Characteristics of steel grade 40
Steel 40 is a structural carbon quality steel with limited weldability. Welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, ESW. Preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. CTS without restrictions.
Not prone to flake sensitivity, no tendency to temper brittleness. Machinability by cutting in the hot-rolled state at HB 170 and σв=530 MPa, K υ solid. spl=1.2 and Kυ b.st=1.05. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1250 to 780 0C, with air cooling of workpieces with a cross-section of up to 400 mm. Steel 40 is used to make axles, crankshafts, pinion shafts, rods, gears, pipes, forgings, fasteners, shafts, discs, rotors, flanges, gears, bushings for long and very long service at temperatures up to 425 degrees.
Decoding steel 40X
In the CIS, the GOST 4543-2016 standard is used, which allows you to determine not only the chemical composition, but also the various performance qualities of the material.
Download GOST 4543-2016
Steel 40X GOST defines the following substances in its composition:
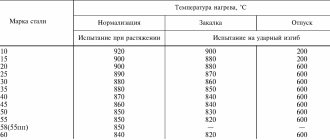
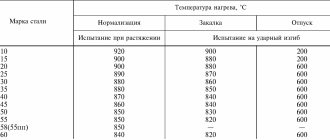
- The first number 40 is used to indicate the main element in the composition, which is carbon. As a rule, most of the composition is iron, and carbon, the concentration of which is 0.44%, determines the main performance characteristics.
- The next letter X indicates that the composition contains an alloying element represented by chromium. The absence of a number after the letter indicates that the concentration of the element is 1.1%. As previously noted, chromium increases the corrosion resistance of the structure. However, the steel grade in question, 40X, is not characterized by high anti-corrosion qualities.
- Considering 40X GOST, we note that the composition includes a fairly large amount of nickel, silicon and manganese. They determine some of the performance characteristics of the metal, but they are not noted in the markings.
Deciphering allows you to determine the chemical composition and basic performance qualities of the material. It is worth considering that foreign manufacturers use different standards when labeling materials, but the chemical composition of analogues is approximately similar.
Supply steel 40
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams , GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flanges , GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flanges , GOST 8281-80 , unequal , GOST 8283-93 steel trough equal flange profiles , GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 85 09-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange , GOST 8510-86 rolled steel angles unequal-flanged , GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels , GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Hot rolled sheet products , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets , GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip , GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel Wide-band universal, GOST 3282-74 Wire Steel low-carbon general purposes , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wires, GOST 10705-80 steel power steel pipes , GOST 10706-76 Pipes steel eight-dimensional , GOST 3262-75 Pipes steel water and gap-pipes .
| Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 8479-70; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 2591-2006; GOST 8319.0-75; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 9234-74; GOST 11474-76; GOST 1133-71; GOST 2590-2006; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 82-70; GOST 14918-80; GOST 19903-74; GOST 16523-97; GOST 103-2006; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8560-78; GOST 8559-75; GOST 1051-73; GOST 7417-75; GOST 10702-78; GOST 14955-77; GOST 1050-88; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 4405-75; GOST 4041-71; GOST 1577-93; |
| Ribbons | GOST 10234-77; GOST 2284-79; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 20295-85; GOST 3262-75; GOST 24950-81; |
| Low carbon steel wire | GOST 1526-81; GOST 5663-79; GOST 792-67; |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 17305-91; GOST 26366-84; GOST 9850-72; GOST 7372-79; GOST 3920-70; GOST 3110-74; GOST 9389-75; |
Analogues and nomenclature
If 40X GOST steel is used as the main component, the designer needs to remember that it is possible to use similar metals. There are Russian and foreign analogues.
Domestic
Russian analogues are used in production:
- 45X.
- 38HA.
- 40ХН.
- Some others.
They are used to create various critical parts: axles, gear rings, plungers and others.
Foreign
Among foreign materials there are the following metal analogues:
- G51400, H51350 - manufactured in the United States.
- 37Cr4, 41Cr4, 41CrS4 - from Germany.
- 35Cr, 38CrA, 40Cr, 40CrA - made in China.
They can be used in the manufacture of mechanisms that are planned to be used at low air temperatures.
