Do you like to do home improvement work yourself, without involving various craftsmen? Self-installation or repair not only allows you to save money on calling specialists, but also greatly increases your self-esteem, right?
During the installation of communications, it is often necessary to prepare threads on pipes. We have to find ways not to spoil the product.
We will tell you how to cut threads using different tools, which method is preferable to use in a given situation. The article discusses methods available for implementation by an unqualified performer. The features of cutting different types of threads and the equipment used for this are covered.
The presented material is provided with visual photographs depicting tools for performing the work. A video with recommendations will help you understand in detail all the intricacies of this process.
Basic cutting methods
You can cut threads on pipes in one of two ways:
- automatic - on machines, power tools;
- manually - using hand tools.
For living conditions, of course, manual technology is more relevant. Cutting threads on water pipes or other pipes by hand is often done using a die.
Solid dies for pipe threads, made of strong alloy steel, are available with a body diameter of up to 65 mm. Dies with a body diameter of up to 120 mm are available for metric threads. On the body of metric products there is a symbol “M”
A die is a simple device for cutting threads on pipes at home. The same tool is successfully used on industrial machines.
The device looks like a disk with several axial holes drilled along its inner diameter. The edges of these holes form several incisors (usually 8-10). The material for the dies is alloy steel or other hard alloys.
There are several types of such devices:
- solid;
- spring-loaded (split);
- clamp (sliding).
According to the design, the die is produced in the form of a circle, square, hexagon, or prism. The most common are disc (round) instruments. They are used for threading water pipes up to a diameter of 36 mm.
For ease of working with dies, use:
- simple knobs with locking screws - hand tools;
- threading chucks on lathes.
Cutting threads (metric, conical) of the best quality on pipes manually or on machines is provided by solid dies.
However, this type of tool, due to the rigidity of its own design, has its negative sides. The cutters wear out quickly.
A spring-loaded thread cutting tool is distinguished by the presence of a cut in the area of one of the axial holes. The presence of a cut reduces the load on the cutters, but at the same time the degree of rigidity required to achieve high cutting quality is reduced.
Spring-loaded (split) dies have a less rigid design, which makes it possible to cut threads on pipes and at the same time change the thread diameter in the range of 0.1-0.3 mm.
Such devices are characterized by increased wear resistance of the cutters, but do not provide high accuracy and cleanliness of thread cutting.
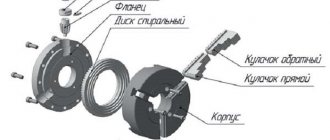
Sliding dies consist of two working parts. They are designed for installation in a fastening module - a clamp.
Fastening in the clamp is carried out by a mechanism consisting of a cracker and an adjusting screw. The screw adjusts the diameter size for thread cutting. Usually the die is equipped with a set of dies for several different diameters.
Method #1 - making pipe threads with dies
The process of creating a thread on a pipe with a die or die requires the mechanic to perform some preliminary actions:
- The surface of the pipe in the cutting area must be thoroughly cleaned.
- The end part of the pipe should be processed with a file (make an entrance chamfer).
- Apply lubricant to the surface to be treated to reduce resistance.
If possible, it is advisable to secure the pipe vertically, for example, in a bench vice, leaving free access to the upper part - the cutting area. The fastening force must be correctly calculated so as not to deform the pipe body.
Then take a pre-prepared driver with a roughing die (No. 1) of the required diameter and suitable thread characteristics.
An example of cutting a thread on a water pipe using a hand wrench. A die is inserted into the working cylinder of the driver and secured with two (four) bolts located opposite each other
The tool is held horizontally - perpendicular to the end area of the pipe. Place the roughing die onto the chamfer of the edge using the internal hole. Light pressure and successive short turns of 25-30° make the initial cut.
This work should be done carefully, slowly, constantly monitoring the right angle between the horizon of the ram and the vertical of the pipe.
