Today, manufacturers make car bodies from a huge number of different materials. Well, since the car body is considered the most important part of the car, safety and strength should be among its main qualities. At the same time, the car body must be optimal and comfortable for passengers, distinguished by a unique style and original design. It is for this reason that manufacturers began to use different technologies and materials for the manufacture of bodies. This post will talk about popular body materials, their advantages and possible disadvantages.
Sheet steel
Most bodies are made from sheet steel for a variety of reasons. The most important of these reasons are:
- high strength;
- deformability (possibility of stretching);
- weldability (as well as suitability for soldering);
- colorability;
- sufficient service life with proper anti-corrosion treatment;
- satisfactory price.
In general, the following sheet steels :
- thin-sheet, cold-rolled mild steel grade RRST 1405 according to DIN 1623 (quality standard), DIN 1541 (dimensional standard) with a tensile strength of 270-350 MPa, elongation of more than 36%, with a matte, clean surface, thickness 0.6-0.9 mm (supplied in 0.1 mm thickness intervals), used for viewable (interrogated) exterior panels (roof, hood, doors, sidewalls, etc.);
- the same grades of steel as indicated above, sometimes thin-sheet boiling steel grade UST 1203 or UST 1303, i.e. of worse quality, with a tensile strength of 270-410 MPa, elongation 28-32%, the same thickness as indicated above, used for non-visible (painted), external panels, as well as floor parts (internal frame, reinforcements, floor panels, cross members, etc.);
- hot-rolled steel strip according to DIN 1624 (quality standard), DIN 1606 (dimensional standard) grade ST 4 with a tensile strength of 280-380 MPa, elongation of more than 38%, thickness of 1.5-2.5 mm and more, used for parts located at the bottom of the body (reinforcements, supports, flanges, etc.), especially thick ones.
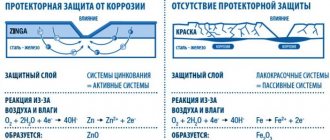
The design and manufacturing technology of parts must be based on the maximum width of the supplied sheet steel (currently 2000 mm). For parts operating in a corrosively aggressive environment, galvanized sheet steel should be used, taking into account that during the manufacture of parts such steel does not allow large deformations (bending, slight stretching). In special cases, aluminized sheet steel can be used. Both surfaces of steel sheets can be subjected to special treatment.
How to carry out body repair?
If the car body is made of steel, you can repair it yourself. You don't need to learn automotive engineering to do this. It is enough to be able to handle the tool, to know the technology of machine production in theory.
Body repair (Photo: Instagram / skr53b)
Material selection
To repair the body, you need to buy a sheet of low-carbon steel. To do this, you can visit a construction market or a car dismantling center. With the second option, you can find a whole replacement part at a low price.
Equipment
To carry out the work you will need a grinder, an argon cutter, a welding machine, metal scissors, and accessories for power tools. To completely hide the damage, you need a primer, putty, paint, brushes, a spray bottle, and an anti-corrosion compound. If the damage site is difficult to reach, you will need a jack or hole.
For the production of machines, metal is used that meets certain requirements. Recently, plastic has been gradually replacing steel and aluminum-based alloys, but the production of metal cars continues.
Source
Light metals
To this day, discussions continue about the advisability of using light metals in body building , since using them can significantly reduce the weight of the structure. No matter how interesting aluminum bodies of special (racing and sports) cars and buses are, the likelihood of using aluminum sheets for mass production of passenger cars is small for the following reasons:
- The cost of aluminum (as a material) is almost 3 times more than steel. The cost of producing the sheet due to the better ductility of aluminum is somewhat lower, at the same time the weight of the sheet is only 30% less, since aluminum has less strength, and therefore it is necessary to use a sheet of greater thickness. However, cars are not sold by weight, and the increase in the cost of materials is too noticeable, since the decrease in the cost of other elements due to a decrease in the overall weight, for example, brakes, tires, etc., is negligible, and the decrease in fuel consumption does not affect the selling price of the car. Consequently, cars with a large number of aluminum parts become significantly more expensive.
