The design and manufacture of TV-4 machines is carried out at the Rostov Specialized. TV-4 has different technical characteristics than professional models, since it is needed for training and developing skills in handling steel workpieces. One of the main standards that are taken into account when designing a device is ease of setup and safety. Buying a new machine today is not difficult. However, don’t forget about used equipment. People who want to turn some metal part at home are unlikely to find a cheaper option.
Short story
This equipment has been produced by the Rostov educational equipment plant since the early 1970s. Due to the specifics of its application, this machine was called “Schoolboy”.
Industrialization required professional personnel, so the country supplied all secondary educational institutions with modern technologies by those standards.
This machine is still produced at the Rostov plant to this day, as it continues to be in demand in private workshops and for turning enthusiasts.
There is also a plant in Ukraine in Grozhno, which also produces a series of this equipment. But the Rostov plant is still considered the main manufacturer of this functional mobile design.
Purpose and scope of application of a school metal lathe
Since the equipment was originally produced as educational equipment, it is small in size. Therefore, it is not suitable for processing large parts.
The TV-4 screw-cutting lathe is designed for processing parts up to 12 cm in diameter and up to 30 cm in length. This is quite enough for those who have turning as a hobby and have a need for individual processing of parts.
The machine allows you to carry out the following types of turning work:
- trimming ends;
- cut;
- cutting metric threads;
- drilling;
- grooving and boring holes.
The school lathe is equipped with all the components of a full-fledged turning tool.
Purpose of the machine
Initially, it was planned to perform the entire range of turning operations on the school model. That is why the TV-4 design has the classic layout of all machines of this type. The following turning operations are performed on it:
- Boring and turning of steel workpieces by rotation.
- High precision end trimming.
- Drilling.
- Thread cutting (metric).
In order to increase functionality, equipment is being modernized. However, you can start this only after familiarizing yourself with the specific design and technical characteristics. Modernization should not adversely affect the performance and safety of operation of the machine.
The differences between training equipment are its layout and the location of controls, which should be such that a short teenager can operate the machine without difficulty.
Specifications
The electric motor power of the equipment in question is 0.6 kW. At the same time, the total weight of the machine is 280 kg, which allows it to be easily located in domestic conditions.
Main settings
The main parameters of TV-4 include:
- distance between centers – 35 cm;
- longest turning length – 30 cm;
- the maximum diameter of the workpiece processed above the upper part of the support is 125 mm;
- diameter processed above the bed – 20 cm.
The components in the machine are classic, with certain technical characteristics that allow you to perform all turning operations typical for this type of equipment.
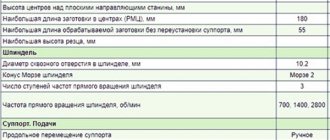
Spindle
It is located in the front spindle headstock and its main function is to rotate the workpiece using a three-jaw chuck. It receives 6 digits of revolutions from the receiving pulley. Maximum – 710 rpm.
The largest diameter of the processed rod on the spindle is 15 mm. The end of the spindle is threaded – M36x4.
Caliper and feed
Designed to move the cutting tool. Has 4 carriages:
- The first one moves in the direction of the bed.
- The second one moves along the transverse guides of the first carriage, moving the cutting tool in the transverse direction.
- The third one rotates 45 degrees from the middle position in both directions.
- The fourth one carries the tool holder and moves in the longitudinal direction along the third carriage.
Cutting slide
According to the technical characteristics, the incisor slide assumes a displacement of 5 cm.
Tailstock
She is also called a stubborn grandmother. This is a structural part whose main function is to support the second end of the workpiece using the center. She fixes the future detail.
It is located on a base that moves evenly along the frame guides. The thrust headstock contains a quill that moves in the longitudinal direction. Its movement is carried out by a flywheel.
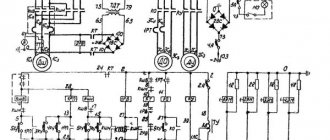
Electrical equipment
The drive is carried out from an asynchronous electric motor ~220V. Through clinometer gears and a single-stage pulley, the movement is transmitted to the running shaft and gearbox.
Electrical equipment also includes an electrical panel, transformer, and fuse links. The electrical panel and magnetic starter are located in the right cabinet, and the electric motor itself with a push-button station is in the left.
