General characteristics of steel 12x18n10t
When considering 12x18n10t (GOST defines all standards), it should be taken into account that the high concentration of the main alloying elements determines the special properties of the metal. Most of the brand contains chromium and nickel.
Download GOST 5632-72
Technical features of stainless steel 12x18n10t can be characterized as follows:
- The density indicator is 7920 kg/m3.
- Hardening is carried out at temperatures of about 1100 degrees Celsius. Special equipment is required to heat the medium to this temperature.
- An analogue of steel 12x18n10t should have a hardness index of 179 MPa.
- An important parameter is the degree of weldability. Stainless steel grade 12x18n10t has no restrictions on weldability; various methods can be used. After welding, it is recommended to carry out heat treatment, which increases the strength and reliability of the connection.
- The application temperature is 650 degrees Celsius. High temperatures can lead to increased ductility and reduced protection from chemical attack.
- It is possible to process the material by cutting in a hardened state. That is why the workpiece is used for cutting when using turning or milling equipment.
Cold-worked blanks are also available for sale, which can be used to produce a wide variety of products.
An analogue of aisi is produced by many foreign manufacturers. In this case, labeling is carried out in accordance with the rules established in the country.
Steel 12x18n10t hardness during hardening
RESEARCH OF THE INFLUENCE OF HEAT TREATMENT ON THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AUSTENITIC STEEL 12Х18Н10Т
(Temirtau, Karaganda State Industrial University)
Ph.D., senior teacher Tayupova E.K.
(Karagandy, Karaganda University “Bolashak”)
The modern development of mankind is inextricably linked with the development of new technologies, the creation of new materials for use in various industries and extending the service life of created parts, machines and equipment.
One of the most important stages in the development of metallurgy was the creation and development of stainless steels. Let's look at the most used and widespread steel 12Х18Н10Т - let's identify the possibility of using it to obtain an ultra-fine-grained structure. Corrosion-resistant steel 12Х18Н10Т contains a large amount of carbide-forming elements (18% Cr, 10% Ni and Ti). Therefore, the heat treatment temperature of such steel must be high. High temperature is necessary for more complete dissolution of carbides. Steel also requires rapid cooling, which fixes the state of a supersaturated solid solution. Slow cooling is unacceptable, since this results in the release of carbides, leading to deterioration of ductility and corrosion resistance. Based on the above, we can conclude that the most optimal heat treatment will be quenching in water. During hardening, recrystallization processes occur, eliminating the effects of plastic deformation.
The purpose of the experiment is to clarify the quenching temperature for corrosion-resistant steel grade 12Х18Н10Т, since at this temperature we need to obtain the finest-grained structure, but the carbides must dissolve completely.
Heating for hardening was carried out in an electric laboratory chamber furnace. The hardening temperature range was chosen depending on the Ac3 point and is 1000-1150 0 C [1].
The samples are placed in an oven, heated to the required temperature (Table 1.1) and held.
Exposure at the hardening temperature is given to complete the processes of structural transformations throughout the entire volume of the sample, and the higher the temperature, the shorter the exposure. The initial holding time was calculated based on the dimensions of the workpiece: 1 mm = 1 min.
Source
Chemical composition and structure of the alloy
The material in question, 12x18n10t, belongs to the class of structural cryogenics. The structure can be characterized by high resistance to aggressive environments. The chemical composition of steel 12x18n10t is represented by a combination of the following elements:
- Almost any metal in its composition has a high concentration of iron. The second most important chemical element is carbon, which has a concentration of 0.12%.
- The second most concentrated element is chromium. Its concentration ranges from 17% to 19%.
- The composition included a high concentration of nickel: from 9% to 11%.
- Recently, titanium has been included in the composition of modern alloys, the concentration of which is about 0.8%.
Chemical composition of steel 12x18n10t
The remaining chemical substances have concentrations within the normal range in accordance with GOST. It is practically impossible to avoid the presence of harmful impurities in the composition, but it is possible to maintain a low concentration: phosphorus about 0.035% and sulfur no more than 0.02%.
Interchangeability of stainless steels
Characteristics of steel 12x18n10t
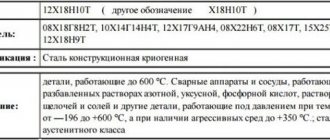
parts operating up to 600 °C. Welding apparatus and vessels operating in dilute solutions of nitric, acetic, phosphoric acids, solutions of alkalis and salts and other parts operating under pressure at temperatures from -196 to +600 °C, and in the presence of aggressive media up to +350 °C; austenitic steel
Weldable without restrictions
Start 1200, end 850. Sections up to 350 mm are cooled in air.
