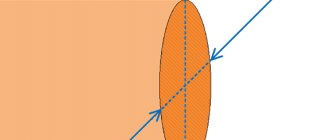
A cross section is a figure formed by the intersection of an oblong body with an imaginary plane, located perpendicular to each other, i.e. when the body is cut strictly across its length.
The section can have a simple or complex shape, or be composite.
The area and dimensions (length and width) of the cross section are equal to the corresponding dimensions of this figure.
Cross-sectional area as an electrical quantity
The conductivity of the wire depends on the cross-section.
As an example of the cross-section, you can consider cutting the product at an angle of 90 degrees relative to the transverse axis. The outline of the resulting figure is determined by the configuration of the object. The cable looks like a small pipe, so when cut it will come out in the form of two circles of a certain thickness. When a round metal rod is cut transversely, the shape of a circle is obtained.
In electrical engineering, the PS area will mean the rectangular cross-section of the conductor in relation to its longitudinal part. The cross-section of the cores will always be round. The parameter is measured in mm2.
Novice electricians may confuse the diameter and cross-section of elements. To determine what cross-sectional area the core has, you need to take into account its round shape and use the formula:
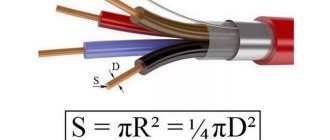
S = πxR2, where:
- S – area of the circle;
- π – constant value 3.14;
- R is the radius of the circle.
If the area indicator is known, it is easy to find the resistivity of the manufacturing material and the length of the wire. Next, the current resistance is calculated.
For convenience of calculations, the initial formula is transformed:
- The radius is ½ the diameter.
- To calculate area, π is multiplied by D (diameter) divided by 4, or 0.8 multiplied by 2 diameters.
When calculating, use the diameter indicator, since its incorrect selection can cause overheating and ignition of the cable.
Application area
The circle is one of the fundamental figures that surround a person everywhere. Pipes, wheels, lamps, stove burners - all of this has the shape of a circle or a cross section in the form of a circle. Calculating the area of such a section may be necessary in the following situations:
- Determination of container volumes.
- Solving problems in strength of materials and electrical engineering.
- Calculation of the amount of materials during design, construction and repair.
- Conducting irrigated agriculture.
General information about cable and wire
When working with conductors, it is necessary to understand their designation. There are wires and cables that differ from each other in their internal structure and technical characteristics. However, many people often confuse these concepts.
A wire is a conductor that has in its design one wire or a group of wires woven together and a thin common insulating layer. A cable is a core or a group of cores that has both its own insulation and a common insulating layer (sheath). Each type of conductor will have its own methods for determining cross sections, which are almost similar.
Our courses to prepare for the Unified State Exam in mathematics, computer science and physics
Courses for those who need to get 90+ and enter a top university in the country.
Mathematics Unified State Exam
Informatics Unified State Exam
Alexey Shevchuk - course leader
- author of a textbook on mathematics, YuKlev, that everyone can understand (with hundreds of grateful reviews);
- graduated from MIPT, taught at a small physics and technical institute;
- tutoring experience - 19 years (since 2003);
- in 2022 I passed the Unified State Exam (mathematics 100 points, physics 100 points, computer science 98 points - stupid mistake as usual :);
- review on Profi.ru: “Rating: 4.87 out of 5. Very praised. This mark is awarded to experienced specialists with the best reviews.”
What does cross section mean?
Before revealing the basic concept, you need to decipher the meaning of the term and understand how a wire differs from a cable. A wire is a conductor that is used to connect several sections of an electrical circuit. May have one or many current-conducting conductor elements. They, in turn, can be bare, insulated, single-core or multi-core.
Conductor cut area
The former are used in overhead electrical transmission lines. The latter are used in electrical devices, panels or cabinets. In everyday life, they are located inside electrical wiring.
For your information! Insulated and single-core conductors are used everywhere, and stranded conductors are used where bends with a small radius are needed.
