Metals began to be used in everyday life in ancient times. Copper was the first element that man began to use, since it was easy to find in nature and easy to process. It is no coincidence that archaeologists have found numerous objects made of copper. In the course of their development, people learned to make alloys from which tools and then weapons were made. Nowadays, research is being carried out to identify the strongest metals. Let's learn more about the properties and uses of the ten strongest metals in the world.
How are metals produced?
Metals are extracted from ores. Various complex methods and calculation systems are used to determine their contributions. Metal production is carried out in several stages:
- Development of an ore deposit. It can be open or closed. Sometimes extraction methods are combined. The open incision method is less dangerous.
- Ore purification. This process is carried out to extract useful components (ore concentrate) that will be used in further production.
- Metal mining. It is carried out using electrolytic or chemical reduction methods.
- Metal smelting. This is achieved in technological furnaces, where raw materials are heated to elevated temperatures. In addition, a reducing agent is used.
Development of an ore deposit (Photo: Instagram / polyus_official)
History of discovery
The concept of “metal” appeared in the Russian language in the 15th–16th centuries. It came from the German language. Since the 16th century, this concept has appeared in various books. This word began to gain popularity under Peter 1. Initially, it was used to describe various ores, alloys, and minerals. Lomonosov shared these concepts.
It is very difficult to find pure metal in nature. More often they are found in various ores and minerals. They can form various natural compounds - carbonates, oxides, sulfides.
Peter I
Characteristics of metals
Metals are a group of more than 90 simple substances from the periodic table. They are rarely found in nature in their pure form, so they are most often extracted from ores. It is the name given to a type of mineral that is a combination of several chemical components such as minerals and the same metals. Metals are characterized by several properties that are used to classify them into groups:
- Hardness - resistance to penetration of another, harder body into the material;
- hardness - resistance to destruction when exposed to external load;
- elasticity - a change in the shape of a material under the influence of external forces and its restoration after the cessation of these forces;
- plasticity - a change in the shape of a material under the influence of external influences and its restoration after eliminating this influence
- Abrasion resistance - maintaining the appearance and physical properties of the material after severe friction
- Viscosity is the ability of a material to stretch under the influence of external forces;
- Fatigue is the ability of a material to withstand repeated loads;
- Heat resistance - resistance to oxidative processes when heated to high temperatures.
Scientists have recently created an improved aluminum alloy, 6063, that kills bacteria. It is believed that it can be used to make door handles in hospitals and other public places.
Interesting Facts
- Titanium alloys, whose specific gravity exceeds the specific gravity of aluminum by approximately 70%, are 4 times stronger than aluminum. Therefore, from the point of view of specific strength, alloys containing titanium are more viable for use in aircraft construction.
- Many aluminum alloys exceed the specific strength of steels containing carbon. Aluminum alloys are very ductile, resistant to corrosion and can be easily processed by pressure and cutting.
- Plastics have higher specific strength than metals. However, due to insufficient rigidity, mechanical strength, aging, increased fragility and low heat resistance, laminates, textolite and sandwich plastics have limited use, especially in large-sized structures.
- It was found that ferrous and non-ferrous metals and many of their alloys are inferior to fiberglass in terms of corrosion resistance and specific strength.
The mechanical properties of metals are an important factor influencing their practical use. When designing any structure, part or machine and choosing a material, it is necessary to take into account all the mechanical properties that it possesses.
Ruthenium
The second place in the ranking of the most durable metals in the world is occupied by ruthenium, a silvery metal belonging to the platinum group. Its peculiarity is the presence of living organisms in the muscle tissue. Valuable properties of ruthenium are high strength, hardness, refractoriness, chemical resistance, and the ability to form complex compounds. Ruthenium is considered a catalyst for many chemical reactions and acts as a material for the manufacture of electrodes, contacts, and sharp tips.
Tungsten
It is characterized by high refractoriness and also belongs to the strongest metals on planet Earth. Being a solid element of white-gray color with a characteristic shine, tungsten is high-strength, refractory, and resistant to acidic and alkaline environments. Endowed with malleability, as temperatures rise, W self-heats and also stretches into a thin thread used in lamps.
Rating of the strongest elements in the world
There are a large number of well-known metals and alloys. Among the strongest are 10 elements.
