If strength is generally understood as the ability of solids to resist destruction and maintain the shape of a product, then the following metals can be classified as super-strong and durable metals.
Name titanium
was appropriated by Martin Klaproth, a German researcher who discovered a new metal not for its chemical qualities, but in honor of the mythological heroes of the children of the earth - the titans.
The occurrence of titanium in nature is in 10th place; it is most concentrated in minerals. Without this metal, the latest discoveries in the field of rocket, ship and aircraft construction would not be possible. Titanium is used in all areas of industry, in the manufacture of medical implants and body armor in the food industry and agriculture.
2nd place
Light gray tungsten
, literally translated as wolf's cream, is the most refractory metal, so it is indispensable in the manufacture of heat-resistant surfaces and products. The filament in a regular light bulb is made of tungsten filament.
That metal is used in ballistic missiles, in the manufacture of shells and bullets, and in gyroscopic high-speed rotors.
3rd place
Tantalum
It is almost impossible to modify, because it begins to melt at a temperature of 3015 degrees Celsius, and boils at a boiling point of 5300 degrees. It is impossible for an ordinary person to even imagine such heat. The bluish-gray metal is the most indispensable in modern medicine; wire and sheets are made from it to cover damaged bones.
Molybdenum discovered in 1817
, steel-gray metal is practically never found in its pure form. The refractoriness of this metal is amazing, the melting point of which exceeds 2620 degrees. Molybdenum has found its greatest use in the military industry, where gun and armor steels are made.
5th place
Aviation and mechanical engineering, nuclear energy and astronautics use niobium
, a metal very similar in its properties to tantalum. Niobium is practically unaffected by any substances, neither salts nor acids, it is difficult to melt and difficult to oxidize, which is what makes the unique metal so in demand.
6th place
The heaviest metal on earth is iridium
It has the most durable anti-corrosion properties; even aqua regia cannot melt it. Adding iridium to other alloys increases their ability to resist corrosion.
7th place
Beryllium
is one of the rare metals that are mined in the earth. Its unique qualities, such as high thermal conductivity and fire resistance, have made this metal indispensable in the manufacture of nuclear reactors. Beryllium alloys rightfully occupy a leading place in the aerospace and aviation industries.
8th place
Light blue chrome
, which is also one of the strongest metals, due to its unique properties, when added to steel alloys, it makes them harder and more corrosion-resistant. Chrome parts have a beautiful appearance that does not change over time.
9th place
The Saxons treat their legends with care; the name of the hero of one of them, Kobold, was immortalized in the name of the metal - cobalt
. Very often, when mining ore, seekers mistook the gray-pink metal for silver.
Refractory metal, as an additive, increases the heat resistance, hardness and wear resistance of steel. Thanks to its unique qualities, cobalt is indispensable in metal-cutting machines.
Hafnium
– a light gray metal with unique qualities is mined from zirconium ore. Solid, refractory hafnium has a unique feature; the fact is that its temperature-capacity dependence is anomalous and does not fall under any laws of physics.
Hafnium is used in nuclear energy and optics, for strengthening various alloys and making glass for X-rays; it is difficult to imagine military production without it.
The use of metals in everyday life began at the dawn of human development, and the first metal was copper, since it is available in nature and can be easily processed. It is not without reason that archaeologists during excavations find various products and household utensils made of this metal. In the process of evolution, people gradually learned to combine various metals, obtaining increasingly durable alloys suitable for making tools, and later weapons. Nowadays, experiments continue, thanks to which it is possible to identify the strongest metals in the world.
- high specific strength;
- resistance to high temperatures;
- low density;
- corrosion resistance;
- mechanical and chemical resistance.
Titanium is used in the military industry, aviation medicine, shipbuilding, and other areas of production.
The most famous element, considered one of the strongest metals in the world, and under normal conditions is a weak radioactive metal. In nature, it is found both in a free state and in acidic sedimentary rocks. It is quite heavy, widely distributed everywhere and has paramagnetic properties, flexibility, malleability, and relative ductility. Uranium is used in many areas of production.