- Due to the lower strength of aluminum, most body parts, especially frame elements, must have increased thickness. Due to the lower modulus of elasticity, the rigidity due to the body shape and its service life are relatively short, so energy absorption during impact is also low. All this is undesirable from a security point of view.
- Pure aluminum alloys have sufficient corrosion resistance. However, not all parts and connecting elements of the body can be made of light metal; at least at the junctions of aluminum and steel parts there is an increased risk of corrosion. The latter can be reduced by using anodized steel sheet, but in this case the costs increase sharply.
- Difficulties arise with welding and soldering, which become feasible only under certain conditions (oxidation protection).
For the reasons listed above, the use of light metal in passenger car bodies is limited to internal parts made from sheet metal, castings or wrought alloys, as well as moldings, possibly bumpers. It’s unfortunate that the price of aluminum on the world market constantly fluctuates greatly. Ultimately, the mass of aluminum parts, including chassis parts, in European passenger cars is about 2.2% of the total mass.
Meanwhile, some mass-produced models are equipped with an aluminum hood.
Plastic body: advantages and disadvantages
The second half of the twentieth century was marked by the emergence of plastic. The popularity of this material is explained by the fact that any structure can be made from it, which will be much lighter than even aluminum.
Plastic does not require paint coating. It is enough to add the necessary dyes to the raw materials, and the product acquires the desired shade. In addition, it does not fade and does not need to be repainted when scratches appear on it. Compared to metal, plastic is more durable; it does not react with water at all, so it does not rust.
The Khadi model has a plastic body
The cost of manufacturing plastic panels is much lower, since powerful presses are not needed for embossing. The heated raw material is fluid, thanks to which the shape of body parts can be absolutely any, which is difficult to achieve when using metal.
Despite these obvious advantages, plastic has a very big drawback - its strength is directly related to operating conditions. So, if the air temperature outside drops below zero, the parts become fragile. Even a small load can cause the material to burst or break into pieces. On the other hand, as the temperature increases, its elasticity increases. Some types of plastics warp when heated in the sun.
Here are some other reasons why plastic bodies are less practical:
- Damaged parts can be recycled, but this process requires special, expensive equipment. The same goes for plastic production.
- During the manufacture of plastic products, large amounts of harmful substances are released into the atmosphere;
- Load-bearing parts of the body cannot be made from plastic, since even a large piece of material is not as strong as thin metal;
- If a plastic panel is damaged, it can be easily and quickly replaced with a new one, but this is much more expensive than welding a metal patch to the metal.
Although these days there are various developments that eliminate most of the listed problems, it has still not been possible to bring the technology to ideal. For this reason, bumpers, decorative inserts, moldings are mainly made from plastic, and only in some car models - fenders.
Plastics
Recently, the possibility of using plastics in bodybuilding , although solid plastic bodies or even plastic load-bearing units are a matter of the distant future. However, there are many proposals on this topic. Since 1953, it has been producing a fairly large number of Chevrolet Corvettes with a body stamped from fiberglass-reinforced polyester material. The body had a supporting frame made of steel pipes. Of particular interest is the floor of a multilayer structure, experimentally manufactured for an open plastic body reinforced with fiberglass. In the future, it will be possible to produce lightweight, open thermoplastic bodies for special vehicles in small quantities.
The advantages of plastics are low weight, high strength and rigidity, good noise-absorbing properties due to high internal damping, easy assembly of components achieved due to the ability to manufacture large parts, and high corrosion resistance.
These undoubted advantages of plastics are countered by significant disadvantages, in particular, the high cost of materials and their manufacture, the long duration of the technological cycle, difficult installation and repair, and low energy absorption.
