general information
It is customary to distinguish several classes of reinforcement. The division is based on the following characteristics:
- periodic profile;
- mechanical parameters.
Reinforcing steel comes in the following classes:
- AII.
- AIII.
- AIV.
- AV.
For several years now, there has been quite a strong demand on the market for the A500C class of reinforcing steel. If you study GOST 5781-82, you will not be able to find descriptions similar to it in terms of its parameters. These products are manufactured in accordance with the following standards:
- STO ASChM 7-93;
- technical conditions.
Such a standardization system, according to which hot-rolled reinforcing steel of periodic profile is grouped into categories, was introduced by enterprises operating in the field of ferrous metallurgy. They are united into a single association, which has also taken upon itself the development of rules for the production of goods.
Difference between A500C and A-III
The type of reinforcement that will be used in the construction of a new building is selected at the project development stage. For residential buildings weighing up to 80 tons, A3 rolled steel is mainly used. This category includes fittings A400 and A500C. These classes are often considered the same or very similar, but they have significant differences:
- Scope of application. Both classes are used for repair and finishing, construction, production of reinforced concrete products, creating frames, etc. The difference between A500C and A3 (A400) is that the first class can be used in both loaded and unloaded structures, and the second - in areas of high stress.
- Appearance. Rolled products of class A500C have a profile with crescent-shaped protrusions that do not intersect with the longitudinal ribs. This shape provides higher plastic and strength characteristics. Also, thanks to the profile, the material does not have stress concentrators at the intersections of longitudinal and transverse ribs. Different manufacturers offer different versions of this material, which may differ in the angle of inclination of the crescent-shaped elements in relation to each other and the distance between them.
- Welding capability. A3 reinforcement, produced by the hot-rolled method from high-carbon type 25GS steel, complies with GOST 5781-82. The fluidity index of the product is 400 N/mm 2, which is specified in the A400 marking. This material cannot be welded. To connect individual elements, only knitting wire can be used (as fastenings at seams).
We have collected all the main characteristics by which these two classes of rolled metal can be compared in the table below:
Rolled products of class A400 (A-III) can be replaced with A500C without re-calculating the project. Reverse replacement is allowed only in case of additional recalculations. This provides a significant increase in the strength and reliability of the structure, and also increases its service life. By choosing A500C class rental, you can reduce the amount of required material by an average of 10%. Reducing the volume of working reinforcement allows you to reduce the final cost of the project.
A special case
The described reinforcing steel A500C is not the only exception in the world of hot-rolled products. The AI class also deserves special attention, which in GOST is usually designated as A240. The key feature is the sleek profile. 3 SP (PS) steel is used as a raw material for the production process. The diameter and deviations from it for any product with a smooth profile are regulated by GOST 2590-88. This regulatory document also specifies rolling accuracy for general cases.
Smooth reinforcing steel is produced in the following formats:
- rods;
- bays.
In skeins you can find sizes from 6 to 14 mm (pitch - 2 mm). The choice of reinforcement in rods is somewhat wider. The minimum possible diameter is 16 mm, and the largest available is 40 mm. From 16 to 22 mm the step is 2 mm, from 25 to 40 mm it increases to three.
How to mark fittings
In addition to the letter “A” (indicates that the rolled metal is produced in the form of rods) and the yield strength indicator (from 240 to 800 MPa), the marking of the reinforcement may also reflect its other features:
- rolled metal produced in the form of wire is designated by the letter “B” at the beginning of the marking;
- reinforcement made in the form of ropes - letter “K”;
- rolled metal, strengthened by drawing, is designated by the letter “B” at the end of the marking;
- reinforcement reinforced by heat treatment - letter “T”;
- rolled metal products to be welded are designated by the letter “C” at the end of the marking;
- corrosion resistance – letter “K”.
Additionally, the reinforcement is identified using paint. For example, class A600 is usually indicated by yellow on the tail parts of the rods, and A800 by green.
You can order steel reinforcement, as well as any other rolled metal products, from SPK Region. Send your application by mail or call – our consultants will answer any questions.
How and why?
The A240 grade of reinforcing steel is necessary in construction and other areas where reinforced concrete structures are used, as it is used for their reinforcement. Some experts call this category of materials “loop”, since it is customary to use reinforcement to form loop-shaped elements that strengthen reinforced concrete products. This is most relevant when the element stands out from the main plane of the structure. Hot rolled reinforcing steel A1 is suitable for creating elements that simplify loading of finished blocks, transportation and unloading. In addition, it is easier to connect different elements directly on the construction site.