General dimensions (dimensions) and weight
The machine belongs to the light class of equipment. Its parameters in mm are 1100x470x1020. Processing accuracy class H, which allows an error of no more than 10 microns.
Thanks to its comfortable size, it is even suitable for installation in an apartment or on a balcony. That is why the machine is popular among household craftsmen.
Characteristics and parameters
TVSh 3 first appeared in the early sixties of the 19th century on the territory of modern Germany.
Some of the documents regarding the equipment were lost, but experts assure that at that time the machine was massive and heavy. Since the 70s, TVSh 3 has become smaller in size. Modern versions of turning equipment are lightweight and easy to install; they are used not in professional activities, but for conducting training courses for beginners. The purpose of the device is to teach turning. A screw-cutting machine allows you to comfortably perform most turning operations, with a minimal degree of error. The fact that it is intended primarily for training is determined by its high degree of safety. Compared to other lathes that are used for identical activities, the risk of injury is many times lower. This quality is ensured by special design changes in the equipment.
Using a lathe, various operations related to material processing are performed. The most common:
- the ability to grind even cones from the material;
- carving with rectangular and square lines;
- formation of bars and beams;
- cutting material;
- cutting off pieces of material to the required size;
- processing the ends of already turned products;
- production of through holes of the selected diameter;
- drilling blind holes.
Of course, in comparison with professional machines, the school version has a limited set of functions. It allows you to carefully examine how the mechanism works, form smooth parts, and thereby hone your level of skill. Students of turning will learn how the tailstock is adjusted, how the cutter works, and what additional parts the lathe is equipped with. In professional models, which are intended for large productions, this is impossible to trace.
The technical characteristics are fully consistent with the intended purpose. The operating sheet states that:
- the maximum diameter of the part that is installed under the caliper area does not exceed 9 centimeters;
- the maximum diameter of the part that is installed above the frame is up to 10 centimeters;
- center-to-center size - 35 centimeters;
- setting the center axis - up to 19 centimeters;
- the maximum diameter of the workpiece being processed is up to 1.4 centimeters (for a rod);
- turning length - 35 centimeters;
- maximum caliper displacement is adjusted - 10 centimeters;
- maximum longitudinal displacement of the caliper is 30 centimeters;
- number of revolutions - from 120 to 170;
- number of speeds - three;
- number of gearbox shift stages - six;
- power - up to 600 W.
The height of the TV 3 lathe is 101 centimeters, length - 143 centimeters, and width - 470 centimeters. The weight without the installed cartridge is about 280 kilograms.
General design and operating principle
The cabinet of this machine is made of thick-walled sheet steel. Additionally, stiffeners are installed. An electric motor is located at the back of the cabinet. On the front part there is an operation control unit, including a reverse button, as well as an on/off button.
The rear cabinet, which is U-shaped, also has stiffening ribs at the top and bottom. Inside this structure there is an electrical panel with all the main electrical equipment of this mechanism.
On the left side of the frame there is a spindle head, to which a gearbox is connected. The spindle rotates due to a three-jaw chuck.
From the spindle block to the gearbox, rotation is transmitted by a transmission mechanism. A special feature of the mechanism of this machine is that it is impossible to install other pairs of gears, and therefore the gear ratio is always the same.
Characteristics and design features
Since the machine is not professional equipment and has few functional capabilities, it is designed so that a teenager can work on it without difficulty.
The advantage of TV-4 is the indestructibility of the machine. Modern similar foreign-made devices, in the event of any breakdown, will significantly hit your pocket, and besides, it is not always possible to get the necessary part in workshops. The TV-4 model is difficult to break, and finding the necessary spare parts in the event of a breakdown is not difficult.
Overall dimensions of the workspace
TV-4 is a small-sized equipment - 47x102x144 cm and weight - 280 kg. Due to its similar dimensions, the machine is suitable for work in small training workshops.
General view of the machine
To understand the principle of operation of the unit, you need to familiarize yourself with its main mechanisms. In general appearance, it is a metal structure based on an electric motor, which includes standard elements that determine its technical capabilities.
