Float level gauge: in detail in simple language
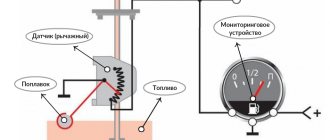
A float gauge is a liquid level measuring instrument designed so that it floats half submerged in the liquid and the other half is above the surface of the liquid.
Floats are hollow objects that always come into direct contact with the liquid being measured. You can use the vertical movements of the float as a direct measurement of the equivalent change. The movements of the float can be transmitted to a number of different devices, with the help of which either continuous level measurement or level determination with setpoints is carried out.
Float level gauge We recommend that you understand what a level is, and also pay attention to other devices for measuring level.
Reviews about using the device
Users primarily praise float switches for their accuracy and high repeatability. Despite the simple design and the absence of complex technical components, such devices provide decent measurement results. The advantages also include advantages in the form of an affordable price and independence of measurements from the chemical state of the liquid. Again, special device models are used to assess the density, viscosity and other indicators of the medium, but float level gauges specialize specifically in the volume of the medium. However, there are also negative reviews. The fact is that the operation of the float may depend on fluctuations in the liquid. Splashing and slight vibrations can distort the float readings.
Operating principle of a float level gauge
Buoyancy is the upward force or lift that pushes upward an object immersed in a liquid. Any object immersed in a liquid is subject to a lifting force equal in magnitude to the weight of the displaced liquid.
Demonstration of displacement, lift and apparent weight loss
The figure above illustrates the relationship between displacement, lift and weight, and also shows how an object immersed in a liquid experiences an apparent loss of weight corresponding in magnitude to the weight of the liquid it displaces.
The figure shows: a cylindrical object suspended on scales; a large vessel filled with liquid to the level of the overflow pipe; an empty, smaller vessel to collect liquid spilled from a large vessel, provided that the liquid is displaced from the large vessel. The weight of the item is shown on the scale.
When an object is immersed in a liquid, some of the liquid is poured into an empty container. A change in the weight reading on the scale indicates that the weight of the item is decreasing. The magnitude of this apparent weight loss is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced into the empty container.
If the weight of an object is greater than the weight of the fluid it displaced, the object will be submerged, but its weight loss will still be equal to the weight of the fluid it displaced. If an object (when fully submerged) weighs less than the volume of liquid it displaces, the object will rise to the surface and will float on the surface of the liquid. A drifting object will float precisely at the level at which the weight of the liquid displaced by it will be exactly equal to the weight of the object itself.
Buoyancy using the example of two objects
The figure above illustrates the phenomenon of buoyancy using the example of two suspended objects descending into a tank of liquid. The object on the left floats: the lifting (buoyant) force of the liquid is greater than the weight of the object. The action of the object on the right is similar to the action of the displacer. As the liquid level rises, it will sink into the liquid because the buoyant force of the liquid is less than the weight of the object.
The movement signals of the float gauge as it rises or falls in response to changes in liquid level can be translated into level readings using a number of different devices, including calibrated rods; lever connections; tapes (or chains); pulleys and counterweights; ropes and sliding arrows; lifting mechanisms and mechanical switches.
A rod with an indicator arrow and a scale are mounted on the outside of the tank. The float gauge, which is attached to the bottom of the stem, is visible in this example through the capped hole at the top of the tank. Any change in the position of the float is indicated by the displacement of the arrow along the scale.
The float can also be connected directly to the indicator needle using a lever connection. This mechanical connection is routed directly to the arrow on the indicator device. When the float inside the tank is raised or lowered, the linkage moves the needle along the scale on the indicator.
Content
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of displacer level gauges is based on Archimedes' law, according to which a special buoyant force acts on a displacer immersed in the measured medium. The amount of displaced liquid directly depends on the immersion level of the displacer in the tank.