The AI grade of reinforcement, like round reinforcement, is necessary for a wide range of structures. When using it, they make:
- fencing;
- furniture;
- railing
The circle and metal fittings A1, if they are manufactured in accordance with specialized standards, are used as raw materials: wire can be drawn from them. It is allowed to produce profiles:
- periodic;
- smooth.
If the reinforcement plant has the appropriate equipment, then A1 steel can be used for the manufacture of various products on lathes or milling machines. The material is processed mechanically.
Areas of application of steel reinforcement
The characteristics of steel reinforcement determine the scope of its application. Smooth profile rods are used:
- For dressing the working rods of the frame;
- Knitting of decorative items for design;
- Installation of individual elements of complex mechanisms.
Periodic profile bars are more in demand:
- Strengthening concrete structures in areas of greatest tension and compression;
- Installation of supporting elements and structures;
- Reinforcement of plaster layers, floor screeds;
- Construction of road surfaces and sidewalk areas;
- Installation of reinforcing belts for laying blocks and bricks.
The main purpose of bar reinforcement with a periodic profile is to strengthen concrete structures. Their rods are knitted into flat or spatial frames. The fittings in them perform different functions:
- Compensation for concrete fracture by creating tensile stress on the rod. Maximum loads are concentrated in the lower part of beam-type structures on two supports or with rigid pinching;
- Compensation for compression that is concentrated in the upper part of the same beam.
Without losing sight of the standards
Talks about what reinforcing steel should be like, GOST 5781.82. According to the standards, the carbon content of the metal can be no more than 0.3%, only then is the product applicable for reinforced concrete. Reinforcement is used both for previously stressed raw materials and for ordinary ones.
If pre-treated and stressed reinforced concrete is used, then the reinforcement is chosen that can cope with the fairly serious loads inherent in this environment. As a rule, the stress is quite high, which requires that the metal fittings be of increased strength and made strictly from reliable steel. If wire is used, then high demands are also placed on its strength.
If hot-rolled reinforcing steel is to be used in structures that are not subject to stress, then the use of ordinary raw materials is acceptable. The following steel grades are relevant here:
- ST3.
- ST5.
For prestressing, it is customary to take steel containing carbon:
- average;
- high.
Steel reinforcement can also be used, thermally treated to increase strength parameters.
What steel grades are used in production?
Reinforcing metal differs according to steel grades. There are alloyed, low-alloyed, with low and high yield strength. For greater clarity, generally accepted designations were introduced, for example A240 or A500. In this abbreviation, the numbers indicate fluidity, and the presence or absence of the “C” index indicates the possibility of welding. To check whether the purchased product meets the standards, you can always conduct an analysis using a special class table. For the production of fittings, steel grades specified in GOST are used:
Brands of smooth reinforcement
A240 or A1 are installation types made of smooth metal, used for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures in accordance with GOST 5781-82
. According to the regulations, production is allowed from low-alloy carbon 3sp(ps), st3(kp), st3(sp). These are structural steels of ordinary quality. In industry they are used in load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures at positive temperatures; use in toxic environments is allowed.
| Name of product | Retail (10 tons), rub/t. | ||
| Reinforcement A1 8.0 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 18.00 rub. | RUB 39,800 | 39,000 rub. |
| Reinforcement A1 10 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 27.00 rub. | RUB 39,800 | 39,000 rub. |
| Reinforcement A1 12 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 39.00 rub. | RUB 38,800 | 38,000 rub. |
| Reinforcement A1 14 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 51.00 rub. | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
| Reinforcement A1 16 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 66.00 rub. | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
| Reinforcement A1 20 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 104.00 rub. | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
| Reinforcement A1 25 mm | Length – 11.7 m | 160.00 rub. | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
| Reinforcement A1 28 mm | Length – 11.7 m | — | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
| Reinforcement A1 32 mm | Length – 11.7 m | — | RUB 38,300 | RUB 37,500 |
Marks of fittings with corrugation
A500 is a popular class of products with corrugated profiles, made from steel grades 35GS, 25G2S, 35G2Rps. The advantages of use are that they can withstand greater loads than the profile marked A240, 300 can cope with, and act as a frame for highly stressed structures. The chemical composition of the metal used is characterized by a high content of silicon - alloying elements. The main purpose is to reinforce critical structures, for example, bridges. Reinforcing steel grade 25G2S has the best mechanical properties.