Silicon:0.8, Manganese:2.0, Copper:0.30, Nickel:9.0-11.0, Sulfur:0.020, Carbon:0.12, Phosphorus:0.035, Chromium:17.0-19.0, Titanium:0.6-0.8,
Mechanical characteristics of steel 12Х18Н10Т
Quenching 1050 – 1080 C, Cooling water
Alloying elements of steel 12x18n10t
The main alloying elements are chromium and nickel. They have the following effects:
- Almost all common stainless steels are obtained by including chromium in the composition, which determines corrosion resistance. In addition, the structure's ability to passivate increases.
- Nickel is added to the composition in order to improve the performance of the structure. An example is that the brand in question rolls well in cold and hot conditions.
Other alloying elements only slightly change the performance characteristics of the metal in question. An example is ferritic properties, as well as intercrystalline corrosion resistance associated with high titanium concentrations.
Physical properties
When choosing a metal, you should pay attention to its physical properties. They largely determine the scope of application and its main performance qualities. In the case under consideration, the density of stainless steel is 7920 kg/m3. The fairly high density of 12x18n10t determines that the manufactured parts are durable.
Other physical properties include the following:
- The melting point of stainless steel is more than 1000 degrees Celsius. It is almost impossible to carry out such processing in a home workshop.
- Corrosion resistance is the main reason for the demand for common stainless steels. It can be used if operating conditions include exposure to high humidity and chemical environments.
- Low magnetic properties make it possible to use it in the manufacture of various products. They are achieved by adding titanium.
The coefficient of linear expansion and the coefficient of thermal conductivity determine the possibility of using the material in the manufacture of products that can be used when exposed to high temperatures.
The specific gravity of stainless steel largely depends on the chemical composition and the processing method used.
What is metal hardening and its types
Hardening is understood as a type of heat treatment of a metal, consisting of heating it to a temperature, upon reaching which a change in the structure of the crystal lattice occurs (polymorphic transformation) and further accelerated cooling in water or an oil medium. The purpose of this heat treatment is to increase the hardness of the metal.
Hardening is also used, in which the heating temperature of the metal prevents a polymorphic transformation from taking place. In this case, its state is recorded, which is characteristic of the metal at the heating temperature. This state is called a supersaturated solid solution.
Polymorphic transformation hardening technology is used mainly for products made of steel alloys. Non-ferrous metals are subjected to hardening without achieving a polymorphic change.
After such treatment, steel alloys become harder, but at the same time they become more brittle, losing their ductility.
To reduce unwanted brittleness after heating with polymorphic change, a heat treatment called tempering is used. It is carried out at a lower temperature with gradual further cooling of the metal. In this way, the stress of the metal is relieved after the hardening process, and its fragility is reduced.
When hardening without polymorphic transformation, there is no problem with excessive brittleness, but the hardness of the alloy does not reach the required value, therefore, during repeated heat treatment, called aging, it is, on the contrary, increased due to the decomposition of the supersaturated solid solution.
Features of steel hardening
Mainly stainless steel products and alloys intended for their manufacture are hardened. They have a martensitic structure and are characterized by increased hardness, leading to brittleness of products.
If you heat treat such products by heating to a certain temperature followed by rapid tempering, you can achieve an increase in viscosity. This will allow the use of such products in various fields.
Types of steel hardening
Depending on the purpose of stainless steel products, it is possible to harden the entire item or only that part of it that must be functional and have increased strength characteristics.
Therefore, hardening of stainless steel products is divided into two methods: global and local.
Cooling medium
Achieving the required properties of stainless materials largely depends on the choice of cooling method.
Different grades of stainless steel undergo cooling differently. If low-alloy steels are cooled in water or its solutions, then for stainless alloys oil solutions are used for these purposes.
Mechanical properties
When considering the metal, the mechanical properties of steel 12x18n10t are also taken into account. they are characterized as follows:
- Brinell hardness corresponds to 179 MPa. This point determines that the surface of the material can withstand impacts of various types.
- The tensile strength varies in a different range, usually 279 MPa.