What is a cross section
A cross section is a figure that is formed from a conductive section by a directional plane. The area obtained from a perpendicular cut of any type of wire is indicated in square millimeters. This is an important parameter for calculating the electrical network.
Units
Square meters
Area is measured in SI units in square meters. One square meter is the area of a square with a side of one meter.
Read also: How to determine that there is a demon in front of you?
Unit square
A unit square is a square with sides of one unit. The area of a unit square is also equal to one. In a rectangular coordinate system, this square is located at coordinates (0,0), (0,1), (1,0) and (1,1). On the complex plane, coordinates are 0, 1, i
and i
+1, where
i
is an imaginary number.
Ar or weaving, as a measure of area, is used in the CIS countries, Indonesia and some other European countries, to measure small urban objects such as parks when a hectare is too large. One are is equal to 100 square meters. In some countries this unit is called differently.
Hectare
Real estate, especially land, is measured in hectares. One hectare is equal to 10,000 square meters. It has been in use since the French Revolution, and is used in the European Union and some other regions. Just like the macaw, in some countries the hectare is called differently.
In North America and Burma, area is measured in acres. The hectares are not used there. One acre is equal to 4046.86 square meters. An acre was originally defined as the area that a farmer with a team of two oxen could plow in one day.
Section according to GOST or TU
A large assortment of electrical products helps to quickly solve problems associated with electrical installation work. The quality of these products plays a very important role and all products must comply with GOST requirements.
As a result, the market is oversaturated with low-quality and cheap goods that need to be double-checked before purchasing.
If the cables available in retail outlets of a suitable price do not correspond to the declared characteristics, the only thing that can be done is to purchase a wire with a reserve cross-section. The power reserve will never negatively affect the quality of electrical wiring. It would also be useful to pay attention to products from manufacturers who value their name - although they are more expensive, they are a guarantee of quality, and wiring replacement is not done so often that you can save on it.
Simplifications
Images (types, sections, sections) can be simplified to make them easier to understand. Standards and norms regulate this process.
For symmetrical figures, it is allowed to draw only one half of the cut or most of it, drawing a break line. When an object has several identical elements, only one of them is drawn. The remaining identical parts are drawn schematically.
Projections of intersection lines may be depicted in a simplified manner. But only if their detailed image is not required.
When drawing simple figures, for example, if you need to consider the types of sections of a cone, you use a certain approach to graphics. This makes the drawings easier to understand. When one surface changes in a particular pattern, it can be interrupted.
If one surface smoothly passes into another, their boundary is not indicated or is indicated conditionally.
Non-hollow symmetrical parts and products in the drawing are shown uncut in a longitudinal section. And if the size of a part of the product in the drawing is less than 2 mm, it is depicted with a deviation from the main scale.
To indicate flat surfaces, diagonals can be drawn with solid lines.
It should also be taken into account that permanent connections of electrical or radio devices are simplified by standards corresponding to the type of product. These are the main simplifications that are regulated by the Unified System of Design Documentation. They are most often used to create drawings in large industries, where it is necessary to depict complex parts, assemblies or mechanisms.
Calculation goals
Cross section of wires for lighting
It is necessary to calculate the parameters of the cross-sectional area of the conductor for several purposes:
- obtaining the required amount of electricity to power household appliances;
- eliminating overpayments for unused energy;
- wiring safety and fire prevention;
- the ability to connect high-power equipment to the network;
- prevention of melting of the insulating layer and short circuits;
- proper organization of the lighting system.
The optimal wire cross-section for lighting is 1.5 mm2 for the line, 4-6 mm2 for the input.
Tensile strength and tensile elongation
When choosing wires, in addition to the cross-section, wire material, and insulation, it is necessary to take into account their mechanical strength. This is especially true for overhead power lines. The wires are stretched. Under the influence of force applied to the material, the latter elongates. If we denote the initial length as l1 and the final length as l2, then the difference l1 – l2 = Δl will be the absolute elongation.
Attitude
called relative elongation.