A600, A800 - made of steel grades 80С, 20ХГ2Ц, purchased exclusively for large-scale construction projects, as they have a high safety margin, and are expensive. These are high-rise housing construction, bridges, tunnels, large industrial and chemical facilities. For production, exclusively innovative materials with special alloying components are used.
For the manufacture of fittings, metals are used that are officially permitted by regulatory documents. When ordering products, pay attention to additional markings. The addition “C” in the nomenclature means that the profiles are easy to weld, “K” - the steel for the reinforcement was treated with special compounds, is characterized by long-term operation and increased anti-corrosion characteristics.
Where can I buy metal products for construction at a profit?
Metal warehouse "Stal-Invest" sells rolled metal in a wide range of products wholesale and retail. The products are supplied by the official manufacturer and comply with GOST requirements. You can order any batches of profile pipes, angles, sheets at competitive prices. To leave a request, call the hotline number listed on the website. Cooperate with a responsible and reliable supplier of metal products!
Steel: which one should we take?
In order to produce high-quality reinforcing steel, GOST 5781.82 recommends using reliable steel:
- carbon;
- low alloy.
There are several grades available for different types of material mentioned. As a rule, the customer, when sending an order to the valve plant, indicates from what raw materials he wants to see the finished product. If the manufacturer does not receive such recommendations, then the manufacturing enterprise independently makes a decision in favor of the optimal option for a particular type of product. In particular, for the A800 it is customary to use the following brands:
- 22Х2Г2АУ.
- 22Х2Г2Р.
- 20X2G2SR.
What else is important?
When creating unstressed reinforced concrete structures, you should choose classes from first to third, and higher ones are useful if the structure has undergone prestressing.
If you have to work at low temperatures, and the object will continue to be operated in extreme conditions, then a brand of fittings that has a lower percentage of carbon is more suitable. As an alternative, you can choose raw materials that have undergone additional high-temperature processing.
But if it was decided to use wire as a reinforcing material, then it is better to give preference to one in which carbon is either completely absent or its content does not exceed 0.8%. This material is characterized by increased strength - up to 180 kgf/mm2 inclusive. The following parameters are provided:
- high temperature treatment;
- hardening
Fittings for private housing construction
Of the 15 positions (Table 1), four are enough for an individual developer.
- A240 (Commonly AI). Hot rolled smooth. Distribution, anchor for embedded parts, diameter 6-8 mm. Bay.
- A400 (AIII). Hot rolled, periodic profile. Working, diameter 10-12 mm. Rods 12 m long.
- A500 (AIII). See point 2.
- В500 (ВрI). Wire for masonry, reinforcing mesh. Diameter 3-5 mm. In the form of ready-made meshes.
It is recommended to purchase fittings by the metre. This is time consuming. But it guarantees that exactly the footage that is needed is paid for.
When bending rods, it is recommended to adhere to the radii and angles indicated in Table 4 for welded reinforcement (C) with a special notch.
Table 4
These tables will help to distinguish low-quality fittings. Rods made from melted down rails break at smaller angles. It belongs to class 500.
A400 class rods cannot be welded; the bending angle should not exceed 90°.
Universal class
A500C is the most popular fittings. Due to its lower carbon content, it is perfectly welded together (including arc welding), which strengthens the frames for the concrete structure.
A reduced amount of alloying additives has increased ductility; brittleness is not inherent in it. This is clear from αmax, which is 180°. This additionally makes it possible to use this class as anchor reinforcement.
A500 can replace A400 without recalculating design loads. At the same time, reverse replacement only with a new calculation. Due to the increased strength of A500, up to 10% of material can be saved on reinforcement. This is a significant value for any project.
It is also important that the A500 is operated at -55 ° C, which is 10 ° lower than the A400. Weldable reinforcement is 15% more expensive than conventional reinforcement of the same class
But the A500C is 6-8% cheaper than the A400. This is explained by the fact that steel for 500th due to the lack of alloying elements costs less
Weldable reinforcement is 15% more expensive than conventional reinforcement of the same class. But the A500C is 6-8% cheaper than the A400. This is explained by the fact that steel for 500th due to the lack of alloying elements costs less.