When the level of the liquid medium changes, the degree of immersion of the sensor displacer changes, which leads to a change in its mass. The change in the weight of the device buoy is directed through a lever to the torque tube. The rotating motion of the torque tube is transmitted through a magnetic field sensor to the controller, which converts the angle of rotation into an electrical signal. It is processed by a microprocessor automated unit and converted into a digital level value, displayed on the display of the level meter’s electronic unit and transmitted via a special HART protocol. In this case, the level value is converted into an output current signal (4-20 mA). The action of the buoyancy force is assessed by special devices. In fact, there are 2 options for the technical design of the sensor:
Scope of application of displacer level gauges
Displacer level transmitters are used primarily to solve problems of level control, phase separation and density measurement. Most often they are used for research:
Also, buoy-type level gauges are often used to collect information in automated control systems (phase boundaries, level, medium density), metallurgy, or in the chemical and petrochemical industries (including oil production and oil refining). The exact scope of operation of the equipment is determined by the features of its structure and is indicated in the device passport.
Advantages of displacer level gauges
Displacer level sensors have many advantages, which include the convenient measurement method by which they work (this method is well known: it minimizes the likelihood of possible errors and inaccuracies when monitoring liquids). Also, the advantages of displacer level gauges include simplicity of design, a wide range of operating temperatures and pressures, a wide range of applications, etc. At the same time, the products are capable of:
Easy technical measurements
The main advantage of the displacer sensor is its fairly simple measurement method. Today it is one of the lightest, most correct and high-quality. Moreover, due to complete automation, this method eliminates errors in the course of research in almost all cases.
Simplicity of designs
The design of float buoy level gauges is created in accordance with all international and national rules and regulations, which ensures its mobility, safety and efficiency of use. The structure of the devices allows them to be used even in hard-to-reach places for measuring liquid materials with any characteristics.
Wide measuring range of working medium
Displacer level gauges for tanks are multi-functional and versatile. They can be used in many household and industrial areas. The only exception: the device should not be used in places where foreign substances may stick to the float.
Disadvantages of displacer level gauges
The main disadvantages of displacer level gauges are:
What to check when purchasing displacer level gauges
When purchasing displacer type sensors for liquids, you should check their labeling and data regarding:
This and other information can be found in the equipment passport, operating instructions and other technical documents for the device.
Measures for the safe operation of displacer sensors and transducers
When using a displacer-type level gauge, certain safety precautions must be observed (regardless of the pressure and temperature of the liquid being tested). Personnel of the company that operates the equipment may be allowed to install, maintain, use and repair the equipment only after studying the equipment description, safety instructions, as well as testing their knowledge and receiving the necessary instructions. Before installing the devices you need to check:
After this, you need to adjust the level gauge. All work must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST R 51330.16 “Inspection and maintenance of electrical installations in hazardous areas.” At the same time, during the operation of displacer level gauges, maintenance personnel are prohibited from:
Maintenance of displacer level gauges
Maintenance of the working medium level sensor consists mainly of adjusting the “zero”, checking the general structural condition and periodic verification. If the tightness of the flange seals is broken, the sealing gasket must be replaced.
During operation, an explosion-proof displacer sensor must undergo regular external inspection, during which it is necessary to check for breaks or damage to the insulation of connecting lines, reliability of cable installation, absence of dents and various visible mechanical damage to the device shell.
Setting up level gauges
The level gauge for liquids is adjusted in such a way that the device displacer is immersed directly at the maximum level of the working medium under study. Pre-installation testing of sensors is usually carried out using the weight method. After this, experts adjust the measuring system so that the reading error does not exceed a certain tolerance (regardless of other characteristics of the material: pressure, temperature, mass, etc.).
Source
Design features and operating principle
The design of liquid level meters in a tank is determined by the following characteristics:
- Functionality. Based on this parameter, all measuring devices of this class are classified into level meters and liquid level alarms. The latter determine the specific filling point of the container (maximum and minimum), while the former constantly monitor the liquid level.
- Operating principle. This parameter is based on acoustics, optics, magnetism, electrical conductivity, and so on. The scope of its application depends on the principle of operation of the device.
- Measurement technique (non-contact or contact).
In addition, the design features of the device determine the type of process environment. For example, level gauges in drinking water tanks are different from devices that are designed to measure the fullness of tanks with industrial wastewater.