Due to these disadvantages, plastics are not suitable for mass-produced bodies. Nevertheless, the high manufacturability of plastics, the possibility of producing parts by casting or using vacuum drawing, make it possible to widely use plastics for both small and large stamped parts. When choosing plastics, one is mainly guided by the mechanical and thermal properties of the materials. The following most important types of plastics are used in bodybuilding:
- Thermosetting plastics (so-called thermosets) according to DIN 7708, DIN 16911, DIN 16912 standards are used for heavily loaded parts (levers, handles); if the plastic is reinforced with fiberglass, then it is also used for large parts of special (sports) cars called fiberglass, for example, for hoods, trunk lids, decorative grilles, fenders, side panels, etc.
- Various thermoplastics (the following are just some of the possible materials that are offered under various brand names). For example, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is used for vacuum drawn parts such as radiator trims, instrument panels; acrylic glass - for transparent parts, windows, diffusers, lanterns; polyamide - for wear parts such as moving elements of locks, air duct housings, etc.; polyvinyl chloride - for elastic and soft parts, artificial leather, film coatings, hoses, seals, insulation; polyurethane—for high-strength parts; foam polyurethane - for linings, insulating materials; polyurethane with a hard surface area - for handles, armrests, trims, instrument panels, deformable front trim, etc.
- Elastomers (ethylene propylene rubber) with a monolithic shell are used, for example, for weather and aging resistant seals (doors, windows).
This list should be considered indicative only. The polymer industry is able to offer or develop materials suitable for specific applications. Plastics have the following advantages:
- low costs for manufacturing parts and low weight;
- satisfactory stability of given dimensions;
- simple processing and connection technology (gluing);
- the possibility of obtaining a surface of various colors and embossing (shiny and matte metallization is possible);
- High resistance to weather conditions and corrosion.
Due to the wide range of possibilities for the use of plastics, it is not surprising that the proportion of plastic parts (by weight) in the body is constantly increasing and currently accounts for approximately 7.8% of the total weight of European cars. Plastics offer great opportunities for reducing body weight.
Popular automotive companies in Russia and the USSR
Companies that made the greatest contribution to the development of the automotive industry:
- AvtoVAZ - Volzhsky Automobile Plant. Was founded in 1966. Now about 20% of all cars in Russia are manufactured by this company.
- KamAZ - Kama Automobile Plant. It is considered the best manufacturer of trucks in Russia.
- UAZ - Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant. Founded in 1941. In recent years, the company has modernized equipment for car production and increased sales.
- GAZ - Gorky Automobile Plant. The oldest automobile manufacturer in Russia. The company was founded in 1932. The pedigree begins with the legendary representatives of the Ford company.
Less well-known manufacturers are LiAZ, PAZ, GolAZ, BAZ.
Results
Having understood the reasons why modern cars have thin bodies, we note that you should not be afraid of changes. Not all of them imply a deterioration in certain qualities. In particular, this applies to the thickness of the car body.
As we found out, this does not make traveling in your favorite car any less safe. On the contrary, driving becomes safer. Plus, motorists receive pleasant bonuses in the form of savings on fuel, maneuverability and improved aerodynamics.
Do you agree that thin metal cars are safer?
Source: mycary.ru
Modern realities
Finally, we note that designers have developed a large number of different types of bodies (the ones listed above are the main ones). Because of this, in some cases the difference between layouts is leveled out.
For example, the liftback has a three-volume layout. But its trunk lid is combined with the rear window, so it is, in fact, a rear door. So it turns out that there seems to be a separate trunk, but at the same time it is part of the interior compartment (since by opening the trunk we simultaneously gain access to the interior). And there are several such examples.
But in general, a wide variety of load-bearing bodies allows us to make cars of different types and purposes.
Surprise at car maintenance
Against the background of posts about car services.
The previous car had thick pile mats on a foam base. They collected dirt and dust perfectly, and they looked great. But there was a problem - cleaning the rugs themselves. It is impossible to wash them completely; after any washing with any means or equipment, a little sand or something like that remained in them. And most importantly, they need to be dried specially; they do not dry on their own in the salon, but go out.
