Strength class of threaded fasteners
The strength class of nuts is determined by its mechanical properties. To classify the product according to this parameter, GOST 1759 4-67 is used. According to regulatory documentation, the strength class is divided into 11 categories.
Download GOST 1759.4-87 Bolts, screws and studs. Mechanical properties and test methods"
The screw designation used has the following features:
- It is quite easy to decipher strength class 10 or 9. The applied marking rules make it possible to simplify the task of selecting suitable fasteners.
- The strength class of washers or other fastening materials can be determined by reviewing the regulatory documentation. The first digit of the designation is multiplied by 100, resulting in an indicator of tensile and tear strength. Tensile strength determines how strong the fastener used is.
- There is also a second number in the labeling, which can be used when calculating the main indicators. For example, accuracy class 8.8 indicates that the second indicator corresponds to the ratio of yield strength to tensile strength. In this case the figure is 80%.
When making fasteners from stainless steel or other materials, the following points should be considered:
- Yield strength is the value of the load at which a material cannot be restored after deformation. When calculating the load that affects the thread, the point that there must be a threefold safety margin is taken into account.
- The bolt strength chart is used to select the most suitable fastening material.
Breaking loads for bolts
The bolts used in accordance with GOST with a resistance of 800 MPa and more can withstand significant loads. That is why they have become widespread in the construction of bridges or other critical structures.
Kinds
There are a number of standard studs. They are produced in accordance with regulatory documentation - GOST, OST, TU and DIN. If existing options are not enough, engineers design products with unique shapes and properties.
In general, the stud has a smooth cylindrical shape with a solid profile, with two threaded ends. This design is called rigid, and its only drawback is that it is impossible to cut a thread into the passage, since there is no room for the tool to exit. Therefore, the carving is performed with a run, but no more than 2 steps.
Lightweight studs have a stepped profile, and the smooth part is 20..40% smaller than the outer diameter of the thread, or corresponds to the diameter of the recesses. This design ensures uniform strength of the product, makes it possible to slightly reduce the total mass of the fasteners and allows for cutting the threaded ends right through - with dies, cutters, combs. To exclude the occurrence of a zone of dangerous stresses that can destroy the metal, the transition from the threaded part to the rod is made with a conical fillet.
According to existing standards, studs are made with conventional metric threads. If necessary, non-standard fasteners are designed with trapezoidal, inch and triangular threads, as well as an asymmetric profile.
Centering holes are allowed at the ends of the parts. Lead-in chamfers must be removed and sharp edges dulled. Studs that are developed to special order may have an intermediate thrust end or a turnkey surface (hexagon, square, flats).
Nuances of choosing fasteners
The choice of fasteners should be treated with great responsibility. This is due to the fact that their strength indicator may differ significantly. The selection is made taking into account which grade of steel bolts has more suitable performance properties. The key points include the following information:
- Type of material used in manufacturing.
- Accuracy class.
- Applied methods of thermal and chemical treatment.
High-strength bolts can be made from a variety of metals. Let's call the key points:
- In most cases, the following metals are used: 10KP, 20KP, steel 10, steel 20, 20G2R, 40X. These metals meet all established requirements for physical and mechanical properties.
- To improve performance, heat treatment can be carried out. To perform this operation, special electric ovens are used. By creating a special protective environment, the required performance qualities are ensured.
- Carbon steels are the most widely used. This is due to their relatively low cost, as well as high performance.
Galvanized bolts
The diameter of the bolts is also an important selection criterion. Diametrical dimensions can vary over a fairly large range. With an increase in the cross-sectional area, the strength and reliability of the connection increases. The length of the bolts is considered the most important geometric indicator that must be taken into account. The materials used can have very different characteristics. For example, attention is paid to the hardness of the bolts.
Too low a value can cause deformation of the threaded surface when a longitudinal load occurs.