Mechanical characteristics of steel 12x18n10t
When choosing 12x18n10t, the yield strength is also taken into account, which determines the possibility of its use when casting various products.
Other features of the metal in question include the following points:
- When doped, silicon is included in the composition. It increases density and flow rate. The concentration of this chemical element in the composition adversely affects plasticity.
- Sufficiently high ductility and impact strength are attractive performance qualities of the metal.
- As the ambient temperature decreases, the mechanical properties of the metal begin to decrease significantly.
The disadvantage is that the metal does not withstand the effects of substances that contain chlorine ions. In addition, corrosion resistance is low in relation to hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. Therefore, the scope of application is somewhat limited.
Steel 12Х18Н10Т hardening methods
Let us dwell on the methods of hardening stainless steel grade 12Х18Н10Т. One of the common ways to increase the strength of long rolled metal products is High Temperature Heat Treatment (HTHT). When studying the possibility of increasing strength using HTMT technology, it turned out that the best strength was found in rolled products subjected to high-temperature heat treatment at minimum deformation temperatures and the length of time from the end of rolling to quenching. Thus, with HTMT of steel 08Х18Н10Т, the yield strength increased by 45-60% compared to the same level after conventional heat treatment (OTT) and by 1.7-2 times compared to GOST 5949-75 . At the same time, the plasticity properties decreased slightly and did not go beyond the permissible values of the standard.
Scope of application
The use of steel 12x18n10t is very extensive:
- Food industry. It is worth considering that there are quite a lot of requirements for products used in the food industry. The metal should not interact with food and drinks.
- Chemical and oil industries. These industries also often create various containers and elements that come into contact with petroleum products and various chemicals.
- Mechanical engineering. In the mechanical engineering industry, various products are manufactured by cutting. If they will be used in high humidity and exposure to chemicals, then the material in question is often selected.
- In the fuel industry and energy sector. The metal can withstand high temperatures.
Application of steel 12x18n10t in the production of building materials
Sheet steel 12x18n10t
Tank made of steel 12x18n10t
Application of steel 12x18n10t in automotive production
Metal can be processed using automatic and manual welding. A high thermal conductivity coefficient determines the use of steel in the manufacture of heat exchange equipment. Sheet metal is also used in the manufacture of collector elements for the transmission and distribution of exhaust gases.
Seamless stainless steel pipes, which are operated under high pressure, have become widespread. In addition, the chemical composition contains titanium, which determines low magnetic qualities. A sufficiently high concentration of carbon determines a high level of strength.
Description
Steel 12Х18Н10Т is used : for the manufacture of forgings of general mechanical engineering parts; chemical equipment parts; parts operating at temperatures up to +600 °C; welding machines and vessels operating in dilute solutions of nitric, acetic, phosphoric acids, solutions of alkalis and salts; parts operating under pressure at temperatures from -196 to +600 °C, and in the presence of aggressive media up to +350 °C; aircraft manufacturing parts; household consumer goods; devices and parts in the food industry; connections of equipment operating in radioactive environments and in contact with aggressive environments; as a cladding layer in the production of hot-rolled two-layer corrosion-resistant sheets; solid-rolled rings for various purposes and welded rings from sheets profiled by rotational deformation for power engineering and chemical industry equipment; cold-rolled steel and bent profiles intended for the manufacture of skins and frames for passenger car bodies; sheet metal with a thickness from 40 mm to 160 mm used in the production of shipbuilding parts and structures operating in seawater conditions; double and triple lay ropes for special working conditions; seamless cold-rolled, cold-drawn and warm-rolled pipes intended for pipelines and high-quality fittings; wire woven mesh of twill weave, used as a reinforcing material in the manufacture of asbestos steel sheets, for separating bulk solids by grain size, filtration and other purposes; spring wire intended for the production of cylindrical springs operating in air and aggressive environments (sea water, salt and chlorine solutions, sea water vapor, in tropical climates) at temperatures from -253 ° C to +300 ° C and used in turbine seals, safety valves, pumps, regulators, compressors; torsion springs; bimetallic sheets with aluminum alloy AMg6, intended for the manufacture of flat adapters for general purposes; centrifugally cast pipes used as components in the equipment of the metallurgical, mechanical engineering, glass, ceramic, mining and processing petrochemical industries, as well as intended for the manufacture of blanks and parts used in the composition of products in the aviation and nuclear industries.