I went to the dealer for my first regular maintenance. There were no questions regarding routine maintenance. He asked me not to touch the rugs. But at the car wash they stupidly wet them and put them back.
He had a fight, cried and took the rugs to the dacha to dry.
At the second maintenance, I decided that I would “outplay” the washers. Before handing the car over to the manager, I put the mats in the trunk.
They gave me a car with damp floor mats inside. Service.
The third time I received a call from the dealer and offered to sign up for the next maintenance. I refused, telling them this fascinating story. The girl on the phone swore and swore that this would never happen again. And the maintenance deadline was approaching and I agreed.
When recording, I asked to do it wherever possible. When handing over the car to the manager, I told him about this three times.
And so I pick up the car. I open the door, and lo and behold. I see a dirty, dry rug. I'm leaving for the office happy. In the middle, I walk up to the car, sit down, and realize that it’s not my car, but a steam room. It's close to +30 outside. What's the matter?
We washed and folded all the floor mats except the driver's! Bingo.
Rigidity
Rigidity is the property of a car body to resist dynamic and static loads during operation. It directly affects handling.
The higher the stiffness, the better the car's handling.
Rigidity depends on the body type, overall geometry, number of doors, car size and windows. The fastening and position of the windshield and rear windows also plays an important role. They can increase stiffness by 20-40%. To further increase rigidity, various reinforcement struts are installed.
Hatchbacks, coupes and sedans are considered the most stable. Typically, this is a three-volume layout that has additional partitions between the luggage compartment and the engine. Insufficient rigidity is shown by station wagon, passenger, and minibus bodies.
There are two stiffness parameters - bending and torsion. For torsion, resistance is checked under pressure at opposite points relative to its longitudinal axis, for example, when hanging diagonally. As already mentioned, modern cars have a solid monocoque body. In such structures, rigidity is provided mainly by side members, transverse and longitudinal beams.
Determining the size of paintwork on a passenger vehicle
Different types of cars have more or less the same level of paintwork. Standards from the factory suggest a level of 100-140 microns.
However, during body modifications and further painting of the car, in some places there is a deviation of the cover from this norm.
Due to the increased presence of putty. In these places, the coating thickness can increase to 200 microns.
For body parts where it is difficult to determine this indicator with the eye, a special tool is used to identify this thickness - a thickness gauge.
If on one car you observe a spread of coating from 110 to 310 microns. Most likely, such a car was undergoing repairs and was repainted.
This device is present in all major auto repair shops. Therefore, if you need a detailed assessment of your car, you always have a chance to contact specialists in this profile.
The most expensive high-level thickness gauges can determine the thickness of paint on individual parts: aluminum or plastic.
Don’t forget that American cars usually have a thicker factory coating layer than Russian or Japanese ones.
The device determines the length of the interval from the sensor to the base of the car body. The closer the thickness gauge magnet is to the metal body, the greater the angle the needle moves.
To accurately determine the thickness of the paint layer, there is a special table of factory indicators. Which must be followed for an accurate conclusion.
Tips for using a thickness gauge
There are simple recommendations for effective use of the thickness gauge. Which experts of this profile give:
- You should purchase a device depending on your situation and the surfaces you intend to inspect. If you need to evaluate the quality of coating on steel. Then an expensive thickness gauge for ceramics is not so relevant for you. You can also rent equipment to reduce costs. Or use the metering service at a service station.
- After purchasing a device, you need to take time to calibrate it. There are special samples made of plastic and steel, on which a layer of paint is applied. Check your measurement data with the readings on the samples and, if necessary, adjust the device.
- For each individual measurement plane, it is better to make separate settings for the thickness gauge. And your measurements will be more accurate.
- Slight differences in values are acceptable. Even in the field of one body component, the values are variable: for example, the roof can show 80 microns, and the doors 140 microns.
- Each body element must be measured in at least five places: in the corners and in the middle. This way your measurements will be as effective as possible.