Mechanical properties of bolts, screws, studs, nuts according to GOST 17594 (ISO 898/1)
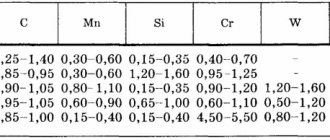
The grades and mechanical properties of carbon and alloy steels used for the manufacture of screws, bolts and studs are given in Table. 1.
Table 1
| Mechanical properties | Strength class | ||||||||||||
| 3.6 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |||
| ≤M16 | >M16 | ||||||||||||
| Tensile strength σ, N/mm2 | Nom. | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1200 | |||
| Name | 330 | 400 | 420 | 500 | 520 | 600 | 800 | 830 | 900 | 1040 | 1220 | ||
| Yield strength σt, N/mm2 | Nom. | 180 | 240 | 320 | 300 | 400 | 360 | 480 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Name | 190 | 240 | 340 | 300 | 420 | 360 | 480 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Conditional yield strength σ0.2, N/mm2 | Nom. | — | — | — | — | — | — | 640 | 640 | 720 | 900 | 1088 | |
| Name | — | — | — | — | — | — | 640 | 660 | 720 | 940 | 1100 | ||
Depending on the mechanical properties, strength classes of materials are established, which are included in the symbols of threaded parts. The strength class is indicated by two numbers. The first number, multiplied by 100, determines the value of the minimum tensile strength σв in MPa, the second number, multiplied by 10, determines the ratio of the yield strength σт to the tensile strength σв in percent; the product of numbers determines the value of the yield strength in MPa; for strength class 3.6, the mechanical properties are approximate.
For example, strength class 5.8 is deciphered as follows:
σв = 5 100 = 500 MPa,
σт/σв=8·10=80% or σт=5·8·10=400 MPa.
Equipment for the production of nuts
The main equipment for production are machines for upsetting and threading.
Most enterprises purchase equipment from Taiwan. Presses must have a closed design for safe cutting of products. It is advisable to choose forming matrices in a round shape, as it provides excellent balancing characteristics. The connecting rod mechanism must be made of alloy steel. An important feature is the oil filtration system (usually magnetic), which reduces costs.
Nut setting machine from Taiwan
For thread cutting, it is recommended to use pneumatic machines with multiple spindles for high speed operation. Such spindles can be programmed for different types of work, for example, for long and short threads or left and right. It is also worth taking care of overload and jam fuses.
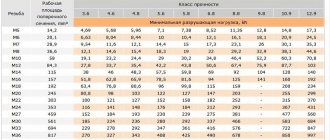
Strength classes of nuts and bolts with metric threads from 1 to 48 mm according to GOST 1759.5
In table 4 shows the recommended combinations of strength classes of mating parts for various thread diameters. In special cases, fasteners can be made from corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, heat-resistant steels, as well as non-ferrous alloys. The strength class of the nuts is indicated by a number which, when multiplied by 100, gives the value of the stress from the test load in MPa.
As a rule, nuts of high strength classes can replace nuts of low strength classes. This replacement is recommended for bolt-nut connections, the stress in which will be higher than the yield strength, or the stress from the test load of the bolt.
Related Pages
- Cylindrical threads
- Tapered threads
- Metric thread
- Runs, undercuts, grooves and chamfers according to GOST 10549
- Thread persistent
- Trapezoidal thread
- Symbols of fasteners according to GOST 1759.0 (ST SEV 4203)
- General Purpose Hex Head Bolts
- General purpose screws
- Captive screws
- Set screws
- Special purpose bolts and screws
- Self-tapping screws for metal and plastics
- Locking the nut against the bolt with additional elements
- Locking the nuts relative to the body
- Locking the nut relative to the bolt due to additional friction, welding and plastic deformation
- Locking bolts. Preventing screws and nuts from being lost
- Locking screws
- Flange connection parts
- Flange connections for pipes and cylinder heads
- Flange connections for metal structure pipes
- Application examples for set screws
- Terminal connections
- Friction screw clamps
- Ties and stops
- Fastening machines to bases
Technological production of bolts
There are two fundamentally different methods for manufacturing this type of fastener:
- Turning is the process of making bolts individually or in small batches from a steel bar on a screw-cutting lathe.
