Even though centrifugal pumps are reliable devices used for pumping liquids, they may also require repairs. Malfunctions of centrifugal pumps are not always caused by improper operation; this may be due to the quality of the pumped medium, and to a number of other factors. If disturbances occur in the operation of the centrifugal pump, then you must first exclude external causes and only then carry out diagnostics of the equipment itself.
Disassembling the centrifugal pump
Content
- Correct operation and maintenance
- Equipment operating rules
- Maintenance Regularity
- Centrifugal pump repair
- Troubleshooting
- Trouble-shooting
- How to apply for spare parts
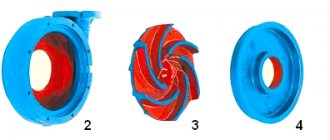
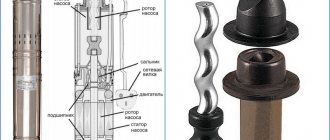
The principle of operation of the device is based on the conversion of the rotational force of the mechanism into fluid energy. The main structural elements are the impeller (impeller), central shaft, inlet and outlet openings, and electric motor.
The units work with different fluids: inert and chemically active, hot and cold, contaminated and purified.
When the electric motor is turned on, the impeller begins to rotate: due to traction, a pressure difference (vacuum) occurs. Under the influence of centrifugal force, the liquid flow is directed into the suction pipe. The water is released through the pressure hole.
Pipes for liquid transfer
Pipes located downstream of the pump are pressure pipes and must be equipped with protective devices. Shut-off valves or more modern ball valves must be on each pressure section of the pipeline. Gate valves and taps regulate the force of liquid supply, and if necessary, they can completely shut off the pipe - for example, in an emergency or for repairs.
gate valves
If the liquid pressure can reach 20 m, a check valve must be installed on the pipeline between the shut-off valve and the branch pipe. The purpose of the check valve is to prevent the reverse movement of fluid in the event of a sudden stop and water hammer in the system. If the check valve breaks, the fluid flow can turn the shaft in the opposite direction - this can lead to mechanical failure. It is also possible to operate at idle speed, which will lead to overheating of the engine.
Correct operation and maintenance
There are no hydraulic systems with identical performance characteristics. It is impossible to develop universal regulations defining the frequency of inspections. There are standards recommended by manufacturers. Regular maintenance of a centrifugal pump is the key to trouble-free operation of the system.
Basic information about the device is indicated in the passport and manual. The documents list the requirements for acceptance, maintenance, repair and storage of equipment. There is a section with a list of reasons leading to unit failure. The main and auxiliary characteristics (pressure, flow) are indicated. Attached are drawings of the mechanism: a view in three projections.
Equipment operating rules
Following the instructions helps reduce the number of repairs and prevent sudden system failure. The submersible pump is turned on when the working chamber is 100% filled with liquid.
To prevent insoluble impurities from entering the system, a mesh filter is attached in front of the suction pipe. The accumulation of solid particles in front of the inlet and inside the structure reduces the fluid pressure. When pumping contaminated water, wear on pumping equipment increases.
The instructions list the operating rules:
- The electric motor must not be allowed to overheat. To protect the drive from overload, a special valve is used. The element is installed on the suction pipe. The purpose of the part is to regulate the flow of fluid.
- When starting the engine, make sure that the impeller and drive shaft rotate clockwise.
- Observe the immersion depth of the water pump. It is prohibited to operate the device if the level of the pumped-out liquid exceeds the mark on the submersible part of the mechanism.
The instructions list the requirements for pipes. To create favorable conditions for the movement of horizontal flow, a slight slope is created. The drainage system is installed at an angle to the liquid supply point. If the surrounding conditions do not allow compliance with the requirement, the centrifugal pump is located as high as possible above the ground.
To ensure that the suction pipe works flawlessly, the following rules are followed when installing the system:
- form few kinks;
- select a pipeline with the largest internal diameter;
- make a minimum number of connection points.
How does the unit work?
In order to understand the principle of repairing pumping equipment, it is necessary to thoroughly understand its structure. Such knowledge will help to identify faults in the mechanism and eliminate them many times faster.