Carbon and material quality
Regulates from what raw materials construction fittings should be made, GOST 5781-82. In particular, the percentage of carbon has a fairly strong influence on the final parameters of the reinforced concrete product, its durability and reliability. The more carbon contained in the metal, the higher the hardness characteristic of the reinforcement will be, but at the same time the fragility increases. In addition, welding high-carbon steel is very difficult, often the result is not of sufficient quality, which affects the reliability of the entire structure as a whole.
The percentage of carbon allows the following classification:
- low-carbon steel reinforcement, where this compound is contained in an amount of no more than a quarter of a percent;
- with an average content level - from a quarter of a percent to 0.6;
- with a high content varying from 0.6 to 2%.
Steel grades in construction fittings
Domestic metal rolling production in the production of building reinforcement is guided by the standards specified in GOST 5781-82. It also indicates the steel grade of construction reinforcement, which is used for the production of metal reinforcement of a certain class. This affects the strength and plastic characteristics, as well as the degree of its adhesion to concrete.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the technical information: steel grades of construction reinforcement, cross-sectional areas, weight of a meter of reinforcement and other indicators in accordance with GOST 5781-82.
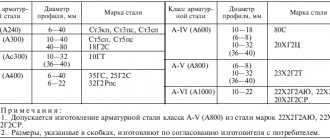
| Reinforcement class | Profile diameter, mm | steel grade |
| A.I. | 6-40 | St3kp, St3ps, St3sp |
| A-II | 10-40 | St5sp, St5ps |
| 40-80 | 18G2S | |
| Ac-III | 10-32 | 10GT |
| A-III | 6-40 | 35GS, 25G2S |
| 6-22 | 32G2Rps | |
| A-IV | 10-18 | 80C |
| 10-32 | 20ХГ2Ц | |
| AV | 10-32 | 23Х2Г2Т |
| A-VI | 10-22 | 22Kh2G2AYu, 22Kh2G2R, 22Kh2G2SR |
Reinforcing steel of class AV can be made from steel grades 22Х2Г2АУ, 22Х2Г2Р, 22Х2Г2СС.
Theoretical weight of reinforcement
| Diameter | Weight 1 meter | Meters per ton | Maximum deviations in % |
| d 6 | 0,222 | 4504,5 | +9,0 -7,0 |
| d 8 | 0,395 | 2531,65 | +9,0 -7,0 |
| d 10 | 0,617 | 1620,75 | +5,0 -6,0 |
| d 12 | 0,888 | 1126,13 | +5,0 -6,0 |
| d 14 | 1,21 | 826,45 | +5,0 -6,0 |
| d 16 | 1,58 | 632,91 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 18 | 2 | 500 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 20 | 2,47 | 404,86 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 22 | 2,98 | 335,57 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 25 | 3,85 | 259,74 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 28 | 4,83 | 207,04 | +3,0 -5,0 |
| d 32 | 6,31 | 158,48 | +3,0 -4,0 |
| d 36 | 7,99 | 125,16 | +3,0 -4,0 |
| d 40 | 9,87 | 101,32 | -+3,0 -4,0 |
| d 45 | 12,48 | 80,13 | +3,0 -4,0 |
| d 50 | 15,41 | 64,89 | +2,0 -4,0 |
| d 55 | 18,65 | 53,62 | +2,0 -4,0 |
| d 60 | 22,19 | 45,07 | +2,0 -4,0 |
| d 70 | 30,21 | 33,1 | +2,0 -4,0 |
| d 80 | 39,46 | 25,34 | +2,0 -4,0 |
Construction reinforcement is used to strengthen prestressed and standard reinforced concrete structures. This indispensable element of construction is necessary for adequate perception of tensile forces in building blocks, as well as for strengthening concrete in places where it is compressed. As a result, the grade of steel in building reinforcement determines its overall reinforcing effect, as well as the load that the reinforcement structures can bear.
Depending on what tasks the construction reinforcement is designed to perform, it is divided into installation and working. Mounting reinforcement serves as a support for the working reinforcement, as it fixes its correct position in the reinforced concrete structure and distributes forces between individual beams. Typically, the construction plan does not take into account the forces that are used to shrink the concrete, as well as the effect of temperature changes. Mounting construction reinforcement helps compensate for the consequences of these processes. Both working and installation reinforcement are produced in the form of metal frames or meshes, which are created by welding or knitting individual reinforcing rods. Reinforcement structures are introduced into reinforced concrete elements by calculating the load that will act on them during and after the construction of the building. Depending on this, brands of building reinforcement are selected.
