Marking, which is used to designate various types of stainless steels, allows you to obtain information not only about the chemical composition of the alloy, but also about the basic properties that it possesses. The rules for the formation of a designation consisting of alphabetic and digital characters are regulated by the provisions of both domestic and international regulatory documents.
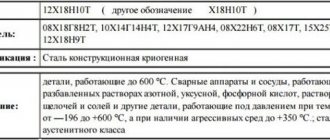
Thin-walled stainless steel pipe 12Х18Н10Т
Classification
In the metallurgical industry, more than two hundred types of alloy alloys are distinguished. They differ in the presence of different amounts of additional chemical elements in their composition.
There are four main types of stainless steel.
- Ferritic. These are low-carbon alloys containing more than 20% chromium and less than 0.15% carbon. They have a bulk crystalline structure. Durable, plastic. This type of steel has magnetic properties.
- Austenitic. Corrosion-resistant alloys containing 18% chromium and 8 to 9% nickel. They retain ductility in cold and hot states, are easy to weld, and have high strength. There are unstabilized and stabilized brands. The latter varieties are characterized by the presence of titanium and niobium.
- Martensitic. Steels of this type contain 17% chromium, 0.05% carbon. Metals are ductile, elastic, and do not react with aggressive environments. They are not exposed to high temperatures and are considered a wear-resistant material.
- Combined. There are austenitic-ferritic and austenitic-martensitic steels. The development and production of such alloys is carried out according to customer requirements.
Electrodes
Electrodes for steel 12Х18Н10Т are intended for welding chromium-nickel steels. These consumables can be used to connect products in any spatial position. Reverse polarity and direct current are selected as the required modes. The choice of alternating current is, in principle, possible, but it is not always advisable. The heat input, that is, the rate of current transfer from the arc to the metal, must have a minimum value.
It is recommended to form seams of small cross-section. To do this, use welding wire with a diameter of up to three millimeters.
Electrodes for welding 12Х18Н10Т have the following advantages:
- arc stability;
- slight metal spattering;
- normal seam formation;
- easy separation of slag from the surface.
Since the electrical conductivity of stainless steel is low, the electrode stickout should be small. You can use various technologies for the welding process, for example, such as semi-automatic welding in a protective gas environment, contact welding. It is best to use argon as a shielding gas.
There is a large selection of different types of consumables, which are electrodes for welding stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т. There are differences depending on which type of current is selected.
Stainless steel markings
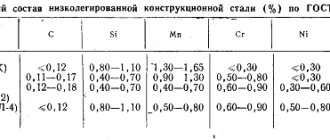
In Russia, alloying alloys are produced in accordance with GOST 5632-2014. Marking is a combination of numbers and letters. The number at the beginning indicates the carbon content of the alloy. The numbers located after the letters indicate the average mass fraction of the alloying element, which is indicated in the form of letters of the Russian alphabet.
The composition of foreign brands is standardized by the standards existing in the country of origin. AISI, named after the American research institute “The American Iron and Steel Institute,” has become popular in the Russian Federation. The first digit indicates the type of alloy, the next two indicate the serial number in the entire group of this class. The reduced amount of carbon in the AISI system is indicated by an additional letter L.
Correspondence table of popular foreign brands with Russian analogues
| steel grade | GOST 5632-2014 | AISI |
| Ferritic | 08Х13; 12X13; 12Х17 | 409; 410; 430 |
| Austenitic | 12Х18Н10Т; 08Х18Н10; 08Х17Н13М2 | 321; 304; 316 |
| Martensitic | 20Х13; 30Х13; 40 X13 | 420 |
Importance of chromium and labeling
Steels marked according to Russian GOST determine the number of alloyed elements. Let's look at the example of 12X15G9ND.
- Digital index 12 indicates 12% carbon content;
- The alphanumeric index X15 determines the content of 15% chromium;
- The G9 index regulates the amount of manganese at about 9% of the total composition of the alloy;
- The H index indicates the content of 1% nickel;
- Index D in the labeling indicates the presence of 1% copper.
Chrome determines the most important quality of this steel: corrosion resistance .