- Cold or hot stamping in a factory followed by thread rolling.
The bolt manufacturing process, regardless of the method, consists of the following steps:
- Preparing a metal rod (wire rod).
- Cutting workpieces to the required length.
- Making a chamfer at the end of the stud.
- Bolt head shaping.
- Thread cutting.
Quality control is carried out at all stages of production. When manufacturing hardware according to an individual drawing, the first manufactured part is checked with the most careful control. If deviations from the technical specifications are detected, the bolt manufacturing process should be reviewed and the cause of the discrepancy should be found.
Manufacturing on a screw-cutting lathe
The stages and methods of processing a workpiece depend on the type of source material (hexagonal or cylindrical rod, characteristics of the metal), as well as on the degree of accuracy of the workpiece. Hot-rolled blanks have less accuracy, which eliminates the possibility of precise centering of the future part on a turret lathe or on a CNC machine.
The technological process of manufacturing a bolt part on a lathe from a cold-drawn hexagonal rod is divided into several stages:
- A workpiece of the required length is cut from a steel bar using a hacksaw.
- The workpiece is fixed in a hexagonal collet so that the head of the part does not mix relative to the central axis of the future bolt.
- Trimming the end of the bar to size, centering it on a screw-cutting lathe.
- Grinding the workpiece to obtain the specified dimensions, chamfering using cutters.
- Cutting threads using a die or thread cutter.
- Grinding the bolt head, chamfering.
- Machining the head with a milling cutter.
If there are special requirements for the hexagon of the head of the part, the technical process of manufacturing the bolt on a lathe becomes more complicated. To prevent displacement of the head axis relative to the cylinder axis, the workpiece is subjected to additional processing.
Manufacturing of bolts by cold stamping
The first stage of the technical process is preparing the metal for the stamping process:
- The surface of the workpiece should be smooth and shiny. Surface cleaning under production conditions is performed mechanically or by calcination.
- Cleaning is carried out to remove scale and grease.
- Lubricating the surface of the workpiece (the surface of the metal is first coated with a lubricating layer; this is mandatory before drawing).
Scale from the surface of metal workpieces is usually removed by etching. To do this, the rod is immersed in a solution of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid of a certain concentration for a period of 5 minutes to half an hour. To eliminate pickling sludge, the workpieces are washed in hot water. If the etching was carried out using a sulfuric acid solution, the residues are washed off and neutralized by liming the rod.
The production of bolts from a metal rod occurs without heating the metal. The deformation of the workpiece during cold stamping is accompanied by cold hardening—an increase in the mechanical strength of the metal. The finished part is obtained by filling a standard die of a given configuration with the workpiece material. Next, the part is upset—the finished metal hardware is removed from the die.
Advantages of the cold stamping method in the production of bolts:
- High level of process productivity.
- Maximum surface cleanliness of parts and dimensional accuracy.
- Manufacturing of bolts with a core diameter of up to 52 mm.
When choosing a cold stamping method, you should take into account the ratio of the size of the head and the diameter of the rod of the part, as well as the ratio of the diameter of the head to its height and indicators of relative and true deformation. If the ratios for the listed quantities are higher than the critical values, the possibility of manufacturing the part by hot stamping should be considered.
Manufacturing of bolts by hot stamping
The essence of hot stamping is the precipitation of metal and its redistribution from the middle to the edges of the die. If stamping occurs in open dies, a metal burr (burr) is formed. Stamping in closed dies is called flashless. The manufacturing process of a bolt part using hot stamping begins with cleaning and cutting the workpieces. Then the blanks go through a full cycle of operations to transform them into durable and reliable fasteners:
- Heating up to 1000 degrees using an inductor.
- Forming the head of a part using an impact press.
- Chamfering on a milling machine.
- Thread cutting on an automatic machine.
To ensure high corrosion resistance of the fasteners, the bolts are galvanized. Coating stages:
- Washing parts in hot water.
- Chemical cleaning of the surface from metal oxides by etching in hydrochloric acid.
- Neutralize remaining acid by repeated rinsing with water.