At metal rolling plants, two technological processes for the production of building reinforcement are carried out. Thus, today there is a difference between hot-rolled rod and cold-drawn wire reinforcement. Construction reinforcement is manufactured in various diameters for use in various construction purposes, which determines the form in which it goes on sale: in coils, rods or coils. Construction reinforcement (the steel grade depends on the class of reinforcing elements produced) is an indispensable means of strengthening reinforced concrete structures.
The process of manufacturing building reinforcement, as a rule, ends with its strengthening. It can be heat treated or cold drawn. In accordance with this, certain markings are applied to construction fittings.
Construction reinforcement also differs in the shape and type of its profile. Reinforcement with a smooth profile belongs to type A1, with a periodic profile - A3. As a rule, corrugated reinforcement provides much better adhesion to concrete than reinforcement with a smooth profile.
Another important characteristic of steel reinforcement is its weldability. When welded, some classes of reinforcing elements produce very unreliable and brittle seams that can collapse during further construction, concrete compaction, or after the building is erected. If you plan to create reinforcement frames by welding, you should give preference to reinforcement that has the letter “C” in its name. It is easy to weld and, due to the low level of alloying elements in the steel, produces strong connections that can withstand the same loads as a solid reinforcing bar, as evidenced by the corresponding marking of construction reinforcement.
You can purchase construction fittings of any marking at. We will ensure prompt delivery of your order to any construction site.
How to improve?
In order for the reinforcing steel to have better quality, additional components can be added to the alloy. It is customary to use the following alloying components:
- tungsten;
- vanadium;
- chromium;
- nickel.
Some alloys add only one or two additional components, while others add a mixture of 5-6 metals. This allows you to obtain high-quality alloy steel with high performance:
- strength;
- hardness;
- corrosion resistance.
To obtain alloy steel, you can include silicon and manganese in the raw materials. Depending on how many additives are contained in a substance, it is customary to say that the material belongs to one of the following classes:
- low-alloy reinforcing steel containing no more than five percent inclusions;
- medium alloyed, in which the amount of additives varies between 5-10%;
- highly alloyed, one tenth or more consisting of additional components.
"What's in a name?"
Reinforcing steel is not just steel, but also a large number of other chemical components. You can find out what inclusions are in the material from the name. Standards have been developed for designating certain additives in the name of the material. Examples:
- X – chrome.
- C – zirconium.
- T – titanium.
Numbers are written after the stamp. They reflect how much carbon a material contains. Hundredths are indicated. Next they write the letters. They designate a chemical element, after which it is indicated how much of it is contained in the reinforcement. If no figure is given, it can be concluded that the substance is included in a volume of less than one percent.
Example: “reinforcing steel 35GS” is deciphered as steel, which contains carbon in a concentration of 0.35%, and also contains silicon and manganese, but the percentage of both components is insignificant, so there is no specified data (they are present in a volume of less than a percent of the total amount of material).
A little about decoding steel
For the manufacture of different fittings, different types of steel are used:
- Alloyed (with impurities of other metals);
- Carbon (its strength characteristics are determined by the amount of this chemical).
Carbon steel is marked as St with digital indices from 0 to 6. This value hides the average amount of carbon in the alloy as a percentage. The higher the value, the stronger and less flexible the rod.
St3...St4 can have different degrees of deoxidation:
- Boiling (“kp”);
- Semi-calm (“dog”);
- Calm (“sp”)
St5-St6 are produced:
- Semi-calm;
- Calm.