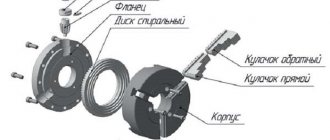
The TV-4 design includes the following equipment components and main mechanisms:
With electrical equipment located on the back side, and buttons to start/stop it on the front side.
Used to place a shield with an electric motor in it.
It is a load-bearing support that supports, secures and connects all equipment units by installing them on two guide pedestals - front and rear.
Headstock
It is a cast iron body, which includes a speed switch and a spindle and is located on the left side of the frame. It is intended to carry out the movement of the machine, that is, it is responsible for transmitting rotation from the electric motor to the workpiece.
TV-4 machine feed box
Controls the movement of the direction of movement from the guitar to the running shaft/screw, which entails a change in the rotation speed and leads to the reproduction of the desired thread pitch. In addition, the gearbox controls the movement of the caliper. The handle for switching from the drive shaft to the screw provides a lock, which prevents them from being turned on together.
Machine support
Includes three movements in the direction of the bed:
- Longitudinal (with automatic feed) – along the guides;
- Transverse - perpendicular;
- Additional movement - upper slide with 4-position tool holders securing the cutting tool, which can rotate 45° in each direction.
Apron
Designed to select the movement of the shaft or screw into the longitudinal feed of the caliper assembly. If you turn up the left apron lever, the dog clutch will engage, which will engage the gear with the running rack, resulting in the movement of the caliper. If you turn the right lever, the split nut will grip the lead screw in motion and cut the thread.
Tailstock
Intended as an installation location for drills, countersinks, reamers and other drilling tools necessary for processing long workpieces and various versions of parts. It can be moved along internal guides located in the frame and fixed into the desired position using a rotating carriage.
Drawings and description of the device
The basis of the entire machine is the bed. It is box-shaped with two prismatic guides. The front guide moves the carriage, and the rear guide moves the headstock. At the front of the frame there is a lead screw and a rack.
General form
General drawing
Location of controls
The controls of a screw-cutting lathe include:
- handles for setting spindle speeds;
- handle for cutting left and right threads;
- changing the direction of gears;
- drive roller shift handle;
- handle for increasing longitudinal mechanical feed;
- device for moving the cross slide;
- flywheel for moving the longitudinal carriage.
Kinematic diagram
Headstock
This is the main and main functioning element of any screw-cutting lathe. The part externally consists of a cast iron body, which includes a spindle and gearbox. Transmits the rotation element from the electric motor to the workpiece being processed.
The front spindle journal rotates in two radial thrust bearings, while the rear spindle rotates only in a radial bearing. So that the master can adjust the axis tension, there are two nuts on the spindle.
Gearbox
This design receives movement from the gearbox itself using transmission gears. The design of this part allows you to obtain metric threads with pitches of 0.8, 1.0, 1.25 mm. You can also obtain longitudinal feed of the caliper within the same limits, per spindle revolution.
On the front of the feed box cover there is a handle with which the threads and feeds are adjusted. The design of the feed box of this model eliminates the possibility of simultaneous rotation of the lead screw and the lead roller.
To lubricate the feedbox mechanism, there is a trough in the design for pouring oil. During operation, it is important to ensure that there is always a small amount of oil in this trough for lubrication.
Apron
With the help of an apron it is possible to carry out longitudinal mechanical and manual transmission from the roller and screw. For manual transmission you need to turn the flywheel, and for mechanical transmission you need to turn the handle, which starts the dog clutch.
Caliper
This design detail is necessary for securing and moving the cutter. In this version of the equipment it is equipped with four skids.
Tailstock
This is a persistent headstock, which is located on the base and secures the second end of the part during processing. The thrust head quill has a conical hole. It includes a thrust center or any other tool currently needed to process the workpiece.
Electrical circuit diagram
Table of contents
photo: lathe TV 6
The TV 6 lathe is designed to teach schoolchildren and students the basics of turning and the production of simple parts in single-unit production conditions.
TV 6, like the TV 4 lathe and TV 16 lathe, allows you to perform the following turning operations:
- External and internal turning of cylindrical and conical surfaces
- Thread cutting, both with a cutter and a tap
- Drilling and hole reaming
- Trimming and cutting off parts, etc.