Known as the most refractory metal in existence, it is one of the strongest metals in the world. It is a solid transitional element of a shiny silver-gray color. It has high strength, excellent refractoriness, and resistance to chemical influences. Due to its properties, it can be forged and drawn into a thin thread. Known as tungsten filament.
Among the representatives of this group, it is considered a high-density transition metal with a silvery-white color. It occurs in nature in its pure form, but is found in molybdenum and copper raw materials. It is characterized by high hardness and density, and has excellent refractoriness. It has increased strength, which is not lost due to repeated temperature changes. Rhenium is an expensive metal and has a high cost. Used in modern technology and electronics.
A shiny silver-white metal with a slightly bluish tint, it belongs to the platinum group and is considered one of the strongest metals in the world. Similar to iridium, it has a high atomic density, high strength and hardness. Since osmium is a platinum metal, it has properties similar to iridium: refractoriness, hardness, brittleness, resistance to mechanical stress, as well as to the influence of aggressive environments. It has found wide application in surgery, electron microscopy, the chemical industry, rocketry, and electronic equipment.
It belongs to the group of metals and is a light gray element with relative hardness and high toxicity. Due to its unique properties, beryllium is used in a wide variety of production areas:
- nuclear energy;
- aerospace engineering;
- metallurgy;
- laser technology;
- nuclear energy.
Due to its high hardness, beryllium is used in the production of alloying alloys and refractory materials.
Next on the list of the ten strongest metals in the world is chromium - a hard, high-strength metal of a bluish-white color, resistant to alkalis and acids. It occurs in nature in its pure form and is widely used in various branches of science, technology and production. Chromium is used to create various alloys that are used in the manufacture of medical and chemical processing equipment. When combined with iron, it forms an alloy called ferrochrome, which is used in the manufacture of metal-cutting tools.
Tantalum deserves bronze in the ranking, as it is one of the strongest metals in the world. It is a silvery metal with high hardness and atomic density. Due to the formation of an oxide film on its surface, it has a leaden tint.
The distinctive properties of tantalum are high strength, refractoriness, resistance to corrosion, and resistance to aggressive environments. The metal is a fairly ductile metal and can be easily machined. Today tantalum is successfully used:
- in the chemical industry;
- during the construction of nuclear reactors;
- in metallurgical production;
- when creating heat-resistant alloys.
The second place in the ranking of the most durable metals in the world is occupied by ruthenium, a silvery metal belonging to the platinum group. Its peculiarity is the presence of living organisms in the muscle tissue. Valuable properties of ruthenium are high strength, hardness, refractoriness, chemical resistance, and the ability to form complex compounds. Ruthenium is considered a catalyst for many chemical reactions and acts as a material for the manufacture of electrodes, contacts, and sharp tips.
The ranking of the most durable metals in the world is headed by iridium - a silver-white, hard and refractory metal that belongs to the platinum group. In nature, the high-strength element is extremely rare and is often combined with osmium. Due to its natural hardness, it is difficult to machine and is highly resistant to chemicals. Iridium reacts with great difficulty to exposure to halogens and sodium peroxide.
This metal plays an important role in everyday life. It is added to titanium, chromium and tungsten to improve resistance to acidic environments, used in the manufacture of stationery, and used in jewelry to create jewelry. The cost of iridium remains high due to its limited presence in nature.
Many lovers of interesting facts are interested in the question, which metal is the hardest? And it won’t be easy to answer this question offhand. Of course, any chemistry teacher will easily say correctly, without even thinking. But among ordinary citizens who last studied chemistry at school, not many will be able to give the answer correctly and quickly. This is due to the fact that since childhood everyone has been accustomed to making various toys from wire and has well remembered that copper and aluminum are soft and bend well, but steel, on the contrary, is not so easy to give the desired shape. A person deals with the three named metals most often, so he doesn’t even consider the other candidates. But steel is certainly not the hardest metal in the world. To be fair, it is worth noting that this is not a metal at all in the chemical sense, but a compound of iron and carbon.