Various chemical elements are added to alloy steels, which affect different properties of the alloy:
| Element | Designation in steel grade | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Relative extension | Hardness | Impact strength | Fatigue strength | Weldability | Corrosion resistance | Cold resistance | Red brittleness |
| Carbon | U | ++ | + | = | ++ | — | — | — | |||
| Manganese | G | + | + | — | + | — | + | + | |||
| Silicon | WITH | + | + | — | + | = | — | — | |||
| Nickel | N | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | ||||
| Chromium | X | + | + | — | ++ | — | ++ | ||||
| Copper | D | ++ | |||||||||
| Niobium | B | ++ | ++ | — | + | + | + | ||||
| Vanadium | F | + | + | — | + | ++ | + | + | |||
| Vanadium nitride | AF | ++ | ++ | — | + | + | + | ||||
| Molybdenum | M | + | + | — | + | ++ | + | + | |||
| Bor | R | ++ | ++ | — | + | — | + | + | |||
| Titanium | T | + | + | + | — | + | |||||
| Aluminum | YU | — | |||||||||
| Sulfur | No | — | — | — | — | — | = | ++ | |||
| Phosphorus | P | + | + | = | + | = | = | — | = | ||
| Arsenic | No | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| Nitrogen | A | ++ | ++ | = | ++ | = | — | — | |||
| Oxygen | No | = | = | = | + | = | = | = | — | — | + |
Designations in the table: (+) - increases; (++) - significantly increases; (-) - reduces; (=) - significantly reduces; (0) - does not have a noticeable effect.
The marking of construction reinforcement made of alloy steel 22Х2Г2Р, from which products of class A1000 are produced, is deciphered as follows:
- 22Х – 0.22% chromium;
- 2G – manganese 0.02%;
- 2P – boron 0.02%.
The remaining volume is iron (Fe).
What to demand and expect?
According to current standards, reinforcing steel must be:
- easy to weld;
- plastic;
- durable.
Strength is usually understood as the ability of reinforcement to withstand destructive loads of the external environment. External influences can stretch and bend metal, twist and compress, and cut. For each type of load, separate strength indicators are identified. Reinforcement is more often used in conditions where tensile loads are high, so it is this value that you should pay attention to first. To assess how much reinforcement can resist tension, you need to evaluate:
- fluid limit;
- breaking resistance.
Plasticity is a parameter that reflects the adaptability of a material to external loads that try to change the shape of the product, its cross-section. If the reinforcement under such conditions retains its initial parameters, then after removing the load it can return to its original state or retain the changes obtained. Plasticity is expressed in elongation at break, bend angle, and the number of bends remaining after cooling of the metal.
Weldability is an indicator that reflects the ability to qualitatively connect with other materials when using a particular welding method. This parameter is defined:
- metal composition;
- smelting method;
- the size of the rods in section;
- connecting features;
- plasticity.
Flaws
Bar reinforcement has several disadvantages that need to be taken into account:
- In the absence of an anti-corrosion coating, the rods are subject to oxidation upon contact with water. Processes can even begin from exposure to water in the cement during its hardening.
- Inability to perform functions with rod products if the rod class and its diameter are incorrectly selected.
- Excessively stressed reinforcement can have the opposite effect and form cracks in the concrete structure.
- A protective layer of concrete is required - at least 2 diameters of the section size to prevent water from entering the rods.
Mechanics and reliability
The above parameters allow us to talk about how good the mechanical parameters of steel are. It is on their basis that technical characteristics and indicators are distinguished.
An important feature of reinforcement is its temporary resistance. To determine it, as well as to determine how large the fluid limit is, how large the elongation of steel can be relative to the initial value, special tests are carried out in production: tensile testing machines designed for this task are used.
The work is carried out as follows: when starting the machine, the load on the placed sample gradually increases. In this case, the reinforcement is located in a rigid fastening system that does not allow the specimen to “slip away.” The mechanisms try to lengthen the rod longitudinally, deforming it. The indicators taken from the reinforcement make it possible to form a tension diagram (the scale is set arbitrarily).
Technical features
The straight sections of the diagram reflect loads under which the sample does not deform. With increasing loads, you can see a proportional increase in length, which allows you to draw conclusions about the reliability of the steel and its ability to resist external influences. The limiting value of the load applied to the test specimen is preset. Upon reaching this value, the influence of mechanical force is also gradually reduced.
In the best case scenario, the rod, stretched under the influence of a large external force, returns to its original state when the load is removed. This ability is due to the elasticity of steel. It is worth understanding that the elastic zone for metal has certain limitations. If indicators exceed these limits, returning to the original values will become impossible. When such a limit indicator is identified, the elastic limit is reached.
If you test reinforcement made of ST3 steel manufactured in accordance with the current GOST, then you will be able to obtain parameters close to the following:
- yield strength - 2,460 kgf/cm2;
- relative elongation - 25;
- tensile strength in a given time period - 4,000 kgf/cm2.
Technologies for assembling reinforcement for strip foundations
Reinforcing the strip foundation with your own hands begins after installing the formwork. There are two options:
- The entire frame is assembled directly in a pit or trench. If the tape is narrow and high, it is inconvenient to work.