WATER AND OTHER LIQUIDS LEVEL SENSOR
Monitoring the level of water and similar liquids is carried out using devices with different types and functionality. The choice of a specific option is made based on the objectives, external conditions and properties of the working fluid.
To avoid mistakes and unnecessary expenses, the selection and installation of sensors for industrial and public purposes is trusted to specialists. Sensors for individual use can be easily selected and installed independently.
This group for measuring the level of water or other liquids is represented by devices with completely different operating principles.
These devices may be mechanical, electronic, magnetic, optical, hydrostatic or locating.
They are installed in locations where access to water is difficult or non-existent, or where direct measurement poses a safety risk.
The simplest level sensors worked due to the basic laws of physics (pushing force or differences in the electrical conductivity of dissimilar media). Modern varieties are suitable for a wide variety of tasks, including:
- online monitoring of actual water level;
- notification of reaching limit or specified values of the liquid level;
- measurement and calculation of the volume of working fluid in containers with complex shapes or its flow rate;
- storage, accumulation and processing of results.
Based on their functional purpose, all water level sensors are divided into level meters and alarms. The first ones are installed for the purpose of continuous monitoring of this parameter and convert its value into an analog or digital signal.
The latter are activated when it is necessary to receive a signal or command that a certain value of the liquid level in the container has been reached.
Types of sensors
All level gauges are classified according to the principle of their operation. Main types of measuring devices:
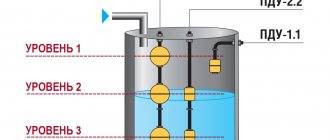
- Float _ This is the simplest option for measuring the water level in the tank. The design of the float level gauge includes 2 reed switches, a magnet and a float. As the fluid level increases, the float rises to the first reed switch, which turns off the motor relay. If the reservoir is empty, the float drops to the second reed switch, which triggers the relay and turns on the pump that pumps liquid from the well. You can make a reed limit liquid level sensor with your own hands. Moreover, it will work even if there is a voluminous layer of foam in the tank.
- Ultrasonic . This type of measuring device is used for both dry and liquid media. Ultrasonic sensors can have a discrete or analog output. That is, the device can constantly monitor the water level or limit the filling of the container when it reaches a specific point. Such a level gauge consists of a receiver, an ultrasonic emitter and a controller responsible for signal processing. Ultrasonic type alarms are wireless and non-contact, so they can be installed even in explosive and corrosive liquids.
- Electrode (conductometric). Such level meters are not suitable for containers with distilled water. The standard design is equipped with a three-level alarm, in which the filling of the tank is controlled by a pair of electrodes, and the third is intended for emergency situations, to start the active pumping mode.
- Capacitive . Using such level gauges, the maximum filling level of a tank can be accurately identified. They are suitable for both liquids and bulk substances. Capacitive level gauges operate on the same principle as capacitors: the measurement is performed between the plates of the sensing element. When the peak value is reached, a corresponding signal is sent to the controller. Sometimes capacitive alarms operate on the “dry contact” principle, in which the device is triggered through the wall of the tank. These devices can operate effectively over a very wide temperature range and their operation is not affected by electromagnetic radiation. Such performance properties expand the scope of use of capacitive level meters.
- Radar . This type of alarm is universal, as it works with any type of process media, including explosive and corrosive liquids. In this case, the readings will not change under the influence of temperature and pressure. The device emits radio waves in a certain frequency range. The receiver picks up the reflected radio signal and determines how full the tank is, based on the signal delay period. The measuring sensor is not affected by temperature and pressure. The dustiness of the process environment also does not affect the readings. Experts note that radar devices have maximum accuracy, since their error does not exceed 1 mm.
- Hydrostatic . This type of alarm allows you to measure both the current and maximum filling of containers. The operating principle of a hydrostatic device is based on measuring the pressure of a liquid column. The popularity of such sensors is due to their low price and sufficient accuracy.
TYPES OF LEVEL SENSORS THEIR ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Depending on the method of contact with the liquid medium, all sensors of this type are divided into:
- contact;
- contactless.