What is titanium?
The hardest metal is titanium. Pure titanium was first obtained in 1925. This discovery created a sensation in scientific circles. Industrialists immediately drew attention to the new material and appreciated the benefits of its use. According to the official version, the hardest metal on Earth got its name in honor of the indestructible Titans, who, according to ancient Greek mythology, were the founders of the world.
According to scientists, the total world reserves of titanium today are about 730 million tons. At the current rate of extraction of fossil raw materials, there will be enough for another 150 years. Titanium ranks 10th in natural reserves among all known metals. The world's largest titanium producer is Russian, which satisfies up to 35% of global needs. The company is engaged in the full processing cycle from ore mining to the manufacture of various products. It occupies about 90% of the Russian titanium production market. About 70% of finished products are exported.
Titanium is a light, silver-colored metal with a melting point of 1670 degrees Celsius. It exhibits high chemical activity only when heated; under normal conditions it does not react with most chemical elements and compounds. It is not found in nature in its pure form. Common in the form of rutile (titanium dioxide) and ilmenite (a complex substance consisting of titanium dioxide and ferrous oxide) ores. Pure titanium is isolated by sintering the ore with chlorine and then displacing the more active metal (usually magnesium) from the resulting tetrachloride.
Uranus
One of the most famous elements, which is one of the hardest metals in the world, is uranium. It is a light gray metal with weak radioactivity. Uranium is considered one of the heaviest metals - its specific gravity is 19 times that of water. It also has relative ductility, malleability and flexibility, and paramagnetic properties. On the Moss scale, the hardness of the metal is 6, which is considered very high.
Previously, uranium was almost never used, but was found only as ore waste during the extraction of other metals - radium and vanadium. Today, uranium is mined in deposits, the main sources being the US Rocky Mountains, the Republic of Congo, Canada and the Union of South Africa.
Despite its radioactivity, uranium is actively consumed by humanity. It is most in demand in nuclear energy - it is used as fuel for nuclear reactors. Uranium is also used in the chemical industry and in geology to determine the age of rocks.
Military engineering also did not miss the incredible specific gravity indicators. Uranium is regularly used to create the cores of armor-piercing projectiles, which, due to their high strength, do an excellent job of the task.
Uranium is the hardest metal, but it is radioactive
Industrial applications of titanium
The hardest metal has a fairly wide range of applications in many industries. Amorphously arranged atoms provide titanium with the highest level of tensile and torsional strength, good impact resistance, and high magnetic qualities. The metal is used to make air transport bodies and missiles. It copes well with the enormous loads that cars experience at great heights. Titanium is also used in the production of hulls for submarines, as it can withstand high pressure at great depths.
In the medical industry, metal is used in the manufacture of dentures and dental implants, as well as surgical instruments. The element is added as an alloying additive to some grades of steel, which gives them increased strength and resistance to corrosion. Titanium is well suited for casting as it produces perfectly smooth surfaces. It is also used to make jewelry and decorative items. Titanium compounds are also actively used. Dioxide is used to make paints, whitewash, and is added to paper and plastic.
Organic titanium salts are used as a hardening catalyst in paint and varnish production. Various tools and attachments for processing and drilling other metals are made from titanium carbide. In precision engineering, titanium aluminide is used to produce wear-resistant elements that have a high safety margin.
The hardest metal alloy was obtained by American scientists in 2011. Its composition included palladium, silicon, phosphorus, germanium and silver. The new material was called "metallic glass". It combines the hardness of glass and the plasticity of metal. The latter prevents cracks from spreading, as happens with standard glass. Naturally, the material was not put into widespread production, since its components, especially palladium, are rare metals and are very expensive.
At the moment, the efforts of scientists are aimed at searching for alternative components that would preserve the properties obtained, but significantly reduce the cost of production. However, some parts for the aerospace industry are already being produced from the resulting alloy. If alternative elements can be introduced into the structure and the material becomes widespread, then it is quite possible that it will become one of the most popular alloys of the future.
