | ||
| 9.3 mm | ||
| 9.4 mm | ||
| 9.5 mm | ||
| 9.6 mm | 184 mm | 121 mm |
| 9.7 mm | ||
| 9.8 mm | ||
| 9.9 mm | ||
| 10.0 mm | ||
| 10.1 mm | ||
| 10.2 mm | ||
| 10.3 mm | ||
| 10.4 mm | ||
| 10.5 mm | ||
| 10.6 mm | ||
| 10.7 mm | 195 mm | 128 mm |
| 10.8 mm | ||
| 10.9 mm | ||
| 11.0 mm | ||
| 11.1 mm | ||
| 11.2 mm | ||
| 11.3 mm | ||
| 11.4 mm | ||
| 11.5 mm | ||
| 11.6 mm | ||
| 11.7 mm | ||
| 11.8 mm | ||
| 11.9 mm | 205 mm | 134 mm |
| 12.0 mm | ||
| 12.1 mm | ||
| 12.2 mm | ||
| 12.3 mm | ||
| 12.4 mm | ||
| 12.5 mm | ||
| 12.6 mm | ||
| 12.7 mm | ||
| 12.8 mm | ||
| 12.9 mm | ||
| 13.0 mm | ||
| 13.1 mm | ||
| 13.2 mm | ||
| 13.3 mm | 214 mm | 140 mm |
| 13.4 mm | ||
| 13.5 mm | ||
| 13.6 mm | ||
| 13.7 mm | ||
| 13.75 mm | ||
| 13.8 mm | ||
| 13.9 mm | ||
| 14.0 mm | ||
| 14.25 mm | 220 mm | 144 mm |
| 14.5 mm | ||
| 14.75 mm | ||
| 15.0 mm | ||
| 15.25 mm | 227 mm | 149 mm |
| 15.4 mm | ||
| 15.5 mm | ||
| 15.75 mm | ||
| 16.0 mm | ||
| 16.25 mm | 235 mm | 154 mm |
| 16.5 mm | ||
| 16.75 mm | ||
| 17.0 mm | ||
| 17.25 mm | 241 mm | 158 mm |
| 17.4 mm | ||
| 17.5 mm | ||
| 17.75 mm | ||
| 18.0 mm | ||
| 18.25 mm | 247 mm | 162 mm |
| 18.5 mm | ||
| 18.75 mm | ||
| 19.0 mm | ||
| 19.25 mm | 254 mm | 166 mm |
| 19.4 mm | ||
| 19.5 mm | ||
| 19.75 mm | ||
| 20.0 mm | ||
| 20.25 mm | 261 mm | 171 mm |
| 20.5 mm | ||
| 20.75 mm | ||
| 21.0 mm | ||
| 21.25 mm | 268 mm | 176 mm |
| 21.5 mm | ||
| 21.75 mm | ||
| 22.0 mm | ||
| 22.25 mm | ||
| 22.5 mm | 275 mm | 180 mm |
| 22.75 mm | ||
| 23.0 mm | ||
| 23.25 mm | ||
| 23.5 mm | ||
| 23.75 mm | 282 mm | 185 mm |
| 24.0 mm | ||
| 24.25 mm | ||
| 24.5 mm | ||
| 24.75 mm | ||
| 25.0 mm | ||
| 25.25 mm | 290 mm | 190 mm |
| 25.5 mm | ||
| 25.75 mm | ||
| 26.0 mm | ||
| 26.25 mm | ||
| 26.5 mm | ||
| 26.75 mm | 298 mm | 195 mm |
| 27.0 mm | ||
| 27.25 mm | ||
| 27.5 mm | ||
| 27.75 mm | ||
| 28.0 mm | ||
| 28.25 mm | 307 mm | 201 mm |
| 28.5 mm | ||
| 28.75 mm | ||
| 29.0 mm | ||
| 29.25 mm | ||
| 29.5 mm | ||
| 29.75 mm | ||
| 30.0 mm | ||
| 30.25 mm | 316 mm | 207 mm |
| 30.5 mm | ||
| 30.75 mm | ||
| 31.0 mm | ||
| 31.25 mm | ||
| 31.5 mm |
Table No. 1: standard sizes and diameters of twist drills for metal with cylindrical shanks
Dimensions and diameters of twist drills for metal with tapered shanks
Tools of this type are made according to GOST 10903-77 from steel grades P9, P18, P6M5, P6M5K5 and HSS. The diameters of twist drills for metal with conical shanks vary from 5 to 80 mm.
