Characteristics of steel grade 5sp
St5sp - Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality, limited weldability, welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, ESW, KTS without restrictions. According to NAKS Group: M07 (W07). Electrodes UONI-13/55U. For thicknesses greater than 35 millimeters, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended; it is not prone to flake sensitivity and there is no tendency to temper brittleness. Machinability by cutting in the hot-rolled state at HB 158 σB = 630 MPa Kυ hard alloy. = 1.2 and Kυ b.st. = 1.2, has found its application in the production of parts for riveted structures; bolts, nuts, handles, rods, bushings, rollers, wedges, rods, sprockets, tube sheets, flanges and other parts operating at temperatures from 0 to 425 degrees, production of At500C class fittings; St5sp steel has relatively high toughness and ductility, slightly higher than St5ps steel. Forging at temperatures from 1260 to 750 0C, cooling is carried out in air. St5sp steel is not prone to temper brittleness and is magnetic.
Steel grade 5ХНМ
| Brand: 5ХНМ (substitutes: 5ХНВ, 5ХГМ, 4ХМФС, 5ХНВС, 4Х5В2ФС) Class: Die tool steel Type of supply: long products, including shaped steel: GOST 5950-2000, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006. Calibrated rod GOST 5950-2000, GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78. Polished rod and silver steel GOST 5950-2000, GOST 14955-77. Strip GOST 4405-75. Wire GOST 10543-98. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 5950-2000, GOST 1133-71, GOST 7831-78. Use in industry: hammer dies of steam-air and pneumatic hammers with a mass of falling parts over 3 tons, press dies and machine high-speed stamping dies during hot deformation of light non-ferrous alloys, matrix blocks for inserts of horizontal forging machines. |
| Chemical composition in % of steel 5ХНМ | ||
| C | 0,5 — 0,6 | |
| Si | 0,1 — 0,4 | |
| Mn | 0,5 — 0,8 | |
| Ni | 1,4 — 1,8 | |
| S | up to 0.03 | |
| P | up to 0.03 | |
| Cr | 0,5 — 0,8 | |
| Mo | 0,15 — 0,3 | |
| Cu | up to 0.3 | |
| Fe | ~95 | |
| Additional information and properties |
| Heat treatment: Quenching 850oC, oil, Tempering 460 - 520oC. Forging temperature: ºС: beginning 1240, end 750. Sections up to 100 mm are cooled in air, 101-350 mm - in a pit. Material hardness: HB 10 -1 = 241 MPa Critical point temperature: Ac1 = 730, Ac3(Acm) = 780, Ar3(Arcm) = 640, Ar1 = 610, Mn = 230 Weldability of the material: not applicable for welded structures. Flock sensitivity: sensitive. Tendency to temper brittleness: not prone. Cutting machinability: in the annealed state at HB 286 and σв =900 MPa, K υ solid. spl=0.6 and Kυ b.st=0.3 |
| Hardness (GOST 5950-73) | |||
| Delivery condition, heat treatment modes | HRC∂ | ||
| Annealed or highly tempered rods and strips Samples Quenching 850 ºС, oil Tempering 550 ºС Heating 700-750 ºС. Hardening 840-860 ºС, oil. Tempering 400-480 ºС (final heat treatment mode) 500-550 ºС (final heat treatment mode) | Up to (241) St. 36 44-48 40-43 | ||
| Mechanical properties of 5ХНМ depending on the cross-section | |||||||
| Section, mm | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | δ4 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) | Hardness | |
| superficial HRC∂ | NV cores | ||||||
| Hardening 850 ºС, oil. Vacation 460-520 ºС | |||||||
| up to 100 100-200 200-300 300-500 500-700 | — 1420 1270 1130 930 | — 1570 1470 1320 1180 | — 9 11 12 15 | — 35 38 36 40 | — 34 44 49 78 | 57 42-47 40-44 37-42 35-39 | — 375-429 352-397 321-375 302-341 |
| Hardness of steel 5ХНМ depending on tempering temperature | ||||||
| Temperature, °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) | HB(HRC∂) |
| Hardening 850 ºС, oil. Temperature holding time 2 hours | ||||||
| 400 450 500 550 | 1370 1400 1270 1180 | 1570 1490 1370 1310 | 10 — — — | 40 36 36 35 | 33 37 46 59 | (47) (45) (43) (40) |
| Quenching 840 - 860 ºС, oil or water oil | ||||||
| 450-510 500-550 560-600 | — — — | — — — | — — — | — — — | — — — | 415-477 341-388 285-321 |
| Hardness of 5ХНМ depending on test temperature | |
| Test temperature, °C | HRC∂ |