The second group is more limited and is represented by high-tech radar microwave level gauges and ultrasonic sensors of both types.
Microwave radar level meters
in turn, they are divided into devices with different operating principles (pulse control or FMCV location), operating range and radiation frequency. These level gauges are recognized as the most advanced; the only limitation to their use is their high price.
Operating principle of ultrasonic level meters and alarms
is based on an analysis of the propagation time of pulses from the sensor-emitter to the liquid medium. The advantages of devices in this group include efficiency, compactness and unpretentiousness; in general, their characteristics are considered universal.
The scope of application of ultrasonic varieties is limited to water and other liquids; they are not suitable for measuring the level of bulk solids. The considered features of these devices also include the need to compensate for certain external influences (wind, presence of a foam layer).
Contact sensors
more widespread and diverse. Depending on the principle of operation, this group is conventionally divided into:
- capacitive and conductometric varieties, which have a similar operating principle and determine the level by changes in the medium’s capacitance and resistance indicators, respectively;
- float meters, in turn, are divided into simple mechanical and improved reed switches;
- hydrostatic level gauges and alarms used to monitor the level of water and liquids with constant density at an external pressure not higher than atmospheric pressure;
- optical electronic limit level alarms that monitor this value by changing the reflectivity of water;
- vibration devices that monitor the achievement of a certain level by analyzing changes in the amplitude of vibration of the sensitive element.
Float mechanical sensors
have the simplest operating principle (the contacts close when the float is pushed out by the working fluid). Devices in this group are valued for their reliability and availability, but because they operate only when a certain limit is reached, their capabilities are limited.
Reed switches
(aka magnetic float) sensors do not have these disadvantages; the contacts of their sensitive elements can close as the magnet approaches. All float varieties do not require complex installation and are cheap, but in sticky and dynamic environments they are of little use.
Capacitive sensors
are equipped with special electrodes that form a primitive capacitor with the housing. They are used to monitor water levels and any liquids that do not foam or splash onto the probe (with the exception of capacitive radio frequency types).
Conductometric
Varieties of liquid level sensors are equipped with rigid rods or flexible cable electrodes. The functions of the common electrode are performed by the metal walls of the working tank or control rods.
The relay closes when the working element comes into contact with food or industrial water, drinks, solutions of salts or alkalis and wastewater. Their advantages and disadvantages are in many ways similar to capacitive ones, but the length of their electrodes is easier to change. Unlike capacitive conductometric varieties, the principle is implemented exclusively in alarm devices.
Hydrostatic varieties have a wide range of applications and are valued for their reliability and unpretentiousness. In particular, with their help, the water level in wells is monitored (no alternative use), pressure in pumping and boiler houses and the operation of irrigation installations are controlled.
But due to the risk of obtaining incorrect results, they are not recommended for monitoring the level of solutions with variable density.
Optical electronic sensors
are used as an alternative to reed switches when monitoring water levels in tanks subject to vibration.
They are valued for their compactness and the ability to obtain results independent of external factors. Due to the high cost, limitations in tank volume and the need for professional installation, they are used less frequently than others.
Vibration alarms are triggered when the vibration of the yoke sensors changes. Such devices have average accuracy and efficiency and perform well when working with foamy and viscous media. Vibration alarms do not have operational drawbacks, but they are not intended for continuous monitoring or providing ultra-precise results.
Selection rules
Selecting a level gauge for tanks must take into account a large number of factors. Among them:
- water composition;
- the volume of the container and the material that was used to make it;
- the need to control the maximum and minimum liquid levels or monitor the actual condition;
- the possibility of introducing automatic control into the system;
- switching capabilities of the device.
To select household devices, it is important to consider the capacity volume, control circuit and operating principle.
Advantages of displacer level gauges
The general advantages of displacer level gauges include the measurement method by which they work - it is well known and practically eliminates errors and inaccuracies when monitoring liquid media. Also, displacer level gauges are distinguished by their simplicity of design, wide range of operating pressures and temperatures, which makes the scope of application of the device very diverse. Perhaps the only drawback of these devices is the prohibition on use in environments that form sticking or deposits of sediment on the float.