Tantalum
A metal called tantalum, which was discovered in 1802, ranks third on our list. It was discovered by the Swedish chemist A. G. Ekeberg. For a long time it was believed that tantalum is identical to niobium. However, the German chemist Heinrich Rose managed to prove that these are two different elements. Scientist Werner Bolton from Germany was able to isolate pure tantalum in 1922. This is a very rare metal. The largest deposits of tantalum ore were discovered in Western Australia.
Due to its unique properties, tantalum is a highly sought-after metal. It finds a variety of uses:
- In medicine, tantalum is used in the production of wires and other components that can bind tissue and even act as a bone substitute;
- Alloys containing tantalum are resistant to aggressive environments and are therefore used in the aerospace and electronics industries;
- Tantalum is also used to produce energy in nuclear reactors;
- It is also widely used in the chemical industry.
Titanium
The last place in the top ten hardest metals is titanium. The first pure form of this element was obtained by the chemist J. J. Berzelius of Sweden in 1825. Titanium is a lightweight, silver-white titanium metal that is very hard and resistant to corrosion and mechanical stress. Titanium alloys are used in many branches of mechanical engineering, medicine and the chemical industry.
Iridium
Iridium is at the top of the list of the hardest metals. It was discovered at the beginning of the 19th century by the English chemist Smithson Tennant. Iridium has the following physical properties:
- It has a silvery-white color;
- Its melting point is 2466 oC;
- Its boiling point is 4,428 °C;
- Its resistivity is 5.3-10-8 Ohm-m.
Because iridium is the hardest metal on the planet, it is difficult to work with. However, it is still used in various industrial applications. For example, it is used to make small balls that are used in pens. Iridium is also used in the production of components for space rockets and some automotive parts.
Very little iridium occurs in nature. Findings of this metal are a kind of proof that meteorites fell where it was found. These cosmic bodies contain significant amounts of this metal. Scientists believe that our planet is also rich in iridium, but its deposits are closer to the Earth's core.
Tungsten
The hardest metal found in nature. This rare chemical element is also the most refractory of the metals (3422 °C).
It was first discovered as an acid (tungsten trioxide) in 1781 by Swedish chemist Carl Scheele. Further research led two Spanish scientists, Juan José and Fausto d'Elhujar, to the discovery of acid from the mineral tungramite, from which tungsten was then isolated using charcoal.
In addition to its widespread use in incandescent lamps, tungsten's ability to perform under extreme thermal conditions makes it one of the most attractive elements for the weapons industry. During World War II, metal played an important role in establishing economic and political relations between European countries.
Tungsten is also used to produce carbide and in the aerospace industry to produce rocket nozzles.
Beryllium
Now it’s better not to protect this metallic beauty. Because beryllium is very toxic and also carcinogenic and causes allergies. If you breathe air containing beryllium dust or beryllium fumes, you may develop beryllium, a disease that affects the lungs.
However, beryllium is not only harmful, but also useful. For example, add just 0.5% beryllium to steel, and you will get springs that will be elastic even when brought to red heat. They can withstand billions of load cycles.
Beryllium is used in the aerospace industry to create heat shields and guidance systems, and to create fire-resistant materials. Even the vacuum tube of the Large Hadron Collider is made of beryllium.
Uranus
This naturally occurring radioactive substance is very widespread in the earth's crust, but is concentrated in certain hard rocks.
One of the hardest metals in the world, it has two important commercial uses - nuclear weapons and nuclear reactors. Therefore, the end products of the uranium industry are bombs and radioactive waste.
Rhenium
Rhenium is a very rare and expensive metal that, although found naturally in its pure form, is usually added to molybdenite.
If Iron Man's suit were made of rhenium, it could withstand temperatures of 2000°C without losing strength. What will happen to Iron Man inside the suit after such a “fire show” is kept silent.
The metal is used in the petrochemical and chemical industries. This metal is used in the petrochemical industry, electronics and electrical engineering, and in aircraft and rocket engines.
Osmium
Silvery, bluish metal of light color.
It belongs to the platinum group and is considered one of the densest elements. It is characterized by hardness. Os is a brittle metal, but it is resistant to mechanical stress and acid-resistant. Scientists have recorded the presence of osmium in metal meteorites. Forming an ideal composition with other elements, it is widely used in medicine, electronics, chemistry and petrochemistry, rocket science, and is widely used in the production of pens.
Chromium
Chrome is a blue-white metal. It has high strength and hardness, as well as strong magnetic properties. It does not become brittle and is resistant to acids and alkalis.
