When choosing technical gas, enterprises, first of all, are guided by the fact that the organization of various technological processes requires flammable gases with different characteristics. The main ones are flame power and temperature, oxygen consumption and areas of gas use.
For metal cutting, welding and other similar processes, an indicator such as flame power plays an important role. Also of great importance is the ability of the flame to transfer energy to the exposed material. In this regard, technical acetylene is better than propane, since its use allows you to create a flame that will quickly heat the metal surface to the required temperature.
The time it takes to complete the work depends on the temperature that the flame produced using technical gas can reach. Therefore, it is very important for the surface heating process. In this regard, again good results can be achieved using acetylene. While propane flame temperatures can reach 2,800 degrees Celsius, acetylene heats up to 3,100 degrees Celsius. However, acetylene is significantly inferior to propane in terms of energy reserve: 55 versus 95 MJ/m3.
To use technical gases, different amounts of oxygen are required. For acetylene, 1.1 cubic meters is enough to form a flame normal for the work, and for propane, almost four cubic meters of oxygen are required.
Another positive feature of acetylene is that its composition can be changed to result in a reducing or neutral fire. All other gases, including propane, at the temperatures required for industrial purposes, can only form an oxidizing type flame. Therefore, welding cannot be done with propane.
But if it is necessary to carry out general heating of a metal surface, then you cannot do without propane. This thermal process requires gas with a significant energy reserve per cubic meter. Propane gas has these properties.
To summarize, we note that acetylene is good because it can be used in oxidative, neutral and reduction processes when hardening, cutting and welding metals. It is highly effective in carrying out processes that need to be interrupted. It can also be used on contaminated surfaces.
Technical oxygen
Technical oxygen is supplied to the production site for welding in specialized blue-colored cylinders. These containers are accompanied by inscriptions and technical data sheets. The purity of oxygen in the cylinder must be at least 98 percent. Otherwise, it is very difficult to achieve high-quality results from welding operations.
Technical oxygen is supplied directly to the place where the electric arc is formed. Mixing oxygen and flammable technical gas is carried out using a gas burner, gas reducer or gas cutter.
When working with oxygen, a number of precautions must be observed. In particular, you should not work with this gas if you have oily clothes or hands. Oxygen can cause spontaneous combustion. Oxygen cylinders should be stored in a room separate from the storage area for flammable gases.
Difference between Acetylene and Propane
The main difference between Acetylene and Propane is that Acetylene has a triple bond between two carbon atoms , whereas Propane has no double or triple bonds between carbon atoms other than single bonds.
Acetylene is denoted as C2H2, while its chemical name is Ethine. It is also a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne that exists as a colorless gas. Propane is denoted as C3H8, and it is a simple alkane that has no unsaturation (no double or triple bonds). It also exists as a gas. However, it is often liquefied.
Acetylene is the gas of choice for industrial cutting methods, all industrial thermal cutting processes, but when propane (LPG) was introduced to the market, the entire thermal cutting process changed and the battle between propane (LPG) and acetylene began.
Content
- Overview and main differences
- What is Acetylene
- What is Propane
- What is the difference between Acetylene and Propane
- Conclusion
What is Acetylene?
Acetylene is the simplest alkyne, having the chemical formula C2H2. The chemical name of this compound is Ethine. Moreover, it is a colorless gas at room temperature and normal pressure.
Acetylene in cylinders
It can be classified as a hydrocarbon because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms with bonds between the carbon atoms. Acetylene gas is widely used for welding, cutting, as a fuel and building material for the synthesis of various chemical compounds.
Chemical structure of Acetylene
There is a triple bond between the two carbon atoms of this molecule. Moreover, the valency of one carbon atom is 4. Therefore, each carbon atom is bonded to a hydrogen atom through a single bond. The molecule has a linear geometry and it is a planar structure. Each acetylene carbon atom is sp-hybridized.
What is Propane?
Propane is a simple alkane with the chemical formula C3H8. It is a colorless gas at room temperature and in its pure form this gas is odorless. Its molar mass is 44.10 g/mol.
Propane tank
To make propane easier to detect in the event of a leak or spill, manufacturers add various chemical compounds to give it a distinctive odor.
This compound is widely used for welding, cutting and as a fuel. LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) contains liquefied propane gas.
Chemical structure of Propane
However, there are some other gases that are used as LPG. Example: butane, propylene, etc. This gas is produced as a by-product of two processes, natural gas processing and petroleum refining.
What is the difference between Acetylene and Propane?
Acetylene is the simplest alkyne, having the chemical formula C2H2. Its molar mass is 26.04 g/mol. It is an unsaturated compound because it has a triple bond between two carbon atoms. Propane is a simple alkane with the chemical formula C3H8. The molar mass is 44.01 g/mol. It is a saturated compound because it has only single bonds between atoms, there are no double or triple bonds.
Difference in combustion temperatures in oxygen:
- The flame temperature when burning propane in oxygen is 2800 degrees Celsius.
- The flame temperature when burning acetylene in oxygen is 3100 degrees Celsius.
Acetylene and Propane for welding
First, propane cannot be used for gas welding. When acetylene burns in oxygen, it creates a reduction zone that cleans the surface of the steel. Propane does not have a reduction zone like acetylene and therefore cannot be used for gas welding.