Controls of the TV 6 lathe
- Knob for setting the spindle head rotation speed;
- Knob for setting the spindle head rotation speed;
- Feed direction change handle;
- Handle for setting the feed and pitch of the thread being cut;
- Handle for turning on the roller and screw;
- Manual movement of the longitudinal carriage;
- Rack and pinion engagement;
- Turning on longitudinal mechanical feed;
- Engaging the lead screw nut;
- Manual movement of the cross slide;
- Manual movement of the upper slide;
- Mounting the cutting head;
- Fastening the tailstock quill;
- Moving the tailstock quill;
- Fixing the tailstock to the bed guides;
- Local lighting;
- Turn on the network;
- Control block
photo: lathe controls
The device of the TV 6 lathe
- Headstock;
- Guitar Replaceable Gears;
- Gearbox;
- Apron;
- Caliper;
- Tailstock;
- Bed;
- Electrical equipment;
- Rear cabinet;
- Front cabinet;
- Protective cover
photo: lathe device
photo: kinematic diagram of a lathe
photo: electrical diagram of a lathe
Headstock of lathe TV 6
The headstock is designed to support the workpiece being processed and transmit rotational motion to it. In the TV 6 lathe, the headstock is also a gearbox and has six speed levels.
The headstock is mounted along the center line in a horizontal plane using two setscrews. The headstock spindle is mounted on two thrust bearings 9 and a radial bearing 19.
The rotational motion is transmitted from the electric motor through a belt drive to the drive shaft of the gearbox. Inside the box, the movement is transmitted through shaft 2 and a fixed gear wheel 3 to a shaft 4 with fixed gears 12, 6 and a gear block 5.
Gear block 5 takes part only in feed reverse.
The rotation of the workpiece, fixed in a three-jaw chuck or faceplate, is transmitted from the spindle. When processing a workpiece at centers, a stationary center is inserted into the spindle.
The gearbox contains a device for changing the direction of the caliper. This is done by moving the gear 15 to the left or right position using handle 3.
In the left position of the gear 15, direct rotation is performed from the gear block 16. In the right position of the gear 15, reverse rotation is performed using the idler gear 6.
photo: lathe headstock
Guitar replacement gears of lathe TV 6
A guitar is a transmission mechanism that serves to transmit rotational motion from the gearbox spindle to the feedbox.
The guitar consists of bracket 1 and gears 2,4,7.
photo: lathe guitar
Feed box for school lathe TV 6
The rotational movement to the feed box is transmitted from the gearbox through a transmission mechanism.
By turning the handle 4 in three positions, the gear block 6 moves along the splines of the shaft 5 and alternately engages in gear engagement with gears 2,3,4. Which makes it possible to cut metric threads in increments of 0.8; 1; 1.25 mm and longitudinal feed of the caliper 0.08; 0.1; 0.12 mm/rev.
Handle 5 turns on the lead screw and the roller.
Lubrication of rubbing surfaces and gears is carried out with wicks.
photo: lathe feed box
Apron for table lathe TV 6
The apron is designed for mechanical longitudinal feed of the caliper from the running roller, screw and manual longitudinal feed.
Handwheel 1 performs manual feed. The flywheel sits on a shaft 4, on which a gear 11 is mounted, which meshes with gear 3. Gear 3 sits on the shaft of rack and pinion 2. The rack and pinion, in turn, meshes with the rack.
Mechanical feed is carried out by a worm 5 mounted on the running roller 10 using a keyed connection. The worm meshes with worm gear 13 and is then transmitted through the clutch to the rack and pinion gear.
photo: lathe apron
Instructions for first start-up and operation
Installation and installation of the TV-4 machine must be carried out strictly by professionals. Before the first start, be sure to read the operating instructions and safety precautions.
To install the equipment, it is necessary to equip a foundation of at least 10 cm. The best option is bars or a concrete structure.
The mechanism is not equipped with level adjustment, and therefore during installation it is important to adjust the height differences. It is best if the machine is installed on adjustable supports.
There are several nuances of work that must be taken into account:
- In preparation for the work process, it is necessary to clean the mechanism from anti-corrosion liquid and fill the container with gearbox lubricant. It is important that the ground loop is configured.