It is used in the production of various alloys that are used in medical equipment. Cr is also used in the synthesis of artificial rubies, and chromium salts are used for wood preservation and leather tanning.
Ruthenium
The name of the second most powerful metal in the ancient language, ruthenium, means Russia. This metal has a silvery color, belongs to the platinum group and is found in the muscle tissue of all living creatures on earth.
It is a high-strength, hard, refractory metal, resistant to chemicals and capable of forming complex compounds. Ruthenium is used in the aerospace, medical and electronics industries, and as an additive to give gold its black color.
Graphene
Molecular lattice of graphene. The first item on our list is a material that is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries. When safety comes first and launching rockets into space seems very dangerous, the use of graphene is simply necessary. It is 200 times stronger than steel. Graphene consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a triangular lattice.
Iron and steel
As a pure substance, iron is not as hard compared to other participants in the rating. However, due to the minimal cost of extracting it, it is often used in combination with other elements to produce steel.
Steel is a very hard alloy made from iron and other elements such as carbon. It is the most commonly used material in construction, mechanical engineering and other industries. And even if you have nothing to do with them, you still use steel every time you cut food with a knife (unless it's ceramic, of course).
Artificial metal
In 2015, Californian scientists created microplates. It is currently the lightest metal on Earth, consisting of 99.99% air. However, due to its special design, the element has high strength. It is an interweaving of tubes, each of which is the size of 0.001 human hair. The amazing properties of microfiber are just beginning to be fully exploited in industry.
Carbon fiber
Black carbon fiber composite. The characteristics of carbon fiber that make it an excellent choice for military vehicles, missiles, and sports car parts are its high stiffness and very low weight. Carbon fiber can also withstand very high temperatures and is highly resistant to a variety of abrasive chemicals. Essentially, carbon fiber is super-dense, aligned carbon atoms that are 5 to 10 micrometers in diameter.
Table of tensile strength of metals
| Metal | Purpose | Strength, MPa |
| News | Pb | 18 |
| Tin | Sn | 20 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 62 |
| Aluminum | Al | 80 |
| Beryllium | Be | 140 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 170 |
| Copper | Cu | 220 |
| Cobalt | Co | 240 |
| Iron | Fe | 250 |
| Niobium | Nb | 340 |
| Nickel | Ni | 400 |
| Titanium | Ti | 600 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 700 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 950 |
| Tungsten | W | 1200 |
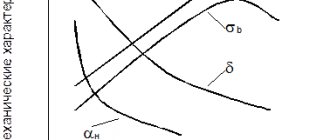
Mechanical properties of metals and alloys
The mechanical properties of metallic materials are as follows:
- Force. It lies in the ability of a material to resist cracking under the influence of external forces. The type of force depends on how the external forces act. It is divided into: compression, tension, torsion, bending, creep, fatigue.
- Plastic. This is the ability of metals and their alloys to change shape under load without destruction and to maintain this shape after applying a load. The ductility of a metal material is determined by its elongation. The greater the elongation that occurs as the cross-sectional area decreases, the more ductile the metal is. Materials with good ductility are well suited for work under pressure: forging, pressing. Plasticity is characterized by two quantities: relative shrinkage and elongation.
- Hardness. This quality of a metal lies in its ability to resist the penetration of a foreign body of greater hardness without causing irreversible deformation. Abrasion resistance and strength are the main characteristics of metals and alloys, which are closely related to hardness. Materials with such properties are used in the manufacture of tools used for metalworking: cutters, files, drills, taps. Often the hardness of a material is used to determine its wear resistance. For example, harder grades of steel wear less than softer grades.
- Impact resistance. The ability of alloys and metals to withstand shock loads. One of the properties of a material that can be used to absorb shock loads during machine operation, such as a wheel axle or crankshaft.
- Fatigue. This is the state of a metal that is constantly under tension. Fatigue of the metal material develops gradually and can lead to destruction of the product. The ability of metals to resist damage from fatigue is called strength. This property is a function of the nature of the alloy or metal, surface condition, nature of processing and operating conditions.
Beryllium
The metal is gray in color with a silvery tint, acquiring a matte tint when in contact with air due to the formation of an oxide film. The metal is characterized by hardness and is highly toxic. Unlike other metals, it conducts heat well and is characterized by low electrical resistance. Possessing unique properties, Be is used in aerospace, rocketry, nuclear energy, the metallurgical industry, nuclear energy, and laser technology. Given the high hardness of Be, it is used to produce alloying alloys, materials distinguished by their fire-resistant properties.