The force that produces a rupture of a material is called the breaking load, and the ratio of this load to the cross-sectional area of the material at the moment of destruction is called the temporary tensile strength and is denoted
Data on tensile strengths for various materials are given below.
Tensile strength value for various metals
| Name of metal | Tensile strength, kg/mm² |
| Aluminum Aldrey Bronze Tungsten Gold Brass Copper Molybdenum Nickel Tin Platinum Mercury Steel Silver Lead Zinc Cast Iron | 8 – 25 30 – 38 31 – 135 100 – 300 – 30 – 70 27 – 44,9 80 – 250 40 – 70 2 – 5 15 – 35 – 70 – 75 15 – 30 0,95 – 2,0 14 – 29 12 – 32 |
Calculation of the cross-section of a stranded conductor
Stranded wire consists of several individual wires. Its cross section is calculated as follows:
- The indicator of the cross-sectional area of one core is found.
- Cable cores are recalculated.
- The quantity is multiplied by the cross-section of one core.
When connecting a stranded conductor, its ends are crimped with a special sleeve using crimping pliers.
Maximum current for different thickness of copper wires
Table 1
(Data from table 1.3.4 PUE)
The ratings of wires used in household electrics are highlighted. “One two-core” is a cable with two wires, one of them is Phase, the other is Zero. That is, this is a single-phase load supply. “Single Three-Wire” is for three-phase power supply.
This table shows at what currents and under what conditions a wire of a given cross-section can be operated.
A burning example from practice - if the socket says “Max.16A”, then it is possible for this one socket
lay a wire with a cross section of 1.5mm2. But be sure to protect the outlet with a circuit breaker for a current of no more than 13A, or better yet, 10A.
In the table, a single-core wire means that no more wires pass nearby (at a distance of less than 5 wire diameters). Two-core wire - two wires side by side, usually in one common insulation. This is a more severe thermal regime, so the maximum current is less. And the more wires in a cable or bundle, the less the maximum current for each conductor must be due to possible mutual heating.
I find this table not very convenient for practice. After all, most often the initial parameter is the power of the electricity consumer, and not the current, and based on this you need to choose a wire.
How to find the current knowing the power? You need to divide the power P (W) by the voltage (V), and we get the current (A): I = P/U How to find the power, knowing the current? You need to multiply current (A) by voltage (V), we get power (W): P = IU These formulas are for the case of active load (consumers in residential premises, such as light bulbs and irons). For reactive loads, a factor of 0.7 to 0.9 is usually used (in industry where large transformers and electric motors operate).
I offer you a second table in which the initial parameters are current consumption and power, and the required values are the wire cross-section and the shutdown current of the protective circuit breaker.
What is the cross section measured in?
After determining the diameter using the indicated methods, the cross-sectional area can be determined using a formula or a special table. It is measured in square millimeters. This unit of measurement is derived according to the Unified International System of Measurements.
You may be interested in this The danger of step tension
Unit of measurement
At the same time, the cut of the vein was always round.
Area of a circle circumscribed around a square
It is very easy to find the area of a circle circumscribed around a square.
To do this, you only need the side of the square and knowledge of simple formulas. The diagonal of the square will be equal to the diagonal of the circumscribed circle. Knowing the side a, it can be found using the Pythagorean theorem: from here. After we find the diagonal, we can calculate the radius: . And then we’ll substitute everything into the basic formula for the area of a circle circumscribed around a square:
Let's consider an example of calculating the area of a circle circumscribed around a square. Problem: given a square inscribed in a circle. Its side is a = 4 cm. Find the area of the circle. First, let's calculate the length of the diagonal d. Now we substitute the data into the formula
Knowing a few simple rules and the Pythagorean theorem, we were able to calculate the area of a circle circumscribed around a square.
Features of self-calculation
Independent calculation of the longitudinal section is performed on a core without an insulating coating. A piece of insulation can be moved or removed on a piece purchased specifically for testing. First you need to determine the diameter and find the cross section using it. Several methods are used for the work.