Photo No. 2: metal twist drills with tapered shanks
The exact size data is given in the table below.
| Drill diameter | total length | Cutting length |
| 5 mm | 133 mm | 52 mm |
| 5.2 mm | ||
| 5.5 mm | 138 mm | 57 mm |
| 5.8 mm | ||
| 6.0 mm | ||
| 6.2 mm | 144 mm | 63 mm |
| 6.4 mm | ||
| 6.5 mm | ||
| 6.6 mm | ||
| 6.8 mm | 150 mm | 69 mm |
| 7.0 mm | ||
| 7.2 mm | ||
| 7.4 mm | ||
| 7.5 mm | ||
| 7.6 mm | 156 mm | 75 mm |
| 7.8 mm | ||
| 8.0 mm | ||
| 8.2 mm | ||
| 8.4 mm | ||
| 8.5 mm | ||
| 8.8 mm | 162 mm | 81 mm |
| 9.0 mm | ||
| 9.2 mm | ||
| 9.5 mm | ||
| 9.8 mm | 168 mm | 87 mm |
| 10.0 mm | ||
| 10.2 mm | ||
| 10.5 mm | ||
| 10.8 mm | 175 mm | 94 mm |
| 11.0 mm | ||
| 11.2 mm | ||
| 11.5 mm | ||
| 11.8 mm | ||
| 12.0 mm | 182 mm | 101 mm |
| 12.2 mm | ||
| 12.5 mm | ||
| 12.8 mm | ||
| 13.0 mm | ||
| 13.2 mm | ||
| 13.5 mm | 189 mm | 108 mm |
| 13.75 mm | ||
| 13.8 mm | ||
| 14.0 mm | ||
| 14.25 mm | 212 mm | 114 mm |
| 14.5 mm | ||
| 14.75 mm | ||
| 15.0 mm | ||
| 15.25 mm | 218 mm | 120 mm |
| 15.5 mm | ||
| 15.75 mm | ||
| 16.0 mm | ||
| 16.25 mm | 223 mm | 125 mm |
| 16.5 mm | ||
| 16.75 mm | ||
| 17.0 mm | ||
| 17.25 mm | 228 mm | 130 mm |
| 17.5 mm | ||
| 17.75 mm | ||
| 18.0 mm | ||
| 18.25 mm | 233 mm | 135 mm |
| 18.5 mm | ||
| 18.75 mm | ||
| 19.0 mm | ||
| 19.25 mm | 238 mm | 140 mm |
| 19.5 mm | ||
| 19.75 mm | ||
| 20.0 mm | ||
| 20.25 mm | 243 mm | 145 mm |
| 20.5 mm | ||
| 20.75 mm | ||
| 21.0 mm | ||
| 21.25 mm | 248 mm | 150 mm |
| 21.5 mm | ||
| 21.75 mm | ||
| 22.0 mm | ||
| 22.25 mm | ||
| 22.5 mm | 253/276 mm | 155 mm. |
| 22.75 mm | ||
| 23.0 mm | ||
| 23.25 mm | ||
| 23.5 mm | ||
| 23.75 mm | 281 mm | 160 mm |
| 23.9 mm | ||
| 24.0 mm | ||
| 24.25 mm | ||
| 24.5 mm | ||
| 24.75 mm | ||
| 25.0 mm | ||
| 25.25 mm | 286 mm | 165 mm |
| 25.5 mm | ||
| 25.75 mm | ||
| 26.0 mm | ||
| 26.25 mm | ||
| 26.5 mm | ||
| 26.75 mm | 291 mm | 170 mm |
| 27.0 mm | ||
| 27.25 mm | ||
| 27.5 mm | ||
| 27.75 mm | ||
| 28.0 mm | ||
| 28.25 mm | 296 mm | 175 mm |
| 28.5 mm | ||
| 28.75 mm | ||
| 29.0 mm | ||
| 29.25 mm | ||
