Physical properties of acetylene:
| Parameter name: | Meaning: |
| Color | no color |
| Smell | without smell |
| Taste | no taste |
| Physical state (at 20 °C and atmospheric pressure 1 atm.) | gas |
| Density (at 20 °C and atmospheric pressure 1 atm.), kg/m3 | 1,0896 |
| Density (at 0 °C and atmospheric pressure 1 atm.), kg/m3 | 1,173 |
| Melting point , °C | -80,8 |
| Boiling point , °C | -80,55 |
| Triple point, °C | 335 |
| Auto-ignition temperature, °C | 335 |
| Self-ignition pressure, MPa | 0,14-0,16 |
| Critical temperature*, °C | 35,94 |
| Critical pressure, MPa | 6,26 |
| Explosive concentrations of gas-air mixture, % volume | from 2.1 to 100 |
| Specific heat of combustion , MJ/kg | 56,9 |
| Flame temperature, °C | 3150-3200 |
| Molar mass, g/mol | 26,038 |
* at temperatures above the critical temperature, the gas cannot be condensed at any pressure.
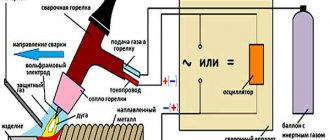
Welding process
The use of acetylene during welding must be carried out carefully and in accordance with certain rules. First, the burner should be purged with gas. This must be done until the smell of acetylene appears. After this, the gas is ignited. In this case, oxygen should be added until the flame becomes more stable. From the reducer at the outlet, the pressure of acetylene should be from 2 to 4 atmospheres, and oxygen - from 2 atmospheres.
Welding ferrous metals requires a neutral flame. It has a clearly defined crown and can be conditionally divided into three bright parts: the core is a bright blue color with a greenish tint, the restored flame is a pale blue hue, and the flame torch. The last two zones are working zones.
Before starting work, all parts must be cleaned and then adjusted to each other. When working with a burner, the left and right methods are also used. In the latter case, the seam cools slowly. The filler material typically moves behind the torch. With the left method, the elasticity and strength of the seam increases. In this case, the flame is directed from the welding site. Filler material should be added to the weld pool only after the torch has moved to the next position.
Acetylene reactions
Acetylene reacts with various compounds, for example, copper and silver salts. As a result of such interactions, substances called acetylenides are obtained. Their distinguishing feature is their explosiveness.
Acetylene production
Acetylene combustion
Acetylene oxidation reaction
Polymerization reaction
Acetylene substitution reaction
Structural isomerism
Alkynes are characterized by carbon skeleton isomerism, multiple bond position isomerism, and interclass isomerism .
Structural isomers are compounds with the same composition that differ in the order of bonding of atoms in the molecule, i.e. the structure of molecules.
Carbon skeleton isomers differ in the structure of the carbon skeleton. For example. Isomers with different carbon skeletons and with the formula C4H6 - butine-1 and butadiene-1,3
Interclass isomers are substances of different classes with different structures, but the same composition. Alkynes are interclass isomers with alkadienes. The general formula of alkynes and alkadienes is CnH2n-2 .
Storage and transportation of acetylene
Acetylene is produced in accordance with GOST 5457 dissolved and gaseous. It is stored and transported in a dissolved state in special steel cylinders in accordance with GOST 949, filled with a porous mass impregnated with acetone. Acetylene dissolved in acetone is not prone to explosive decomposition.
The cylinders are painted gray with the inscription “ACETYLENE” in red letters on the top cylindrical part.
The maximum pressure of acetylene when filling the cylinder is 2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2); when the cylinder settles and cools to 20°C, it decreases to 1.9 MPa (19 kgf/cm2). At this pressure, a 40-liter cylinder holds 5-5.8 kg of C2H2 by mass (4.6-5.3 m3 of gas at 20°C and 760 mm Hg).
The pressure of acetylene in a fully filled cylinder changes with temperature as follows:
| Temperature, °C | -5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| Pressure, MPa | 1,3 | 1,4 | 14 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 12 | 2,4 | 3,0 |
Other safety requirements can be found in the article on the hazard class and safety measures when working with acetylene
Welding work using acetylene
Traditionally, this gas is used when carrying out autogenous welding procedures, as well as cutting metals. The technology involves the use of two gas cylinders, one of which contains oxygen, and the other contains acetylene. The substances enter a specialized burner, and during combustion a very hot flame is formed. Its temperature can reach 3200 degrees Celsius. The most “effective” combination of gases is considered to be one in which the mixture contains 45% acetylene. Under such conditions, it is possible to quickly melt even fairly thick pieces of sheet steel.
Application of alkynes (acetylene hydrocarbons) in medicine
Acetylene
– one of the basic raw materials for the organic synthesis industry. By condensing acetylene with pyrrolidone, N-vinylpyrrolidone is obtained, which easily polymerizes with the synthesis. Polymer compounds based on vinylpyrrolidone have found widespread use in medical practice as substances in the production of drugs, and many of them are themselves medicinal. For example, low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone (12000-13000 molecular weight) forms colloidal solutions in water and is used in the process of preparing hemodesis (blood substitute), medium molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone (with a molecular weight of 35000-40000) is used in pharmacy as a binder for the manufacture of tablets.