| Hardening 850 ºС. Vacation 450 ºС | |
| 400 500 550 600 | 43 39 37 26 |
| Hardening 850 ºС. Vacation 500 ºС | |
| 400 500 550 600 | 39 28 — 26 |
| Heat resistance | ||
| Temperature, ºС | Time, h | HRC∂ |
| 590 | 4 | 37 |
| Physical properties of steel 5ХНМ | ||||||
| T (Grad) | E 10-5 (MPa) | a 10 6 (1/Deg) | l (W/(m deg)) | r (kg/m3) | C (J/(kg deg)) | R 10 9 (Ohm m) |
| 20 | ||||||
| 100 | 38 | 300 | ||||
| 200 | 12.6 | 40 | 250 | |||
| 300 | 42 | 200 | ||||
| 400 | 42 | 160 | ||||
| 500 | 44 | |||||
| 600 | 14.2 | 46 | ||||
Interpretation of steel grade 5ХНМ : the presence of the number 5 at the beginning of the grade indicates that the steel contains 0.5% carbon, and the letters X, H and M indicate the presence of chromium, nickel and manganese in the steel, respectively, in an amount not exceeding 1.5 %, so we have alloy steel.
Application of 5ХНМ steel and heat treatment of products: the following steel grades are used for the manufacture of dies: carbon and alloyed 5ХНМ and some others.
The basic requirements for steel for the manufacture of dies are as follows:
1) high strength, sufficient impact resistance and high wear resistance at elevated temperatures - so that the dies do not collapse and retain their shape during operation;
2) good thermal conductivity for rapid heat removal from the working surface into the depth of the die;
3) significant hardenability (which is especially important for large dies);
4) high resistance to the occurrence of heat cracks that appear on the working surface due to the frequency of heating and cooling of the dies.
Dies made of carbon steel quickly fail due to the shallow depth of the hardened layer and the low temperature limit (325-350°) to which the stamp can heat up during operation. Therefore, carbon steel can be used for small dies with simple shapes.
For the manufacture of dies operating under difficult conditions, 5KhNM steel or its substitute, 5KhGM steel, is most often used. Nickel in 5KhGM steel is replaced by manganese, which, while maintaining the deep hardenability of the steel, somewhat reduces the impact strength. To obtain the required toughness, dies made of 5KhGM steel are tempered at a higher temperature than dies made of 5KhNM steel.
Forged die blanks are annealed to reduce hardness, relieve internal stresses and prepare the structure for subsequent hardening. Forgings that cool slowly after their manufacture, in insulated pits or slag, can be loaded for annealing into a furnace heated to the required temperature, and heated at the speed that this furnace allows. The forgings, which cool quickly after their manufacture, on the workshop floor, are loaded into a furnace at a temperature of 400-500° and heated to the required temperature along with the furnace.
If heating occurs unevenly, then it is necessary in all cases to slow it down by holding one or two times at intermediate temperatures. Slow cooling after heating of small and medium forgings can be achieved by packing them in boxes with backfill, and for large forgings - by periodically turning off and turning on the furnace.
Dies coming for major repairs are subjected to high tempering instead of annealing. To do this, the stamps are placed in an oven heated to the required temperature, kept for 2-3 hours, removed from the oven and left in the air until completely cooled.
Sometimes large dies are hardened in blanks (cubes) before machining. In this case, the loss of hardness is compensated by the absence of deformation of the finished stamp. Such workpieces are heated for hardening without packaging.
When hardening fully processed dies, measures must be taken to protect the working surface from oxidation. Spent carburizer or burnt cast iron shavings are used as an insulating backfill.
Small and medium-sized stamps, as well as cubes, can be loaded into a furnace heated to the hardening temperature without fear of cracks or deformation, especially since the working part of the stamp heats up relatively slowly, since it is located under a layer of backfill. Heating at the quenching temperature should ensure complete dissolution of carbon and other elements in the austenite.
