With this cutting method, a high-temperature plasma jet is used as a cutting tool, the power of which allows cutting ferrous or non-ferrous metals up to 20 centimeters thick.
Most often, plasma cutting of metal is carried out using CNC, that is, using special programmable machines.
Photos of the process:
Such machines allow cutting metals according to specified parameters on an industrial scale, ensuring high speed and efficiency.
In addition, plasma cutting on CNC machines makes it possible to ensure fairly high safety when working with plasma, subject to all safety regulations.
Tools for plasma cutting of metals usually have fairly large dimensions and also require a powerful source of electrical energy.
But modern technologies make it possible to create more compact devices with the help of which manual plasma cutting of metal is carried out.
Tools for manual cutting also consume quite a lot of energy, in addition, manual cutting is carried out at a much lower speed than the same plasma cutting on a CNC machine.
The accuracy of manual plasma cutting is somewhat lower, but on the side of this method there is greater versatility, since devices for manual cutting are small in size and can be easily transported almost anywhere.
To operate such a device, you only need an electrical connection.
Technology and operating principle
Plasma cutting tools allow you to work with almost any metal or alloy, even super-strong ones or those with other special properties.
Also, plasma metal cutting technology can significantly speed up the cutting of metal parts of small and medium thickness compared to gas flame cutting.
Plasma arc method
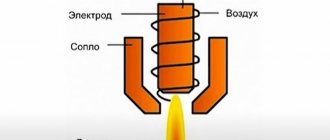
In order to create plasma, an electric arc is created between the electrode of the cutting machine and the metal being cut, and at the same time, high-pressure gas is supplied from a nozzle located next to the electrode.
An electric arc converts a gas stream into a plasma stream with a temperature of 5 to 30 thousand degrees. In this case, the speed of the plasma jet reaches more than one and a half kilometers per second.
Visual video:
A plasma flow with such temperature and speed indicators can easily cope with cutting even the most durable alloys.
At the same time, plasma arc cutting of metals ensures high quality and cleanliness of the resulting cut and low heating of the part being cut, which eliminates thermal deformation of the workpiece, which is often a serious problem with other methods of cutting metals.
Plasma arc cutting of metal involves the inclusion of the metal being cut into an electrical circuit, that is, the cut is carried out using an electric arc.
Thus, they cut metals that are extremely difficult or impossible to process in any other way, these include corrosion-resistant steels, titanium, and copper.
Also, using this method it is easy to cut: aluminum, cast iron and other metals, alloys, ferrous or non-ferrous.
When cutting with a plasma arc, the metal is melted at the cut point, then the molten metal is blown out by a gas stream.
Plasma jet cutting method
There is also a cutting method using a plasma stream. In this case, the metal being cut is not a component of the electrical circuit.
In this case, there is also an electric arc, but it passes from the tip of the electrode to the inner wall of the plasmatron nozzle.
Thus, it is possible to cut non-conductive materials, cutting metal is carried out due to the action of high-speed plasma, the electric arc is used only to create plasma and give it high speed.
It is this method that is used for the manufacture of manual plasma cutting devices.
Plasma cutting technologies
The plasma jet cutting method is indispensable when cutting thin sheets of metal; in other cases (with the exception of manual cutting) it is used quite rarely.
In manual cutting, the plasma flow cutting method is predominantly used, since with the help of this technology it is possible to create compact devices with low weight and energy consumption.
Purpose of nozzles
The nozzles through which the gas is supplied require cooling; air cooling is most often used, but water-cooled equipment is also available.
Nozzles are usually used with an adjustable nozzle diameter, which allows you to fine-tune the speed and force of gas flow.
Thanks to this, the same device can be configured to work effectively with almost any metal, the widest range of thickness and material composition.
Typically, air-cooled injectors are cheaper and more reliable, but liquid-cooled injectors can produce significantly more power than air-cooled injectors.
Purpose of electrodes
The electrodes used in plasma cutting machines are made from tungsten-lanthanum alloys.
This is due to the fact that the electrode must have high electrical conductivity and at the same time must be resistant to high temperatures.
Gases that are used to create plasma are divided into active and inactive.
Oxygen or air plasma cutting of metal works using active gases; these types of methods are used for cutting ferrous metals and their alloys (steel, cast iron).
For cutting non-ferrous metals and alloys, cutting using inactive gases such as argon, nitrogen, hydrogen is best suited.
Schematic drawing of a cutting plasma torch
Since the physical principle of plasma cutting of metal allows you to work with almost any metal, ensure high safety and speed of work, this method of metal processing has become quite widespread in a wide variety of industries.
Metal cutting using a plasma jet allows for complex shaped cutting.
In addition to quickly cutting out complex technical parts, artistic plasma cutting of metal is also possible, which allows you to create real works of art or decorative elements even from very refractory alloys.
The technology involves various modes of plasma cutting of metal, which allow you to quickly adjust the equipment to work not only with a certain type of alloy, but also with workpieces of a certain thickness.
