Acetylene.MAPP/MAF.Acetylene cylinders. Explosion hazard.
Acetylene cylinder Causes of cylinder explosions.
Acetylene cylinders (GOST 5948-51) are made from seamless pipes with a wall thickness of 7-8 mm. The weight of the shell of a 40 liter cylinder is on average 65 kg, and the weight of a charged cylinder is 82-85/st.
VNII Autogen has developed a design for a lightweight welded acetylene cylinder BAS-1-58. It is made of low-alloy steel 4 mm thick, with a water capacity of 60 liters. The weight of the equipped cylinder is 70-71 kg.
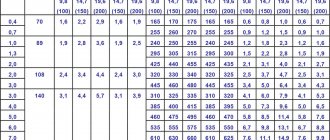
The acetylene pressure in the cylinder depending on the temperature is given below.
Temperature in ° C -10 -5 0 +5 +10 ZSH| +20 +25 +40
Pressure in atm. 7 8 9 10.5 12 14 16 18 25
During operation, cylinders are tested every five years with nitrogen at a pressure of 30 ati.
Acetylene cylinders are painted white and have the inscription “Acetylene” in red letters.
Inside, the acetylene cylinder is filled with a special highly porous mass impregnated with acetone, in which acetylene dissolves well. When storing acetylene in narrow channels of a porous mass, you can increase the pressure of acetylene in the cylinder to 15-16 atm without fear of its explosion. Dissolving acetylene in acetone is done in order to increase the amount of acetylene that can fit in the cylinder. Acetone is a liquid that dissolves acetylene well. One volume of acetone at one atmosphere pressure and room temperature dissolves 23 volumes of acetylene.
Birch activated carbon is used as a porous mass. The condition of the porous mass in the cylinder is checked by the filling plant annually.
When the valve of the cylinder is opened, acetylene is released from acetone in the form of a gas and flows through the reducer and hose into the burner. Acetone remains in the pores of the mass and dissolves new portions of acetylene during subsequent fillings. Acetone losses amount to 40-50 g per 1 m3 and occur due to the entrainment of acetone vapors along with acetylene gas. To reduce acetone losses, it is necessary to keep acetylene cylinders in a vertical position during operation.
When acetylene consumption exceeds 1500 l/h, several acetylene cylinders should be connected. Gas from the cylinder can be consumed to a residual pressure not lower than the following values:
Temperature in ° C……below 0° from 0 to +15° from +15 to + 25° from +25 to +35°
Residual pressure in kg/cm2 .0.5 1 2
At lower pressures, a significant vhoc of acetone with acetylene is observed.
To determine the amount of acetylene in a cylinder, you need to multiply the capacity of the cylinder in liters by the gas pressure in atmospheres and by a factor of 9.2, which takes into account the solubility of acetylene in acetone. For example, if the cylinder capacity is 40 liters, the acetylene pressure is 15 at, then the amount of acetylene in the cylinder will be equal to 40 X 15 X 9.2 = 5520 liters.
Valve device for acetylene cylinder
The acetylene cylinder valve is made of steel. The use of steel here is safe, but the use of copper and its alloys containing more than 70% copper is not allowed, since acetylene with copper can form explosive acetylene copper. The valve is opened and closed using a socket wrench placed on the square head of the spindle. The valve does not have a fitting. The gearbox is connected using a special clamp with a clamping bolt.
Rules for using cylinders. Transportation of cylinders over long distances should be carried out on spring vehicles. It is prohibited to transport oxygen and flammable gas cylinders together. During transportation, cylinders must be stacked with valves in one direction and supported by special wooden spacers with cutouts that prevent the cylinders from rolling over and hitting each other.
Cylinders with liquefied gases are transported in a vertical position with the valve facing up.
It is prohibited to load cylinders onto vehicles and trailers if there is dirt, debris and traces of oil in the body.
The combined transportation of filled and empty oxygen and acetylene cylinders on all types of transport is prohibited. It is allowed to transport two cylinders on a special hand trolley.
In summer, filled cylinders must be protected from heating by the sun's rays. The caps on the cylinders must be screwed in completely.
Loading and unloading of cylinders should be done carefully, avoiding impacts, shocks, and falls. Moving cylinders from one room to another should be done on special carts or stretchers, where the cylinder is tightly secured with a chain or clamp.
Moving cylinders from place to place within one room over a short distance is permitted by tilting.
Filled cylinders are stored in special rooms. If it is necessary to store cylinders outdoors, for example in the field, they must be protected from exposure to precipitation and sunlight by arranging wooden or tarpaulin canopies.
At the workplace, cylinders must be firmly secured in a vertical position to prevent them from falling, and there must also be canopies to prevent oil from falling on the cylinders (for example, from an overhead crane).
When performing installation work on construction sites, oxygen cylinders can be placed in a horizontal position on specially adapted stretchers. Cylinders must be located at a distance of at least 1 m from heating devices and at least 5 m from open flames.
