During operation, the profile of abrasive wheels changes, and their granular surface becomes clogged with processing waste, which ultimately leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of this device. In order to return sharpening and grinding wheels to their original characteristics, a tool such as a roller cutter is used to dress abrasive wheels.
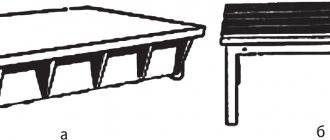
Sprocket cutters: blunt-toothed on the left, sharp-toothed on the right
Star rollers, simple in their design, are divided into two types:
- with sharp teeth;
- blunt-toothed.
They differ from each other not only in the shape of the teeth, but also in thickness and scope of application.
Dimensions of cutters for dressing abrasive wheels
Design features and areas of application of diamond grinding wheels
Grinding wheels are consumable diamond tools for manual and automatic grinding machines.
Photo #1: Diamond grinding wheels.
Let's talk about the key design features of the tools. Let's start with the fact that each circle consists of a body and a diamond layer applied to it. In addition to diamonds, it contains a binder with or without filler.
The markings of diamond wheels include two numbers and one letter. These symbols determine the main characteristics of the instruments.
Image #1: Diamond grinding wheel markings
Let's start with the body shape.
Image No. 2: Shapes of diamond wheel bodies
The letter in the marking indicates the cross-sectional shape of the diamond layer.
Image No. 3: cross-sectional shapes of diamond layers
The last number in the marking determines where exactly the diamond-bearing layer is located on the circle.
Image No. 4: options for the location of diamond-bearing layers on diamond wheels
The most important characteristics of diamond wheels also include the type of bond. It can be organic, metallic and galvanic.
Organic bundle
It is a mixture consisting of an organic binder, diamonds and filler.
Image #5: Organic Bundle
The organic binder has low hardness, heat resistance and thermal conductivity. The use of such a tool is characterized by high productivity and a small amount of time spent on processing workpieces.
Let us list the main areas of application of diamond wheels with an organic binder.
- Grinding, sharpening and finishing of parts and products made of hard alloys and superhard materials.
- Processing of high-precision measuring and medical instruments.
- Manufacturing of products from refractory materials.
- Polishing and cutting of precious stones.
Metal bundle
Its composition looks like this.
Image #6: metal bundle
The metal bond is characterized by high hardness, thermal conductivity and heat resistance. Wheels with such diamond-bearing layers are used for:
- performing rough operations that require the removal of large allowances;
- profile grinding;
- sharpening of carbide parts and products;
- processing of workpieces made of special ceramics and other difficult-to-process materials.
Galvanic bond
It is coated with the addition of diamonds on supporting metal bases. In such circles, the grains protrude far beyond the surface of the binder. This makes chip removal much easier.
Image No. 7: galvanic bond
Diamond wheels with a galvanic bond are distinguished by high cutting ability, good thermal conductivity, low cost and the ability to perform any geometry. Let us list the areas of application of tools in this category.
- Processing of parts and products made of silicon, germanium and other semiconductor materials.
- Grinding and cutting workpieces made of sital and various types of technical glass.
- Textured processing of natural and artificial stone.
- Manufacturing of laps and diamond heads of various shapes.
- Production of hand tools for finishing dies made of alloy steels and hard alloys.
Other characteristics of diamond grinding wheels
Let's list the remaining parameters.
- Case size. The choice of tool depends on the dimensions of the workpiece and the operation to be performed.
- Grain. Determines the cleanliness of the surface after treatment. The finer the grain of the wheels, the smoother the surfaces will be. The main disadvantage of fine grain size is that tools often become clogged during work. It is also possible to burn the surface of the workpiece.
- Diamond concentration. This parameter directly depends on the grain size. The higher the grain size, the more diamonds there are in 1 mm3 of the abrasive layer. High concentration wheels are used to treat small areas. Low concentration tools are designed for processing large surfaces.
- Accuracy classes. There are 3 of them - B, A and AA. The latter are the best in quality. With the help of such diamond wheels, high-precision operations are performed.
- Imbalance classes (1–4). Depends on the quality of the abrasive mass.