- Frame sections are prepared close to the pit. They are transferred in parts and installed in their designated place, linking them into a single whole. It’s more convenient to work this way, except that it is very inconvenient and difficult to move connected structures made of reinforcement.
Both options are imperfect and everyone decides how it will be easier for him. When working directly in a trench, you need to know the procedure:
- The longitudinal rods of the lower reinforced belt are laid first. They need to be raised 5 cm from the edge of the concrete. It is better to use special legs for this, but pieces of bricks are popular among developers. The reinforcement is also 5 cm away from the formwork walls.
- Using transverse pieces of structural reinforcement or molded contours, they are fixed at the required distance using tying wire and a hook or a tying gun.
- Then there are two options: If contours formed in the form of rectangles were used, the upper belt is immediately tied to them at the top.
- If during installation you use cut pieces for crossbars and vertical posts, then the next step is tying up the vertical posts. After they are all tied, a second belt of longitudinal reinforcement is tied.
There is another technology for reinforcing strip foundations. The frame turns out to be rigid, but there is a large consumption of rods for the vertical posts: they are driven into the ground.
The second technology for reinforcing a strip foundation is to first drive in vertical posts, tie longitudinal threads to them, and then connect everything with transverse ones
- First, vertical posts are driven in at the corners of the tape and at the junction of horizontal rods. The racks should have a large diameter of 16-20 mm. They are placed at a distance of at least 5 cm from the edge of the formwork, checking horizontal and vertical, and driven into the ground 2 meters.
- Then vertical rods of the calculated diameter are driven in. We determined the installation pitch: 300 mm, in the corners and at the junctions of the walls it is half as much - 150 mm.
- The longitudinal threads of the lower reinforcement belt are tied to the posts.
- At the intersection of the racks and longitudinal reinforcements, horizontal jumpers are tied.
- The upper reinforcement belt is tied, which is located 5-7 cm below the upper surface of the concrete.
- Horizontal jumpers are tied.
It is most convenient and quick to make a reinforcing belt using pre-formed contours. The rod is bent to form a rectangle with the specified parameters. The whole problem is that they need to be made identical, with minimal deviations. And a large number of them are required. But then the work in the trench moves faster.
The reinforcing belt can be knitted separately, and then installed in the formwork and tied into a single whole on site
As you can see, reinforcing a strip foundation is a lengthy and not the easiest process. But you can cope even alone, without helpers. It will take a lot of time, though. It’s easier to work with two or three people: both carry the rods and set them out.
Parameters and scope
Reinforcement with high strength values is usually more expensive than low-quality material. At the same time, practice shows that the use of such material allows one to achieve significant savings, since the reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures requires more economical consumption of metal.
Pay attention to the plasticity of the reinforcement: there are certain limits beyond which it is extremely undesirable. When this parameter decreases below a certain level, it is impossible to use rolled products at full strength. A structure made using such consumable raw materials becomes fragile and can unpredictably collapse under the influence of external factors. There is another risk associated with a decrease in the ductility of the metal: the likelihood of brittle fracture increases already at the stage of reinforcing reinforced concrete structures.
Steel grades of metal fittings
Metal reinforcement is used in the construction of any building.
For a structure, its importance can hardly be overestimated, because the durability of the building depends on its quantity and quality. The use of steel rods can be found at the stage of applying plaster, erecting columns, creating a reinforcing belt, and laying a foundation. Classic reinforced concrete construction is a competent combination of metal rods and concrete. For maximum effect, you need to choose the correct diameter and type of corrugation, maintain the spacing between the rods, and connect them correctly. However, the grade of steel from which the reinforcement is made plays a decisive role. Both the quality of the metal profile and its durability in operation depend on the last criterion. Choosing the right type of metal is the supplier’s task, with which we are happy to help!
Impact on steel samples
To improve the performance of reinforcement, they resort to various technologies of external influence. In particular, the practice of thermal hardening is widespread. At the same time, the strength of the material doubles, and sometimes even more. This is most applicable for low-alloy, carbon compounds. But the cost of the material increases by only 10-12%. Thermal hardening shows better performance compared to mechanical hardening, but to implement it you need to have serious modern equipment and a team of highly qualified specialists. Even minor errors in the technological process greatly affect the quality of the final product (and the reputation of its manufacturer).