- A common belief about hardness is diamond or damask steel/damascus steel. If the first mineral is superior to all simple substances existing on Earth that nature has created, then the amazing properties of blades made of rare steel are due to the skill of swordsmiths and additives from other metals. Many technical alloys, used, for example, for the production of super-hard cutters in the engineering industry, creating durable, reliable tools with unique properties, are associated with these additives in the usual symbiosis of iron and carbon, in short, traditionally called steel - chromium, titanium, vanadium, molybdenum, nickel. When readers ask what the hardest metal in the world is, they are bombarded with a barrage of conflicting information on the pages of websites. In this role, according to the authors of various articles, either tungsten or chromium, or iridium with osmium, or titanium with tantalum.
- Very high refractoriness.
- Resistant to corrosion and oxidation even when heated to high temperatures.
- Resistant to concentrated acids and other aggressive compounds.
- 10 -11% is their content in the solid shell of the planet.
- The total amount of pure metal produced per year is within the following limits: 4 tons for iridium, 1 t for osmium.
- The price of osmium is approximately equal to the price of gold.
In order to get through the jungle of not always correctly interpreted, albeit accurate facts, it is worth turning to the original source - the system of elements contained both in the composition and in other cosmic objects, left to humanity by the great Russian chemist and physicist D.I. Mendeleev. He had encyclopedic knowledge, made many scientific breakthroughs in knowledge about the structure, composition, and interaction of substances, in addition to the famous table based on the fundamental periodic law he discovered, named after him.
The planets closest to the Sun - Mercury, Venus, Mars, together with our planet, are classified as one - the terrestrial group. There are reasons for this not only among astronomers, physicists and mathematicians, but also among geologists and chemists. The reason for such conclusions among the latter is, among other things, the fact that they all mainly consist of silicates, i.e. various derivatives of the element silicon, as well as numerous metal compounds from Dmitry Ivanovich’s table.
In particular, our planet mostly (up to 99%) consists of ten elements:
But man, in addition to the iron and alloys based on it necessary for survival and development, has always been much more attracted to precious metals, often respectfully called noble metals - gold and silver, and later platinum.
According to the scientific classification adopted by chemists, the platinum group includes ruthenium, rhodium, palladium and osmium with iridium. All of them also belong to noble metals. Based on their atomic mass, they are conventionally divided into two subgroups:
The last two are of particular interest for our pseudo-scientific investigation on the topic of who is the hardest here. This is due to the fact that the large atomic mass compared to other elements: 190.23 for osmium, 192.22 for iridium, according to the laws of physics, implies a huge specific density, and, consequently, the hardness of these metals.
If dense, heavy gold and lead are soft, plastic substances that are easy to process, then osmium and iridium, discovered at the beginning of the 19th century, turned out to be fragile. Here it is necessary to remember that the measure of this physical property is that a diamond, which can be used to inscribe on any other hard material of natural or artificial origin without much effort, is also extremely fragile, i.e. It's fairly easy to break. Although, at first glance, this seems almost impossible.
In addition, osmium and palladium have many more interesting properties:
Therefore, along with platinum, including in the form of compounds with it, they are used in the production of catalysts for many chemical processes, high-precision devices, equipment, tools in the medical, scientific, military, and space sectors of human activity.
It is osmium and iridium, and scientists after research believe that this property is approximately equally given to them by nature, are the hardest metals in the world.
And everything would be fine, but not very good. The fact is that both their presence in the earth’s crust and, accordingly, the global production of these very minerals are negligible:
It is clear that these rare earth, expensive metals, despite their hardness, cannot even be used to a limited extent as raw materials for production; perhaps as additives to alloys, compounds with other metals to impart unique properties.
Mechanical properties of metals and alloys
The mechanical properties of metallic materials are as follows:
- Force. It lies in the ability of a material to resist cracking under the influence of external forces. The type of force depends on how the external forces act. It is divided into: compression, tension, torsion, bending, creep, fatigue.
