Hot metal stamping
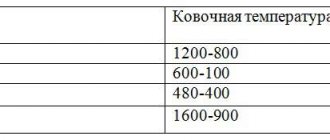
The peculiarity of the method is the deformation of the workpiece after heating it to a certain temperature. Form formation occurs as a result of forced redistribution of heated metal along the recesses of the inner surface of the die.
Features of hot stamping
The process is based on the use of metal plasticity, which increases when heated. Before forming, the blanks are evenly heated in special automatic control units. They ensure maintenance of the required temperature throughout the entire volume of workpieces and eliminate the formation of oxide films.
Equipment used for heat treatment:
- Electrical contact installations. Heating is carried out by electric current passing through the workpiece.
- Induction systems. The heating of the blank occurs due to eddy currents arising in the surface layer of the blank.
- Gas ovens. The temperature of the workpieces increases in an insulated chamber filled with inert gas.
Hot metal stamping is carried out by trained personnel with practical skills and experience in this type of production.
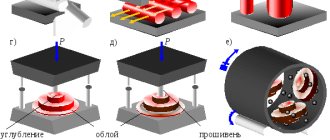
This method produces two types of parts:
- Elongated. These can be: levers, shafts, knobs and others. The work is carried out flat and ends with shaping in blank forging rolls.
- Disk. These include: rings, discs, gears, covers. In this case, the method of upsetting to the end of the workpiece using stamping transitions is used.
Closed method
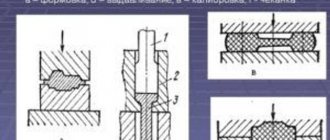
To obtain products of the required shape, presses with a protrusion at the top and voids at the bottom are used. There is a minimum gap between the fixed and moving parts. The connector cavities are located at an angle of 90° relative to each other. The method is used in cases where the dimensions of the finished product and the forging match the parameters.
Open way
In this case, there is a larger gap between the working parts to allow excess metal to drain. Trimming and punching dies and crank presses are used to remove flash. The technology can be used for stamping products of any size. A flawless surface, a uniform structure and metal savings are the advantages of the open method.
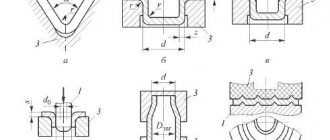
Stamping streams
The creation of complex shapes with differences in thickness and height, protrusions and bends is carried out thanks to surfaces that have special depressions, blanking and stamping grooves.
They come in several types:
- Drawing. They are used to increase the length of individual sections by applying frequent blows while simultaneously turning the part.
- Procurement. Necessary for shaping the workpiece and giving the finished product a shape with minimal metal waste.
- Pinch. They are used to reduce the height while simultaneously increasing the width of a separate section of the workpiece.
- Roll-on. They ensure uniform distribution of metal along the axis of the workpiece with an increase in the diameter of individual parts.
- Bending. They are used to form forgings with a bending angle of 90°.
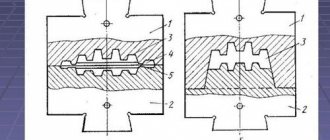
The final necessary shaping of the part occurs in the stamping strands. They are:
- Rough ones. To bring the dimensions of the workpiece closer to the required dimensions of the part and reduce wear on the finishing groove.
- Finishing. They are installed in the middle of the die, and are used for final molding of products. During its manufacture, allowances for shrinkage are taken into account. The extruded metal flows out through the cladding groove.
Additional operations
At the final stage, after removing excess material in the finishing stream, the shape of the part is corrected. This is required to correct its curved axes. Products made of alloy steels and large sizes are processed in a hot state. Small caliber products are adjusted after heat treatment and cooling.
The physical properties are brought to the required values during the final heating. Heat treatment relieves residual stress, reduces grain size and increases ductility.
Cleaning from scale is carried out by mechanical processing. The procedure for large products takes place in shot blasting complexes. Small parts are cleaned in tumbling drums.
Product calibration is used to reduce roughness and obtain accurate dimensions. After this, there is no need to carry out finishing processing; it is enough to sand the resulting parts. For the work, special dies with particularly precise grooves that repeat the configuration of the forging are used.
Advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping
Advantages:
- Saving metal by reducing losses.
- Possibility of manufacturing parts of complex shapes.
- Reduced labor intensity.
- Obtaining products of precise shape and configuration.
- High level of productivity.
The disadvantages of the method include:
- High cost of design and manufacturing of equipment.
- Complexity and energy intensity of the process.
- The maximum weight does not exceed 4 tons.
The hot method is used to produce large series and in cases where the complexity of the shapes and thickness of the products does not allow cold stamping.
Tools and equipment
Main types of forging and stamping equipment:
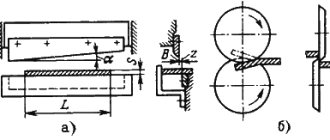
- Shears – long, combined (for cutting various rolled profiles) or sheet. They use the principle of the well-known guillotine, when, due to the difference in the angle of inclination of the movable knife, metal is sequentially separated. The actuator mechanism of the scissors is of the crank type.