Ventkam.ru
During the operation of the grinding wheel, the abrasive grains wear out and lose their cutting ability, and the wheel becomes clogged with processing products. To restore the cutting properties and geometric shape, the wheel is periodically polished. The highest quality straightening is done with diamond tools. Coarser dressing is carried out with cutters equipped with monolithic carbide disks, metal disks and sprockets made of wear-resistant steels or dressing wheels made of silicon carbide, thermocorundum, etc. Dressing is the process of influencing the working surface of the grinding wheel in order to give it the required geometric shape, eliminating damage to the working surface, as well as ensuring the removal of a bunch of necessary parameters of the PKK. Editing can be done directly at the workplace or separately. To effectively manage the parameters of the RPK, the methods of influence must provide the following: — — the ability to influence the ligament directly; — — high selectivity of influences; — — discreteness of impacts in time and space; — — the possibility of combining control actions and processing of a part in time; Not only the accuracy and roughness of the machined surface of the part, processing productivity, but also the consumption of grinding wheels, the wear resistance of the dressing tool and the cost of the grinding operation depend on the correct choice of dressing tools and modes. Widely used grinding wheels with a grain size of 25-40 and a hardness of SM2-ST2 are mainly consumed not in the grinding process, where their wear is extremely small, but in the dressing process. Dressing consumes from 45 to 80% of the useful volume of abrasive wheels during round, flat and internal grinding. The time spent on editing can reach 40% of the piece processing time or more. Depending on the requirements for the accuracy and roughness of the surface being processed, diamond and non-diamond dressing of wheels is used. Dressing is carried out by grinding with a diamond tool, rolling with abrasive, carbide and metal discs, grinding with silicon carbide wheels and diamond-metal rollers, tangential turning of the profile surface of a circle with a diamond tool, rolling with steel profile rollers. 1. Dressing by grinding Dressing by grinding is the turning (destruction) of a brittle abrasive material and the grinding wheel bond with a high-hardness diamond dressing tool. Dressing is carried out either with separate relatively large diamond grains, hammered into mandrels (OST 2-9-70 “Diamonds in Mandrels” and GOST 17504-72 “Diamond Needles”), or with diamond-metallic pencils with a diameter of 8-10 mm. The most widely used are diamond-metal pencils, in which diamond crystals are placed in a certain order, firmly connected by a special alloy. This alloy has a coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of diamond, so when the temperature of a diamond-metal pencil changes during the editing process, diamonds do not experience additional thermal deformation. Diamond-metallic pencils are produced in four types, depending on the location and characteristics of the diamond crystals in the working part: C - with diamonds arranged in a chain along the axis of the pencil; C - with diamonds arranged in layers, non-overlapping and overlapping; N - with non-oriented arrangement of diamonds. Each type of pencil is divided into brands that differ in the weight and number of diamonds, as well as the size of the insert and frame. Type C pencils are made from high-quality diamond crystals weighing from 0.03 to 0.5 carats. They are most widely used for dressing wheels for cylindrical, centerless internal and shaped grinding. Type C pencils are produced in two brands: multi-grained with up to 10 relatively small diamond grains in a layer and small-grained with two to five diamond grains weighing 0.1-0.2 carats. These pencils have increased wear resistance; They are used for dressing abrasive wheels during fine grinding in an automatic cycle. Type H pencils are made from diamonds of various qualities, including crushed and chipped ones, and are used for dressing fine-grained grinding wheels in cylindrical and centerless grinding operations, as well as for dressing single-thread thread grinding, disc and flat wheels for gear grinding and spline grinding. During the editing process, diamond-metallic pencils wear out, pads form on their working surfaces, and therefore pencils are usually installed so that their axis is inclined at an angle of 10-15° in the direction of rotation of the circle and turned towards the direction of feed movement. This allows you to periodically rotate the dressing tool around its axis, thereby introducing undull diamond edges into work, which helps improve the working conditions of the dressing tool and reduce its wear. This installation of diamond tools also protects the diamond from overloads and destruction of crystals and eliminates vibrations in the machine-wheel-diamond system. For dressing large wheels, as well as for profile grinding, large diamonds are used in