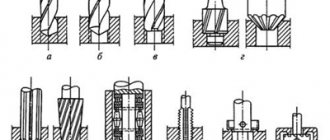
- Classification of metal-cutting tools.
The cutting tool is divided into blade
and
abrasive
.
Blade tool
– a cutting tool, with a given number of blades, of a prescribed shape.
Abrasive tool
Designed for abrasive processing.
By type of material being processed:
(
metal, wood
).
By shape
distinguished:
disk, cylindrical, conical and plate.
By design
,
according to the method of fastening the working part
:
solid, composite, prefabricated.
Solid cutting tool
- This is a cutting tool made from a single workpiece.
Composite –
cutting tool with permanent connection of its parts and elements
Prefabricated –
cutting tool with detachable connection of its parts and elements
By mounting method
–
tail and attachment
.
By type of drive
–
manual, machine and machine-manual
.
Classification of cutting tools
Metal-cutting equipment, which today is used in a variety of industries, as well as in everyday life, allows the use of various types of cutting tools.
The list of these types is very extensive, thanks to which it is possible to select a metal-cutting tool that best suits the characteristics of the operations being performed. The classification criteria for the described instrument are very numerous; this article is devoted to their consideration. One of the main classification criteria is the design feature of the cutting tool . It distinguishes the following types:
- Cutters: a single-edge type tool that allows metalworking with the possibility of multidirectional feed movement;
- Milling cutters: a tool in which processing is performed with a rotational movement with a trajectory having a constant radius and a feed movement that does not coincide in direction with the axis of rotation;
- Drills: Axial-type cutting tools that are used to create holes in a material or increase the diameter of existing holes. Machining with drills is carried out by a rotational movement, supplemented by a feed movement, the direction of which coincides with the axis of rotation;
- Countersinks: an axial type tool, with the help of which the size and shape of existing holes are adjusted, and their diameter is also increased;
- Reamers: an axial tool that is used for finishing the walls of holes (reducing their roughness);
- Counterbodies: metal-cutting tools, also classified as axial and used for processing the end or cylindrical sections of holes;
- Dies: used for cutting external threads on workpieces;
- Taps: also used for cutting threads - but, unlike dies, not on cylindrical workpieces, but inside holes;
- Hacksaw blades: a multi-blade type tool in the shape of a metal strip with many teeth, the height of which is the same. Hacksaw blades are used to cut off part of a workpiece or create grooves in it, while the main cutting movement is translational;
- Shapers: used for gear turning or gear shaping of shaft splines, gears, and other parts;
- Shavers: an instrument whose name comes from the English word “shaver” (translated as “razor”). It is intended for finishing of gears, which is performed using the “scraping” method;
- Abrasive tool: bars, circles, crystals, large grains or powder of abrasive material. The tools included in this group are used for finishing of various parts.
The next classification criterion is the type of surface , the processing of which is carried out using a metal-cutting tool. The following tools are distinguished:
- Used for processing bodies of rotation, external shaped, as well as flat surfaces: this group includes the cutters and cutters described above, abrasive wheels and some other products;
- Used for processing holes: we are talking about countersinks and drills, boring cutters and broaches;
- Tools used to cut threads: this group includes dies, taps, knurling rollers, and a number of other products;
- Used for processing the surfaces of sprockets, splined shafts, wheel teeth: these operations are performed using finger and disk cutters, rolling cutters and cutters, grinding wheels and shaver. It is impossible not to mention broaches, double cutter heads and gear-planing cutters (they are designed for cutting bevel-type spur wheels), as well as worm-type conical cutters and gear-planing heads (with the help of these tools, conical-type wheels with spiral teeth are cut).
Another criterion for classifying a metal-cutting tool is the principle of its interaction with the material . It identifies tools such as:
- Regular;
- Rotary, the circular blade of which is continuously renewed.
In addition, experts point to such a classification criterion as type of manufacture , highlighting:
- Solid cutting tool;
- A composite tool, the design of which is an integral connection of several elements;
- A prefabricated tool characterized by the detachable nature of the connection of the elements that form it.
According to the method of connection to the machine, attachment, tail and prismatic tools are distinguished.
Finally, according to such a criterion as the method of application manual, machine, and machine-hand metal-cutting tools are distinguished.
Types
The set consists of a tool box and its contents. Sockets, screwdrivers, bits, turning tools and wrenches included in a set are classified as parts.
The more parts a kit contains, the more versatile it is. The largest sets contain 500 or more elements.
Boxes are made of metal, plastic or other materials. Sizes range from small pencil cases to large racks on wheels. A common form is a tool case or suitcase.
The tool is grouped into thematic sets of three types:
- Universal, automotive or special kit. This is the most common gradation, which is used as a basis by most manufacturers.
- For car enthusiasts, small household needs and other serial work. These are household kits.
- A series of tools of the same type with different parameters. Most often, such kits are aimed at professional use. Attachments for power tools can also be grouped.
Household series differ from professional series. Home kits most often include a hammer, a pair of pliers and several screwdrivers. For automobiles - devices for minor car repairs.
The number of units of the set is limited to the elements that are necessary to perform most household tasks.
Professional models are made from alloy steel. Kits sometimes include batteries, multimeters, and fasteners in common sizes.