Using this technique, the first two or three threads are carefully cut. Usually, after cutting the first two or three threads, the tool is firmly in its working position. Further, the right angle can no longer be controlled.
But the technology of cutting with short (without particularly strong traction) circular movements should be maintained until the end of the cut. It is recommended to periodically add lubricant at the cutting point.
After the first pass, twist the device and then repeat one or two more times with a finishing die (No. 2).
Image gallery
Photo from
Tapping with a fixed tap
Die cutting of external threads
Manual thread cutting machine
Working side of the thread cutting die
Method #2 - clump cutting technique
The die is a variation of the same die for cutting threads, including on pipes. A distinctive feature of the die is the ability to adjust the cutters.
A set of clamps for different sizes of pipe threads. Each of these devices is equipped with screws for fastening blocks with cutters. These screws can additionally change the thread diameter within small limits
There are clamps for manual use, as well as similar devices with an electric drive.
Option #1 - cutting with a hand clamp . Manual cutting of pipes is usually done with a clamp, which is installed in a ratchet holder. This holder makes the work of cutting pipe threads convenient and less complicated.
Of course, depending on the conditions of plumbing work, you can use other types of hand holders. For example, a standard locking knob with two handles.
The principle of creating a thread with a die is almost the same as the method of working with traditional dies:
- Clean the working surface of the pipe and make sure there are no defects.
- Sand the cut area until it has a distinct metallic sheen.
- Process the outer working part of the end edge at an angle of 45-60º (chamfer).
- Lubricate the prepared surface with technical petroleum jelly.
- Secure the pipe in a mechanical vice or hold it with a gas wrench.
After these procedures, the cutting tool (blank) is placed with the internal hole on the pipe chamfer and, with moderate, uniform pressure, they begin to rotate it with short reciprocating movements.
A convenient tool for working with a clamp is the so-called “ratchet” - a lever with idle reverse. Using such a hand tool, it is easy to cut threads on a pipe under different installation or repair conditions.
If a ratchet clamp is used as a holder, only forward cutting is carried out. It should be noted that the ratchet clamp is convenient to use when working in cramped conditions.
For example, when it is necessary to process a pipe laid in close proximity to a wall.
Option #2 - cutting with an electric clamp . Along with hand tools, electrically driven devices are widely used. The obvious advantage for the mechanic is a significant reduction in labor intensity.
But on the other hand, not all electric machines are capable of performing work in cramped conditions. In addition, when working with hand tools, it is possible to obtain a better result.
To obtain a similar result from electrical sockets, extensive experience with this tool is required.
Equipment for the clamp, supplemented with an electric drive. A modern, effective tool that significantly reduces the physical load of a mechanic. True, electric sockets are more often used in the professional sphere than in everyday life
Working with an electric clamp:
- Preparation of the pipe surface in the cutting area - cleaning, chamfering, lubrication.
- Fastening the pipe with devices capable of providing rigid fixation.
- Fixation at the starting point of the die holder with the clamp included in the kit.
- Checking the stroke and direction of rotation of the die.
- Cutting the first two or three turns in the jog mode.
Next, pipe threads are cut automatically. The cutting length is considered optimal when the upper edge of the die cutting heads reaches the leading edge of the pipe.
At this point, the operation of the device is stopped, the reverse rotation function is turned on, and the bug is twisted from the pipe with a push feed. Be sure to periodically moisten the cut area with oil throughout the process.
Method #3 - using lathes
Large-scale construction and repair work, as a rule, excludes the use of hand tools. Here, lathes are usually used to process the pipes accordingly.
Threading functions are supported by many universal lathes.
Lathes are used to produce threaded parts on pipes of different diameters. You can make threads of any configuration on a lathe
Using the machines, both internal and external pipe threads are made efficiently and easily. The pneumatic (or mechanical) fastening module of the lathe ensures high-quality reliable fastening of the pipe and precise supply of the workpiece to the cutter.
