Recently, the use of plasma flow for cutting materials has become increasingly popular. The scope of use of this technology is further expanded by the appearance on the market of hand-held devices that are used to perform plasma cutting of metal.
Plasma cutting of metal of considerable thickness
The essence of plasma cutting
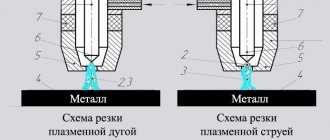
Plasma cutting involves local heating of the metal in the separation zone and its further melting. Such significant heating is achieved through the use of a plasma jet, which is formed using special equipment. The technology for producing a high-temperature plasma jet is as follows.
- Initially, an electric arc is formed, which is ignited between the electrode of the device and its nozzle or between the electrode and the metal being cut. The temperature of such an arc is 5000 degrees.
- After this, gas is supplied to the equipment nozzle, which increases the arc temperature to 20,000 degrees.
- When interacting with an electric arc, the gas is ionized, which leads to its transformation into a plasma jet, the temperature of which is already 30,000 degrees.
The resulting plasma jet is characterized by a bright glow, high electrical conductivity and exit speed from the equipment nozzle (500–1500 m/s). Such a jet locally heats and melts the metal in the processing zone, then it is cut, which is clearly visible even in a video of such a process.
In special installations, various gases can be used to produce a plasma jet. These include:
- ordinary air;
- technical oxygen;
- nitrogen;
- hydrogen;
- argon;
- steam produced by boiling water.
Metal cutting technology using plasma involves cooling the equipment nozzle and removing particles of molten material from the processing zone. These requirements are ensured by the flow of gas or liquid supplied to the area where cutting is carried out. The characteristics of the plasma jet generated on special equipment make it possible to use it to cut metal parts whose thickness reaches 200 mm.
Design and principle of operation of plasma cutting
Plasma cutting machines are successfully used at enterprises in various industries. With their help, they successfully cut not only metal parts, but also plastic and natural stone products. Thanks to such unique capabilities and its versatility, this equipment is widely used in machine-building and shipbuilding plants, in advertising and repair enterprises, and in the public utilities sector. A huge advantage of using such installations is that they allow you to obtain a very smooth, thin and precise cut, which is an important requirement in many situations.
Advantages and disadvantages of plasma cutting
As with other methods of cutting or cutting rolled metal, plasma cutting has both advantages and some disadvantages.
About the benefits
- Plasma cutting equipment is less expensive than laser equipment;
- The plasma torch easily copes with thick-walled rolled metal, which is inaccessible for laser cutting;
- Plasma can be used to cut any rolled metal, as well as conductive metals: steel, cast iron, copper, brass, titanium;
- The thickness of the cut made by plasma equipment depends on the type of device and tips. Devices that have a minimum cutting thickness significantly reduce the percentage of metal loss with an increase in concentrated plasma flow;
- the cut does not require additional processing;
- it is possible to perform complex shaped cutting;
- non-metallic materials can be cut with plasma;
- safety of plasma cutting equipment. This parameter is ensured by the absence of cylinders containing compressed gas. They are the cause of explosions or fires;
- with automatic cutting, especially with CNC machines, user intervention is minimal, which allows rational use of the labor of maintenance personnel.
With so many advantages, there are not so many disadvantages.
- Twenty centimeter thick metal is not available for plasma cutting.
- It is necessary to monitor the deflection angle, which should not exceed 50.
- One machine – one cutter. It is impossible to cut with two cutters at the same time.
Plasma cutting equipment
The modern market offers devices that cut metal using plasma, of two main types:
- indirect action devices - cutting is performed in a non-contact manner;
- direct action devices - contact cutting.
The first type of equipment, in which an arc is ignited between the electrode and the torch nozzle, is used for processing non-metallic products. Such installations are mainly used in various enterprises; you will not find them in a home craftsman’s workshop or in a repairman’s garage.
Plasma cutting machine Resanta IPR-25
In devices of the second type, an electric arc is ignited between the electrode and the part itself, which, naturally, can only be made of metal. Due to the fact that the working gas in such devices is heated and ionized throughout the entire gap (between the electrode and the part), the plasma jet in them has a higher power. This type of equipment can be used to perform manual plasma cutting.
Any plasma cutting machine operating on the contact principle consists of a standard set of components:
- power supply;
- plasma torch;
- cables and hoses used to connect the plasma torch to the power source and the working gas supply source;
- gas cylinder or compressor to obtain a jet of air at the required speed and pressure.
The main element of all such devices is the plasmatron, which distinguishes such equipment from conventional welding equipment. Plasma torches or plasma cutters consist of the following elements:
- working nozzle;
- electrode;
- an insulating element that is highly heat resistant.
Manual plasma cutting torch
The main purpose of a plasma torch is to convert the energy of an electric arc into thermal plasma energy. The gas or air-gas mixture coming out of the plasma torch nozzle through a small diameter hole passes through a cylindrical chamber in which the electrode is fixed. It is the nozzle of the plasma cutter that provides the required speed and shape of the flow of the working gas, and, accordingly, the plasma itself. All manipulations with such a cutter are performed manually by the equipment operator.