So, the design of a standard circulation pump for heating systems looks like this:
- A large horizontally elongated steel case in which all the working components of the system are located. In addition to steel, durable aluminum alloy or stainless steel can be used for the unit body.
- The housing houses a powerful electric motor and rotor.
- Here, an impeller with blades that are curved in the opposite direction from the movement of the wheel is fixed on the rotor. As a rule, this pump element is made from durable polymers.
Maintenance Regularity
The purpose of carrying out maintenance is to promptly identify a part with a breakdown, and, as an option, adjust the parameters of the technological process. Checking the functionality of the system increases the service life of the unit. Timely maintenance reduces the number of unscheduled pump repairs.
The consequences of late maintenance are budget overruns associated with the purchase of components and payment for work of increased complexity.
The frequency of maintenance activities is determined by the following factors:
- type of pumped liquid;
- intensity of equipment use;
- characteristics of the working environment: contamination (presence of abrasive particles), viscosity, temperature, hardness;
- method of installation of the unit;
- characteristics of the supply voltage.
The interval between checks depends on environmental parameters, operating conditions and storage conditions of the mechanism. The general rule is: the harder the equipment works, the more often the parameters are monitored.
Often, servicing of a household centrifugal pump is performed at the customer’s home. The plan includes work:
- checking and replacing bearings;
- crankcase cleaning and flushing;
- bearing lubrication;
- measuring deviations of the shaft and mating parts from the axis of rotation, adjusting the centrifugal pump;
- control of oil seal wear;
- flushing channels to introduce lubricant.
Why doesn't it work and what to do about it?
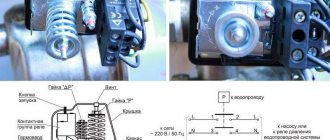
If the diagnostics showed that the pumping station itself is working, then you should pay attention directly to the pressure switch. The algorithm of actions will depend on how the malfunction of this unit manifests itself
Works often
When the pressure in the hydraulic tank is stable, the main reason for spontaneous frequent starts of the pump is a failure of the automation settings. For adjustments, a pressure gauge must be connected to the system.
The most popular relay in local water supply is RDM-5, with preset response threshold settings:
- lower pressure - 1.4 atm.,
- upper - 2.8 atm.
Step by step, this standard relay is adjusted as follows:
- Remove the unit cover.
- By right-hand rotation of the larger spring nut, raise the shut-off pressure to the desired value, for example 3.8 atm. At the same time, the lower launch limit will also rise.
- By turning the regulator of the smaller spiral to the left, set the desired pressure delta.
Spirals, especially smaller ones, are very susceptible to adjustments, so they should be adjusted very carefully, with gradual tightening of the nuts at 45° turns.
Doesn't turn off the pump
The most common reasons why the relay does not operate to turn off the pump include:
- Sticking and, in severe cases with powerful starting currents, melting of the breaker contacts. If the contacts are not damaged, the defect can be eliminated by cleaning them with fine-grained sandpaper, a fine needle file or a nail file.
- The difference between the relay response thresholds is too high. You should set the settings recommended by the manufacturer or optimal for a particular pump.
It is advisable to maintain the pressure delta in the range from 1.2 to 1.6 atm.
Clicks and switches off frequently
In practice, you can encounter another malfunction of the automation unit responsible for water pressure - periodic clicking.
If the reason is not related, as described above, to a breakdown in the water supply system itself (usually airing) or lack of pressure in the hydraulic tank (ruptured membrane), then the problem is in the automation.
Having summarized numerous opinions on this problem on engineering forums, we can conclude that there is only one possible solution to it - try to eliminate the frequent operation of the automation (clicking) by increasing the difference in the relay response thresholds.
If this does not solve the problem, then the only option is to replace the unit.
It just doesn't work
The relay may not close to turn on for the following reasons:
- Insufficient voltage in the network - automation is demanding on this parameter.
- Oxidation of the contact group - it is necessary to disassemble the device and clean the contacts.
- The automatic shutdown pressure limit is set too high.