- Before starting work, all handles must be in their original position. Only after this is it possible to carry out the initial setup of the machine. The workpiece should be firmly fixed between the spindle and thrust head. At the next stage, you should set the desired cutter.
- After finishing the work process, it is necessary to remove chips and metal dust that has collected on the machine after work. Then check the normal operation of all main structural parts so that in case of a breakdown it can be detected in time. Be sure to check the oil level every time before starting.
TV-4 machines are reliable. Therefore, with proper use, their service life is practically unlimited. It is only important to install it correctly from the beginning.
Machine passport
The TV-4 machine does not have increased functionality, but it works successfully with workpieces made of carbide metals. It is specially made so that even a teenager can easily handle it. Equipment specifications:
- the diameter of the through hole in the spindle is 1.6 cm;
- number of possible revolutions per minute – 120, 160, 230, 375, 500, 710;
- number of stages for forward and reverse rotation – 6;
- maximum dimensions of the mounted tool are 10x12 mm;
- the caliper has 3 longitudinal gear stages;
- The tailstock quill moves up to 6.5 cm.
When planning the work process, it is necessary to take into account that this mechanism does not have a structure for braking the spindle or locking the control handles. Due to this feature, a slow stop of the future workpiece occurs.
You can download the entire passport for free from this link - TV-4 machine passport
Equipment Features
Student metal lathes have bridged the gap between amateur tools and professional production equipment. They received their name Shkolnik for their active use for teaching students in vocational schools and high school students in labor lessons.
All models, from TV2 to the modernized 16U04P with increased accuracy, have common characteristics for school lathes:
- small dimensions;
- simplicity of design;
- safety at work;
- manual control and easy maintenance;
- processing of small-sized workpieces;
- low productivity;
- impossibility of producing batches of parts.
Lathe 16U04P
Training models were produced as floor-mounted ones with cast pedestals and table-top ones with only mounting platforms in the form of wide legs under the frame. They can be installed on a workbench in a workshop and study the principle of operation of a lathe, gaining skills in working as a turner.
The design of the lathe is simplified. There is no gearbox. Speeds are changed by rearranging the gears and flipping the belt. The caliper slide can be moved manually in one direction only. There is no ability to sharpen cones at a given angle.
Taking into account the specificity of Shkolny metal lathes, they were equipped with casings and screens that eliminate the possibility of injury from rotating parts or flying chips. As soon as the guard rose, the cartridge stopped.
There is no space for large-diameter parts in the frame. The maximum workpiece diameter is up to 200 mm. The center-to-center distance on most models is 220 - 350 mm, and only shafts with lengths of 525 and 750 mm can be installed on modernized machines.
Moving the caliper and slide along the dial manually did not allow us to work quickly and make batches of parts. Most Shkolnik series machines have 6 chuck rotation speeds from 120 to 975 rpm. The direction of rotation is switched by the motor.
TV-11 machine diagram
Despite their simplicity, training lathes provide good finishing. They can be used to sharpen parts with an accuracy of 0.05 mm and perform turning for grinding. The gearbox connected to the screw contains thread cutting with 3 pitch sizes on early models and 6 threads on modernized machines, starting with TV7.
Teenagers were taught carpentry on TV4 and on a specially produced wood lathe Shkolnik series STD-120. Using this equipment, those who like to make furniture with their own hands at home make curly legs, stands and other round elements.
Currently, compact lathes are used in mobile workshops to produce parts for repairs. Craftsmen willingly buy compact equipment for home use.
Modern analogues
Despite the reliability and durability of the TV-4 screw-cutting lathe, it has modern analogues that are in no way inferior to the mechanism in terms of functionality and capabilities, these include:
- JET BD-7.
- JET BD-X7.
- Optimum TU1503V.
- Proma SM-300E.
- Triod LAMS-02/300.
The first two models are distinguished by high quality, as well as ease of speed adjustment. These are brands from well-known global manufacturers that can easily compete with TV-4 both in small workshops and on school desks.
The screw-cutting lathe of the Rostov educational equipment plant has been serving faithfully in small workshops and in everyday life for almost half a century. This is a functional and at the same time reliable equipment that will help you master any lathe.
The mechanism is lightweight and small in size and will fit in any mini-workshop. Also, its obvious advantages are ease of operation and durability during service.