- Plastic. This is the ability of metals and their alloys to change shape under load without destruction and to maintain this shape after applying a load. The ductility of a metal material is determined by its elongation. The greater the elongation that occurs as the cross-sectional area decreases, the more ductile the metal is. Materials with good ductility are well suited for work under pressure: forging, pressing. Plasticity is characterized by two quantities: relative shrinkage and elongation.
- Hardness. This quality of a metal lies in its ability to resist the penetration of a foreign body of greater hardness without causing irreversible deformation. Abrasion resistance and strength are the main characteristics of metals and alloys, which are closely related to hardness. Materials with such properties are used in the manufacture of tools used for metalworking: cutters, files, drills, taps. Often the hardness of a material is used to determine its wear resistance. For example, harder grades of steel wear less than softer grades.
- Impact resistance. The ability of alloys and metals to withstand shock loads. One of the properties of a material that can be used to absorb shock loads during machine operation, such as a wheel axle or crankshaft.
- Fatigue. This is the state of a metal that is constantly under tension. Fatigue of the metal material develops gradually and can lead to destruction of the product. The ability of metals to resist damage from fatigue is called strength. This property is a function of the nature of the alloy or metal, surface condition, nature of processing and operating conditions.
Who is for them?
But a person would not be himself if he had not found a replacement for iridium with osmium. Since it is inappropriate and too expensive to use them, then attention was not without success turned to other metals that have found their application in different situations and industries for the creation of new alloys, composite materials, production of equipment, machines and mechanisms for both civil and military use:
Although the hardest metal in the world, or rather two of them - iridium and osmium, have shown their unique properties only in laboratory conditions, and also as negligible percentage additives to alloys, other compounds for creating new materials necessary for humans should be grateful to nature and for this gift. At the same time, there is no doubt that the inquisitive minds of talented scientists and brilliant inventors will come up with new substances with unique properties, as has already happened with the synthesis of fullerenes, which turned out to be harder than diamond, which is already surprising.
When it comes to hard and durable metal, in one’s imagination a person immediately pictures a warrior with a sword and in armor. Well, or with a saber, and definitely made of Damascus steel. But steel, although durable, is not a pure metal; it is produced by alloying iron with carbon and some other additive metals. And, if necessary, the steel is processed to change its properties.
Interesting Facts
- Titanium alloys, whose specific gravity exceeds the specific gravity of aluminum by approximately 70%, are 4 times stronger than aluminum. Therefore, from the point of view of specific strength, alloys containing titanium are more viable for use in aircraft construction.
- Many aluminum alloys exceed the specific strength of steels containing carbon. Aluminum alloys are very ductile, resistant to corrosion and can be easily processed by pressure and cutting.
- Plastics have higher specific strength than metals. However, due to insufficient rigidity, mechanical strength, aging, increased fragility and low heat resistance, laminates, textolite and sandwich plastics have limited use, especially in large-sized structures.
- It was found that ferrous and non-ferrous metals and many of their alloys are inferior to fiberglass in terms of corrosion resistance and specific strength.
The mechanical properties of metals are an important factor influencing their practical use. When designing any structure, part or machine and choosing a material, it is necessary to take into account all the mechanical properties that it possesses.
Lightweight, durable silver-white metal
Each of the additives, be it chromium, nickel or vanadium, is responsible for a certain quality.
But titanium is added for strength - the hardest alloys are obtained. According to one version, the metal got its name from the Titans, the powerful and fearless children of the Earth goddess Gaia. But according to another version, the silvery substance is named after the fairy queen Titania.
Titanium was discovered by German and English chemists Gregor and Klaproth independently of each other, six years apart. This happened at the end of the 18th century. The substance immediately took its place in Mendeleev’s periodic table. Three decades later, the first sample of titanium metal was obtained. And the metal was not used for quite a long time due to its fragility. Exactly until 1925 - it was then, after a series of experiments, that pure titanium was obtained using the iodide method. The discovery was a real breakthrough. Titan turned out to be technologically advanced, and designers and engineers immediately paid attention to it. And now metal is obtained from ore mainly by the magnesium-thermal method, which was proposed in 1940.