Storing cylinders with gases - acetylene substitutes - at workplaces after work is completed is prohibited. Cylinders must be stored in a special storage room.
It is prohibited to remove the cap from the cylinder using a hammer, chisel or other means that can create a spark. If the cap does not unscrew, the cylinder must be sent to the filler plant (workshop).
When working indoors, you must carefully monitor the tightness of the cylinders.
If gas leakage is detected, the cylinder is removed to a safe place and, if it is impossible to close the valve, left under observation until the gas is completely released.
If a leak of flammable gases from a cylinder into a room is detected, work with open fire must be stopped immediately. Work can be resumed only after the cylinders have been removed and the room has been thoroughly ventilated.
If gas leakage is detected through the stuffing box, tightening the stuffing box nut should only be done with a wrench after closing the valve to the cylinder.
The use of a cylinder with a valve that allows gas to pass through is prohibited.
In cases where the gas cannot be used due to a malfunction of the cylinders, the cylinder must be sent to the filling plant (workshop) with the inscription in chalk “Caution—full.”
To open the acetylene cylinder valve, you must have a special socket wrench.
During operation, this key must be on the cylinder valve spindle at all times. The use of regular wrenches is prohibited.
If the oxygen cylinder valve freezes, heating should be done using clean hot water or steam. Usually the valve is heated by covering the upper spherical part of the cylinder and the valve itself with a rag soaked in hot water. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the rags are not oily and that smoldering embers do not stick to them.
Do not heat the valve with a burner flame or heated metal.
In workshops with up to 10 welding stations, it is allowed to have no more than two oxygen cylinders and two flammable gas cylinders at each workplace. With a large number of posts, gas supply should be provided centrally from the ramp. Do not allow the cylinders and especially the shut-off valves to become contaminated with oil or grease. There should be fire extinguishers and sand boxes in the cylinder warehouse and work sites in case of fire. If a fire occurs, “cylinders must be immediately removed to a safe place (especially when they are filled).
Causes of cylinder explosions
Oxygen cylinders can explode for the following reasons:
1) when oil or grease gets into the cylinder or its fitting;
2) if there is any flammable gas in the oxygen cylinder (before filling with oxygen, the cylinder was used for flammable gas);
3) with too much gas extraction; in this case, the gas, passing at high speed through the valve, can electrify the neck of the cylinder and then a spark may occur. This phenomenon is especially often observed during the cutting process and when the cylinder is standing on a material that insulates it from the ground;
4) when the gas pressure in the cylinder is higher than permissible (the pressure may increase due to heating of the cylinder by sunlight or another heat source);
5) if the material is of poor quality, i.e., a decrease in thickness due to corrosion of the metal of the cylinder; When transported in winter, there may be a significant decrease in the ductility of steel, and then when the cylinder is struck, the metal may collapse.
6) when the valve and neck are dirty with calcium carbide.
When oxygen passes under the hood, an explosive mixture of oxygen and acetylene is formed.
Acetylene cylinders can explode for the following reasons:
1) with sharp shocks and impacts leading to the destruction of the metal of the cylinder or, as a rule, to the settling of the porous mass with the formation of voids in it. The settling of the mass, in turn, helps to increase the volume of the hollow space in the upper part of the cylinder. If the volume of the hollow space exceeds 75-150 cl3, then acetylene, released into this space and being in it under high pressure, becomes explosive;
2) with strong heating (over 30-40 ° C), which reduces the solubility of acetylene in acetone, as a result of which its pressure increases;
3) if the connection between the valve and the gearbox is not tight, as a result of which acetylene can escape into the atmosphere, creating the danger of an explosion of the acetylene-air mixture in the room and, as a consequence, of the acetylene cylinder.
https://electrowelder...-acetylene.html
Safety precautions for gas welding: general information
Safety precautions when performing gas welding apply to:
- On the behavior of the specialist responsible for welding work.
- To organize a work space for performing work.
- On the equipment used.
- At the end of gas welding work.
The main sources of danger during gas cutting and welding can be:
Before starting welding work, all workers must undergo safety training and sign for completion in a special journal.
Requirements for premises for gas welding work
Welding work involving the use of flammable and explosive gases is carried out in a room specially designed for these purposes. They must fully comply with the workflow.
The workplace should not be less than 4 square meters. m. This value does not apply to the placement of welding equipment. There must be a passage at least a meter wide between welding stations.
The height of the work room should not be less than 3 meters, and there should be no protrusions above the workplace. The room must be well lit and heated: the lighting level cannot be less than 80 lux. Also, the room must have good ventilation and a volume of at least 300 cubic meters. m.
In the process of performing gas-flame work in compartments, pits and tanks in which accumulations of harmful poisonous gases are allowed, supply and exhaust measures must be in place.