Below is the heat treatment regime for dies made of 5ХНМ steel in an N15 electric furnace, which has been used at one of the plants for a number of years and has fully justified itself (die Ø 150 mm, height 140 mm):
1) loading into an oven heated to a temperature of 830-850° and holding for 2 hours;
2) hardening in oil, holding until the temperature reaches 100-200° for about 15-20 minutes;
3) loading into a tempering furnace heated to a temperature of 350-400°, heating to a temperature of 520-560° with a total holding time of 6 hours;
4) unloading into air, cleaning and hardness control (Rc = 41 -47).
When loading several dies into the oven, they should be placed at a distance of 100-150 mm from one another to speed up heating.
Dies are large and have very sharp transitions and need to be heated up more slowly. Below are the heat treatment regimes for large hammer dies made of 5ХНМ steel, used at the Kirov plant:
| Modes | Stamp 250x250x305 mm | Stamp 500x500x360 mm |
| Hardening | ||
| Furnace temperature when loading the die Holding at 650 °C Heating time up to 830-850 °C Holding at 830-850 °C Hardening in oil at 30-50 °C, holding | 650 2.5 hours 1.5 hours 4.5 hours 20-25 min | 650 3.5 hours 1.5 hours 7.5 hours 40-50 min |
| Vacation | ||
| Furnace temperature when loading the die Holding at 400 °C Heating time up to 480-520 °C Holding at 480-520 °C Cooling Cleaning and hardness control HB | 400 1.5 hours 1 hour 7 hours in air 364-418 | 400 3 hours 1.5 hours 9 hours in air 340-387 |
When hardening dies, especially large ones, it is necessary to ensure good drainage of heated oil. To do this, oil showers are installed in oil quenching baths or a tube from a fan is inserted into the tank and the oil is cooled by blowing air. Small and medium-sized dies can be cooled by rocking them in oil (pressed in pliers).
To reduce internal stresses, alloy steel dies are cooled in oil not until completely cooled, but to a temperature of 150-200°, after which they are removed and immediately transferred for tempering, since complete cooling of the dies can lead to the formation of cracks. The total residence time of the dies in the tempering furnace should be within 2.5 minutes. for each millimeter of the smallest section, of which holding at the tempering temperature is approximately 70% of the total time required.
Examples: 1. The release of a die with a diameter of 200 mm and a height of 150 mm should last 2.5 x 150 = 375 minutes. 6 o'clock 15 min., exposure at tempering temperature = 6 hours. 15 minutes. x 0.7 = 4 hours 20 minutes.
2. The release of a stamp with a diameter of 100 mm and a height of 150 mm should last 2.5 minutes. x 100 = 250 min. = 4 hours 10 min., exposure at tempering temperature = 4 hours. 10 min. x 0.7 = 2 hours 55 minutes.
In hammer dies, it is necessary to additionally release the shank to a hardness of Hb = 250 - 300 in order to avoid breakage upon impact. To do this, the working surface and one side of the stamp are cleaned with emery cloth, after which the stamp is placed with the shank on a specially heated plate or in the oven window. The exposure continues until a tarnish color appears on the working surface and the shank heats up to a dark red color.
Dies made of carbon steel undergo the following heat treatment regime (when heated in an electric furnace).
1. Normalization: a) loading into an oven heated to the required temperature; b) exposure at this temperature at the rate of 0.8 minutes. for each millimeter of the smallest section; c) unloading and cooling in still air.
2. Quenching: 1) loading into a furnace heated to the quenching temperature; b) exposure at the rate of 0.8 minutes. for each millimeter of the smallest section; c) cooling in water to a temperature of 150-200° and transferring to oil.
3. Tempering: a) loading into a furnace heated to the tempering temperature (350-430°C); b) exposure at the rate of 2.0 minutes. for every millimeter of cross-section; c) air cooling; d) release of the shank.
The required hardness of the working part of the dies is Rс = 45 - 50.
Before loading the dies into the furnace for normalization and hardening, measures are taken to protect the working surface from oxidation. The exposure in water should be minimal and the transfer to an oil bath should be done as quickly as possible so that self-tempering of the surface does not occur due to the internal heat of the stamp.
To harden dies with deep streams, a shower is arranged in water tanks, similar to an oil shower.
Dies of small and medium sizes can be hardened with self-tempering according to the following regime: 1) heat the die for hardening; 2) cool the working surface in water under the shower, while leaving the tail part hot; 3) remove the stamp from the water, quickly clean the working surface and one side surface; 4) when a blue tarnish appears on the working surface, immerse the stamp in oil until completely cooled.