The amount of chromium determines how much steel has these properties:
- The minimum chromium content for steel to be classified as stainless steel must be at least 12%;
- In the range of 12-17%, steel is slightly rusty, i.e., with constant contact with water or short-term contact with even mildly aggressive acids, pitted corrosion may appear on the surface;
- With a chromium content of 18% or more, steel has the full properties of stainless steel.
Advantages of stainless steels
With the development of economic, scientific and technological progress, the requirements for the quality of materials used in areas of the national economy are growing.
Advantages of alloy metals:
- High level of anti-corrosion properties.
- Compliance with the standards stipulated by fire safety regulations.
- Reliability, long service life without changing technical characteristics.
- Ideal combination with any building materials.
- Variety of surfaces: polished, polished, matte, decorative.
- Wide selection of rolled metal products.
- Ease of processing, molding, and assembly of parts made from this type of steel.
- A wide range of brands with unique properties.
- Environmental safety, hygiene.
AC or DC
To create permanent connections from stainless steels, it is permissible to use direct and alternating current. Each welding technology has certain pros and cons.
Thus, the use of direct current leads to a reduction in the consumption of electrodes, due to the fact that when using this current, the material practically does not splash. In addition, direct current allows for high welding speed and quality of the weld. But the equipment used for the work is highly expensive, and this, as a result, leads to an increase in the cost of work.
The use of alternating voltage allows the use of equipment that costs significantly less than that used to generate direct current. A welder using alternating current results in a high-quality weld. But, at the same time, the use of alternating current leads to the production of more drops of metal, and this leads to increased consumption of stainless steel.
DC electrodes on stainless steel
Before starting welding work, the welder must make the correct choice of electrodes. It should be understood that coated rods can guarantee high quality seams. Manual welding is performed using direct current of reverse polarity. To obtain a high-quality result, welders use the following brands of consumables intended for stainless steel:
- TsL11 is one of the most widely used brands among welders. It is used for processing steels with a fairly high content of chromium and nickel. The weld produced using this material has high strength and impact toughness. There is virtually no metal spattering during operation.
- OZL8 - suitable for assembling structures subject to operation at temperatures up to 1000 ⁰C. Its remaining parameters are close to the TsL11 brand.
- NZH13 – this grade is in demand when processing food grade stainless steel products. In addition, this consumable is intended for joining products with a high content of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. The disadvantage inherent in this brand is the formation of slag, which spontaneously flakes off and thus can cause damage to the worker or people around him.
OZL-8
In fact, in practical work, several brands of electrodes are used that are designed for welding with stainless steel. Among them are the following:
- ZIO-8, which is used for products made of heat-resistant stainless steels.
- NII-48G is in demand in the manufacture of critical structures.
- OZL-17U are suitable for parts that will be operated in an atmosphere with a high content of sulfuric or phosphoric acid vapors.
AC electrodes for stainless steel
Not all organizations can afford technological equipment that operates using direct current. But you can also use equipment that uses alternating voltage. To work effectively with it, the following brands are used: OZL-14, LEZ-8, TsT-50, EA-400, OZL-14A, N-48, ANV-36.
In addition, the use of tungsten rods for welding stainless steel parts under a cloud of protective gases allows the use of alternating current with straight polarity. This technology is used for:
- connecting parts with a thin wall;
- there are increased requirements for the quality of the weld.
OZL-14A
The practice of welding stainless steel products suggests that the use of alternating current is less popular, and accordingly, rods of this type are less in demand.
Application
The listed advantages contribute to maintaining a leading position in the rolled metal market. Anti-corrosion alloys are an indispensable material in heavy engineering, energy, oil and gas and agricultural sectors.
The material is in demand in the following areas of the national economy:
- Construction, architecture;
- production of equipment and medical instruments;
- pulp and paper production;
- food industry;
- transport engineering;
- chemical industry;
- electrical power and electronics;
- production of household appliances and household items.
The decorative qualities of stainless metals and the high level of anti-corrosion properties make it possible to use parts and elements made from them for facades, advertising installations, shop windows, and fountains. Railings, doors, stairs, and elevators are made from alloyed material.
