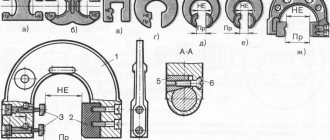
Types of turning
Manufacturing parts on lathes and centers is a technically complex process. To quickly and efficiently carry out work, it is necessary to use appropriate equipment, if possible with numerical control. Particular attention is paid to processing tools - cutters and drills. The accuracy of the parts and their compliance with the drawings depends on their quality.
Standard types of turning work performed at specialized enterprises and workshops are as follows:
- metalworking of cylindrical surfaces of workpieces of any size to give the part the desired shape and size (a);
- processing the outer surfaces of conical parts for the initial and final removal of the desired metal layer (b);
- metalworking of ends and ledges with subsequent finishing preparation of workpieces (c);
- turning grooves and grooves, cutting metal parts to size using cut-off cutters and other tools (d);
- drilling, boring, reaming holes in workpieces (e, f);
- cutting external and internal threads of the required size (g, h).
All of the above types of work are standard operations that are performed using domestic and imported equipment. The choice of machine depends on the required accuracy, speed of order fulfillment, and volume of product batches. To reduce unit costs and improve quality, it is best to use CNC machines.
Metalworking of cylindrical parts
Features of the process are the gradual removal of metal from the workpiece using standard cutters. The speed of passage, the thickness of the cut layer, and the final dimensions of the workpiece are determined by the grade of steel. Before the work begins, the technical specifications are studied, and metalworking parameters are set based on the input data.
Standard cutters are thrust and through-type tools. Finished parts are presented in the form of axes, shafts, and fasteners. The processing of cylindrical surfaces is carried out on metal blanks; it is possible to modify finished parts provided by the customer. The configuration and dimensions of the products exactly correspond to the customer's drawings. Similar operations are performed on machines with manual and numerical control.
Metalworking of external surfaces of conical type
Processing conical workpieces, as well as removing the metal layer from the outer surface of the part, are quite complex and have the following features:
- processing of the workpiece is carried out simultaneously in the horizontal and vertical plane, which excludes high accuracy when using standard equipment;
- the tool is fed simultaneously in the transverse and longitudinal directions in exact accordance with the specified parameters;
- the use of CNC machines allows you to maintain the dimensions of the part as accurately as possible, additionally chamfer, and ensure high speed of production of parts.
Turning of metal with a conical surface on machines with numerical control is one of the popular areas of work of INTEC-M LLC. The company has all the necessary technical and human resources to quickly and efficiently fulfill orders of any complexity.
Metalworking of ends and ledges
One of the simple operations performed on lathes is the processing of end surfaces. The workpiece is clamped in the chuck and centered. Metalworking of ledges and ends is carried out using through cutters.
The operator is required to set the rotation speed of the cartridge and other necessary parameters. The part is processed from edge to center, the speed is determined by the grade of steel and the requirements for the final product. These operations are most often performed on manually operated machines.
Cutting workpieces on a lathe
Metalworking using cutting tools is one of the main operations on cylindrical and conical workpieces. Cutting is carried out in the direction from the outer edge of the part to the center. At the final stage, it is necessary to provide support for the workpiece to prevent it from falling and damaging the processing tool.
To process long parts, a special tool called a rest is used. With its help, the product is fixed in the middle part. The steady rest serves as a support and allows you to perform operations with maximum precision and without chipping the cutter.
Metalworking holes
Such operations include:
- Drilling is most often the first and main operation. The workpiece is fixed by the jaws of the chuck. The cutting tool is mounted in a frame on the headstock. When using a lathe, drilling is only possible in the center of a cylindrical or conical part;
- internal and external boring are performed after drilling. The part is fixed on the headstock, processing is carried out gradually with special cutters. The thickness of the removed metal layer depends on the grade of steel and the requirements of the technological process;
- reaming holes, preparing internal grooves, cutting threads, internal and external, left and right, metric, conical and trapezoidal - standard operations performed on CNC lathes. Turning of cylindrical and conical parts is carried out with a special tool according to customer drawings.
The use of machines with manual and numerical program control is allowed. The second option makes it possible to increase productivity and increase the accuracy of workpiece processing. INTEK-M company uses high-precision equipment, the choice of which is determined by the parameters, complexity and volume of the order.
Equipment and tools
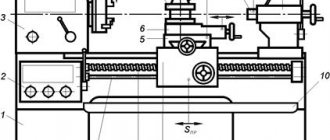
When familiarizing yourself with the technology of turning work, it is important to pay attention to the equipment used in its implementation. The main equipment of a screw-cutting lathe includes an electric motor with a set of starting capacitors and an emergency protection unit. Auxiliary devices are represented by a lighting lamp, a coolant supply mechanism and an exhaust fan.
The main toolkit of any lathe is a set of cutters used in processing. Most work operations are impossible without such names as:
- Cut-off.
- Walkthroughs.
- Threaded.
- Shaped.
- Scoring, etc.
Please note: According to the existing classification, cutters belong to the main equipment of the machine.