When a fully heated stamp is partially cooled in water, deep cracks often form at the point where it comes out of the water, so the stamp in the water must be moved up and down so that there is no sudden transition from high to low temperature.
One should categorically warn against sudden local heating of red-hot dies. Welding of shanks, handles, etc. should be done before hardening.
Molds for casting are made from alloy steels ЗХ2В8, 4Х8В2, 5ХНМ, 5ХГМ, 4ХВ2С, 5ХВ2С, 40ХН, 40ХС.
The main requirements for steel for molds are: high thermal conductivity, ensuring rapid heat removal; high strength at elevated temperatures; high resistance to stresses arising in molds from sudden changes in temperature when pouring metal.
Heat treatment of molds is carried out according to the same regimes as for dies made of the corresponding steel grades.
The hardness of the finished molds should be within the range R0 = 40-43.
Interpretation of steel grade 5sp
Decoding of steel: The letter at the beginning indicates a group of steel which defines the criteria for the ultimate strength for the chemical composition; if there is no letter, then such steel belongs to group A, and is supplied to consumers based on mechanical properties (such steel may have a high sulfur or phosphorus content). Letters St. indicate that the steel is of ordinary quality, although most steels are high quality. The numbers from 0 to 6 are the conventional brand number depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. Typically, the higher the number, the more carbon and the greater the strength. In our case, 5 indicates the carbon content in the alloy is 0.28–0.37%. The letters after the brand number indicate the degree of deoxidation: cn - calm. In terms of price, calm steels have become more expensive than semi-calm and boiling steels. Mild steel is steel obtained as a result of deoxidation. It is obtained by deoxidation with aluminum, manganese and silicon. The level of oxygen in it is so reduced that during metal processing no reaction occurs between carbon and oxygen, and the presence of non-metallic slags and their inclusion is reduced to a minimum. Calm steel has a dense structure and good mechanical properties. It is less prone to negative reactions to welding heat and to aging. The features of a homogeneous microstructure give the alloy maximum corrosion resistance and ductility.
Steel 5, steel grade St 5 its characteristics and description
Steel grade: St. 5
No. GOST 380-50
Replacement steel grade: Mst. 5
Type of heat treatment and steel hardness 5: Without heat treatment
Recommended area of application for steel 5: Welded parts, lightly loaded parts that are not subject to wear during operation: handles, rods, etc.
Note: Welded products with complex configurations or products with a significant number of welds are annealed to relieve stress arising during the welding process.
Brinell hardness: Hb kg/mm: 156-197
Rough processing with high-speed tools (turning, drilling, milling, etc.):
- Cutting speed Kv: 1.3
- Machine productivity Kpr: 1.15
High-speed machining with carbide tools (turning and milling):
- Cutting speed Kv: 1.20
- Machine productivity Kpr: 1.1
Fine machining with high-speed tools:
- Cutting speed Kv: 1.0
- Machine performance Kpr: 1.0
- Getting a good surface finish: difficult
Note: the main criteria for machinability are cutting speed and machine performance
Mechanical properties of steel Art. 5:
- ?in kg/mm2: 50-53; 54-57; 58-62;
- ?t kg/mm2: >28
- ? kg/mm2: >17; >16; >15;
- ? %: >21; >20; >19;
- ?k kgm/cm2: —
- Hardness Hb: <170;
Characteristics of steel Art. 5 and its meanings: Low carbon steel of ordinary quality. Available only according to mechanical properties. It welds well, is stamped in cold and hot conditions, and is drawn. It is used without heat treatment for welded and stamped parts: machine troughs, tanks, covers, casings, gaskets, etc. Steel is produced in the form of long and shaped rolled products, strips and sheets.