Characteristics of steel 12x18n10t
First of all, you need to understand that this is a high-carbon steel, resistant to corrosion, with a certain percentage of titanium content. This type of steel belongs to complex alloys. Among other things, it contains chromium and nickel, which is why in some sources this type of steel is called chromium-nickel.
At the moment, this particular version of steel is called the most popular, affordable and widespread. If we talk about the main advantages of the fabric, then we can highlight a high level of strength, hardness, and ductility. Excellent weldability makes this steel option almost irreplaceable.
The potential of steel is simply enormous, including in terms of temperature conditions, because steel can operate from -196 to +600 degrees without loss of properties.
Heat resistant stainless steel
The category of heat-resistant materials includes alloys that are capable of maintaining their structure and not changing their quality characteristics when exposed to temperatures above 550º C. The chemical composition and marking of this type is regulated by GOST 5632 - 2014. According to the production method, such stainless steel can be cast or deformable.
Metals vary in their ability to withstand certain loads at high temperatures. In accordance with these indicators, three types of stainless steel are distinguished.
- Heat resistant stainless steel. Does not corrode at 600°C.
- Heat resistant. Shows inertness to aggressive media at temperatures above 550°C.
- Heat resistant. Resists mechanical loads at 400 - 850°C.
In terms of composition, materials with increased heat resistance are:
- Martensitic. Brands produced using perlite additives. The mixture of metals is hardened at 950 - 1100 ºС. The resulting alloys contain more than 0.15% carbon, 11-17% chromium and small amounts of nickel, tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium. They do not react with alkalis and acids. Prolonged exposure to a humid environment does not affect their technical characteristics.
- Austenitic. Steels have a homogeneous or heterogeneous structure. The homogeneous composition, which is not subjected to hardening, contains an increased amount of carbon and a maximum of alloying elements: Ni, Cr, Mn, Mo, V, Nb. Such alloys are resistant to temperatures up to 500°C. This class includes: 06Х14Н6Б, 08Х18Н12Т, 20Х23Н18, 07XI6H9M2. Heterogeneous grades undergo hardening and aging during the production process. This is necessary for the formation of carbide, carbide-nitride and intermetallic compounds. They strengthen the boundaries of the matrix and impart the necessary heat resistance to the alloy at temperatures from 700 to 750°C. Representatives of this type are steels: 08Х17Н13М2Т, 20Х25Н20С2, 45Х14Н14В2М.
- Nickel and cobalt. These are some of the best heat-resistant materials, capable of maintaining all technical parameters unchanged at temperatures up to 900°C. These grades are divided into homogeneous and heterogeneous alloys. These include: KHN77TYU, KHN55VMTFKYU, KHN70MVTYUB.
Application of heat-resistant steels
Alloy metals, resistant to high thermal loads, are used for the production of pipes, parts, components of machines, units, and industrial equipment. This list includes:
- parts of thermal furnaces;
- parts of conveyor belts for furnace conveyors;
- heat treatment units;
- fuel combustion chambers;
- motors, gas turbines;
- methane conversion devices;
- furnace screens;
- exhaust systems; heating elements.
Heat-resistant stainless metal is the best material for the production of parts and mechanisms that will be used in aggressive environments at elevated temperatures.
Conformity table of foreign and Russian brands
| Steel grade | AISI | GOST 5632-2014 |
| Austenitic | 303 | 12Х18Н9 12Х18Н10Э |
| 304 | 08Х18Н10 12X18H10 | |
| 304 L | 03Х18Н11 | |
| 316 | 08X17H13M2 | |
| 316 L | 03X17H13M2 | |
| 316 Ti | 08X17H13M2T | |
| 321 | 12Х18Н10Т 08Х18Н10 | |
| Ferritic | 409 | 08Х13 |
| 430 | 12X17 | |
| 439 | 08X17T | |
| Martensitic | 420 | 20Х13 |
| 431 | 20Х17Н2 |
Stainless steel welding options, GOSTs, methods
GOST 14771-76 Arc welding in shielding gas. This standard establishes the basic types, structural elements and dimensions of welded joints made of steels, as well as alloys on iron-nickel and nickel bases, performed by gas-shielded arc welding.