Classification of cutting tools
There are quite a large number of different classification features for cutting tools; the main ones can be called design features. Depending on the geometric shape and basic parameters, the following options are distinguished:
- cutters;
- incisors;
- countersinks;
- drill;
- sweeps;
- countersinks;
- taps;
- dies;
- shaver;
- hacksaw blade;
- abrasive type tool.
All of the above types of cutting tools are characterized by their own specific features. An example is a hand-held cutting tool called a die. By using a special fastening it is possible to obtain a threaded surface on a cylindrical surface.
Incisors have become quite widespread. They are classified as cutting tools that are designed to process exclusively rotating bodies.
Among the features of this version, we note the following:
- There is a working part and a holder.
- The sharpening angle may vary significantly depending on the purpose of the product.
- A variety of alloys are used in manufacturing, which determine the scope of application of the product.
Milling cutters have been seen quite often lately. This is due to the fact that such a cutting tool can be used to produce cabinet products. A special feature is that the main rotation is transmitted to the cutter, while the workpiece is stationary at this time. Structurally, cutters are much more complex than cutters, which determines their higher cost.
Guarantee
In most cases, hand tools are covered by a standard warranty, the duration of which varies from 1 to 3 years. Warranty service does not apply to cases of incorrect operation and mechanical damage to the instrument.
Repair or replacement is carried out only if there are manufacturing defects confirmed by the manufacturer. It is also necessary to keep a complete set of documents on hand: a warranty card with the signature and seal of the seller, sales and cash receipts.
Limited Lifetime Warranty
Some manufacturers offer a lifetime warranty on tool sets.
It is worth considering the nuances of this type of guarantee. Repair and maintenance are carried out under the same conditions as under standard terms, but often include a number of additional restrictions:
- The product is considered to have a warranty of no more than one year if it is a product with electrical or electronic components.
- The Lifetime Warranty does not apply to products that have been misused, altered, or repaired without service.
- The warranty does not cover repairs or replacement of consumable items - knife blades, glue sticks, drills, etc.
Defective products that meet the warranty conditions will be repaired or replaced by the manufacturer at its own expense.
Full Lifetime Warranty
The manufacturer undertakes to replace a mechanical tool that fails, regardless of the cause of the failure.
As a rule, an additional request is indicated not to try to return the broken instrument to the store, but instead to use the hotline.
Most manufacturers that offer this type of warranty state that they will not require proof of purchase of the product.
In the case of universal sets, even wrenches, ratchets and drive accessories are replaced.
This full lifetime warranty excludes all incidental or consequential damages to the buyer, except as required by local law.
Areas of use
The scope of application of cutting tools is very extensive. Most of the products are found in mechanical engineering, since the workpieces are represented by various alloys. Considering the scope of application, we note the following points:
- Most products can cut metal only if a large force is transferred when the workpiece is rigidly secured. That is why they are manufactured in such a way that they can be installed in machines and other similar equipment. Scope of application: industry with varying levels of labor productivity. A distinctive feature of this group is its long service life and wear resistance.
- Processing of workpieces can also be carried out in a home workshop. For such a case, design options that are used for manual processing or the use of desktop equipment are suitable. Experts recommend choosing low-price options for your home workshop. This is due to the fact that they are excellent for machining at low feed rates and cutting speeds. Cutting tools for industrial machines are much more expensive and require professional periodic sharpening.
In general, we can say that the scope of application of cutting tools is very extensive. Mechanical cutting can only be carried out if there is a cutting edge.
Malfunctions
In ready-made sets, handles often break and sets of attachments become unusable due to weakness of the metal, excessive load or mechanical damage.
The specificity of hand tools is such that self-repair is not practiced. Of course, you can straighten the slot one time, weld the attachment, or attach a tire to a broken handle, but this will inevitably affect the functionality of the tool.
Wear and tear of consumable parts is normal. A broken drill, tap or drill is replaced with similar elements. Unless the functional part of the tool is damaged, these parts are not eligible for warranty replacement.
Selecting a cutting tool
Only a properly selected tool can be used to obtain a quality product. With such a large selection to choose from, it is difficult to choose the most suitable product design. Metal cutting tools are selected taking into account the following recommendations:
- To begin with, the task at hand is determined. As a rule, the production technology is drawn up by the technologist, who also indicates the most suitable cutting tool. For example, you can obtain a body of revolution with the required diameter by using a cutter or drill hole. In this case, one part can be manufactured using one type of product with different parameters.
- The next step is to determine what kind of equipment will be used to transmit rotation. Examples include industrial machines or manual structures. From this point depends which holder is suitable.
- At the time of drawing up the technological map, the main cutting parameters are indicated. Taking into account this indicator, a cutting tool is selected according to the type of material used in the manufacture of the main or working part.
- The performance of the equipment used is also taken into account. To produce a large number of products, you need to choose a version with increased wear resistance.
Advantages
The advantages of hand tools correspond to their types:
- Car kits are suitable for most routine maintenance work and eliminate the need to go to a car service center for minor breakdowns; they are indispensable on the road.
- Universal series are convenient with an abundance of shapes, sizes and functional elements. The main advantage is the interchangeability of individual components.
- Special kits are designed for professional use. As a rule, they do not contain unnecessary elements. Each component is usable for the job.
The basic advantage of any set over a separate, albeit high-quality, tool is the ability to flexibly select it for a specific task without the need to visit a hardware store if some detail is missed.
The kit contains basic parts and attachments at hand.