To perform thread-cutting functions, different types of cutters are used:
- rod,
- lamellar,
- intercalary
Work on lathes is carried out by specialists trained in this field and having the appropriate qualifications. Without experience and professional skills, trying to cut threads with your own hands on a machine is not recommended.
For home craftsmen who decide to take up plumbing and carve metal workpieces, the following tips will help them in their work:
Image gallery
Photo from
Selecting the appropriate drill diameter
Processing the workpiece with a file before cutting
Tapping in several stages
Parts with external and internal threads
What kind of cutters are used for thread cutting?
On a turning unit, you can carry out cutting operations - both on the outer and inner surfaces. In this case, different types of cutting elements are used. They can be divided into three main groups:
- Rod;
- Prismatic;
- Round.
The first group includes the instrument of the simplest type. By design, it is a working head on a rod of different sections and shapes. The profile shape matches the head. Some models of rod cutters have carbide brazing on the working edges. This increases the service life of the latter, which are less subject to abrasion of the working surface, and, as a result, are not sharpened as often.
Thread cutters
Prismatic-type devices process workpieces only from the outside. Compared to the previous group, they can cope with larger surfaces and can be sharpened more times. In a lathe, the element is secured using a dovetail holder.
Round cutting elements can be used to make internal and external threads. They are more convenient to work with than prismatic ones, they are more versatile - they have a wide range of applications. They lend themselves well to regrinding many times. Fasten the cutters in the holder into the end hole. Prismatic and round elements are classified as shaped tools for turning equipment.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
All the nuances of cutting pipe threads in one video:
Knowledge about the creation, operation, and maintenance of threaded connections on pipes is always relevant for every person who deals with housekeeping, plumbing, and other utilities..
Without this information, it is impossible to carry out quality repairs, modernize pipeline systems, or simply maintain the operation of household economic systems.
Do you have anything to add or have questions about cutting threads on pipes? Please leave comments on the publication and suggest your own methods and effective tools for creating carvings. The contact form is located in the lower block.
Thread cutting equipment
Turret machines, CNC turning and milling (machining center) provide cutting modes in which profiling without transitions fits into 1 processing cycle.
Turret equipment, after installation on a universal lathe, does not require re-installation of the tool in the initial position for multi-pass completion of the operation. Multi-cut threading heads are used.
B8D turning and milling machine
Upon completion of the operation, the combs are separated and returned to their original position without contact with the part. Tangential, radial, round are used. The latter are more common due to ease of maintenance and suitability for regrinding.
Long worms and screws are cut using cutting heads capable of internal and external cutting. Prismatic combs with an entry cone on a turret machine are used for internal cutting.
In addition to universal screw-cutting lathes, turrets, and machining centers, thread-rolling machines, automatic nut-cutting machines, and CNC are used for cutting screw surfaces of great depth and area using the vortex milling method.
Cutting threads using a lathe
On turning equipment, any tool can be used for thread cutting: taps, dies, cutters, special cutting heads, as well as the rolling method. If they work with a cutter, then the process looks like this:
- The workpiece is fixed in a lathe, the cutter is fixed in a holder.
- When the part rotates, the cutting head is moved along its axis, drawing a helical line on the body of the workpiece.
The resulting thread is characterized by the helix angle, which depends on the speed of rotation of the part and the speed of movement of the cutting element in a straight line. The thread pitch depends on the size of the cutting edge.
Precautionary measures
You should not try to make internal threads using small mechanization methods, that is, insert a tap into the chuck of a drilling machine, especially into the chuck of an electric drill. You will not be able to correctly adjust the force and angle of attack. It will all end with a broken tool, and in the worst case, damaged threads.
The worst thing is when the broken working part of the tap gets stuck and remains in the hole. Then you will have to find a special extractor for removing debris and a diamond drill in a retail chain or on the market. Without these additional devices, it is difficult to get the fragment, but you can sacrifice aesthetics and make a depression in the metal around the fragment in order to capture it. This is done using a small angle grinder. If part of the product protrudes above the plane of the part, you can try to grab it with pliers or jaws of a hand vice and turn it out.