Thanks to the various operating modes of the equipment, you can easily select the desired mode in most cases, which allows you to save both energy and equipment life.
Restrictions
| Limitation | Laser cutting | Plasma cutting |
| Minimum hole diameter | (0.3..0.4)S | (0.9..1.4)S* |
| Material to be cut | Metals, plastics, wood | metals |
| Maximum effective cutting thickness, mm | Up to 40 | Up to 150 |
| Cutting inside corners | + | With radius |
* - but not less than 2..3 mm, because plasma beam diameter 1..2.5 mm;
S – material thickness.
Main advantages
Plasma cutting of metals is one of the most modern and technically advanced methods of working with various metals.
This technology has emerged relatively recently, but has become widespread due to the number of advantages it offers over classical instrumental methods of working with metals.
The main advantages of plasma metal cutting are:
- cutting speed;
- versatility (you can work with any metals and alloys);
- there are no restrictions on the shape of the processed parts and the complexity of the cut out shapes;
- the cut that is formed during the cutting process has high surface cleanliness and quality.
In order to make the most of all the advantages of plasma cutting of metals, it is necessary to correctly and accurately select the operating modes of the installation for a specific material, and it is necessary to take into account many factors, such as:
- material properties;
- its thickness;
- plasma speed and temperature;
- cutting speed.
With the correct selection of these, as well as some other specific parameters, plasma cutting will be carried out quickly and with high quality.
Cutting metal using plasma is safer than conventional flame cutting, since the cutting process does not use cylinders with oxygen or flammable gases.
Plasma cutting speed table
Plasma cutting machines can have different dimensions and purposes.
Devices for manual plasma cutting are produced, but automatic plasma cutting of metal is most often used, due to the higher speed and accuracy of such equipment.
Devices for manual plasma cutting can be produced with various design features of the nozzle and cooling systems.
The most compact and versatile of them can work outdoors, in open construction or installation sites.
At the same time, plasma can be created both directly - from air, and from supplied gases, such as hydrogen or argon.
Another difference in such devices is the cooling system of the plasma torch; it can be either liquid or air.
The air system is better suited for working in open areas, but is less efficient and does not allow the device to develop truly high power.
If 20-30 years ago cutting metal with plasma was not widespread and was considered an exotic method of working with metals, today you can easily find companies that provide such services, or you can independently purchase equipment for manual plasma cutting.
Plasma cutting techniques
CNC plasma cutting machines can be equipped with various additional functionality and systems. One of the most useful is automatic height control, since the gap between the nozzle and the material being processed affects the bevel of the edges. As the distance increases, the bevel angle also increases, and as the distance decreases, the service life of the electrode and nozzle decreases. Cutting while maintaining a constant height has a positive effect on the quality of edges and the service life of consumables.
The speed of movement of the plasma torch during operation should ensure that the cutting angle of the lower edge from the upper edge is no more than 3-5°.
When developing control programs, the technologist is recommended to adhere to the following requirements to ensure minimal deformations:
- The holes are cut first.
- Cutting blanks starts from one edge, sequentially moving from one part to another in the direction of the opposite edge.
- When developing cards for cutting a set of workpieces, combined cuts are used, in which the cutting line cuts 2 parts at once.
- Long blanks are located closer to the edge of the sheet, from which cutting will begin, and short ones - closer to the middle and the opposite edge.
- Cutting workpieces more than 3 m long and more than 0.5 m wide is performed from the corner, and starts from the long edge.
- The parts that occupy most of the sheet are cut out first.
Photo 10. The process of cutting out a part
Popular metals
The most common is plasma cutting of sheet metal, this is due to the fact that this method today is one of the cheapest and fastest ways to work with sheet metal.
As a rule, equipment for working with metal sheets allows cutting sheets up to 50 mm thick, regardless of the alloy from which the sheet is made.
In addition, modern plasma cutting machines allow you to cut products of almost any geometric shape with a cutting accuracy of up to 0.5 mm.
There is often a need to cut pipes accurately and quickly. Unlike cutting sheet metal, plasma cutting of pipes is carried out in special machines that allow the pipe to be rotated during the cutting process.
The speed of such cutting can reach 9000 mm, and the cutting accuracy is up to 0.1 mm.
Thanks to these parameters, as well as its low price, plasma pipe cutting is one of the most affordable methods for accurately cutting pipes of a wide range of diameters and almost any alloy.
One of the most difficult materials to work with is aluminum and its alloys; this metal oxidizes quite easily, making it difficult to obtain a clean and accurate cut when cutting.
Aluminum
At the same time, plasma cutting of aluminum using air or active gases is not the best choice, since the cut surface will be covered with a thick layer of oxides, which will negatively affect the quality of the resulting parts.
To work with aluminum, plasma cutting machines that operate on inactive gases such as argon or nitrogen are required.
When used, there will be virtually no oxides on the aluminum cut surface; this type of method is one of the most suitable for working with this metal.
Despite the versatility of the method, plasma cutting of steel is the most common area of application of plasma equipment, due to the fact that steel is the most common alloy.