- Lime and other deposits in the five-pin fitting with a pressure gauge connecting the relay to the pump (five-pin), or the hole in the membrane compartment is clogged - you need to remove the relay and clean the part.
- Sand gets into the membrane part of the block, which interferes with the action of the diaphragm on the piston. The latter is often observed if the pump has pumped sand. It is necessary to disassemble the relay, carefully clean and rinse everything.
Centrifugal pump repair
Manufacturers recommend contacting a service center after 4,500 hours of equipment operation. Planned repairs include the following:
- dismantling the unit, disassembling the structure into components, inspecting each part;
- determination of gaps in seals;
- monitoring the technical condition of the electric motor rotor;
- replacing bearings if wear exceeds permissible limits;
- checking the shaft journal for leaks (if defects are found, grooving and grinding are done).
At the end, the equipment is inspected again to make sure that the unit is assembled correctly (the first time - without load, then - when the power is turned on).
More serious repairs of centrifugal pumps are carried out after 26,000 hours of operation. The service center will replace the working shaft, impeller, sealing elements: casing, clamping and spacer bushings. If the wear of the multistage pump exceeds the norm, specialists will install a new section.
The overhaul includes restoration of the body: surfacing and boring of seats. The last stage is measuring parameters during hydraulic testing.
Common breakdowns
If no external factors have a harmful effect on the pump, but it does not work correctly or does not work at all, you should begin to thoroughly check it.
Most often, problems are caused by worn out seals.
There are a number of reasons that accelerate this process:
- Uneven shaft movement, especially with frequent runout.
- The unit cover bolts are too tight. Oil seals cope best with the sealing task when they have sufficient moisture, which can be judged by the seepage of liquid drops through the packing.
- Engine overheating.
- The repair technology was violated, for example, not all o-rings were replaced.
In addition to problems with seals, pump breakdowns occur due to insufficient accurate centering of the housing and power unit. In this case, both the seals and bearings are destroyed, leading to failure of the unit, and such problems can only be solved by a major overhaul.
Lack of proper care of bearings (their regular lubrication) can also pose a threat.
You may be interested in an article on the classification of centrifugal pumps. Read the article about centrifugal self-priming water pumps here.
Troubleshooting
There are no fail-safe centrifugal pumps; each design has its own bottlenecks. In self-priming models, components that often fail are the Venturi flow meter, diffuser tube and impeller.
Multistage devices stop pumping water due to deformation (or soldering) of the spiral channels (diffuser) and impellers. When a centrifugal pump is operated at its limit for a long time, the stator burns out and the electric motor jams. The defect appears in all structures.
A common cause of failure is rust. Owners do not prepare equipment for storage during the winter. The accumulation of moisture inside gradually destroys the metal parts. The mechanism jams when the first start is made in the spring. To restore functionality, the structure is disassembled and corrosion is removed.
The centrifugal pump can operate for a long time without complaints. Common causes of failure are related to non-compliance with the manufacturer's instructions for installation, maintenance, operation and storage. The result of violations is that the centrifugal pump does not work at full capacity. In some cases, the device switches to cavitation or “dry running” mode. Malfunctions lead to overheating of the electric motor and breakdown of internal components.
Common causes of system malfunction
- Narrowed section at the inlet. When selecting components, the following rule applies: the diameter of the suction pipe is equal to the size of the nozzle. If the immersion depth exceeds five meters, the diameter of the suction channel must be one size larger than the nozzle. Practice shows: the shorter and straighter the pipeline, the more efficient the centrifugal pump works. The pressure decreases if the movement of water is impeded by clogging or narrowing of the intake channel.
- Insufficient filling of internal cavities. The malfunction appears when the unit is first started, after dismantling, storage and repair. A distinctive feature is weak pressure. Alternatively, the pumping equipment does not pump water at all. To remove air from the system, turn off the device. The pipes and suction path are refilled with liquid.
- Violation of the tightness of structural elements. Due to a loose connection of the mating parts, air leaks occur. If the system is stopped, some of the liquid flows out spontaneously from the suction tract. When an automatic pumping station is operating, the malfunction manifests itself in frequent startup and low pressure. If the tightness of the parts is broken, the bus station may not pump liquid at all. The solution to the problem is to disassemble the system and seal the leaks.