| 29.5 mm | ||
| 29.75 mm | ||
| 30.0 mm | ||
| 30.25 mm | 301/306 mm | 180 mm |
| 30.5 mm | ||
| 30.75 mm | ||
| 31.0 mm | ||
| 31.25 mm | ||
| 31.5 mm | ||
| 31.75 mm | ||
| 32.0 mm | 334 mm | 185 mm |
| 32.25 mm | ||
| 32.5 mm | ||
| 32.75 mm | ||
| 33.0 mm | ||
| 33.25 mm | ||
| 33.5 mm | ||
| 34.0 mm | 339 mm | 190 mm |
| 34.5 mm | ||
| 35.0 mm | ||
| 35.25 mm | ||
| 35.5 mm | ||
| 35.75 mm | 344 mm | 195 mm |
| 36.0 mm | ||
| 36.25 mm | ||
| 36.5 mm | ||
| 37.0 mm | ||
| 37.5 mm | ||
| 38.0 mm | 349 mm | 200 mm |
| 38.25 mm | ||
| 38.5 mm | ||
| 39.0 mm | ||
| 39.25 mm | ||
| 39.5 mm | ||
| 40.0 mm | ||
| 40.5 mm | 354 mm | 205 mm |
| 41.0 mm | ||
| 41.25 mm | ||
| 41.5 mm | ||
| 42.0 mm | ||
| 42.5 mm | ||
| 43.0 mm | 359 mm | 210 mm |
| 43.25 mm | ||
| 43.5 mm | ||
| 44.0 mm | ||
| 44.5 mm | ||
| 45.0 mm | ||
| 45.25 mm | 364 mm | 215 mm |
| 45.5 mm | ||
| 46.0 mm | ||
| 46.5 mm | ||
| 47.0 mm | ||
| 47.5 mm | ||
| 48.0 mm | 369/374 mm | 220 mm |
| 48.5 mm | ||
| 49.0 mm | ||
| 49.5 mm | ||
| 50.0 mm | ||
| 50.5 mm | ||
| 51.0 mm | 412 mm | 225 mm |
| 51.5 mm | ||
| 52.0 mm | ||
| 53.0 mm | ||
| 54.0 mm | 417 mm | 230 mm |
| 55.0 mm | ||
| 56.0 mm | ||
| 57.0 mm | 422 mm | 235 mm |
| 58.0 mm | ||
| 59.0 mm | ||
| 60.0 mm | ||
| 61.0 mm | 427 mm | 240 mm |
| 62.0 mm | ||
| 63.0 mm | ||
| 64.0 mm | 432 mm | 245 mm |
| 65.0 mm | ||
| 66.0 mm | ||
| 67.0 mm | ||
| 68.0 mm | 437 mm | 250 mm |
| 69.0 mm | ||
| 70.0 mm | ||
| 71.0 mm | ||
| 72.0 mm | 442 mm | 255 mm |
| 73.0 mm | ||
| 74.0 mm | ||
| 75.0 mm | ||
| 76.0 mm | 514 mm | 260 mm |
| 77.0 mm | ||
| 78.0 mm | ||
| 79.0 mm | ||
| 80.0 mm |
Table No. 2: sizes and diameters of standard twist drills for metal with tapered shanks
Diameters and sizes of core drills for metal
Core drills for metal are used to produce through holes with small depths but large diameters. They can reach 150 mm. The cutting depth varies from 5 to 50 mm.
Photo No. 3: core drills for metal
Study the design features of core drills in the diagram.
Image No. 1: design features of a core drill for metal.