The lightest non-ferrous metals
The most common way of classifying non-ferrous metals according to their physical and chemical properties is into seven groups, among which the so-called heavy and light non-ferrous metals are distinguished. This traditional definition is based on the density of the material.
The main list includes aluminum, magnesium, titanium, lithium, tin and beryllium. This group also includes cadmium, thallium, gallium, bismuth, indium and other elements.
The production of light alloys is extremely energy-intensive, so enterprises specializing in this area of metallurgy are located near sources of cheap energy.
Rating of the lightest metals on earth
In this chapter, we'll focus on the world's lightest metals: what properties they have, what they're used for, and why they're interesting.
Lithium
Lithium is in group 1 of the periodic table of elements. It has the lowest atomic mass of all metals - only 3, after hydrogen and helium. A simple substance, lithium, under normal conditions has a silvery-white color.
It is the lightest alkali metal, its density is 0.534 g/cm³. Thanks to this, it floats not only in water, but also in paraffin. For its storage, paraffin, gasoline, mineral oils or petroleum ether are usually used. Lithium is very soft and pliable and can be easily cut with a knife. To melt this metal, it must be heated to 180.54 °C. It will only boil at 1340°C.
In nature, there are only two stable isotopes of this metal: lithium-6 and lithium-7. In addition to them, there are 7 artificial isotopes and 2 nuclear isomers. Lithium is an intermediate product in the reaction of converting hydrogen into helium, thereby participating in the formation of stellar energy.
Which metal is the lightest on earth
Lithium is known as the lightest metal and is widely used in alloys.
Lithium is used in:
- in the production of chemical anodes for energy sources;
- in optical work and experiments;
- High performance lasers.
For example, lithium hydroxide is used to produce the electrolyte in alkaline batteries. Lithium silicate and aluminate are also used in the production of ceramics as a base. This ceramic hardens at room temperature.
This property of lithium is used
- in metallurgy;
- in military affairs (in the development of advanced technologies);
- in the production of thermonuclear energy.
Lithium is also widely used in industry, as some compounds of this metal help whiten fabrics.
Interestingly, the use of lithium has expanded into medicine and pharmaceuticals. In psychiatry, lithium compounds are used to stabilize the emotional state of patients.
Magnesium (Mg)
Magnesium is a malleable metal with an atomic mass of 24.307 °u and a density of 1.7 g/cm^3, which ranks 12th in the periodic table. It was first obtained in its pure form in 1808. It is malleable and easy to press and cut.
It has a high melting point (650 °C) and corrosion resistance. When creating magnesium-based alloys, the mechanical properties of the metal are significantly improved, which significantly expands the range of applications of this type of material.
One of the most abundant elements on Earth, it is found in both the Earth's crust and seawater, usually in salts and minerals. Natural deposits of native magnesium are extremely rare; only a few deposits have been found in Russia, Eastern Siberia and Tajikistan. It is believed that in 2020 the United States will become the largest producer of magnesium in the world.
Its main application is the production of various alloys, both light and ultra-light, which can be used in aircraft and automobiles. Due to its flammable properties, it is also used in pyrotechnics and in the production of incendiary and illumination projectiles for the defense industry.
In the past, photography would not have been possible without magnesium powder with oxidizers - although magnesium flashes are used much less frequently than before, they are still in great demand. Magnesium is also important for the proper functioning of the body and metabolic processes, therefore magnesium-based preparations are used in medicine, cardiology, neurology and gastroenterological diseases.
Potassium
Potassium is the second most abundant element on the periodic table and ranks 19th in molecular weight. Like lithium, it is not found in lump form due to its increased activity, so potassium is extracted from minerals.
It is very soft, silver in color and produces a purple flame when burned. Potassium interacts with oxygen, acids and water. Explosions are not uncommon, so working with this dangerous metal requires extreme caution and the use of protective equipment. If potassium particles come into contact with the skin, they will cause severe chemical burns. It should be stored in airtight containers with added substances that prevent the penetration of oxygen. This could be silicone or mineral oil.
Potassium obtained from rocks in its pure form is used:
- For the production of electrodes;
- In lamps, photovoltaic cells.