- Check valve malfunction. The defect occurs due to the accumulation of foreign objects at the inlet: dirt, solid particles, debris. The consequences of a malfunction of the check valve are that liquid leaks from the suction path, as a result, the unit does not pump water. To improve the workflow, the system is dismantled. The valve is cleaned and washed.
- Filter clogged. The standard approach is to install a protective mesh on the suction valve. The perforated part prevents small objects from entering the system: fallen leaves, branches, insects. When the filter becomes clogged, the suction capacity of the equipment decreases. If the flow of water encounters significant resistance, the mesh may break. To remove blockages, the filter is periodically cleaned.
- Deviation from the permissible suction depth. When the parameter is greater than the recommended value, the effect of cavitation appears. The worst case scenario is that the integrity of the water flow is compromised. If the standard suction depth is exceeded, the unit does not pump water. To resolve the issue, use a vacuum gauge, which is mounted on the suction pipe. The device helps you select the optimal characteristics for a particular model: immersion depth and traction force.
For industrial enterprises, water utilities, thermal power plants, as well as service organizations, the reliability of pumping equipment is an important component. Pump downtime can be expensive in terms of stopping ongoing processes and life support systems, as well as the cost of the repair itself. Therefore, it is important to carry out diagnostics and preventive maintenance of the pump to avoid this.
Maintenance is generally divided into two types: service and preventive maintenance. Service maintenance is carried out to repair pump malfunctions that have already occurred. This must be done as quickly and reliably as possible in order to restart the pump. And important - taking into account the cause of failure, perhaps using more suitable components in a different material design and design.
However, service maintenance is more complex and unpredictable in terms of repair costs and downtime. This maintenance will not prevent it from occurring. To avoid downtime caused by unexpected pump failure, it is important to perform periodic diagnostics and preventive maintenance . Identifying the problem early is one of the best ways to troubleshoot and prevent pump failure.
The frequency of maintenance is determined according to the Service Instructions on the recommendation of the pump manufacturer. An approximate list and frequency of work is given on the Diagnostics .
Obvious reasons for calling service:
- Leaks. Check for leaks at the mechanical seal or flange connections. Mechanical seals are a wearing part and must be replaced regularly.
- Unusual noise. One of the first signs of a pump problem is noise. A constant hum when the pump is running is quite normal. However, excessively noisy or rattling noises may indicate a problem, such as worn bearings. Noise in the flow path may indicate that the pump is operating in cavitation mode, which can lead to wear on the impeller and other parts.
- Strong vibration. A properly installed, adjusted operating pump should not vibrate excessively, so the vibration level and tolerances should be checked. Common causes include imbalance of the impeller, misalignment of the pump and motor, and poor attachment to the foundation.
- Overheat. Heating of the pump, motor or bearings should not be ignored as they always indicate a problem. Some reasons may be the pump operating outside its operating range, lack of current protection, internal friction/wear of parts, incorrect network connection.
- Clogging. The presence of large solids can clog the impellers or valves if the pump is not designed for this purpose. In this case, the pump will not provide the required performance.
Calling or consulting a professional when you notice signs of system instability or security warnings will allow you to repair your system early before it fails, avoiding more expensive repairs later.
Professional diagnostics of a failed pump will allow you to determine the actual cause of the malfunction in order to prevent and eliminate its occurrence in the future.
Our service engineers first carry out Diagnostics, and then Technical and Service Maintenance , the list of which may include:
- Replacement of wear parts: mechanical seal, throat seals/rings
- Replacing bearings
- Replacing the impeller and other housing parts
- Laser shaft alignment. Leveling the unit
- Pouring oil into the oil chamber
- Electric motor rewinding and repair
- Setting up a control cabinet, frequency converter, pressure switch and other automation
After diagnostics, your engineers can independently carry out maintenance , replacing failed parts and assembling the unit. But in our experience, mechanics and engineers who do not have the necessary knowledge and skills miss a number of important points during assembly (the need for sterile surfaces, tolerances, tightening torques, etc.), as a result of which the pump, even with new components, again requires service.