- Immersion of parts in a zinc solution heated to a temperature of 450 degrees.
In chemical galvanization, a layer of zinc is deposited on the part in an electrolyte solution. The finished bolts are polished and mechanical defects are eliminated.
Hot stamping provides high strength characteristics of finished hardware. This primarily concerns stamping in closed dies. The increased strength is explained by the fact that the fibers, oriented according to the shape of the stamp contour, are not cut off along with the burr (flare-free stamping).
25Х1МФ
A relaxation-resistant material that can withstand the highest temperatures and is manufactured on the basis of state standard 20072-74. Such fasteners can easily work in the range of -40 to +500 degrees. This type of steel has the following characteristics:
- reliable crystal lattice;
- spontaneously reduces pressure and, as a result, mechanical stress decreases;
- long period of use;
- not fragile;
- effective hardening property.
A high level of durability, strength, and anti-corrosion properties appears due to the inclusion of additives such as nickel, chromium, and manganese.
Types of threaded fastening
To make a threaded connection, you need at least two parts, one of which has an external thread and the other has an internal thread. There are several structural types of threads.
Through holes are drilled in the parts to be connected, after which a bolt is inserted inside, which is tightened on the other side with a nut.
In this type of connection, the role of the nut is played by the part itself, in which a hole is first drilled, then a thread is applied, after which another part is fastened using a bolt or screw. If you use self-tapping screws, then it is not necessary to drill a preliminary hole, since the part itself automatically makes a thread when screwed.
Using studs
One end of such a pin is screwed into the component part, and a suitable nut is screwed onto the second in a special way.
Stud with screw-in end
Rules for tightening BVP
Tensioning of high-strength bolts is carried out in two stages:
- Align the holes of the parts for high-strength bolts and fix the position of the structural parts using mounting plugs.
- At the first stage, bolt fasteners are inserted and plugs are removed. Next, using wrenches, the bolt fasteners are tightened only to 50-90%. At the beginning of tensioning, the fastener head must be held from turning. If it is impossible to eliminate the scrolling, the element is replaced.
- At the second stage, fastening is carried out completely, using torque wrenches. The tension of the bolts is carried out after checking the compliance of the geometry of the entire structure with respect to standards and rules, and checking the tightness of the structure's screed.
Excellent technical characteristics of connections made with high-strength bolts ensure the strength of the entire structure. If all instructions are followed, the structure will last for many decades.
Did you manage to solve your problem using the recommendations from the article?
Yes!
46.43%
No. More answers required. I'll ask in the comments now.
38.42%
Partially. There are still questions. I'll write in the comments now.
15.14%
Voted: 799
12Х18 Н10Т
The composition of stainless steel includes chromium in a ratio of 19%, as well as nickel (11%), titanium (0.8%). Thanks to the presence of alloying elements, the metal is passivated and its anti-corrosion properties are strengthened. Due to the sufficient presence of nickel in the composition, it strengthens steel and allows it to withstand the effects of aggressive chemicals. Titanium also reduces the risk of crystalline corrosion forming. The metal becomes more viscous and ductile. Thanks to the high-quality combination of characteristics, it makes it possible to produce metal fasteners for various applications.
Copper fasteners
Copper has even greater conductivity than aluminum, and therefore copper fasteners are also used in connecting power lines and in the production of equipment powered by electricity. The disadvantage of copper is its high cost, which is why it is used less often than cheaper aluminum.
Another disadvantage of copper is that when exposed to moisture, it quickly oxidizes, becoming covered with a dense coating. To prevent copper from oxidizing, other metals are added to its composition - nickel, zinc, etc. The alloys obtained by adding other metals do not oxidize, due to which they can be used in the production of structures whose operation involves constant contact with water.
08Х18Н10
Heat-resistant steel, which contains nickel (up to 11%), chromium (up to 19%), successfully combines the following properties:
- environmentally friendly material;
- resistant to corrosion;
- mechanical resistance;
- does not magnetize;
- withstands high loads.
For most consumers, this brand has gained popularity under the name A2. The steel firmly retains its original characteristics even when exposed to temperatures of + 425 degrees.