mandrels, which are a steel holder in which a rough diamond with a sharp tip is fixed. Diamonds with natural facets, set in settings, have an advantage over diamond-metallic pencils in that they are made from more. high-quality diamonds, and, therefore, their wear resistance is much higher. Diamond settings are made in cylindrical, stepped, conical and threaded versions. To secure diamonds in settings, mechanical clamping, soldering, and embossing are used. The installation of the diamond in the frame must be carried out in such a way that the planes of the chips of the crystals do not coincide with the direction of the forces acting on the diamond during editing; after fastening, the diamond must protrude from the frame by no more than 1/4 of its length. The industry produces diamond needles especially for dressing single-thread, slotted grinding wheels in accordance with GOST 17564-72
READ ALSO: Fire safety of the 21st century
Natural diamonds in the form of octahedral, sawn and crushed crystals are used to make needles. The working part of the needles is cut in the shape of a tetrahedral pyramid without a bridge at the top visible under tenfold magnification. The diamond is secured in the holder by soldering with PSr5OKd silver solder, or another solder or method that provides the necessary strength while excluding graphitization of the diamond. Holders for needles are made of steel grades 20, 25, 30, 35, 40. The cost of cut diamond tools is higher than the cost of diamond in frames, since the diamond crystal is ground. However, the high productivity of wheel dressing, as well as increased grinding accuracy, in many cases justify the cost of manufacturing a dressing tool. Dressing wheels using the grinding method allows you to obtain high accuracy of the working surface of the wheel, which, by changing the value of the longitudinal feed of the diamond tool, can provide different roughness of the workpiece. In the process of dressing wheels by the grinding method, forces arise that do not exceed 3-5 kgf and contribute to less destruction of the abrasive grains of the wheel during dressing and their wear during grinding 2. Dressing wheels by the rolling method Dressing wheels by the rolling method allows you to obtain high accuracy of the working surface of the wheel, which due to changes in the longitudinal feed of a diamond tool can provide different roughness of the workpiece. In the process of dressing wheels using the grinding method, forces arise that do not exceed 3-5 kgf and contribute to less destruction of the abrasive grains of the wheel during dressing and their wear during grinding. Dressing by the rolling method is the process of crushing and chipping abrasive grains on the working surface of the wheel using a dressing tool. receiving rotation due to frictional forces from the grinding wheel. As dressing tools in the rolling method, silicon carbide wheels KCh80VT-ChTK, steel disks, sprockets and cutters, solid carbide rollers, coarse-grained carbide rollers with a metal bond are used. Under the action of the cutting edge of the dressing tool, moving along the generatrix of the grinding wheel at a certain speed, the surface layer of the wheel bond is destroyed, the protruding grains are chipped, and the grains located deeper in the bond are split into pieces. Slippage between the grinding wheel and the dressing tool leads to smoothing of the abrasive grains on the straightened surface of the wheel. When dressing by rolling, two orientations of the dressing tool relative to the grinding wheel are possible: the rotation axes of the grinding and dressing tools are either in the same plane (j = 0) or in intersecting planes located at an angle (j ¹ 0). As the angle j increases in the dressing zone, the destructive forces increase, the action of which intensifies the process of restoring the working surface of the circle, and the wear of the dressing tool increases. Dressing of wheels by rolling in with non-diamond dressing tools is most often used as preliminary dressing, when it is necessary to remove a large layer of abrasive from an insufficiently well-balanced wheel and when there is unevenness in the removed layer of abrasive. For this type of straightening, steel disks, sprockets and cutters (GOST 4803-67) are used, installed in special straightening devices. You should pay attention to the dressing of grinding wheels with discs made in versions a and b from steel grades 10, 20 and 30, case-hardened to a depth of 0.3-0.5 mm and hardened to a hardness of HRC 55-60. The presence of a soft, non-hardened layer of material on these discs helps to intensify the straightening process. Ruler disks, the dimensions of which are given in table. 