Therefore, we recommend replacing bearings, mechanical seals, and shaft alignment only at service centers class=”aligncenter” width=”756″ height=”1080″[/img]Professional maintenance and assembly by experienced engineers will allow your pump to operate for a long time without repairs guarantee.
If you want to be sure that your pump is working reliably and won't suddenly fail, you need to invest in preventive maintenance. The frequency of maintenance is determined according to the Service Instructions on the recommendation of the pump manufacturer.
Pumps vary greatly depending on their application, and it is important to keep this in mind when searching for maintenance information on these systems. When servicing submersible pumping stations, the list of key points will be different.
When should the pump be replaced?
Most pump wear occurs on the internal parts of the unit and is therefore not visible until the pump is disassembled. Therefore, this can only be assessed by recommendation during routine maintenance.
Besides replacing a damaged or worn pump, there is also an economic reason to replace an old, inefficient pump.
At Vodoconstructions LLC, we service a wide range of pumps that are used in a variety of systems, including booster systems, wastewater treatment plants, plumbing, heating and air conditioning systems. We have extensive experience working with pumps from Wilo, Grundfos, Lowara, Dab, KSB, Kolmeks, Salmson, Ebara and other companies.
After preliminary diagnostics, you will be issued a diagnostic report with the results of the analysis of the pump and/or pumping station with recommended work and replacement of spare parts.
After agreeing on the scope of work, all necessary work is carried out, the results of which guarantee the reliable and stable operation of the pump.
When concluding a Service Agreement, we are responsible for the uninterrupted operation of your system and carrying out all necessary work on time.
For consultation, you can always call our service engineers by phone +7 (495) 772-41-71 or leave a request in the form below.
Trouble-shooting
To restore the functionality of the equipment, the unit is first dismantled, and after repair it is reassembled. The greatest difficulties are caused by operations: disassembling bearing units, liners, hydraulic bearings, pressure flange, coupling half.
Removing the impeller from the shaft requires maximum care. To prevent seizing, it is important to carefully remove the impeller. The process is performed alternately with each section. If the impeller is jammed (or the element is difficult to remove), the assembly is slightly heated.
Sometimes inexperienced users cannot assemble the structure. To prevent mistakes, it is recommended to take photographs of sections and individual parts after dismantling.
The assembly plan includes operations:
- reconciliation with the drawing to determine how well the new element complies with the regulatory documentation (drawing);
- monitoring the compatibility of components: recently purchased and previously installed;
- grinding and lapping of mating surfaces;
- uniform tightening of fasteners using a torque wrench (the purpose of the tool is to control the force);
- checking the accuracy of installation of the impeller on the shaft: the axial clearance in all directions must be the same;
- error control of the end side of the hydraulic foot: permissible deviation from the perpendicular axis - no more than 0.02 mm.
Experts warn: welding should not be used to restore the integrity of the housing or impeller. Statistics show the fragility of repaired parts.
How to apply for spare parts
In an application for spare parts for any industrial equipment, incl. for centrifugal pumps, it is recommended to indicate the most complete data from the identification tag (nameplate): model, serial number and date of production of the equipment.
Our company is the official distributor of Italian manufacturers of centrifugal pumps SAER and CALPEDA with the right to sell a full range of equipment, supply spare parts and consumables.
Applications and requests for spare parts are processed in the spare parts department.
Department managers will provide you with professional advice on selection, place an order and provide full information on availability and prices. SAER spare parts CALPEDA spare parts
How to prevent problems from occurring?
To avoid possible problems, it is necessary to correctly select a pressure switch. The characteristics of the automation must be optimal for working with specific equipment. It is better to seek the help of a specialist in this matter.
Preventative measures to prevent problems are:
- The use of a magnetic starter to remove the load from high currents from relay contacts.
- Periodic external inspection of the relay and checking the most critical points - the connecting pipe and contacts.
- Check at least once every 2 months and, if necessary, adjust the settings.
Important! The pressure threshold for turning on the relay to start the pump should be 0.2 atm. lower than the pressure in the accumulator.