Before choosing the most suitable fastener, you need to take into account the features of connecting parts when using this fastening material:
- The conducted studies indicate that with the correct choice of strength class and tightening torque, the highest quality connection can be ensured. In addition, it provides protection against spontaneous unscrewing and long service life of the product.
- High-quality fasteners can withstand transverse and axial loads. In the manufacture of fasteners, special metals and alloys are used that effectively withstand loads acting in any direction.
- The installation and dismantling process is greatly simplified. It is worth considering that some metals can oxidize, and after some time it will be difficult to dismantle the structure. However, the task can be simplified by using a special substance.
- It is possible to obtain detachable connections. Very often you can encounter a situation where in order to perform various works it is necessary to disassemble the structure. To carry out dismantling work, simple tools are required, and the work usually takes little time to complete.
- The cost of the resulting product is significantly reduced. Welding a joint is expensive, as it requires the use of a special welding machine.
The quality of connections can be significantly improved by using additional various elements. For example, washers and locknuts are used, which significantly improve the quality and reliability of the connection. However, threaded connections also have several significant disadvantages:
- Stress concentration at the root of the thread profile. It is worth considering that the use of special metal can significantly increase the reliability of the threaded surface.
- There is a possibility that the nut will unscrew under strong mechanical stress. Of course, to exclude such a possibility, various fixation methods can be used.
In addition, there are several types of threaded fastening. An example is a bolted and screwed connection. Some connections can be made using studs. The choice of a more suitable fastening element is carried out taking into account what qualities the product should have.
GOST standards
There is a range of standard general purpose hardware. This is a universal fastener that can be used to solve almost any problem. The range of acceptable sizes is from M2 to M48 mm. Outside the specified limits, products are produced according to the drawing.
To order threaded rods to a specific standard, use the designator. It usually includes the size, pitch and tolerance of the thread, as well as the length. The extended format contains information on the selected material, strength class and protective coating code.
Studs for threaded holes are distinguished by the length of the screwed end and the accuracy class.
Class A products (high precision):
- GOST 22033-76 - with a length equal to the thread diameter;
- GOST 22035-76 - with a length equal to 1.25d;
- GOST 22037-76 - with a length equal to 1.6d;
- GOST 22039-76 - with a length equal to 2d;
- GOST 22041-76 - with a length equal to 2.5d.
Class B products (high precision):
- GOST 22032-76 - with a length equal to the thread diameter;
- GOST 22034-76 - with a length equal to 1.25d;
- GOST 22035-76 - with a length equal to 1.6d;
- GOST 22038-76 - with a length equal to 2d;
- GOST 22040-76 - with a length equal to 2.5d.
Studs of accuracy class C according to GOST are not produced. This format is intended for non-standard parts, in single production conditions, for a specific non-critical order or trial mechanism.
The length of the threaded end is selected taking into account the metal into which the fastener will need to be screwed. The stronger the material, the lower the height of contact of the turns is needed to ensure a reliable connection.
Optimal wrap length:
- for steel and high-strength cast iron - 1.25..1.5d;
- for bronze, brass and gray cast iron - 1.5..2d;
- for aluminum and magnesium alloys - 2..2.5d.
Studs intended for installation in through smooth holes are produced in accordance with GOST 22043-76 for accuracy class A and GOST 22042-76 for accuracy class B.
According to the standards, it is possible to produce threads with large and fine pitches, and the pitch size for the nut and screwed ends can be different.
Technical standards of the European Union partially overlap with domestic GOSTs. Some similar pairs can be identified:
- DIN 938 - GOST 22033-76 (L = 1d);
- DIN 939 - GOST 22035-76 (L = 1.25d);
- DIN 949-1 - GOST 22039-76 (L = 2d);
- DIN 949-2 - GOST 22041-76 (L = 2.5d).
And also for special conditions:
- DIN 2509 - double-sided fasteners for flange connections. There is an additional protruding step on a turnkey basis (the flats are removed along the cylinder).