Chemical composition of steel 5 in%:
- C (carbon): 0.28-0.37;
- Mn (manganese): 0.50-0.80;
- Si (silicon): 0.17-0.35;
- S (sulphur): <0.055;
- P (phosphorus): <0.050
omashinostroenie.com
Supply St5sp
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel, GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel, GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams, GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flange, GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flange, GOST 8281-80 Bent steel channels, unequal flange, GOST 8283-93 Bent steel trough equal flange profiles, GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 8509-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange, GOST 8510-86 Hot-rolled steel angles unequal flange, GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels, GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Rolled sheets hot rolled , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets, GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip, GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel broadband universal, GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire, GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wire, GOST 10705-80 Electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 10706-76 Straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 3262-75 Steel water-gas pipes.
| Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 8479-70; |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 380-2005; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 10884-94; GOST 535-2005; GOST 5422-73; GOST 5781-82; GOST 8509-93; GOST 8510-86; GOST 8240-97; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 11474-76; GOST 8320.0-83; GOST 9234-74; GOST 17152-89; GOST 18662-83; GOST 19240-73; GOST 19425-74; GOST 8239-89; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; GOST 14637-89; GOST 16523-97; GOST 19903-74; |
| Ribbons | GOST 6009-74; GOST 3560-73; |
| Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | GOST 12135-75; GOST 8194-75; GOST 7056-77; GOST 3280-84; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 8731-87; GOST 8732-78; GOST 9567-75; GOST 3262-75; GOST 53383-2009; |
Comparison of chemical composition
Please note carbon tolerance limits. Within certain limits, St20 can easily replace St3. There are fewer inclusions of harmful impurities in the alloys in the form of sulfur and phosphorus. The presence of permanent impurities in the form of manganese and silicon is associated with steel production technology.
Table 2. Comparison of the chemical composition of st3sp5 according to GOST 380-05 with st20 according to GOST 1050-13
| steel grade | Mass fractions of elements, % | |||||||
| C (carbon) | Si (silicon) | Mn (manganese) | P (phosphorus) | S (sulfur) | Cr (chromium) | Ni (nickel) | Cu (copper) | |
| St3sp5 GOST 380-2005 | 0,14-0,22 | 0,15-0,3 | 0,4-0,65 | >0,04 | >0,05 | >0,3 | >0,3 | >0,3 |
| st 20 GOST 1050-2013 | 0,17-0,24 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,35-0,65 | >0,03 | >0,035 | >0,25 | >0,3 | >0,3 |
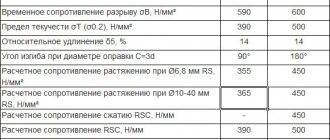
Mechanical properties St5sp
Mechanical properties of steel St5sp according to GOST 535-2005 regulations is sold in the form of hot-rolled steel with a cross section of up to 10 mm, from 10 to 20 mm, from 20 to 40 mm, from over 40 mm to 100 mm, and also from more than 100 mm. Rolled thickness: 10-20 mm, yield strength: > 285 MPa, tensile strength: 490-630 MPa, relative elongation: >20%, bending until the sides are parallel: d=3a. Rolled thickness: 20-40 mm, yield strength: > 275 MPa, tensile strength: 490-630 MPa, relative elongation: > 19%, bending until the sides are parallel: d=4a. Rolled thickness: 40-100 mm, yield strength: > 265 MPa, tensile strength: 490-630 MPa, relative elongation: >17%, bending until the sides are parallel: d=4a. Rolled thickness: > 100 mm, yield strength: > 255 MPa, tensile strength: 490-630 MPa, relative elongation: > 17%, bending until the sides are parallel: d=4a. Rolled thickness: < 10 mm, yield strength: > 295 MPa, tensile strength: 490-630 MPa, relative elongation: > 20%, bending until the sides are parallel: d=3a
| Type of rental | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Pipes, GOST 8731-87 | 490 | 274 | 17 | |||||
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 490-630 | 255-295 | 17-20 | |||||
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 490-630 | 255-285 | 17-20 | |||||
| Fittings, GOST 5781-82 | 490 | 295 | 19 |
St5Gps | "ConcordMetal"
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade St5Gps.