Standard diameters and sizes of core drills for metal are presented in the table below.
| D | d 1 (limit trip according to A3) | d | b | Number of records |
| 16 | 11 | 4 | 8 | 3 |
| 20 | 15 | 6 | 12 | |
| 25 | 18 | 15 | 4 | |
| (30) | 24 | 21 | ||
| 32 | 10 | 20 | ||
| (36) | 28 | 24 | ||
| 40 | 32 | 28 | ||
| (45) | 36 | 32 | ||
| 50 | 42 | 38 | ||
| 75 | 68 | 64 | 6 | |
| 85 | 78 | 74 |
Table No. 3: standard diameters and sizes of carbide core drills for metal (GOST 17013-71)
Shank types
The tail part of the drill has different configurations - cylindrical, conical and hexagonal. Most often, cylindrical models are used in practice. They have a small feature: the diameters of the drill and shank may not match. Experts say that if you equip the drilling tool with a cylindrical shank of a slightly larger diameter, this maneuver will make the fixation stronger. There is also a minus - an increase in the recommended power of the tool. But the drill will not be damaged if such a drill jams during operation. Tapered shanks are suitable for drill bits in industrial drills. This is how workpieces are processed on factory machines. The hex shank tool holds well in special clamps and jaw chucks.
Which manufacturers can you trust?
The quality and service life of metal processing drills depends on the manufacturer. Craftsmen who use drills every day claim that good tools can be found both from domestic and foreign companies. Russian-made drills are wear-resistant, strong and durable, but, unfortunately, there are fewer and fewer of them on the market every year. Now products and “Zubr” are in demand. These brands produce inexpensive but reliable high-quality instruments. Drills and “ATTACK” have also proven themselves well. Among imported ones, professionals prefer metal cutting tools, Bosch, Haisser and Makita. Their characteristics are approximately the same: they can withstand extreme loads, work “for wear”, and wear occurs slowly. Good value for money. There are two more and Dewalt. Their products differ from others in their high drilling speed. The price of a tool depends on the country of manufacture, length, diameter, strength and what it is intended for.
| Rating of the best drills for metal processing |
| Bosch 2607017154 |
| Attack N802-6 |
| Wurth Zebra Spiralbohrersatz HSS |
| Anchor 25219 |
| Metabo Bestell-Nr. 27 094 HSS-G |
| AEG HSS-G 4932430416 |
| Bison MET-SH H19 R6M5 |
| DeWALT DT7926 Extreme2 HSS |
| Hawera HSS-C Spiral Bohrer GQ-32692 |
| Irwin TurboMax 10503992 |
On what basis should you choose a drill?
When choosing a drill, focus on the following indicators:
Weight - a quality drill should not be light; Experts recommend buying cutting tools weighing 14 grams or more. If the store doesn’t have scales, rely on your feelings.
Strength - for a metal product to yield to a drill, it must be strong; You can check the strength using a glass bottle. Scratch something on the glass with the working surface of the tool - there should be impressive scratches on the bottle and glass chips around them.
Workmanship - craftsmen advise using drills made by milling followed by grinding.
Sharpening angle - for metal it is better to choose drills sharpened at an angle of 130-135 degrees.
Steel grade - buy tools that will fit your equipment (drill, drill press, etc.).
Sharpening rules
The sharpening angle of a drill is how sharp the working surface and edges are sharpened. According to the technology of execution, turning can be single-plane and conical. Using single-plane technology, small drills up to 3 mm in diameter are sharpened. To sharpen such a cutting tool, you need a special emery wheel. The drill is brought to the circle at an angle of 30 degrees so that its cutting part comes into contact with the emery surface of the circle. Conical sharpening is considered more difficult. This method is used for drills with a diameter of more than 3 mm. The tool must be held with both hands at the same time by the shank and the spiral part and rotated during the grinding process, giving it a cone shape. Drills are sharpened at a certain angle. The sharpening angle depends on the purpose of use. For example, to work with products made of bronze or high-strength steel, the sharpening angle must be at least 120 degrees, the optimal option is 130-140. And for drilling soft metals, equipment with a sharpening angle of 100 will be sufficient.