The best way is to learn how to cut threads correctly and carry out the work as recommended, calmly and without haste.
Threading
General information about the tool
Internal threads in holes are cut manually or by machine using special tools - taps, which are found in two versions: machine-manual and machine. Types and versions of tools for cutting internal threads:
- Machine products are designed to be secured in a chuck or collet clamp of a metalworking machine on which this type of work can be performed. The machine-manual version provides a square shank so that the tool can be installed in a manual crank.
- Depending on the cutting method, taps can be universal (through) or complete. The latter are a set of two or three tools of the same diameter, which should be used in the same hole alternately: first - roughing. then - and 3, if there is one. In the case of some alloys, sets of five products are used. A universal tap makes all the threads at once, but requires great physical effort and breaks more often.
- According to the thread configuration, cutting products are divided into pipe, metric and cylindrical.
- Based on the type of holes, there are tools for through and blind holes. The first ones have a long lead-in part. Most often they are universal, while the latter have a cut-off approach. Such work is performed in a set of 2-3 products.
- According to the design of the working part, the products come with straight, screw or shortened grooves. They are used to work with regular, carbon or low-alloy steels. For stainless or heat-resistant ductile steels, a tool with a staggered arrangement of teeth is used.
How to correctly determine the hole diameter?
Before cutting a thread, a hole is made, the diameter of which is determined according to standardized tables. If you prepare a hole whose cross-section is smaller than the recommended size, the tool will fail; if it is larger, the result will be of poor quality.
| Thread designation | Diameter, mm | Thread designation | Diameter, mm | Thread designation | Diameter, mm |
| M 2 | 1,6 | M 8 | 6,7 | M 22 | 19,4 |
| M 2.2 | 1,75 | M 9 | 7,7 | M 24 | 20,9 |
| M 2.5 | 2,05 | M 10 | 8,5 | M 27 | 23,9 |
| M 3 | 2,5 | M 11 | 9,5 | M 30 | 26,4 |
| M 3.5 | 2,9 | M 12 | 10,2 | M 33 | 29,4 |
| M 4 | 3,3 | M 14 | 12,0 | 31,9 | |
| M 5 | 4,2 | M 16 | 14,0 | M 39 | |
| M 6 | 5,0 | M 18 | 15,4 | M 42 | 37,4 |
| M 7 | 6,0 | M 20 | 17,4 | M 45 | 40,4 |
| Thread size, inches | Diameter, mm | Thread size, inches | Diameter, mm |
| 1/8 | 8,8 | 7/8 | 28,1 |
| 1/4 | 11,7 | 1 | 30,5 |
| 3/8 | 15,2 | 1 1/8 | 35,2 |
| 1/2 | 18,9 | 1 1/4 | 39,2 |
| 5/8 | 20,7 | 1 3/8 | 41,6 |
| 3/4 | 24,3 | 45,2 |
How to properly cut a thread with a tap: algorithm, recommendations, size tables
The question of how to cut a thread with a tap arises in cases where a pre-made hole needs to be prepared to accommodate a bolt, screw, stud or any other type of threaded fastener. it the tap that is the main tool that allows you to quickly and accurately cut an internal thread with the required geometric parameters.
Manual cutting of internal threads is performed using metalworking taps complete with a wrench
Thread cutting with a tap and screwdriver. Internal thread cutting
Rules for working with taps:
When cutting threads in deep holes, in soft and tough metals (copper, aluminum, bronze, etc.), the tap must be periodically unscrewed from the hole and the grooves must be cleared of chips; to cut a thread with a full set of taps - rough, medium and finishing. The middle and finishing taps are inserted into the hole without a driver and only after the tap follows the thread correctly, a driver is put on the head and threading continues; during the cutting process, you need to use a square to carefully ensure that there is no skew of the tap; The thread cutting area should be lubricated with oil.
READ Remake Screwdriver Interskol 18 Volt