- DIN 976-1 and DIN 976-2 - studs with a fully threaded surface, without dividing into ends and a smooth intermediate part. They can also be used as chassis, for a simple “screw-nut” transmission.
- DIN 940 - with a thread length of 2.5d and a different tolerance range for connections with and without interference.
- DIN 525 - long studs with one end threaded for welding. Basically, such fasteners are used for construction purposes, less often - as a centering element when assembling furniture.
- DIN 835 - studs for screwing into parts made of aluminum alloys. The threaded part is made with a length of about 2d.
When assembling a pipeline or shut-off and control valves, special hardware is placed on the flanges. GOST 9066-75 establishes requirements for products that will operate in the temperature range from 0 to +650˚С. Additionally, OST 26-2040-96 can be mentioned. This document describes fasteners for conditions from −70 to +600˚С.
Studs intended for flange connections with a lens seal are produced in accordance with GOST 10494-80 and are used in the chemical and oil refining industries. The operating temperature range for these products is from −50 to +510˚С, with pressure inside the pipeline up to 100 MPa.
Threaded connections for nuclear power plants are subject to the conditions of GOST R 54786-2011. A special feature of such studs is increased reliability requirements. On average, the strength level for nuclear power fasteners is 1.7..2.0 times higher than for general purpose products.
For assembly and installation of pipeline systems, U-shaped studs with two or one threaded end are used. Otherwise called “bracket bolt” or clamps, they are a bent metal rod. For such products, GOST 24137-80, GOST 24139-80 and DIN 3570 are provided.
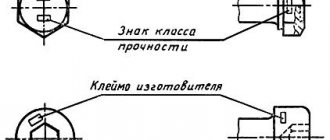
Bolt markings
Marking of bolts can be carried out using developed ISO standards. The labeling system involves the use of special tables. In addition, all standards used in Russia were developed several decades ago. The strength class is considered the most important indicator, which is taken into account in the production of almost all fasteners. When considering the designation of bolts, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Mandatory marking is carried out in the manufacture of screws whose diameter is more than 6 mm. Bolt strength and other indicators are marked on products of smaller diameter only at the request of the manufacturer.
- The range of fasteners used with cross-shaped or straight slots does not provide for marking. Products with hexagonal slots must be marked.
- Non-stamped versions that are manufactured by turning and cutting are not subject to mandatory marking. Marking is applied only if required by the customer. However, decryption can be carried out in different ways; standards are not applied in all cases.
When considering the parts of the bolt on which markings are applied, attention should be paid to the end and side surfaces. If a side surface is used, then the designations are applied with recessed signs.
About the strength of washers
The properties of these elements are not determined by tensile strength and fluidity, since their main task is to uniformly distribute the load on the supporting surface. An analogue of strength is their hardness - the value can range from 35 to 45 HRC. The purpose of the elements is determined by the material of manufacture and the protective coating. Uncoated elements are used in places where there is no exposure to moisture; zinc or oxidized coating makes it possible to use fasteners outdoors without the threat of corrosion.
Bolt classification
There are many different types of bolts. The choice is made depending on what performance qualities the product being created should have. Bolts can be classified according to several criteria:
- Strength class. If we consider the most common tables, the strength class becomes the main criterion. It determines the possibility of using the product in certain cases. Special bolts can have high strength and are used in the construction of bridges or other critical structures. The strength class of fasteners is indicated by almost all manufacturers. This is due to the fact that the strength class determines the possibility of using products in certain conditions.
- Size classification is important. This is because as the cross-sectional area increases, the torsional resistance increases. However, larger fasteners require larger diameter holes. As for the length of the rod, it is selected depending on the thickness of the elements to be connected and the required length of the threaded connection.
- There are different types of heads. An example is a product with a hexagonal head or in the form of an octagon. It is worth considering that this indicator only determines which tool is most suitable for the job.
Types of bolts
Other indicators may be used to classify fasteners. For example, in some cases, the most attention is paid to surface hardness. However, the choice is often made taking into account the accuracy class. That is why the classification is carried out according to the accuracy class, which is indicated in regulatory documentation and during design.