What is the difference between small diameter drills and conventional tools?
Small-class microdrills include tools for producing round holes with a diameter of 0.1 to 1 mm. A standard set of wood drills includes up to ten units with a range of 3 to 12 mm. Sets for fine work are equipped with sizes from 0.3 to 3.2 mm.
The main difference between small-diameter drilling tools and the usual size range is the design features, material used and operating conditions:
- Microdrills with a diameter of 0.5 mm - 1 mm are made of high-speed steel P6M5K5 or HSS-Co, according to the Western classification of alloy materials. Thinner ones, from 0.5 mm and less, are pressed and sintered from tungsten-cobalt or tungsten-molybdenum alloy;
- Shanks and holders for drilling tools of the smallest diameter are made with an increased diameter, usually up to 3 mm. Tools based on tungsten alloys are highly brittle, so it can be fixed in a collet clamp or in a special chuck only if the shank is enlarged to its normal size.
For your information! Drilling with microdrills is carried out using drills of a special design, the rotation speed of which is an order of magnitude higher than the standard 1200-2000 rpm for conventional screwdrivers. Therefore, the drilling of micro-holes in solid materials is carried out using several drills, with a consistent increase in diameter.
Drill design with a diameter of up to 1 mm
High rotation speeds of the cutting edge ensure good cutting quality of the material. Tungsten tools are sharpened with a cutting edge angle of up to 120°, which allows you to drill even alloy steels. As a rule, the manufacturer of high-quality micro drills has special markings on the box indicating what types of metal the tool is intended for.
The standard design of a thin carbide microdrill is shown in the photo. The length of the carbide spiral cutting part for all drills in the set, as a rule, does not exceed 15 mm, with a shank length of up to 20 mm and a diameter of 3 mm. The hole is drilled to a maximum depth of 4-5 mm.
Chinese micro drill sets can have a hex shank with a seat size of 2.5 mm and a length of 15 mm.
By using a standard diameter shank set for all carbide drills, you can secure a carbide drill of any size using a regular collet with a centering sleeve with a 3mm hole. In addition to collet devices, lightweight chucks for an engraving machine or Dremel are also used.
Microdrills made from high-speed steel P6M5K5 or HSS-Co are manufactured according to a standard design with a cylindrical shank and a double-fluted cutting surface.
This approach greatly simplifies mounting in a drill chuck, but complicates the work if it is necessary to drill several holes of different diameters at the same time. For drilling tools with a diameter greater than 2 mm, material and size information is engraved on the shank.
For your information! Information about the diameter of the microdrill is applied by the manufacturer to the cells of the kit in which the tool is laid out, or is provided in the form of a diagram on the back of the box.
Therefore, if the drills from the set, for some reason, were removed or scattered, they can only be collected and placed into the cells of the box after checking with a micrometer.
What devices are used for sharpening drills?
You can sharpen a dull cutting tool on a special industrial machine. It can be professional or domestic. The first is used for mass sharpening of drills in enterprises or professional firms. The second one is convenient to use at home or in the garage. A metal drill can be sharpened with a highly specialized machine (only for one type of equipment) and a universal one, which is used to work with other types of drills. Depending on the type of work, sharpening tools can be electrical or mechanical. You can make a device for sharpening cutting tools yourself or purchase it in a special store. Professionals prefer to use such machines as “REZER”, as well as domestic devices, “Caliber”, “Kraton”.
What is the difference between drills for metal and wood processing?
Cutting tools for metal and wood have several differences: - drills for metal do not have a center peak (a sharp corner or pin necessary to prevent the tool from jumping off during operation). — drills for metal surfaces are made of durable alloys so that they can easily drill holes in metal. — tools for metal are black or gold (yellow) in color. For drilling wood and chipboard products, the strength of gray ones is sufficient. — a drill for metal has a sharpening angle of at least 100 degrees. But for wood, 90 degrees or less is enough.