Acetylene and Propane for soldering
Propane and acetylene can be used for soldering. For capillary soldering (silver soldering), a result of equal quality is obtained. For “welding” solder (high-melting alloys for soldering), acetylene will be an advantage
Acetylene and Propane for cutting
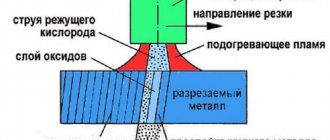
Both Propane and Acetylene can be used for cutting. If you are cutting with acetylene, you usually place the tip of the inner flame cone on the metal (1mm from the surface of the plate). If you do the same with propane, you'll be waiting a long time. If you raise the burner so that the outer cone of flame is used, the preheating process will begin faster. Propane produces only a small portion of the heat in the inner cone of the flame (less than 10%), so most of the heat in the flame is in the outer cone. Acetylene releases almost 40% of its heat in the inner cone of the flame.
Therefore, acetylene is better for cutting than propane. Although acetylene has a higher temperature than propane, the fact is that people use propane incorrectly for cutting. The mistake they make is that they cut with propane like they cut with acetylene. Where it is warm with propane, the preheating flame is not where it is with acetylene. In short, propane requires a different technique, and acetylene generally heats up faster. Shipbreaking yards and scrapyards often use propane for cutting because the quality of the cut is not important.
Acetylene and Propane for heating
To say that propane produces less heat is incorrect. Acetylene is hotter but produces less heat. Most of the preheating is done with oxygen/propane. It is a fact. The available heat from propane is higher.
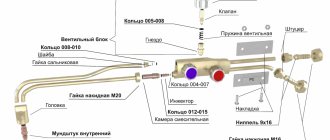
Acetylene and Propane cutting equipment
Cutting requires various cutting attachments and cutting nozzles
Nozzle for cutting with Propane and Acetylene
Economics when cutting with Acetylene and Propane
Propane has a higher stoichiometric oxygen requirement than acetylene. For maximum flame temperature in oxygen, the volume ratio of oxygen to fuel gas is 1.2:1 for acetylene and 4.3:1 for propane. Thus, when using propane, much more oxygen is consumed. Although propane is cheaper than acetylene, it is hampered by its higher oxygen consumption.
Difference in oxygen consumption
Safety of Acetylene and Propane
The biggest disadvantage of using propane is the safety aspect.
The specific gravity of acetylene is 0.9, so it is lighter than air (air has 1). If gas leaks, it will rise. Propane has a specific gravity of 1.6 and is heavier than air (the same for other hydrocarbon gases such as butane and MAPP gas (modified propane gas). Any propane leak in a confined space will sink and concentrate at a lower level and accumulate there.
For propane to burn effectively, the oxygen-gas mixture must be within a certain range. For ideal conditions it should be four parts propane to 96 parts oxygen. When gas burns outside these parameters, the result is incomplete combustion, which produces excessive amounts of carbon monoxide. This can be very dangerous if the area is not properly ventilated. Carbon monoxide poisoning can cause death as the toxic gas replaces oxygen in the blood.
Basic Information - Acetylene vs Propane
Acetylene and Propane are hydrocarbon compounds and are gaseous at room temperature. They are used for welding, cutting and as fuel. The difference between Acetylene and Propane is that Acetylene has a triple bond between two carbon atoms, whereas Propane does not have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms, but only single bonds.
Types of propane cutters and their differences from acetylene cutters
A propane cutter is a powerful and economical tool for cutting sheet blanks and dismantling metal structures. Simplicity of design and reliability, high mobility, and no need for power supply have made the propane cutter popular not only among professionals, but also among home craftsmen. Low prices for equipment and consumables allow you to save significant amounts compared to other methods of metal cutting. An acetylene torch can also be converted to use propane.
Basic methods of maintaining the torch and filler material
Specialists use two ways of holding the instrument: “pull” and “pull”.
When driven from yourself, a wire is located in front of the burner. This method is used when welding structures of large thickness. In this case, the molten metal of the parts and additives simultaneously fills the weld pool.
This method requires the welder to ensure uniform mixing of the base and filler metal. If there is insufficient amount of wire melt, the seam becomes weakened.
With the “pull” acetylene welding method, the torch comes first, and when the base metal is melted, metal from the wire is added to the bath. Here you need to position the burner correctly.
It should go at an acute angle in relation to the parts. This method is the simplest. You need to heat the metal, remove a drop from the wire and stretch it along the seam. According to this principle, the seam leg is formed.
For greater convenience and to prevent the formation of burns, the burner is moved either in a crescent or in a circular motion.
A major role in the quality of the connection is played by the correct joining of parts and the absence of large gaps when welding thin sheets or pipes. It should be remembered that before acetylene welding, the parts must be grabbed in several places. On small diameter pipes, tacks are made after about 1200.
The performance of welding work is also influenced by the characteristics of the metal being welded.
Why is acetylene dangerous?
The use of acetylene is limited by its extraordinary properties. This gas is self-igniting. This occurs at a temperature of 335°C, and its mixture with oxygen - at a temperature from 297 to 306°C, with air - at a temperature from 305 to 470°C.
It is worth noting that technical acetylene is explosive. This happened when:
- Increasing the temperature to 450-500°C, as well as at a pressure of 150-200 kPa, which is equal to 1.5-2 atmospheres.
- A mixture of acetylene and oxygen at atmospheric pressure is also dangerous if it contains 2.3-93% acetylene. An explosion can occur from intense heat, an open flame, or even a spark.
- Under similar conditions, an explosion of a mixture of air and acetylene occurs if it contains 2.2-80.7% acetylene.
- If the gas comes into contact with a copper or silver object for a long time, acetylene explosive silver or copper may form. This substance is very dangerous. An explosion can occur from a strong impact or as a result of increased temperature. You should work with gas carefully.