Protective coatings
To prevent the development of corrosion and give products a “marketable” appearance, special protective coatings are applied to the surface. Typically these are metal-based layers or thin films produced by a chemical reaction.
The following types of coatings are used for studs:
- zinc;
- zinc followed by chromating;
- cadmium;
- cadmium followed by chromating;
- nickel;
- tin;
- copper;
- silver;
- multilayer (copper-nickel, copper-nickel-chrome);
- oxide;
- phosphate
In addition to the main protective function - protection against oxidation and corrosion - some coatings have their own unique properties:
- Tin can be used in the food industry, in direct contact with food.
- The copper layer successfully protects steel from diffusion processes. With its help, they extend the service life of fasteners in machines for various chemical processing.
- Cadmium coating is more resistant when working in acidic and alkaline environments than others.
The thickness of the deposited layer is usually from 9 to 20 microns. This is enough to eliminate the possibility of damage to the base metal under the shell. However, if the stud is subjected to regular assembly and disassembly, the coating may deteriorate due to friction.
High Strength Bolts
In most cases, conventional connecting elements are used, in the manufacture of which carbon steel is used. However, if necessary, you can purchase high-strength bolts that can be used to create high-strength connections. Marking of high-strength bolts is carried out according to general standards. The production of high-strength bolts is carried out taking into account the information below:
- In manufacturing, special alloys are used, which are characterized by high strength and hardness. They are more expensive than carbon steel, but still the use of the resulting products is advisable in a wide variety of cases.
- Heat treatment is carried out to increase strength and hardness. It involves changing the chemical composition of the metal and the structure of the resulting material.
High Strength Bolts
High-strength bolts may require their own regulatory documentation. In addition, the classification is carried out as follows:
- Fasteners with the letter “U” in the marking are used for operation at temperatures below -40 degrees Celsius. However, the letter in question is not indicated in all cases of marking.
- Offers with HL design can be operated in more severe operating conditions, for example, at temperatures from -40 to -65 degrees Celsius. When marking in this case, the accuracy class is indicated.
High-strength bolts and nuts are quite common today. This is due to high performance qualities, which allow you to expand the scope of the product.
Materials
The main guidelines in the selection of materials for manufacturing are the magnitude of the load and operating conditions.
Conventional threaded rods are produced from steel grades with a relatively low carbon content: 10, 10kp, 20, 20kp. Due to their low strength, they are easy to process and do not cause additional difficulties on thread rolling machines.
Some sources recommend cutting non-critical fasteners from St3 construction steel. But this material does not hold the thread profile well, and parts made from it can be practically disposable. In the worst case, the thread will be crushed even when the stud is first tightened.
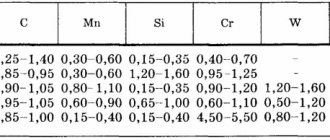
For high-strength hardware, medium-carbon and alloyed grades are prescribed that respond well to hardening: 35, 45, 40G, 35X, 38ХА, 45G, 40G2, 40X, 40HFA. Heat treatment can increase the temporary tensile strength by 45..60%. Operation of such steels is possible at temperatures no higher than 250˚C; with further heating, the drop in strength becomes critical and at approximately 400˚C it is possible to re-temper to the state of raw metal.
Loaded flange fasteners for vessels and apparatus operating under pressure are made of high-alloy heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels: 15Kh11MF, 20Kh12VNMF, 18Kh11MNFB, 18Kh12VMBFR, 31Kh19N9MVBT, 25Kh1MF, 25Kh2M1F, 20Kh1M1F1TR.
For studs used in critical mechanisms and heavy metal structures (for example, in cranes), grades containing chromium, nickel, molybdenum and vanadium should be used: 35ХМ, 30ХМА, 30Х3МФ, 30Х2НММА, 20Х2НМТРБ, 40Х2Н2МА and 38ХН3ММА. These materials can be hardened, nitrided and nitrocarburized.