Mechanical properties of rolled steel 40
| GOST | Forging condition | Section, mm | σв(MPa) | δ5 (δ4 ) (%) | ψ % | KCU, J/cm2 | NV, no more |
| no less | |||||||
| 1050-88 | Hot-rolled, forged, calibrated and silver steel of the 2nd category after normalization | 25 | 570 | 19 | 45 | 59 | — |
| Calibrated steel, category 5: | |||||||
| after cold hardening | |||||||
| after annealing or high tempering | Samples | 610 | 6 | 35 | — | — | |
| Steel calibrated and calibrated with special finishing after tempering and annealing | Samples | 510 | 14 | 40 | — | — | |
| 10702-78 | Heat-treated sheet of category 1-2 | — | Up to 590 | — | 40 | — | 197 |
| 4041-71(Transverse samples) | 4-14 | 510-650 | 21 | — | — | 167 | |
| Normalized and hot rolled sheets | |||||||
| 1577-93 | Annealed or high tempered sheets | 80 | 560 | 20 | — | — | — |
| Normalized or hot rolled strips | 80 | 520 | 21 | — | — | — | |
| Hot rolled sheet | 6-25 | 570 | 19 | 45 | — | — | |
| 16523-70 (Transverse samples) | Up to 2 | 510-660 | -16 | — | — | — | |
| Cold rolled sheet | 2-3,9 | -17 | — | — | — | ||
| Up to 2 | 510-660 | -17 | — | — | — | ||
| 2284-79 | Cold rolled strip: | 2-3,9 | -18 | — | — | — | |
| annealed | |||||||
| cold-worked strength class H2 | 0,1-4 | 450-700 | -14 | — | — | — | |
| 10234-77 | Annealed flattened tape | 0,1-4 | 850-1050 | — | — | — | — |
| 0,1-4 | Up to 700 | 10 | — | — | — | ||
Chemical composition in % of material steel 40Х
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 0.36 — 0.44 | 0.17 — 0.37 | 0.5 — 0.8 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.035 | up to 0.035 | 0.8 — 1.1 | up to 0.3 |
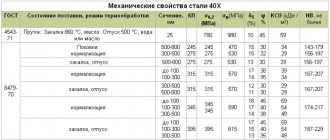
Mechanical properties of steel 40 forgings
| Heat treatment | Section, mm | KP | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) | NV, no more |
| Normalization | 300-500 | 215 | 215 | 430 | 18 | 40 | 44 | 123-167 |
| 500-800 | 16 | 35 | 39 | |||||
| 100-300 | 245 | 245 | 470 | 19 | 42 | 39 | 143-179 | |
| 300-500 | 17 | 35 | 34 | |||||
| Up to 100 | 275 | 275 | 530 | 20 | 40 | 44 | 156-197 | |
| 100-300 | 17 | 38 | 34 | |||||
| Hardening. Vacation | 300-500 | 275 | 275 | 530 | 15 | 32 | 29 | 156-197 |
| 500-800 | 13 | 30 | 29 | |||||
| 100-300 | 315 | 315 | 570 | 14 | 35 | 34 | 167-207 | |
| Up to 100 | 345 | 345 | 590 | 18 | 45 | 59 | 174-217 |
Advantages and disadvantages
The positive and negative qualities of a metal determine its properties. Among the qualities of type 40x steel, the characteristics of endurance and hardness are important. The admixture of chromium in the composition gives the components the following positive features:
Advantages
They are highly durable and rust resistant.
Withstands strong and long-term loads.
Withstands extreme temperatures from -40 to +425 °C.
The magnetic properties of the material do not affect the quality of the steel.
They can be used in various environmental conditions.
Surfaces do not need to be cleaned or treated.
They tolerate warping well.
Flaws
The negative features of the alloy include the fragility of steel and its flake sensitivity. But heat treatment makes it possible to reduce these properties to minimum values.
Interesting: At what temperature does lead melt?
Mechanical properties of steel 40 at elevated temperatures
| Test temperature, °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % |
| Sample with a diameter of 6 mm and a length of 30 mm, rolled. Deformation speed 16 mm/min. Strain rate 0.009 1/s | ||||
| 700 | 99 | 140 | 48 | 85 |
| 800 | 70 | 110 | 53 | 97 |
| 900 | 54 | 71 | 55 | 100 |
| 1000 | 28 | 58 | 69 | 100 |
| 1100 | 24 | 37 | 60 | 100 |
| 1200 | 16 | 26 | 87 | 100 |
| 1300 | 12 | 18 | 56 | 100 |
Description of mechanical symbols
| Name | Description |
| Section | Section |
| sT|s0.2 | Yield strength or proportional limit with tolerance for permanent deformation - 0.2% |
| σB | Short-term strength limit |
| d5 | Elongation after break |
| d4 | Elongation after break |
| d10 | Elongation after break |
| d10 | Elongation after break |
| y | Relative narrowing |
| kJ/m2 | Impact strength |
| HRB | Rockwell hardness (steel indenter, spherical) |
Mechanical properties of steel 40 at normal temperature
| Type of rental | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Heat treated sheet, GOST 4041-71 | 4-14 | 510-660 | 21 | |||||
| Cold rolled pipes. | 580 | 320 | 17 | Normalization | ||||