If we touch upon the physical properties of titanium, we can note its high specific strength, strength at high temperatures, low density and corrosion resistance. The mechanical strength of titanium is two times higher than that of iron and six times higher than that of aluminum. At high temperatures, where light alloys no longer work (magnesium and aluminum based), titanium alloys come to the rescue. For example, an airplane at an altitude of 20 kilometers reaches a speed three times higher than the speed of sound. And the temperature of its body is about 300 degrees Celsius. Only titanium alloy can withstand such loads.
The metal ranks tenth in terms of prevalence in nature. Titanium is mined in South Africa, Russia, China, Ukraine, Japan and India. And this is not a complete list of countries.
Titanium is the world's strongest and lightest metal
The list of possibilities for using metal is respectable. These are the military industry, osteoprostheses in medicine, jewelry and sports products, mobile phone circuit boards and much more. Rocket, aircraft, and shipbuilding designers constantly praise titanium. Even the chemical industry has not left the metal unattended. Titanium is excellent for casting because the contours when cast are precise and have a smooth surface. The arrangement of atoms in titanium is amorphous. And this guarantees high tensile strength, toughness, excellent magnetic properties.
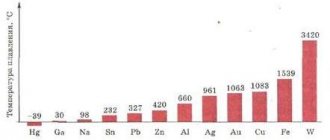
Table of tensile strength of metals
| Metal | Purpose | Strength, MPa |
| News | Pb | 18 |
| Tin | Sn | 20 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 62 |
| Aluminum | Al | 80 |
| Beryllium | Be | 140 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 170 |
| Copper | Cu | 220 |
| Cobalt | Co | 240 |
| Iron | Fe | 250 |
| Niobium | Nb | 340 |
| Nickel | Ni | 400 |
| Titanium | Ti | 600 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 700 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 950 |
| Tungsten | W | 1200 |
Hard metals with the highest density
Some of the hardest metals are also osmium and iridium.
These are substances from the platinum group; they have the highest, almost identical, density. Iridium was discovered in 1803. The metal was discovered by a chemist from England, Smithson Tennat, while studying natural platinum from South America. By the way, “iridium” is translated from ancient Greek as “rainbow”.
The hardest metal is quite difficult to obtain, since it is almost absent in nature. And often the metal is found in meteorites that fell to the ground. According to scientists, on our planet the content of iridium should be much higher. But due to the properties of the metal - siderophilicity - it is located at the very depths of the earth's bowels.
Iridium is quite difficult to process both thermally and chemically. The metal does not react with acids, even combinations of acids at temperatures less than 100 degrees. At the same time, the substance is subject to oxidation processes in aqua regia (this is a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acids).
The iridium isotope 193 m 2 is of interest as a source of electrical energy. Since the half-life of the metal is 241 years. Iridium has found widespread use in paleontology and industry. It is used in making pen quills and determining the age of different layers of the earth.
But osmium was discovered a year later than iridium. This solid metal was found in the chemical composition of a precipitate of platinum, which was dissolved in aqua regia. And the name “osmium” comes from the ancient Greek word for “smell.” The metal is not subject to mechanical stress. Moreover, one liter of osmium is several times heavier than ten liters of water. However, this property has not yet been used.
Osmium is mined in American and Russian mines. Its deposits are also rich in South Africa. Quite often the metal is found in iron meteorites. Of interest to specialists is osmium-187, which is exported only from Kazakhstan. It is used to determine the age of meteorites. It is worth noting that just one gram of the isotope costs 10 thousand dollars.
Well, osmium is used in industry. And not in its pure form, but in the form of a hard alloy with tungsten. Produced from the substance of incandescent lamps. Osmium is a catalyst in the production of ammonia. Cutting parts for surgical needs are rarely made from metal.