Mechanical hardening is achieved using:
- winches;
- hydraulic jacks;
- profiled rolls.
The latter are needed to flatten steel. During hardening, it is possible to achieve plastic deformations, due to which the strength increases by 50% relative to the original value.
The most popular - what is it?
Traditionally, the most in demand in the metal market is reinforcement 8 mm in diameter. It belongs to the third class and is produced in coils, skeins, and rods. 8 mm is the parameter for the average diameter of the building material. The production of such fittings must comply with GOST 30136-95. The reinforcement produced in coils is called “wire rod” by specialists.
8mm reinforcement is made from low carbon steel. Brands ST0, ST3 are used. During the manufacturing process there are two (sometimes one) cooling stages, which makes it possible to achieve high reliability of the material. Wire rod in coils is wire.
A3 reinforcement is steel with a circular cross-section. It is necessary for the subsequent production of wire and springs. Raw materials are also indispensable in the production process of cold-drawn construction reinforcement.
GOST requirements: B500 fittings, features of its manufacture
A500C reinforcement is successfully used in compressed elements. At the same time, the quality of concreting increases due to a reduction in the number of metal structures in the columns. Profiles can be used in projects where sections of classes АІ and АІІІ are specified. An analogue of the universal fittings A500C can be the fittings B500.
The B500C fittings meet European standards in terms of the chemical and technological characteristics of the raw materials and structure. The main advantage is flexibility. The high degree of plasticity of reinforcement structures prevents the destruction of buildings. Reinforcing products of this class in the Russian Federation are produced in accordance with GOST R 52554. They are intended for the construction of structures made of lightweight and weighted concrete.
Such buildings are used in aggressive environments. Reinforcement is used both in the form of independent rods and in frames and welded products. According to its characteristics, B500С is an effective substitute for fittings marked A400, A400C, A240. The B500С fittings have the following basic parameters:
Class B500 fittings meet all European standards.
- is produced in accordance with European Union standards, which makes it possible to use it on European equipment;
- does not curl due to the absence of stripes;
- elongates by 1.4%, withstanding loads over 3%;
- characterized by excellent weldability.
As for the pricing policy, it is different and depends on the characteristics of the fittings and the volume of required products.
Production and sales
8 mm reinforcement is usually made on wire-section machines from raw materials that comply with GOST 380. This is a standard technology that involves the presence of bar steel processed by a shaft system. On machines, the material is rolled and drawn, heated and cooled. Depending on the characteristics of a particular product, it will be cooled naturally or forcibly.
This product is available for sale both by linear meters and in large skeins (for wholesale buyers).
Why is this necessary?
8 mm reinforcement is indispensable in the construction of reinforced concrete and metal structures. The wire rod is quite thin, so it is used in the manufacture of meshes, frames, and ropes. The reinforcement is effective as a base for staples. It is used to strengthen building structures. A specific option is selected by analyzing the operating conditions of the building, on the basis of which a decision is made in favor of one brand or another.
Reinforcement is more often used as a raw material for the manufacture of other construction products, and not as an independent material. If wire rod is needed to produce nails or cables, then you need to control the evenness of the products: rough surfaces are unacceptable, this will significantly reduce the strength of the finished product. When manufacturing thick reinforcement and staples, the requirements for surface smoothness are not so significant. The reinforcement used to construct load-bearing walls cannot contain air-filled cavities or cracks. If 8 mm diameter reinforcement is purchased in rods, quality control involves tracking the identity of the products.
How fittings are made
There are two ways to make steel reinforcement:
- Rolled products with a diameter of up to 8 mm can be produced by cold rolling. When using it, the semi-finished product (wire rod) is processed under pressure in cold rolling mills. To do this, it is passed through a system of profiled rollers without heating, and the resulting finished product is wound into coils or cut into equal parts. In addition, smooth reinforcement can be obtained by processing wire rod using the drawing method. Cold-rolled metal products are characterized by high surface quality and excellent weldability. It is most often used for the manufacture of small architectural forms or decorative objects.
- Rolled products with a diameter of up to 80 mm are produced by hot rolling. To do this, steel blanks are heated and passed through a system of calibrated rolls. The result is a smooth or ribbed surface. Additionally, the resulting rolled products can be strengthened by stretching, pressure, or thermomechanical treatment. Hot rolled metal is highly durable. It is most often used for the manufacture of highly loaded elements.