If the operation of fasteners involves heating above 350˚C and exposure to relatively aggressive environments (water, steam, acids, alkalis), then corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels and alloys are used. These include brands 12Х18Н9, 12Х18Н10Т, 08Х18Н10Т, 10Х17Н13М2Т, 06ХН28МДТ, 12Х13, 20Х13, 08Х21Н6М2Т, 14Х17Н2, 10Х11Н23Т3МР, 13Х11Н2В2МФ, 07 Х16Н6. The main alloying elements are chromium and nickel. They are what give steel the properties to resist corrosion and high temperatures. Molybdenum, vanadium and boron stabilize these characteristics and increase the red resistance and elasticity of the material. In exceptional cases, chromium-nickel alloys are used - KhN35VT, KhN77TYUR, but they are very difficult to process.
For special working conditions, studs made of non-ferrous metals and alloys are used. This usually applies to cases where there are no serious loads, but resistance to oxidation in air and water, as well as increased electrical conductivity, are required.
Aluminum-based alloys are used for electrical products and where it is necessary to radically reduce the overall weight of the structure. These are brands AMg5P, AMg5, D1, D1P, D16, D16P.
Some devices are assembled using fasteners made from industrial copper alloys. This is bronze grade BrAMts9-2, brass L63 and LS59-1. Studs based on them are used to tighten the ends of flexible copper busbars in power and distribution equipment.
Bolt accuracy
Another important indicator is the accuracy class of bolts. This is due to the fact that during manufacturing a variety of thread cutting and cylindrical surface processing methods can be used. Considering the accuracy indicator, we note the following points:
- With increased precision, the resulting threaded connection lasts much longer.
- The proposal has a more precise geometric shape.
- There is no space between the fastener and the hole created that could cause the connection to become loose.
As accuracy increases, the cost of fasteners also increases.
That is why fastening materials used in the manufacture of non-critical mechanisms have an average accuracy rating. The use of modern equipment for turning allows us to obtain fasteners with a high level of accuracy. In conclusion, we note that various companies are engaged in the production of the materials in question. In many ways, the quality of the resulting product depends on the equipment used and production technology. Some manufacturers may reduce the quality of fasteners in order to reduce their cost.
How to properly tighten and loosen a bolt
Most often, when tightening bolted connections on various structures in the household, ordinary wrenches are used - socket, open-end and box-end wrenches. However, in this case, it is difficult to accurately determine the tightening torque, so in industrial production and repair shops, experienced mechanics use special torque wrenches or pneumatic impact wrenches, the main advantage of which is the ability to set the required tightening level, depending on the type of mechanism.
To unscrew the bolt, the same keys are used, however, in old designs, most often the bolts “stick” strongly to the nut due to corrosion. For safe unscrewing, several simple methods are used:
- use of aerosol-type penetrating lubricant WD-40;
- lightly tapping the rusty bolt with a hammer to destroy the rust in the profile of the threaded connection;
- Turn the nut slightly in the direction of tightening (just a few degrees).
Threaded connections are used in many structures and mechanisms, since in practice they have proven their high reliability and efficiency. The correct type of bolt, tightened to the required tightening torque, is able to cope with the load throughout the entire life of the mechanism.
Source: met-all.org
Marking of stainless steel elements
Separately, it should be said about the fasteners made of stainless steel. It has a special marking. For example, A2-70, where A-2 is the steel grade, 70 is the tensile strength. To calculate the tensile strength, you need to multiply the indicated value by 10: we get 700 MPa (which corresponds to the strength class of carbon steel fasteners 5.6).
We hope that this article will be useful when choosing fasteners for a specific type of work. You will be able to determine if a metric fastener is suitable for the load and type of construction. You can order bolts, screws, studs, nuts and washers in our online store. It’s easy to select suitable elements - the product cards provide detailed information about each of them.
Source: www.vseinstrumenti.ru