3, are used for dressing wheels used in fine and semi-finish grinding, when it is necessary to obtain a processing roughness within the range of Ra = 0.63-2.50 microns. In table Table 4 shows the recommended modes for dressing grinding wheels using the rolling method. To intensify the dressing process with silicon carbide wheels, the axis of the dressing tool should be set at an angle j = 8-10° relative to the axis of the grinding wheel. In other cases, the tools carry out editing of circles with parallel axes. Usually, after working moves, two to four nursing moves are made. 3. Dressing by grinding Dressing by grinding is the process of cutting and crushing abrasive grains with a rotating dressing tool, which receives forced rotation from an independent drive or from the drive of the grinding head of the machine. Diamond rollers on a carbide bond (GOST 16014-70) and wheels made of high-hardness silicon carbide (GOST 6565-67) are used as dressing tools. With the method under consideration, due to the difference in the rotation speeds of the grinding wheel and the dressing tool, chipping of particles of abrasive grains occurs, and sometimes chipping of entire grains. For this type of dressing, diamond rollers are increasingly used, receiving forced rotation, coinciding in the direction of the rotation of the grinding wheel or directed against it. According to GOST 6565-67, wheels made of silicon carbide on a PP ceramic bond are used for dressing wheels by grinding. Diamond rollers for dressing abrasive wheels in accordance with GOST 16014-70 are made from natural diamonds with their uniform arrangement on the working surface of the roller. The roller consists of a housing 1, made of steel grade 35 or 45, and a diamond-bearing layer 2, firmly connected to the housing. The diamond-bearing layer contains diamonds cemented with a special carbide binder using powder metallurgy. Diamond rollers are increasingly being used, making it possible to edit wheels on several working surfaces: straight, curved and their combinations. Such dressing can significantly increase grinding productivity due to the concentrated simultaneous processing of several surfaces of the part, as well as by reducing the time spent on wheel dressing, which is carried out either with a roller of a complex shaped profile, or with a set of rollers using the plunge method or the longitudinal feed method. Diamond dressing rollers with complex profiles are used, in particular, in automobile factories for automatic dressing of abrasive wheels. You should strive to use dressing devices with an independent drive, installed outside the working area of the machine - behind the tailstock, on the grinding headstock or behind it. This allows the wheel to be adjusted during installation and removal of the part, which minimizes the amount of time spent on guiding. To facilitate manufacturing, the rollers are made of two parts; They are installed at the required axial size of the part using a spacer sleeve. The presence of a roller cut along a plane inclined to its axis eliminates the appearance of grooves and other defects on the grinding wheel when dressing. Dressing by grinding is carried out on cylindrical and centerless grinding machines, as well as on special machines (for example, for grinding crankshaft journals and camshaft cams). The use of diamond rollers and special dressing devices makes it possible to reduce the time for dressing, and in some cases completely eliminate it and, thus, increase labor productivity during processing by 20-30%. When dressing wheels with diamond rollers using the grinding method, less forces are generated than when dressing with silicon carbide wheels. Diamond rollers contribute to obtaining high accuracy of the straightened surface of grinding wheels and their rational consumption during grinding. 4. Dressing by tangential turning Dressing by tangential turning is a process similar to turning. Dressing is carried out by cutting (partly chipping and chipping) abrasive grains with a diamond stone. The operation is performed on surface grinding machines over the entire working surface of the circle with longitudinal movement of the table. A block with a profile corresponding to the profile of the part to be ground is secured on the machine table behind the part. With each feed to depth, the grinding wheel is brought into contact with the shaped surface of the block. As a result of interaction with the bar, the profile of the circle is constantly updated and thereby ensures high quality of the processed surfaces of the parts, dimensional accuracy and stability of the processed profile. When using profiled diamond bars on grinding and special machines (for example, on machines for grinding the fir-tree lock of turbine blades), the productivity of operations is significantly increased by eliminating the time for dressing. 