Various modifications have their own characteristics and advantages. For example, SKB-02 displacer level transducers have the ability to:
Popular models
The modern market offers many models of alarms . The most popular of them:
- DE-1 (capacitive sensor). Most often, this alarm is used in aggressive environments in the chemical and metallurgical industries. It allows you to control the temperature and level of bulk and liquid substances. Often used in emergency protection installations.
- ESU-1 (electronic level switch). The body of this model is made of high quality steel and fluoroplastic. Most often, ESU-1 is installed in explosive and aggressive environments. The power source is located outside the process environment. The sensor measures the level of oil, alcohol and water. The power supply is made of durable aluminum alloy.
- RU-305 (level relay). This device is designed to monitor the condition of liquid media. Its body is made of special material and can easily withstand temperatures from -50 to +50 degrees Celsius. However, RU-305 must not be used in aggressive chemical environments. Among the disadvantages of this level gauge, consumers note only that it works only in one position, without tilt. Level measurement is carried out by moving a magnet with a float and triggering a reed switch. Measurements have an accuracy of no more than 5 mm.
- SU-100 (level alarm). Sensor for measuring the level of bulk and liquid substances. The SU-100 design contains an electromagnetic relay.
- Rosemount 5600 This radar level sensor allows non-contact measurement of any type of substance. To achieve the most accurate readings, the level gauge must be installed correctly. The device's reading accuracy may be degraded by exposure to electromagnetic radiation. The housing has an explosion-proof design and a display that displays all the necessary information. The Rosemount 5600 can be used to measure tank temperatures. To fully evaluate the capabilities of this equipment, it requires qualified adjustment taking into account the diameter of the pipeline, the length of the level gauge and the distance between the level and the reference point.
It is advisable to purchase complex models only for industrial use. The simplest versions of level meters are suitable for domestic purposes.
Float level gauge
is a level gauge based on measuring the position of a float partially immersed in a liquid, and the degree of immersion of the float (sediment) at a constant liquid density does not depend on the controlled level. The float moves vertically along with the liquid level, and therefore the level value can be determined from its position. In static mode, the float is acted upon by the force of gravity G and the buoyant forces of the liquid and gaseous medium. When the float moves, a resistance force also appears in the moving elements of the level gauge. If we neglect the kinematic resistance force and the buoyancy force of the gas phase, then the forces acting on the float are related by the equation
Manufacturers and prices
NivoFlip offers high-quality models, producing single and complete solutions for level measurements in liquid media. In its line you can find models with a measurement scale of up to 3500 mm, while the company notes a 10 mm accuracy in reflecting the result. The competition for this manufacturer is RizurNBK. Its family includes a wide range of high-quality magnetic devices, including those with roller bypass indicators. In both cases, a float level gauge is offered, the price of which varies on average from 1 to 3 thousand rubles. If you need a simple budget device, then you can turn to the products of the Albatross company, which produces models with price tags of about 500-700 rubles. These are quite good-quality, functional and flexible devices for a variety of tasks.
Level gauges for bulk materials
Designed for continuous monitoring of the level of bulk materials: cement, sand, crushed stone, flour, grain and others. Our company's product range includes contact and non-contact level transducers from the manufacturer NIVELCO: capacitive, microwave, ultrasonic.
| Level gauges for bulk solids | ||
| View | Description | Example |
| Capacitive | Presented in different modifications, used for specific production conditions. There are models with different probe shapes and lengths for different measured substances | Capacitive level transmitter NIVOCAP |
| Microwave | Microwave reflex level meters for bulk solids determine the level of the substance in the tank. Designed specifically for use in extreme conditions: high pressure, temperature fluctuations, heavy dust | MicroTREK Reflex Microwave Level Sensor |
| Ultrasonic | Similar to ultrasonic liquid level gauges. They are used in silos and gutters up to 60m deep. They will be indispensable in the chemical industry, petrochemistry, production of building materials, food industry, etc. | Ultrasonic level gauge EasyTREK for bulk materials |