Considering the fact that the operator has to hold the plasma cutter suspended, it can be very difficult to ensure high quality metal cutting. Often, parts produced using manual plasma cutting have uneven edges, traces of sagging and jerking. In order to avoid such disadvantages, various devices are used: stands and stops, which allow for smooth movement of the plasma torch along the cutting line, as well as a constant gap between the nozzle and the surface of the part being cut.
Air or nitrogen can be used as the working and cooling gas when using manual equipment. This air-gas jet is also used to blow molten metal out of the cutting zone. When using air, it is supplied from a compressor, and nitrogen comes from a gas cylinder.
Quality of parts
Comparing the quality of the resulting parts and based on the cost of consumables, we can come to the conclusion that laser cutting is more effective than plasma cutting for thinner sheet materials, and plasma cutting for thicker ones. It should be taken into account that operating costs for both types of cutting vary widely and are largely determined by the geometric parameters of the workpiece, the number of holes in it, and the type and thickness of the material being cut.
| Options | Laser cutting | Plasma cutting |
| Cutting width | The cutting width is constant (0.2 - 0.375 mm) | The cutting width is not constant due to the instability of the plasma arc (0.8 - 1.5 mm) |
| Cutting accuracy | Typically ±0.05 mm (0.2 - 0.375 mm) | Depends on the degree of wear of consumables ±0.1 - ±0.5 mm |
| Taper | Less than 1° | 3° — 10° |
| Minimum openings | In continuous mode, the diameter is approximately equal to the thickness of the material. For pulse mode, the minimum hole diameter can be one third of the material thickness. | The minimum diameter of the holes is 1.5 times the thickness of the material, but not less than 4 mm. Pronounced tendency towards ellipticity (increases with increasing material thickness). |
| Internal corners | High quality corners | Some corner rounding occurs and more material is removed from the bottom of the cut than from the top. |
| Scale | Usually absent | Usually present (small) |
| Burns | Invisible | Present on sharp outer edges of parts |
| Thermal impact | Very little | More than laser cutting |
| Metal cutting performance | Very high speed. For small thicknesses, usually with a noticeable decrease as the thickness increases, prolonged burning of large thicknesses. | Fast burn; very high speed at small and medium thicknesses, usually with a sharp decrease as thickness increases. |
Required Power Sources
Although all plasma cutter power supplies operate on AC power, some can convert it to DC power, while others can amplify it. But those devices that operate on direct current have higher efficiency. Installations operating on alternating current are used for cutting metals with a relatively low melting point, for example, aluminum and alloys based on it.
In cases where too high power of the plasma jet is not required, conventional inverters can be used as power sources. It is these devices, characterized by high efficiency and ensuring high stability of the electric arc, that are used to equip small industries and home workshops. Of course, it will not be possible to cut a piece of metal of considerable thickness using a plasma torch powered by an inverter, but it is optimal for solving many problems. A big advantage of inverters is their compact dimensions, which makes them easy to carry and use for work in hard-to-reach places.
Transformer-type power supplies have higher power, with the use of which both manual and mechanized cutting of metal using a plasma jet can be carried out. Such equipment is distinguished not only by high power, but also by higher reliability. They are not afraid of power surges that can damage other devices.
Pattern cutting
Any power source has such an important characteristic as on-time (ON). For transformer power supplies, the duty cycle is 100%, which means that they can be used the whole working day, without a break for cooling or rest. But, of course, such power supplies also have disadvantages, the most significant of which is their high power consumption.
What metals can be cut?
Using plasma technology, almost any metal can be processed:
- Cutting and cutting of sheet metal from steel, titanium, non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, etc.) and their alloys (including bronze, brass, etc.).
- Cutting steel of different thicknesses and workpiece shapes. Processing of carbon and alloy steels of almost all grades is provided, incl. high alloy stainless steels. Plasmatrons can be used to cut strips (narrow long steel strips) and cut rolled steel.
- Cutting cast iron. Plasma ensures deep cutting, which makes the method more effective compared to other technologies.
- Cutting and processing of pipes of different diameters. Special pipe cutters with centralizers are used. In addition to cutting, you can process the surface of pipes, chamfer, clean welds, and process edges.
- Formation and processing of holes.
- Shaped cutting of metal blanks. Special equipment even allows for artistic carving and production of parts of complex shapes.
How is manual plasma cutting performed?
The first thing you need to do in order to start using a machine for plasma cutting of metal is to put together all its component elements. After this, the inverter or transformer is connected to the metal workpiece and to the alternating current network.
Further, the cutting technology involves bringing the device nozzle closer to the workpiece at a distance of about 40 mm and igniting the so-called pilot arc, due to which the working gas will be ionized. After the arc has ignited, an air-gas flow is supplied to the nozzle, which should form a plasma jet.
When a plasma jet with high electrical conductivity is formed from the working gas, a working arc is created between the electrode and the workpiece, and the standby arc is automatically turned off. The task of such an arc is to maintain the required level of ionization of the plasma jet. It happens that the working arc goes out, in which case you should shut off the gas supply to the nozzle and repeat all the described steps again. It is best, if you have no experience in performing such a process, to watch a training video that shows in detail how to manually cut metal.