Using a caliper
The method is justified if the parameters of a truncated or defective cable are measured. For example, VVG may be designated as 3x2.5, but in fact be 3x21. Calculations are made as follows:
- The insulating coating is removed from the conductor.
- The diameter is measured with a caliper. You will need to place the wire between the legs of the instrument and look at the scale markings. The integer value is on top, the decimal value is on the bottom.
- Based on the formula for finding the area of a circle S = π (D/2)2 or its simplified version S = 0.8 D², the cross section is determined.
- The diameter is 1.78 mm. Substituting the value into the expression and rounding the result to hundredths, we get 2.79 mm2.
For domestic purposes, you will need conductors with a cross section of 0.75; 1.5; 2.5 and 4 mm2.
Using a ruler and pencil
Calculating PS using a ruler and pencil
If you don't have a special meter, you can use a pencil and ruler. Operations are performed with the test image:
- An area of 5-10 cm is cleared of the insulating layer.
- The resulting wire is wound around a pencil. Full turns are laid tightly, there should be no space between them, the “tails” are directed up or down.
- Ultimately, a certain number of turns should be obtained; they need to be counted.
- The winding is applied to the ruler so that the zero division coincides with the first winding.
- The length of the segment is measured and divided by the number of turns. The resulting value is the diameter.
- For example, it turned out 11 turns, which occupy 7.5 mm. When dividing 7.5 by 11, 0.68 mm is the cable diameter. The cross section can be found using the formula.
The accuracy of the calculations is determined by the density and length of the winding.
Table of correspondence between wire diameter and cross-sectional area
If it is not possible to test the diameter or make a calculation when purchasing, you can use a table. The data can be photographed, printed or transcribed, and then used to find the standard or popular core size.
| Cable diameter, mm | Conductor cross-section, mm2 |
| 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 0,98 | 0,75 |
| 1,13 | 1 |
| 1,38 | 1,5 |
| 1,6 | 2 |
| 1,78 | 2,5 |
| 2,26 | 4 |
| 2,76 | 6 |
| 3,57 | 10 |
When purchasing an electrical cable, you will need to look at the parameters on the label. For example, VVNG 2x4 is used. The number of cores is the value after “x”. That is, the product consists of two elements with a cross section of 4 mm2. Based on the table, you can check the accuracy of the information.
Most often, the cable diameter is smaller than stated on the package. The user has two options - use a different one or choose a cable with a larger cross-sectional area in diameter. Having chosen the second one, you will need to check the insulation. If it is not solid, thin, or varies in thickness, choose products from another manufacturer.
Some special cases of simplifications
If the drawing shows sections, sections, views for regularly changing surfaces, they can be broken. This is done in a certain way. There are three restriction options.
The first type involves using a solid thin broken line. It can extend beyond the image border by 2-4 mm. Also, the outline of parts of a part can be connected by a solid wavy line or hatching.
To simplify the drawing, it is allowed to cut with a dotted line between the cutting plane and the observer. Complex slices are also used to improve understanding of graphics.
When depicting the holes of some parts (gear hubs, keyways, pulleys), only their outline is given. If the recess located on the round flange does not fall into the cutting plane, it is depicted in a section.
If there is an ornament or a continuous mesh on a part, it is allowed to depict only a small part of it or to simplify the elements of the design.
Such methods allow you to achieve purity of the drawing and make it easier to understand. After all, the use of engineering graphics to create all kinds of objects implies the use of a single symbolic language. Every specialist whose work involves this type of image should know it. The quality of the final result depends on this.
Having studied the types of sections, you can understand the basic principles of their implementation and understanding. By applying the recommendations of the standards, you can achieve good cleanliness of the drawing. This makes the process of its interpretation easier. Understanding the difference between view, section and section, knowing their classifications and the technology for correct drawing, a specialist can create the correct image. It can be easily understood by the technician who produces the workpiece or finished product, and will be able to create units and parts that meet all the requirements. The quality of the entire production depends on this process.