It should also be noted such welding methods as: spot, roller, laser, high-frequency, resistance welding and others.
So, the next stage is processing the welds. The surface of a stainless steel weld joint forms a porous oxide layer, which contains chromium. This layer contributes to a significant weakening of corrosion resistance. The surface of the oxide layer arises from the steel, after which a so-called steel is formed under the oxide layer. low chromium content. When there is a need to increase the corrosion resistance of a welded joint, the oxide layer and the layer with low chromium content must be removed. This process is carried out using heat treatment, in this case heat treatment is capable of dissolving inside the steel structure, thanks to this process all possible differences in filler materials are smoothed out. You need to know that you are allowed to use only those accessories that are intended for processing stainless steel, these can be: belts and wheels for grinding, brushes for processing stainless steel, stainless steel shot.
Weld processing
An effective method for treating weld seams is etching. If the etching method is performed correctly, this will qualitatively remove the oxide layer and the zone with a low chromium content. The processing of this method is carried out by coating, dipping or external application of paste, all depending on the conditions. Basically, mixed acids (nitric acid/hydrofluoric acid) are used for etching in proportions of 8 - 20% nitric acid and 0.5 - 5% hydrofluoric acid, with the addition of H2O (water). The etching time depends not only on the concentration of acids, but also on temperature, type of rolled product and thickness of scale (acid-resistant rolled steel, compared to stainless steel, requires long-term processing). After the etching method, the structure becomes resistant to corrosion.
We have become familiar with the basic methods of welding stainless steel and now we can safely talk about the special requirements for welding in the manufacture of stainless steel. When preparing the above alloys and steels, special requirements and main features must be taken into account:
Welded structures of MCC and base metal in the area near the seam can be welded to temperatures of 450 - 650 degrees; If crystallization cracks form, this is a consequence of the formation of an austenitic structure of the weld metal; Embrittlement can occur in temperature ranges of 350 – 550 degrees due to the high ferrite content and in the ranges of 550 – 850 degrees when stigmatization occurs. For example, embrittlement of welds can occur during the stamping process of hot bottoms, if welding occurs with the use of filler materials that produce an excessive ferrite content. In order to avoid embrittlement of welded joints during processing, the ferrite content should be limited to 8 - 10%. Increased warping of welded structures is a consequence of low thermal conductivity and a coefficient of thermal expansion, which is 1.5 times greater in comparison with carbon steels;
Increasing the length of the tacks and reducing the distance between them in comparison with connections of low-alloy steels, welded connections and due to the large coefficient of linear expansion; If there is ferrite in the structure of the weld metal, then at temperatures below 100 degrees its ductility and embrittlement decrease;
To increase the resistance of welded joints to corrosion, it is necessary:
Use steels and filler materials containing a minimum amount of carbon; Add other auxiliary elements (titanium, niobium, nickel) to alloy steel; Apply stabilizing annealing from 870 to 900 degrees, hold for two to three hours and cool in air.
It is possible to reduce overheating of stainless steel and ensure optimal mechanical properties for resistance to external factors by welding joints at the highest possible speed. Each subsequent welding pass must be performed after cooling and thoroughly cleaning the structure.
Increasing the corrosion resistance of welded joints
If you comply with the following requirements, you will be able to increase the corrosion resistance of welded joints:
All external seams are welded last, and in cases of double-sided welding, a third facing seam is made, which faces the external environment. If this is not possible, then all necessary measures should be taken to reduce the heating of the metal of the first layer. To prevent heating of the metal, welding should be carried out at the highest possible speed using minimal currents. In order to eliminate hot cracks during welding, it is necessary to use filler materials that form welds; these seams have an austenitic-ferritic structure and contain a ferrite phase of more than 2%.
If it is necessary to prevent hot cracks in joints with a thickness of 10 mm or more, it is recommended to do the following:
The manual arc welding method is performed with a minimum arc length; Perform submerged arc welding at low speed with minimal approaches; Carefully sand or fill all craters. It is prohibited to expose all craters to the base metal. If the arc breaks, you need to make sure that there is no hot crack; if a crack is found, then the crater must be removed mechanically; Welding of thick joints should be carried out using electrodes that provide increased resistance of the metal to hot cracks (but at the same time poor resistance to corrosion). Only those welders who already have experience and skills in dealing with hot cracks are allowed to weld stable austenitic steels.