- Steam-air, pneumatic and hydraulic stamping hammers, in which the energy carrier is steam, compressed air or high-pressure liquid, respectively. They are impact equipment; they deform the metal not by pressing force, but by the energy acting on the forging.
- Crank presses, divided into equipment for hot stamping (HSE), universal presses for sheet stamping and hydraulic presses. The change in shape occurs due to the force developed by the actuator.
- Rotary machines, the tools of which perform a rotational movement - rollers, disc shears. This type of equipment deforms metal using torque.
- Screw machines with mechanical, electromechanical or hydromechanical drive. Their energy characteristics are intermediate between presses and hammers.
- Hydro- and gasostats are machines that develop extremely high static pressures, which are sufficient to compact metal powders.
Stamping technology involves the use of specialized tools - stamps. They are distinguished:
- By number of positions: single- and multi-position;
- Time of execution of stamping transitions: dies of sequential, combined and series-parallel action;
- By relative location; into vertical and horizontal;
- Design of guides and fixing units;
- According to the degree of accuracy - ordinary or precision.
Dies of automatic presses are usually called a set of deforming tools. For some types of stamping (for example, for explosive or electromagnetic forming), there are no stamps as a tool.
Modern die designs must include units for feeding, removing or moving the workpieces being processed.
Cold metal stamping
The cold method is a technological operation in which a metal workpiece is subjected to deformation without preheating.
Sheet stamping
Parts using this method are produced by pressing metal sheets, strips or rolls. The thickness of the resulting product does not exceed 10 mm. Sheet metal stamping is in demand for mass production of products that are absolutely identical in shape and size.
Two types of presses are used to carry out the work:
- Universal. They are designed for cutting, bending and drawing.
- Special. With their help, deep drawing and specific bending of parts is carried out.
Sheet metal stamping can be carried out using mechanized equipment or automatic presses.
Workpieces for work are cut, if necessary, using mechanical or hydraulic shears. Wide sheets are cut on disc tools with cylindrical legs. The curved contour is made with disk or conical scissors.
Types of operations carried out during sheet stamping
Parts are made in two ways:
- Shape-changing. This includes: twisting, bending, winding, crimping, molding, stretching, flanging. During the operation, the workpiece material is not destroyed, only the shape and size changes.
- Separating. It includes: slicing, piercing, trimming, punching and stripping. In this case, the workpieces are separated during shearing along a given contour.
Pros and cons of the method
The disadvantages of cold sheet metal stamping include the high cost of equipment. The process pays off quickly only in mass production.
The advantages of this method are:
- Ability to perform multiple operations in parallel.
- Obtaining interchangeable parts.
- Increased productivity and efficiency.
- Cost-effectiveness of mass and serial production.
- Obtaining durable parts while maintaining their minimum weight.
- Dimensional accuracy and high surface quality.
Cold stamping is designed to produce products weighing no more than 1 ton. Production of heavier weight products is not recommended.
Volumetric cold stamping
This universal method is in demand in the production of a variety of metal products. There are several types of volumetric stamping.
Cold extrusion
The workpiece is placed in a cavity, from which the metal is extruded into holes located in the working mechanism. It is carried out on crank or hydraulic presses. There are four options for extrusion:
- direct;
- reverse;
- lateral;
- combined.
The ability to obtain products without destruction or deformation of the workpieces is the advantage of extrusion.
Disembarkation
The process is carried out on special machines. A rod or wire is stamped. They are placed in the working area and cut into blanks of established sizes. The cut parts are transferred to the stamping mechanism.
Cold metal stamping in open dies
The method is based on molding parts by filling the die cavity with metal. To facilitate the process and weaken the resistance of the metal base, the parts are divided into transitions, between which they are annealed. Thanks to this, the ductility of the metal increases, the risk of destruction of parts is reduced and the permissible degree of forming increases.
Cold die forging is carried out in open dies. Under cold deformation conditions, closed stamping is used to produce products from non-ferrous metals.
Advantages and disadvantages of die stamping
The main disadvantage of this method is the rapid wear of the dies. The reason for this is the significant mechanical loads experienced by the equipment used.
Advantages of volumetric stamping:
- Producing high-quality products without scale.
- Strength of manufactured parts and dimensional accuracy due to the absence of oxidation.
- High performance.
- Minimum surface roughness of products.
- Possibility of full or partial automation.
- No need to heat the material.
- Efficiency of metal use.
The quality of production depends on the correct assembly and operation of the die.
Features of the technology
You can familiarize yourself with the GOST requirements for metal stamping processing by downloading the document in pdf format from the link below.
GOST 18970-84 Metal forming. Forging and stamping operations. Terms and definitions Download
In addition to the division into hot and cold, stamping of metal products is also divided into a number of other categories depending on its purpose and technological conditions. Thus, stamping operations, as a result of which a part of the metal workpiece is separated, are called separation operations. This, in particular, includes cutting, chopping and punching metal parts.
Another category of such operations, as a result of which the stamped sheet of metal changes its shape, is form-changing stamping operations, often called forming. As a result of their implementation, metal parts can be subjected to drawing, cold extrusion, bending and other processing procedures.