Potassium is used in the form of alloys:
- In peroxide synthesis;
- In work to determine the age of rocks;
- As an indicator in biology and medicine;
- As a coolant in reactors.
Potassium is most in demand in medicine for the production of various types of alloys. A significant portion of drugs are synthesized on the basis of this metal. In addition, it is the basis of vitamin complexes, the purpose of which is to support the cardiovascular system and acid-base balance in the body.
Sodium
Sodium is an inorganic compound that is also an alkali and does not occur in nature in its pure form. It is found in minerals such as borax, thenardite, halite and others. Sodium is obtained in the laboratory by melting table salt. This industrial process also synthesizes chlorine.
Like lithium and potassium, this metal reacts violently with oxygen, acids, carbon dioxide and alcohols. It may spontaneously ignite when mixed with fluorine or chlorine. When water is added, a small explosion occurs and caustic soda is formed.
Externally, it is very similar to potassium. Its color is silver, although it quickly darkens in open air. Useful characteristics for industry are its excellent conductivity of electricity and heat.
Sodium has the greatest temperature difference between its boiling and melting points. Thus, the first process occurs at a temperature of +883 °C, and the second at +98 °C. This is the reason why sodium is used in nuclear reactors because it can withstand critical temperatures.
In the human body, Na is necessary for normal metabolism. The lack of this useful element leads to neuralgia and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. However, too much of it can lead to high blood pressure and swelling.
Aluminum
The hardest metal among light and non-ferrous metals is aluminum. This element is identified with the golden mean, when you need a material that is not only weightless, but also resistant to any impact.
The baby rattle was the first product made of aluminum.
It is one of the few chemical elements that is directly involved in the production of everything that forms the basis of a modern household. The world's most popular metal has won the title of most useful in the 20th century. However, in the 21st century, little has changed. Aluminum alloys (harder than pure metal) are used in construction, cutlery, tools, furniture and more.
Uranus
The most common metal, it is highly durable and weakly radioactive under normal conditions. The discovery of uranium by scientists is considered a discovery on a planetary scale. It is endowed with paramagnetic properties, flexible, malleable and relatively plastic, thanks to these qualities it has found application in a variety of industrial fields: it is the basis for nuclear weapons, uranium compounds are used in the production of glass, as dyes.
Iridium
Iridium is considered the leader among all metals with high strength. The hard and refractory gray-white element belongs to the platinum group. Today it is almost never found on the surface of the Earth, but is often found in compounds with osmium. Due to its hardness, the impact on metal is difficult, and therefore processing is resistant to chemicals. Its significance in everyday life is very great. Iridium is used to give metals such as titanium, chromium and tungsten better resistance to acidic and alkaline environments. It is used for the manufacture of thermocouples, fuel tanks, thermoelectric generators, in medicine, and is widely used for alloys with platinum among jewelers.
Nature
Chromium
Chrome is a blue-white metal. It is characterized by high strength, hardness, pronounced magnetic properties, is not subject to hydrogen embrittlement, and is resistant to acidic and alkaline environments. It is used to create various alloys, which in turn are in demand for the manufacture of medical equipment. In addition, Cr is used in the synthesis of artificial rubies; chromium salts are used to preserve wood and tan leather.
How to increase the strength of metal
There are several ways to increase the strength of metals and alloys:
- Creation of alloys and metals with a defect-free structure. Work is underway to produce fibrous crystals (whiskers) that are several tens of times stronger than conventional metals.
- Obtaining an increase in volume and surface pressure artificially. Metal processing under pressure (forging, drawing, rolling, pressing) produces volumetric riveting, while rolling and shot blasting produces surface riveting.
- Formation of metal alloys using elements from the periodic table.
- Cleaning metal from impurities it contains. As a result, the mechanical properties of the metal are improved, and the propagation of cracks is significantly reduced.
- Elimination of metal surface roughness.
Rhenium
The transition silver metal rhenium takes the seventh position on our list. The assumption about the existence of this element was made by D.I. Mendeleev in 1871, and chemists from Germany managed to discover it in 1925. Just 5 years after this, it was possible to establish the extraction of this rare, durable and refractory metal. At that time, it was possible to obtain 120 kg of rhenium per year. Now the amount of annual metal production has increased to 40 tons. It is used for the production of catalysts. It is also used to make electrical contacts that can self-clean.
Rhenium