Auxiliary equipment includes drills and additional tools used during drilling operations. The latter are represented by the following names:
- Countersinks and countersinks used to machine the surfaces of the walls and bottoms of holes.
- Reamers that allow you to achieve high precision boring of hole walls.
- Counterbodies used for processing the bottom of sockets and grooves in the original workpieces.
This category also includes taps and dies (with their help, internal or external threads are manually cut).
What tools are used for metalworking on lathes?
For metalworking, equipment parameters such as the number of revolutions of the chuck per unit of time, the thickness of the steel layer to be removed are adjusted, and the necessary tool is selected.
The type of material is decisive for setting the parameters and selecting the cutter. The stronger and harder the metal, the smaller its layer is removed in one pass and the better quality the cutters should be.
The following tools are used in metalworking:
- For rough grinding of workpieces, tools with a larger cutting plate, straight, bent and reinforced, are used. Such cutters are capable of removing a thick layer of material in one pass without damaging the working part;
- Finishing cutters with a narrow insert are used to remove metal in thin layers. Depending on the parameters of the workpiece, the appropriate cutting tool is used;
- Special cutting tools are used to cut workpieces to size. In appearance, the tool differs from its through and thrust analogues, since its movement is carried out only in the transverse direction;
- Boring and reaming of holes is also performed using special cutters, the working surface of which faces outward. There are many varieties of such instruments.
When choosing a tool, special attention is paid to the angle of rotation of the cutting part. For example, if the work is done with workpieces made of hard steel and large diameter, then the standard angle of rotation of the cutter varies from 35 to 40 degrees. To process smaller workpieces made of soft steel, the reamer angle increases to 60-90 degrees.
Types of processed parts
A lathe allows you to process workpieces such as bodies of rotation:
| Workpiece name | Classification | Products |
| Cylindrical rotation parts | Bushings | Bushings, liners, axle boxes, sleeves |
| Shafts | Shafts, rollers, axles, rods, journals, pins, pins | |
| Flat rotation parts | Discs | Discs, rings, flywheels, pulleys, flanges |
| Multi-axis parts | Eccentric products | Crankshafts, eccentrics |
| Rotating parts with intersecting axes | Crosspieces | Crosses, fittings |
| Other blanks | Gears | Single- and multi-ring gears, rims, gear-shafts, wheels-discs |
| Shaped jaws | ||
| Lead screws and worm products | ||
| Fasteners | Bolts, nuts, screws |
Machines used by INTEK-M for turning operations
Standard equipment for rough grinding and finishing metalworking are turning and turning-milling machining centers. They are universal, have excellent technical characteristics, and are suitable for performing most operations ordered by clients.
Imported machines include a headstock, a spindle with a chuck and a gearbox. Also included in the package is a tailstock, a mount for installing mandrels or a rotating center, and a clamp for the slide. The bed and feed box are included in each device.
The MAZAK SMART TURN 200 ML turning and milling processing center provides high speed and quality work with metal parts. The machine is capable of performing diverse work in accordance with the established algorithm. The MAZAK QT100MSG turning center has compact dimensions and high productivity, and is capable of working with different materials.
Technical and economic indicators
Metal turning combines two determining factors - technical feasibility and feasibility. In the conditions of multi-product production, which is characterized by instability of objects and the size of production batches of parts, choosing a profitable technological process option from among competing ones is a complex and time-consuming task that requires a large number of calculations related to the determination of technical and economic indicators.
The main performance indicators of machine-building enterprises are:
- labor productivity;
- profit;
- production cost;
- intensity and efficiency of use of financial resources;
- material and energy intensity of products;
- profitability;
- capital intensity and capital productivity;
- equipment utilization rate and others.
An important task is to ensure the competitiveness of products, taking into account the constantly growing requirements for product quality and limiting the costs of labor, material, financial and energy resources.
Why is it profitable to order turning work from INTEC-M LLC?
Our company has been working in this field for several years and has accumulated extensive experience in fulfilling orders of any volume and complexity. The advantages of cooperation with INTEC-M LLC are:
- We carry out all types of turning work using modern equipment, guaranteeing high quality and accuracy of workpieces.
- We provide a full production cycle. In addition to turning, operations are available on other types of CNC machines.
- Quality control is carried out at all stages of order fulfillment. For this purpose, the company has its own quality control department.
- An individual approach to each client is practiced. The company accepts orders for piece and serial production of finished products and components.
- Attractive prices for turning and other types of work.
- The technical capabilities of the enterprise allow us to successfully work with ferrous and non-ferrous metals, composites and plastics.
Process selection
The determining influence on the choice of type of lathe is the size of the production batch of parts and its design and technological features:
- maximum diameter;
- length;
- required accuracy;
- surface roughness.
The diversity of lathes leads to an increase in the number of competing process options. For example, using the scheme for generating competing shaft processing options, you can generate 20-30 possible processing options for a stepped shaft. Therefore, it is necessary to choose the right (optimal) lathe, providing minimal labor intensity with maximum economic efficiency. When choosing a TP option, the volume of production and other production conditions are also taken into account.