5. Dressing by rolling method Dressing by rolling method of the working surface of a wheel is a process of crushing abrasive grains and binders with relatively slow rotation of a metal knurling roller and wheel. The method is used exclusively for dressing profile grinding wheels. The ruling tool is a steel shaped roller having the profile of the workpiece. Profiling is carried out at a rolling speed of 1-1.5 m/s with a transverse feed of 0.05-0.06 mm/min. Depending on the design features of the machine, either the grinding wheel or the roller receives rotation during knurling. As a result of the mutual rotation of the roller with the wheel and the significant pressure created in the contact zone by the transverse feed, the abrasive grains and binder on the working surface of the wheel are destroyed. Dressing continues until the wheel takes the shape of the profile of the given part. The wear of the roller due to insignificant relative sliding during straightening is relatively small, therefore, straightening can be done multiple times with the same roller. It is preferable to carry out rolling with a roller, which is driven into rotation from a separate electric motor or from the spindle of the product headstock, since this ensures greater accuracy in profiling the circle with less wear on the roller. Profiling wheels with knurling rollers is characterized by the simplicity of the design of the devices, the possibility of straightening along several surfaces of the wheel profile, and the high cutting ability of the straightened surfaces. For the manufacture of rollers, steel grades 45, 40X are used, hardened to a hardness of HRC 30-32, as well as U8A, U10A, KhG, P18, hardened to a hardness of HRC 60-64. Profiling with rollers made of steel 45, 40X is more effective for preliminary grinding operations, since the process of rolling the wheel is more intensive, and the production of rollers is simpler. Although rollers hardened to a hardness of HRC 60-64 are more wear-resistant and provide increased precision in wheel profiling, special profile grinding machines are required for their production. In Fig. Figure 5 shows the design of a knurling roller with grooves of uneven pitch parallel to the axis. The presence of grooves intensifies the process of wheel profiling, and the uneven step of their location eliminates the appearance of groove marks on the wheel, as well as the wheel beating after straightening. The diameter of the roller is selected depending on the diameter of the circle D1=(0.2...0.25)D, and its width H must correspond to the length of the profile.
READ ALSO: The main advantages of real estate outside the city
6. Dressing grinding wheels with free abrasive The impact on the bond when dressing a wheel with free abrasive is carried out as follows: A suspension consisting of abrasive grains and clay is fed through the hole in the lap. When the grinding wheel rotates, an abrasive gets into the gap between the wheel and the lap, which is carried away by the surface of the wheel and keeps the lap at a distance. In the process of rolling the free abrasive grain over the bond, it is removed, while “supports” are formed behind the grain. The advantage of this method is its high productivity. Disadvantages include poor selectivity of the dressing process and the possibility of deterioration in the quality of the surface of the workpiece when abrasive grains get on it. The method is used for periodic impacts on the RPC. www.almazmarket.ru
Why do you need to edit diamond grinding wheels?
No matter how high-quality diamond grinding wheels are, they sooner or later deteriorate and wear out during use. Happens:
- smoothing in some areas;
- breaks;
- abrasion;
- salting
There are much fewer problems when using soft grinding wheels. They have the property of self-sharpening. As grains fall out, new layers are exposed. Solid instruments do not have this property. To restore the characteristics of such diamond grinding wheels, editing is needed. After it, the instruments get a new life. The cutting properties and geometric shape of products are restored.
Methods for dressing diamond wheels
There are three ways to dress diamond wheels. Let's talk about the technologies used.
Grinding method
Involves the use of high-strength and hard tools. They are used to grind circles in order to destroy the bond and subsequently sharpen the diamonds.
The following devices are used for dressing diamond grinding wheels.
- Diamond needles.
- Rods with large diamond stones at the ends.
- CBN cutters.
- Diamond pencils, etc.
Photo No. 2: devices for dressing diamond grinding wheels using the grinding method
The technology involves simple treatment of the surfaces of a worn circle rotating at a speed of up to 35 m/s. Everything happens either manually or using special tools.
Grinding method
The following categories of tools are suitable for this.
- Diamond rollers.
- Grinding wheels (diamond, CBN).
- Disks made of tungsten carbide alloys.
Dressing diamond wheels using grinding technology has the following features.
- The worn tool is set to a working rotation speed.
- The rotation speed of the straightening device is low. The indicator does not exceed 25 m/min.
- Editing is performed using special equipment.
- The axis of the grinding apparatus can be located either perpendicular or parallel to the axis of rotation of the diamond wheel.
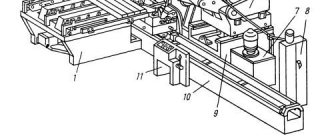
Photo No. 3: machine for dressing diamond grinding wheels
Run-in method
Involves the use of special round tools. These include:
- silicon carbide circles;
- steel discs with cemented and hardened surfaces;
- carbide rollers;
- star balls.