In addition, there is no need to use inert gases for cutting steel, which allows you to use even the simplest and most inexpensive equipment, obtaining excellent results both in terms of accuracy and speed.
Stainless steel
If plasma cutting of stainless steel is carried out, then it also does not require technical tricks, since this alloy is resistant to oxidation and it is quite possible to cut it using an air-arc type of plasma cutting, which is the cheapest and most accessible.
Another undoubted advantage is the ability to work even with very thin layers of metal without loss of cutting quality and accuracy.
It is plasma cutting of thin metal that is the main and almost the only competitor in this area for laser cutting.
This is due to the fact that it is extremely difficult to cut thin metal using mechanical processing methods, and they do not meet modern requirements for accuracy, speed and quality of the resulting cuts.
Cut quality
Requirements for cut quality are determined by the specifics of a particular production. For example, for a welded flange, the working surface is the plane of the flange. Accordingly, roughness, taper and edge burnout do not have a significant impact on the final quality of the product. In contrast, for a chain drive sprocket, surface finish, thermal distortion, and tooth profile accuracy are paramount, and laser cutting often provides a solution to these challenges.
The table shows the main differences in cut quality between laser and plasma cutting:
| Level of quality | Laser cutting | Plasma cutting |
| Edge taper | 0..2° | 0..10°* |
| Surface roughness Ra, µm | 1.25..2.5 | 6.3..12.5* |
| Scale (burr) | minimally | absent* |
| Melting of inserts, corners | minimally | Present* |
When plasma cutting, the amount of edge taper and the amount of scale can be reduced or completely removed by selecting optimal parameters, such as cutting speed and direction, the height of the plasma torch above the metal surface, and the current strength of the plasma source.
The quality of the cut is greatly influenced by the condition of the consumables (nozzle, electrode, protective screen, etc.). Surface roughness also depends on the cutting speed and operating current of the source. The lower the speed and the higher the current, the lower the roughness, but the greater the scale and overheating of the edge. Melting at corners and cutouts can be reduced by proper placement of cutouts and looping around the corners.
It should be noted that the accuracy of the positioning of the cutter and the dynamic characteristics of the coordinate system of the installations are of utmost importance for a high-quality result.
With a competent approach to operating a good plasma cutting machine, you can achieve excellent cut quality: in the foreground is a part cut with a laser machine, in the background - with a plasma cutting machine.
in the foreground there is a part cut out by a laser machine, in the background – a plasma cut one
How to choose a CNC machine?
To choose the right CNC plasma machine, you need to decide on the following points:
- Types of work - only straight cutting or with the possibility of cutting out parts of complex configurations.
- Maximum dimensions of sheet metal - the dimensions of the working area of the coordinate table depend on this.
- Maximum Material Thickness – Determines the wattage rating of the power source and the type of cutting gas used.
Photo 15. Cutting out a single part
One of the main characteristics of the equipment is the on-time (or duty cycle). This parameter determines the intensity of operation, namely the time period during which the machine can operate without interruptions for cooling.
PV is indicated as a percentage - if the on-time is 80%, this means that during a 10-minute operating cycle the installation can operate for 8 minutes at maximum loads. If this norm is exceeded, it may overheat and fail. However, most industrial CNC plasma cutters have a 100% duty cycle and are therefore designed for continuous operation throughout the entire work shift.
An equally important characteristic of the installations is the current supplied by the power source - it is this that determines the maximum thickness of the processed metal.
Types of machines
Plasma equipment with numerical control is produced in several types:
- Portable – installations of relatively small size, on which you can cut rolled metal of limited dimensions. Typically, the width of their working area is 1.5-3 m. If desired, such devices can be moved within the workshop or to another production site or facility.
Photo 12. Portable plasma cutting device
- Stationary – powerful automated lines with a coordinate table width of up to 8 m. They are installed permanently, movement is possible only with prior dismantling using special lifting equipment.
Photo 13. Stationary machine
Cost of CNC machines
Prices for CNC plasma machines vary widely. It all depends on the type and technical characteristics of the equipment, functionality, and overall dimensions of the working area.
The cost of a full-fledged automatic line starts from 1.5 million rubles. However, for most machines, the price is determined upon request, taking into account the individual needs of the customer, the expected types of work, installation configuration and other parameters.
Additionally, the total price may include costs for auxiliary equipment (compressors, ventilation system), as well as services such as installation, commissioning, personnel training, maintenance, etc.
Equipment Manufacturers
Today, plasma CNCs are produced by both foreign and domestic manufacturers. There are cars on sale in different price categories, but what costs more is not always of higher quality.
The domestic manufacturer PURM develops and produces CNC plasma machines taking into account the harsh Russian operating conditions. Equipment of this brand is successfully used by enterprises in central Russia and even in the Far North.
Photo 14. Equipment of the domestic manufacturer PURM
The company is engaged not only in the manufacture of installations, but also in the supply of spare parts, consumables, and components. If desired, you can order installation supervision, commissioning, and post-warranty service.