Characteristics of metals
Metals are a group of more than 90 simple substances from the periodic table. They are rarely found in nature in their pure form, so they are most often extracted from ores. It is the name given to a type of mineral that is a combination of several chemical components such as minerals and the same metals. Metals are characterized by several properties that are used to classify them into groups:
- Hardness - resistance to penetration of another, harder body into the material;
- hardness - resistance to destruction when exposed to external load;
- elasticity - a change in the shape of a material under the influence of external forces and its restoration after the cessation of these forces;
- plasticity - a change in the shape of a material under the influence of external influences and its restoration after eliminating this influence
- Abrasion resistance - maintaining the appearance and physical properties of the material after severe friction
- Viscosity is the ability of a material to stretch under the influence of external forces;
- Fatigue is the ability of a material to withstand repeated loads;
- Heat resistance - resistance to oxidative processes when heated to high temperatures.
Scientists have recently created an improved aluminum alloy, 6063, that kills bacteria. It is believed that it can be used to make door handles in hospitals and other public places.
The hardest pure metal
The hardest of the purest metals on the planet is chromium.
It lends itself perfectly to mechanical processing. The bluish-white metal was discovered in 1766 in the vicinity of Yekaterinburg. The mineral was then called “Siberian red lead.” Its modern name is crocoite. A few years after the discovery, namely, in 1797, the French chemist Vauquelin isolated a new metal from the metal, already refractory. Experts today believe that the resulting substance is chromium carbide. The name of this element is derived from the Greek “color”, because the metal itself is famous for the variety of colors of its compounds. Chromium is quite easy to find in nature and is common. You can find the metal in South Africa, which ranks first in production, as well as in Kazakhstan, Zimbabwe, Russia and Madagascar. There are deposits in Turkey, Armenia, India, Brazil and the Philippines. Experts especially value certain chromium compounds - chromium iron ore and crocoite.
How to increase the strength of metal
There are several ways to increase the strength of metals and alloys:
- Creation of alloys and metals with a defect-free structure. Work is underway to produce fibrous crystals (whiskers) that are several tens of times stronger than conventional metals.
- Obtaining an increase in volume and surface pressure artificially. Metal processing under pressure (forging, drawing, rolling, pressing) produces volumetric riveting, while rolling and shot blasting produces surface riveting.
- Formation of metal alloys using elements from the periodic table.
- Cleaning metal from impurities it contains. As a result, the mechanical properties of the metal are improved, and the propagation of cracks is significantly reduced.
- Elimination of metal surface roughness.
The hardest metal in the world is tungsten
Tungsten is a chemical element that is the hardest when compared to other metals.
Its melting point is unusually high, higher only for carbon, but it is not a metallic element. But the natural hardness of tungsten at the same time does not deprive it of flexibility and pliability, which allows you to forge any necessary parts from it. It is its flexibility and heat resistance that makes tungsten an ideal material for smelting small parts of lighting fixtures and TV parts, for example.
Tungsten is also used in more serious areas, for example, weapons manufacturing - for the manufacture of counterweights and artillery shells. Tungsten owes this to its high density, which makes it the main substance of heavy alloys. The density of tungsten is close to that of gold - only a few tenths make up the difference.
On the website you can read which metals are the softest, how they are used, and what is made from them. Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.Zen
How are metals produced?
Metals are extracted from ores. Various complex methods and calculation systems are used to determine their contributions. Metal production is carried out in several stages:
- Development of an ore deposit. It can be open or closed. Sometimes extraction methods are combined. The open incision method is less dangerous.
- Ore purification. This process is carried out to extract useful components (ore concentrate) that will be used in further production.
- Metal mining. It is carried out using electrolytic or chemical reduction methods.
- Metal smelting. This is achieved in technological furnaces, where raw materials are heated to elevated temperatures. In addition, a reducing agent is used.
Development of an ore deposit (Photo: Instagram / polyus_official)