Classification of material and application of the St5Gps brand
Brand: St5Gps Material classification: Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality Application: I-beams, channels, angle steel
Chemical composition of the St5Gps material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | N | Cu | As |
| 0.22 — 0.3 | up to 0.15 | 0.8 — 1.2 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.05 | up to 0.04 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.008 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.08 |
Mechanical properties of St5Gps at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 450-590 | 255-285 | 17-20 | |||||
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 450-590 | 255-285 | 17-20 |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o— T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o—T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Other brands in this category:
Please note that this information about the St5Gps brand is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of the actual St5Gps brand material may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about the St5Gps brand can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
www.c-met.ru
Foreign analogues of 5sp grade steel
| USA | A57050, A57250, K02305, K02507 |
| Germany | 1.0050, E295, Fe490-2, St50-2 |
| Japan | SS490, SS50 |
| France | A50-2, E295 |
| England | 4360-50B, 50B, E295, Fe490-2FN |
| European Union | E295, E335, Fe50-2FN, Fe50-3FN |
| Italy | E295, Fe490 |
| Belgium | FE490-2FN |
| Spain | A490-2, E295, Fe490-2FN |
| China | Q275 |
| Sweden | 1550, 2172 |
| Bulgaria | ASt5, E295, WSt5ps, WSt5sp |
| Hungary | E295, Fe490-2 |
| Poland | MSt5, St5 |
| Romania | OL50.1 |
| Czech | 11500 |
| Austria | St50F |
| Switzerland | St50-2 |
| South Korea | SS490 |
Buy 5SP steel in Moscow and the Moscow region
5SP steel is widely used in various fields of industry, used in mechanical engineering, involved in the manufacturing industry, covers a wide range of construction, shipbuilding, and is partially used in aircraft production and many other areas of industry. There are a large number of steel grades, a huge part of the alloys are made to order, and those steel grades that are in great demand are partially stored for regular customers. The Metallpro company carries out wholesale and retail sales on the territory of the Russian Federation; 5SP steel is partly in our warehouse in the form of rolled metal products, and partly we ship directly from the metallurgical plant. With constant demand, we are ready to offer mutually beneficial cooperation, delivery directly from the factory by carriage standards, as well as by motor vehicles. You can buy 5SP steel in Moscow and the Moscow region at a favorable price from the Metallpro Trading Company under a mutually beneficial contract for a long partnership period.
Reviews from knife owners
Vesuvius. Low price, high quality scabbard. Great for rough work. The design of the knife is satisfactory. Quickly dulls when interacting with wood. Sharpens well.
Valentin M. At first glance, a very good knife. Beautiful and comfortable. Then it turned out that steel has a low scope of application.
Hunter. More like a souvenir item, despite its beauty. Perhaps excellent as a military weapon. It is not convenient to use it in everyday life. But the carcass can be cut up.
Yaroslav. Cutting is inconvenient, and if you chop, it will quickly become dull. However, it is easy to sharpen. It fits nicely in the hand. Fits tightly in the sheath.
Price for steel 5SP
The favorable price for the 5SP steel grade is explained by the presence of a competitive environment, low markups and loading from leading metallurgical plants directly, sometimes bypassing storage at transshipment points. Metalpro company bears full responsibility for the chemical composition of the supplied products and guarantees the quality of delivery. The cost of 5SP steel in warehouses in Moscow and the Moscow region is determined by the costs of warehousing and logistics. The Metallpro Company can also supply 5SP steel directly from the metallurgical plant, which gives our partners an advantage to consistently save money and develop their business in a broad format.
The price for 5SP grade steel is determined personally with each company, monthly needs are individually negotiated and the form of payment is discussed. Warehouse services for custom-made items and logistics to the production site also form the cost of 5SP steel. The Metalpro company maintains an open dialogue personally with each of its clients; each transaction is accompanied by a personal manager from the production stage to the delivery of rolled metal to the customer. Full control at any stage from payment to delivery to the customer’s site gives the latter a complete picture.
Material St5sp Chelyabinsk
Not a single production can operate without steel, be it heavy engineering or the manufacture of household electrical appliances. There are many brands of this product, as well as a large number of dispensing forms. Our company sells St5sp material in large quantities and with a minimal margin. To clarify the properties and characteristics of a particular brand, you can contact the company’s managers.
Like all products, St5sp material is purchased from leading manufacturers. Therefore, we are ready to provide a quality guarantee with full responsibility. The minimum number of intermediaries determines the low cost. Coupled with fast delivery, this enables our business partners to conduct stable and mutually beneficial cooperation.
In addition to tempering, in the form of one or another part (blank), our company carries out metal processing. All events undergo strict control for compliance with GOST and rules. The specialists of our company carry out such work as galvanizing, creating parts according to customer drawings, producing castings, manufacturing various profiles and much more.
Having the latest equipment and vast experience in our arsenal, we can offer product testing for a number of parameters, such as strength characteristics, chemical composition, alloy purity, and so on.
Each buyer is offered a huge range of products in various formats, as well as current services and works. To quickly understand and choose a product that meets your needs, you need to contact the company manager and receive detailed information on all issues of interest.