As noted above, there are types of stamping, such as cold and hot, which, although implemented according to the same principle, which involves deformation of the metal, have a number of significant differences. Stamping of parts, which involves preheating them to a certain temperature, is used mainly in large manufacturing enterprises.
This is primarily due to the rather high complexity of such a technological operation, for the high-quality implementation of which it is necessary to make a preliminary calculation and accurately observe the degree of heating of the workpiece being processed. Using hot stamping, sheet metal of various thicknesses is used to produce critical parts such as boiler bottoms and other hemispherical products, hulls and other elements used in shipbuilding.
Characteristics and types of parts produced on hot stamping presses
To heat metal parts before hot stamping, heating equipment is used, which is able to provide precise temperature conditions. Electrical, plasma and other heating devices may be used in particular for this function. Before starting hot stamping, it is necessary not only to calculate the heating rates of the parts being processed, but also to develop an accurate and detailed drawing of the finished product, which will take into account the shrinkage of the cooling metal.
When performing cold stamping of metal parts, the process of forming the finished product occurs only due to the pressure exerted by the working elements of the press on the workpiece. Due to the fact that the blanks are not preheated during cold stamping, they are not subject to shrinkage. This allows us to produce finished products that do not require further mechanical modification. That is why this technology is considered not only a more convenient, but also a cost-effective processing option.
If you skillfully approach the issues of designing the size and shape of workpieces and the subsequent cutting of the material, you can significantly reduce its consumption, which is especially important for enterprises that produce their products in large batches. The material from which workpieces are successfully stamped can be not only carbon or alloy steels, but also aluminum and copper alloys. Moreover, an appropriately equipped stamping press is successfully used for processing workpieces made of materials such as rubber, leather, cardboard, and polymer alloys.
Separation stamping, the purpose of which is to separate a part of the metal from the workpiece being processed, is a very common technological operation used in almost every manufacturing enterprise. Such operations, which are performed using a special tool mounted on a stamping press, include cutting, punching and punching.
During the cutting process, metal parts are separated into separate parts, and such separation can be carried out along a straight or curved cutting line. Various devices can be used to perform cutting: disc and vibrating machines, guillotine shears, etc. Cutting is most often used to cut metal workpieces for further processing.
Punching is a technological operation during which parts with a closed contour are obtained from a metal sheet. Using punching, holes of various configurations are made in sheet metal blanks. Each of these technological operations must be carefully planned and prepared so that the result is a high-quality finished product. In particular, the geometric parameters of the tool used must be accurately calculated.
Technological stamping operations, during which the initial configuration of metal parts is changed, are forming, bending, drawing, flanging and crimping. Bending is the most common form-changing operation, during which bending areas are formed on the surface of a metal workpiece.
Drawing is a volumetric stamping, the purpose of which is to obtain a volumetric product from a flat metal part. It is with the help of drawing that a metal sheet is transformed into products of a cylindrical, conical, hemispherical or box-shaped configuration.
Along the contour of sheet metal products, as well as around the holes that are made in them, it is often necessary to form a side. Flanging successfully copes with this task. The ends of the pipes on which flanges need to be installed are also subjected to this treatment, performed using a special tool.
With the help of crimping, unlike flanging, the ends of pipes or the edges of cavities in sheet metal blanks are not expanded, but narrowed. When performing such an operation, carried out using a special conical matrix, external compression of the sheet metal occurs. Molding, which is also one of the types of stamping, involves changing the shape of individual elements of a stamped part, while the outer contour of the part remains unchanged.
Volumetric stamping, which can be performed using various technologies, requires not only careful preliminary calculations and the development of complex drawings, but also the use of specially manufactured equipment, so implementing such technology at home is problematic.
History of the process
It has been known and used since ancient times, since it was invented before the Middle Ages and even then allowed our ancestors to make weapons, jewelry and other things needed in everyday life. It has been steadily improved over the centuries, always distinguished by its comparative simplicity and high productivity, but it was performed manually until the 1850s, after which the level of technological development allowed it to be mechanized in earnest.
From the middle of the 19th century, technical operations began to be carried out on machine tools; from the beginning of the 20th, they began to produce car bodies; from the 1930s, the hulls and mechanisms of sea and river vessels and aircraft; from the 1950s, functional units and elements in rocket science.
Metal stamping has remained popular for centuries due to the following features and advantages:
- Versatility - it can be used to produce parts of any size and shape, both those that require further processing and those that are already ready for use.
- Precision manufacturing, especially at the current level of technology, which makes it possible to ensure the interchangeability of manufactured elements even without finishing.
- A penchant for mechanization and automation - high productivity has always been an obvious advantage, and today it is achieved through the use of rotary conveyor lines.
- Durability of final products, even thin, light, large ones.
The process is especially relevant for mass production - both small elements, like gears for watches, and large objects, for example, car bodies.
Areas of use
The method is in demand in various industries where it is necessary to give metals a given shape. The production of parts using stamping is used in the following areas:
- automotive industry;
- production of electronics, watches, etc.;
- construction;
- printing;
- mechanical engineering;
- aircraft manufacturing, etc.
Thanks to high-tech devices during the processing process, it is possible to obtain workpieces of a given shape of different sizes with a minimum of waste.