Application
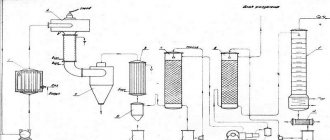
Acetylene production
There are industrial and laboratory methods for producing acetylene. Thus, in industry, acetylene is produced by high-temperature cracking of methane:
2CH4→CH≡CH +3H2.
In the laboratory, acetylene is produced by hydrolysis of calcium carbide:
CaC2 + 2H2O = Ca(OH)2 + C2H2.
In addition to the above reactions, dehydrogenation reactions of alkanes and alkenes are used to produce acetylene:
CH3-CH3→ CH≡CH +2H2;
CH2=CH2→CH≡CH +H2.
Use in industry and everyday life
However, autogenous welding and cutting of metals is not the only area of application. Quite often, acetylene is used as a source of bright white light in self-contained lighting devices. In this case, it is obtained by the reaction of water and calcium carbide.
Such lamps were in great demand in the last century; they were used to illuminate carriages and cars. But even today, carbide devices, that is, those created using acetylene, are used in the improvement of remote lighthouses. The key advantage of carbide lamps is their efficiency and the absence of the need to connect to an electrical outlet. Accordingly, when installing them on a lighthouse, there is no need to connect a power line, that is, to pay for an expensive service. Lamps are also in demand on long-distance vessels.
Acetylene is used in industry. It is used in the preparation of various organic synthesis products. For example, it is used to create:
- acetic acid;
- synthetic rubber;
- solvents;
- some types of plastics.
It should be noted that acetylene has also found application in medicine, for example, it is sometimes used for inhalation anesthesia.
Chemical and physical properties
Some chemical properties
The properties of acetylene are largely determined by its formula. That is, the presence of carbon and hydrogen atoms connected to each other.
Mixing acetylene with water, with the addition of catalysts such as mercury salts, leads to the production of acetaldehyde. The triple bond of the atoms contained in the acetylene molecule leads to the fact that during combustion it releases 14,000 kcal/cu. m. During the combustion process, the temperature rises to 3000 °C.
This gas, under certain conditions, can turn into benzene. To do this, you need to heat it to 4000 °C and add graphite.
The hydrogen contained in the molecules shows acidic properties. That is, they are quite easily separated from the molecule in the form of protons. Acetylene is able to decolorize water containing bromine and a solution of potassium permanganate.
The molar mass of acetylene is 26.04 g/mol. Acetylene density is 1.1 kg/m³.
Physical properties
Under standard conditions, acetylene is a colorless gas that is practically insoluble in water. It begins to boil at -830 °C. When compressed, it begins to decompose, releasing a large amount of energy. Therefore, steel cylinders capable of storing gas under high pressure are used to store it.
This gas must not be released into the atmosphere. Its formula may have a negative impact on the environment.
Acetylene, formula, gas, characteristics:
Acetylene (also ethyn) is an organic substance of the alkyne class, an unsaturated hydrocarbon consisting of two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms.
The chemical formula of acetylene is C2H2. Structural formula of acetylene CH≡CH. Has no isomers.
The structure of the acetylene molecule:
Acetylene has a triple bond between carbon atoms.
Acetylene is a colorless gas, tasteless and odorless. However, technical acetylene contains impurities - hydrogen phosphorous, hydrogen sulfide, etc., which give it a pungent odor.
Lighter than air. Density compared to air density 0.9.
Very flammable gas. Fire and explosion hazard.
Acetylene is one of the few compounds whose combustion and explosion are possible in the absence of oxygen or other oxidizing agents.
Mixtures of acetylene with air are explosive over a very wide range of concentrations. Explosiveness is reduced when acetylene is diluted with other gases, such as nitrogen, methane or propane.
Acetylene requires great care when handling. May explode on impact, when heated to 500 °C, or when compressed above 0.2 MPa at room temperature. A stream of acetylene released into the open air can ignite from the slightest spark, including from a discharge of static electricity from a finger. To store acetylene, special cylinders filled with porous material impregnated with acetone are used. In them, acetylene is stored in the form of a solution with acetone.
Slightly soluble in water. Very soluble in acetone. It dissolves well in other organic substances (gasoline, benzene, etc.)
Acetylene has a slight toxic effect.
What to do if there is a fire
Improper use of acetylene can lead to dire consequences. This gas explodes and causes great destruction. What to do if there is a fire?
If a fire occurs, all containers filled with acetylene should be immediately removed from the hazardous area. Those cylinders that remain should be constantly cooled with ordinary water or a special composition. The containers must cool completely.
If the gas that comes out of the cylinder ignites, the container should be closed immediately. To do this, use a non-sparking key. After this, the container must be cooled.
In the event of a severe fire, extinguishing the fire should only be done from a safe distance. In such a situation, it is worth using fire extinguishers filled with a composition containing a phlegmatizing concentration of nitrogen 70% by volume, also carbon dioxide 75% by volume, sand, jets of water, compressed nitrogen, asbestos sheet, and so on.