Instruments of the latter category have become the most widely used.
The principle of the technology is that worn discs, upon contact with the device, begin to smoothly slide over the surface of the tool (roll it in). As a result:
- the diamond grains are released;
- a new layer of the working surface is exposed;
- the circle is leveled.
We will tell you in detail about the use of cutters for dressing diamond grinding wheels.
Editing by rolling method
Rolling is the process of leveling the surface of a wheel by crushing abrasive granules using a knurling disk or roller. This method can be used to edit only profile disks. The following are used as sharpening tools:
- shaped roller;
- metal knurling wheel.
The rotation speed of the tool when processing a wheel does not exceed 1.5 m/s. During the grinding process, either the roller itself or the wheel being processed undergoes rotation. The mutual rotation of the tools with increasing pressure in the area of their contact ensures the destruction of the worn abrasive layer. Editing is carried out until the disk acquires a geometric shape identical to the shape of the part profile.
Important points:
- The rotation of the roller must be ensured by the operation of an electric motor;
- To effectively crush abrasive grains on a wheel, it is advisable to use rollers made of steel grade 40 with a hardening hardness of up to HRC 60-64;
- The roller rotation speed should be within 1-1.5 m/s.
The diameter of the roller should be selected taking into account the diameter of the wheel being processed. Its width must correspond to the length of the profile. Only in this case, when rolling, will the grinding wheel acquire the correct geometric shape.
Dressing diamond grinding wheels with cutters: technology and features
Let's start with the fact that the standard cutters most often used for dressing diamond wheels can have blunt and sharp teeth.
Photo No. 4: sharp-toothed (right) and blunt-toothed (left) cutters
Devices of the first type are used for dressing diamond grinding wheels with grains of minimal size. This is due to the fact that a sharp-toothed cutter will only spoil the circle with grains of large and medium fractions. Blunt-toothed devices are suitable for straightening such products. As you might have already guessed, you can’t edit circles with fine grains using blunt-toothed cutters!
Note! To dress diamond grinding wheels, not just one type of cutter is used, but sets of devices. They are fixed in special holders.
Photo No. 5: cutters fixed in a holder
Technology for dressing diamond grinding wheels with cutters
The process of dressing diamond grinding wheels with cutters looks like this.
- A set of devices is assembled into a single block.
- It is secured in a holder.
- The resulting device is installed on a special axis equipped with a handle for the operator.
- The tool is brought into contact with a rotating worn diamond blade.
This grinding wheel dressing technology has its advantages and disadvantages. Let's start with the positives.
- Editing goes very quickly.
- Cutters for dressing diamond wheels are cheap.
- High efficiency of editing is ensured. The working surfaces of the circles are not smoothed.
- The technology is easy to use.
The main disadvantage of the method is the release of a large amount of dust, but the problem is easily solved with the help of an industrial vacuum cleaner.
Rules and features of dressing diamond grinding wheels with cutters
- Wear safety glasses and use a dust mask.
- Do not use cutters that are not the right size for straightening.
- Work the circles above their centers. This will prevent the teeth from excessively deepening into the abrasive surfaces.
- Move the holder with the cutters as smoothly as possible.
- When dressing, try to maintain a steady pressure on the diamond wheel.
- When sparks appear, increase the pressure.
Dressing with free abrasive
In this case, the dressing of wheels is carried out with free rotation of the tool during its contact with the rotating workpiece. It is also possible that discs may be processed when the sharpening tool is rotated under the influence of an electric drive. Dressing with free abrasive is implemented as follows:
- Through a special hole in the lap, a viscous mixture of clay and abrasive particles is supplied to the grinding area;
- During rotation of the wheel being processed, an abrasive suspension enters the gap between the lap and the workpiece, which is subsequently entrained by the outer surface of the wheel;
- The tool axis is positioned to the axis of the wheel being processed at an angle of up to 6° vertically and 15° horizontally during internal grinding;
- When the workpiece rotates, the free abrasive removes dull grains from the surface of the wheel.