| Hot rolled pipes. | 600 | 340 | 16 | |||||
| The rod is calibrated, GOST 10702-78 | 590 | 40 | Annealing | |||||
| Rolled products annealed, GOST 1050-88 | 510 | 14 | 40 | |||||
| Rolled products cold-hardened, GOST 1050-88 | 610 | 6 | 35 | |||||
| Rolled products, GOST 1050-88 | up to 80 | 570 | 335 | 19 | 45 | Normalization | ||
| Cold-worked tape, GOST 2284-79 | 690-1030 | |||||||
| Annealed tape, GOST 2284-79 | 440-690 | 14 | ||||||
| Strip, GOST 1577-93 | Jun.60 | 570 | 335 | 19 | 45 | Normalization |
Mechanical properties of steel 40 depending on tempering temperature
| Temperature, °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) | HB |
| Hardening 850 °C, oil | ||||||
| 200 | 750 | 930 | 7 | 45 | 29 | 267 |
| 300 | 710 | 860 | 8 | 51 | 69 | 247 |
| 400 | 640 | 790 | 10 | 57 | 88 | 225 |
| 500 | 550 | 730 | 12 | 62 | 127 | 208 |
| 600 | 450 | 660 | 16 | 66 | 167 | 188 |
| 700 | 380 | 620 | 17 | 71 | 206 | 170 |
Physical properties of steel 40
| Temperature | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| 0C | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.13 | 51.5 | 7850 | 483 | 160 | |
| 100 | 2.01 | 11.6 | 50.6 | 486 | 221 | |
| 200 | 1.98 | 12.7 | 48.1 | 497 | 296 | |
| 300 | 1.9 | 13.5 | 45.6 | 512 | 387 | |
| 400 | 1.85 | 14.5 | 41.9 | 529 | 493 | |
| 500 | 1.79 | 14.5 | 38.1 | 550 | 619 | |
| 600 | 1.67 | 14.9 | 33.5 | 574 | 766 | |
| 700 | 1.6 | 15.15 | 30 | 628 | 932 | |
| 800 | 12.5 | 24.8 | 674 | 1110 | ||
| 900 | 13.5 | 25.7 | 657 | 1150 | ||
| 1000 | 14.5 | 26.9 | 653 | 1180 | ||
| 1100 | 15.2 | 28 | 649 | 1207 | ||
| 1200 | 15.8 | 29.5 | 649 | 1230 |
Alloy properties
The physical and mechanical properties of 40X steel allow it to withstand high loads without destroying its structure:
- density – 7820 kg/m3; elastic modulus – 2.14Х10-5;
- coefficient of linear expansion – 11.9Х106 1/deg.;
- electrical resistivity – 210Х109 Ohm*m;
- impact strength – 160 J/cm2;
- forging temperature – from 1250 to 800 degrees.
Almost all indicators change depending on temperature. As it increases, the following increases:
- resistivity;
- linear expansion coefficient;
- specific heat.
The inverse dependence on temperature is demonstrated by:
- elastic modulus;
- metal density;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity.
An important characteristic is the yield strength indicator. It is determined by the magnitude of the load at which irreversible deformations occur in the product. The indicator depends on several factors: heat treatment mode; type of alloying additives and amount of harmful impurities; crystal lattice structure.
For steel 40X, the yield strength decreases in the temperature range of 100-500 degrees from 490 to 345 MPa. Tempering brittleness and flake sensitivity have a negative impact on the quality of the alloy. Steel is difficult to weld and requires preheating and subsequent heat treatment.
Hardness of steel grade 40
| Hardness steel 40, heat-treated sheet GOST 4041-71 | HB 10 -1 = 167 MPa |
| Hardness steel 40 Rolled calibrated cold-worked GOST 1050-88 | HB 10 -1 = 241 MPa |
| Hardness steel 40 Hot rolled products GOST 1050-88 | HB 10 -1 = 217 MPa |
| Hardness steel 40 Rolled calibrated annealed GOST 1050-88 | HB 10 -1 = 197 MPa |
| Hardness steel 40 Hot-rolled annealed products GOST 1050-88 | HB 10 -1 = 187 MPa |
Endurance limit steel 40
| σ-1, MPA | Steel condition |
| 231 | Annealing 850 °C, σ0.2 =275 MPa, σв =520 MPa Quenching 845 °C, water. Tempering 550 °C, σ0.2 =600 MPa, σv =710 MPa, HB 209 Quenching 845 °C, oil. Vacation 430 °C, σ0.2 =415 MPa, σв =630 MPa |
| 393 | |
| 230 | |
| σ4001/100000 = 100 MPa, σ4501/100000= 50 MPa, σ5001/100000 = 30 MPa, σ4001/10000= 260 MPa, σ5001/10000= 70 MPa, σ4001/100000 = 190 MPa, σ5001/100000 = 44 MPa | |
Foreign analogues steel 40
| USA | 1040, 1042, G10400, G10420 |
| Germany | 1.0511, 1.1186, C40, C40E, C40R, C42D, Ck35, Ck40, Cm40 |
| Japan | S40C, S43C, SWRCH38K, SWRCH40K |
| France | 2C40, C40E, FR38, XC3841, XC38H1, XC42, XC42H1, XP42HI |
| England | 060A40, 080A40, 080M40, C40, C40E, CS40 |
| European Union | 1.1186, C35, C40, C40E |
| Italy | C40, C40E, C40R |
| Belgium | C40-2 |
| Spain | C40E |
| China | 40, ML40 |
| Sweden | 1555, 1650 |
| Bulgaria | 40, C40E |
| Hungary | C40E |
| Poland | 40, 40A, 40rs, D40, P40 |
| Romania | OLC40, OLC40X |
| Czech | 12041 |
| Australia | 1040, M1040 |
| South Korea | SM40C |
- Structural steel
- Tool steel