What you need to know to reduce welding deformations: It is recommended to carry out the welding process at high speed, with a short arc and with minimal currents; For manual welding, separate the seams into separate sections and perform the welds in sequence to ensure minimal warping; To avoid cracks in the heat-affected zone, it is necessary to wrap the slag at a temperature of 100 -150 degrees; The method of manual arc welding of stainless steel is performed with a short arc without using transverse vibrations of the electrode. Stainless steel fittings for fencing.
Polished stainless steel
This type of stainless steel is a material with an absolutely smooth surface and a high reflective effect. The technological process of its production differs from other types of stainless steel in the method of surface treatment. It is carried out on special equipment using control and measuring instruments.
Stages of grinding sheet metal.
- Processing with abrasive materials using a special tape.
- Sanding with fine-grained sandpaper or brushes.
- Finish with grinding wheels to a mirror finish.
Areas of application of polished stainless steel:
- Sanded pipes are used to transport oil, gas, liquid foods and alcohol.
- Polished metal products are in demand among designers. It allows you to create creative architectural projects.
- The material is widely used for the manufacture of household appliances, medical equipment and tools, and devices for the food industry.
Polished alloy metals are used in all areas of the national economy where an absolutely smooth and durable material that meets environmental safety standards is required.
What electrodes should be used to cook 1 mm stainless steel?
One of the most difficult processes in welding processes is processing parts with thin walls. This is because:
- Excessive heat generated during welding can cause a hole to form.
- High temperatures may cause surface deformation.
- The electric arc, which is used when processing thin-walled parts, is small in size. Even a small separation of it from the surface of the workpieces being processed can lead to its disconnection.
Welding steel 1mm
All of the above difficulties significantly complicate the work of the welder. The correct choice of welding material can help eliminate these problems. For example:
- OK 63.34 - can be classified as universal electrodes; they can be used to work with workpieces of different thicknesses.
- OK 63.20 - they are used for processing pipes and thin-walled material.
Food grade stainless steel
This type of rolled metal is ground and differs from other types in a special way of treating its surface. The final layer of food-grade material is sanded until shiny. This type of stainless steel is environmentally friendly and does not react with acids, alkalis, or detergents.
Popular brands and their applications:
- 08Х18Н10 – widely used for the production of food equipment.
- 08Х13 – metal suitable for making kitchenware and cutlery.
- 20Х13, 40Х13 are ideal materials for the production of sinks and containers in which thermal and hygienic processing of products is carried out. It is used to produce equipment intended for the production of wine, alcohol, and food.
- 08X17 is a popular material for cookware exposed to high temperatures.
The optimal amount of alloying elements included in the composition of stainless steel forms a protective film on the surface of the metal. The use of this type of steel is necessary for the production of products that are exposed to long-term exposure to water vapor, heating and boiling of liquid food products. Due to the properties of food grade steel, when cooking food, there is no chemical interaction between the products and the container in which they are located.
Food grade stainless steel according to GOST
There is no official concept of food grade or technical stainless steel. This is the name given to any brand that is suitable for making cookware. Requirements for products intended for contact with products are set out in GOST 27002-86.
The list of possible alloys includes grades with an amount of carbon of at least 12%, chromium of at least 13%, possible presence of nickel in an amount of 5-13%, and molybdenum of about 2%.
Their selection is influenced by the following criteria:
- will the cookware be used for cooking?
- how long the contact is expected to last.
Also, there are no alloys that are used only for the manufacture of dishes, cutlery, etc. Dishes, pipes and tools can be made from the same grade. In this case, the final thermomechanical treatment can be applied in the same way.
Preferably, 12X13 stainless steel is used to make utensils that do not come into contact with food for a long time and are not subject to shock or heat.
Grade 12Х18Н10Т is a classic version of food-grade stainless steel, and since it is used in the mass production of not only tableware, its second name is medical steel.