Before you start welding indoors, you need to ventilate the room to remove any accumulation of gases.
The welder's workplace must always be kept clean, and the functionality of the tools must be checked regularly.
At the welding station, the presence of wood that has not been previously treated with a special compound, rags, plastic and other flammable items is unacceptable. There cannot be any containers with fuel near the welder’s workplace.
Fire extinguishing means must be present at the place where gas welding work is carried out. Other fire safety rules must also be observed. Acetylene can only be extinguished with dry sand; extinguishing with water is unacceptable.
It is not allowed to install gas welding equipment in rooms with high temperatures (for example, in forges, boiler rooms).
If welding work is carried out in a room in which other people work, then protection is installed around the perimeter.
Why gas cylinders explode: main reasons and preventive measures
Agree, the news that a gas cylinder exploded somewhere, which we, unfortunately, sometimes hear on TV or from friends, makes us think about our own safety. And there is no place for complacency that this will not happen to us in this situation.
The consequences that such an explosion and the fire caused by it lead to can be the most tragic, and not only for property, but also for the health and life of people nearby. We will help you understand why gas cylinders can explode and how, without sacrificing the convenience of their use, you can protect yourself from big troubles.
To do this, we conducted a study of the features of existing types of household gas vessels, analyzed the reasons why explosions occurred in a number of real cases, and studied the competent opinions of experienced users about this. The proposed article can be presented as a compilation of sets of rules, presented in an understandable form, that allow, in practice, the correct and safe use of gas in cylinders.
Rules for completing gas welding work
Extinguishing the burner should occur in the following sequence:
- The acetylene valve closes.
- The oxygen valve is closed.
- Close the valve on the oxygen cylinder.
- The gearbox is removed.
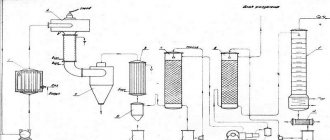
- The retort is unloaded on the generator (it is not allowed to be opened until the carbide has completely cooled down).
- The generator is cleaned and the housing is washed with water . For cleaning, use a scraper (brass or aluminum) or a hair brush.
- in which the generator was located is ventilated
Only after completing all the above steps can the work be considered completed.
Thus, gas welding is a particularly dangerous job. This welding method involves the use of explosive gases such as acetylene and oxygen. Compliance with safety regulations allows you to protect the welder’s work. Safety requirements apply to the room in which welding work will be performed, the welder’s clothing, the work process and the equipment used.
source
Safety precautions during gas welding work
Separate requirements apply to welder clothing. Gas welding can only be carried out in special clothing made from special materials with fire-resistant impregnation. Before starting work, clothing is checked for burns and torn spots.
Gas welding work can only be performed by adult citizens who have previously completed training (theoretical and practical). While performing work, the welder must wear personal protective equipment: overalls, mask and gloves.
Robes and mittens protect not only from molten metal, but also from radiation (thermal or ultraviolet). The welding helmet can protect the worker's eyes from UV radiation, IR light, and metal splashes.
Welders must use light filters while performing work. If cutting and welding, as well as other gas-flame processing processes are carried out, then welders will have to work in safety glasses with glasses G1, 2, 3 (the level differs in the degree of darkness, where 3 is the darkest), and support personnel will have to wear glasses V-1, 2 , 3.
Smoking is not permitted at the welding station . It is worthwhile to inspect the workplace not only before starting work, but also during the welding process. It is necessary to ensure that no other work is carried out near the place of welding work: for example, degreasing and painting.
Before lighting the burner, you need to open the oxygen valve slightly, and then the acetylene valve. After the hoses are purged, the combustible mixture is ignited. It is unacceptable to operate the burner with contaminated channels, as this can lead to popping and backfire.
It is strictly unacceptable to handle the burner with oily hands, as the oil in this case can become a detonator. When a backfire occurs, the valves on the cutter, cylinders and mash immediately close.
Fire spreads through the hoses slowly enough that immediate action can prevent an explosion. But in order to prevent kickbacks during welding, you need to ensure that situations such as:
- A sharp decrease in oxygen pressure when it runs out in the cylinder , or freezing of the reducer or clogging of the injector.
- Approaching a working mouthpiece to an object that reduces the speed of gas flow.
- Overheating of the cutter's mouthpiece and tubes.
- Clogged mouthpiece (reduced flow area and decreased flow rate).
When operating the generator, loading carbide into wet containers, exceeding the pressure by a greater amount than indicated in the passport, or using faulty loading devices is not allowed.
When working, you need to ensure that gas does not leak from taps and plugs. A soap solution can be used for this.
Welding of containers and pipelines that are under pressure is prohibited. Welding of containers and pipelines is carried out only after they have been completely cleaned, washed and steamed.
During technical breaks, the valves on the burner must be tightly closed, and during a long break, the cylinders must also be closed.