Repairing the underbody of a car is not a frequent task, but it is one of the most difficult types of body work that requires qualifications and experience. The bottom, sills, and wheel arches are subject to the greatest destruction from corrosion and mechanical damage.
Operating a car on bad roads, flying gravel, winter use of salt reagents on the streets, incorrect or minimal application of anti-gravel and anti-corrosion protection are the first reasons for the rapid destruction of metal. 70% of drivers are faced with the need to digest sills, change or repair the underbody 5-7 years after purchasing a new car.
Repair tools and materials
In half of the cases, the need for a full underbody repair is discovered by technicians at a service station during routine vehicle diagnostics. When the car is lifted onto an overpass, it is easier for a mechanic to see corrosion plaques on the metal, dents from impacts, etc. The cost of repairs depends on the degree of damage; in a workshop this is a justifiably high price of 10,000 rubles. only for overcooking the thresholds.
But in the case of a body, the degree of damage to the metal may be excessive and it will not be necessary to repair the bottom with patches, but to completely or partially replace the load-bearing elements. Many drivers choose garage repairs; it is 10-15 times cheaper; if the technician has skills in gas or electric welding, the cost of the work is minimal.
Before welding the underbody of a car with your own hands, you need to prepare the following tools and materials:
- calcium carbide, oxygen cylinder if gas welding is used;
- copper wire, carbon dioxide, if welding is performed semi-automatically;
- metal for patches;
- replacement wheels for a grinding machine;
- bitumen mastic, paraffin anticorrosive for treating the external and internal surface of the bottom;
- putty.
Equipment and tools that will be required for repairs:
- grinder (angle grinder);
- chisel with a wide blade;
- welding machine;
- metal scissors;
- straightening hammers;
- electric drill.
During the work, you may need a degreaser, a spot welding machine for tack, and R-80 sandpaper.
What metal to use to weld the underbody of a car, its thickness
The thickness of the metal for over-welding the floor must be at least 2 mm. Technologists recommend using sheet steel, material st2, to save money. Stainless steel or alloy steel can be used if the repair is done by a professional welder. In 70% of cases, non-professionals experience welding joints bursting due to engine vibration when moving.
Stainless steel can be used as small patches for partial bottom replacements. Aluminum sheets are used to strengthen the bottom of the car without welding. Aluminum oxidizes the metal, causing rapid corrosion. If aluminum is used to strengthen the bottom, it is necessary to avoid its contact with the metal of the body through the use of rubber bushings or gaskets.
Steel body
A steel body can be of different alloy variations, which gives completely different properties to its varieties. So, for example, sheet steel has excellent ductility, which also makes it possible to produce outer panels of body parts, which can sometimes have a rather unusual and complex shape. It is logical that high-strength grades have considerable energy intensity and excellent strength, which is why this type of steel is used in the production of power body parts. It is also beneficial that throughout the history of the automotive industry, manufacturers have managed to simplify and fine-tune the craftsmanship of steel bodies, which makes them quite inexpensive.
It is this factor that has made steel bodies the most popular in the automotive market today.
With all these advantages, steel still has significant disadvantages. For example, it is inconvenient that steel parts are not light in weight and are also susceptible to corrosion processes, which forces manufacturers to use galvanizing techniques for steel parts and at the same time look for alternative options for body materials.
Stages of work
Only in the video tutorial does it take a short period of time to independently overcook the bottom. In fact, repair work takes from 3 days and goes through the following stages:
- dismantling the interior, interior lining;
- bottom preparation;
- welding work;
- anti-corrosion treatment;
- interior installation, electrical connections.
Dismantling the interior involves disconnecting most of the electrical cables that go to power windows, batteries, sensors, also removing seats, carpet, sound insulation, dismantling doors, installing the car on an overpass or lift. Be sure to drain the fuel from the tank.
Some drivers turn the car on its side if the bottom and sills are partially overcooked.
After dismantling the attachments and panels, it is necessary to check the quality of the metal on the sills and wheel arches. These elements are the first to be damaged by corrosion.
Preparatory work
Before the main stage of repair, it is necessary to prepare the bottom. Algorithm of work step by step:
- Use a grinder to clean the outer part of dirt and rust.
- Check the jacks.
- After cutting away the rusty areas of metal, sand the outside of the bottom to white metal.
- Cut patches to the required size if a partial replacement is being carried out. Drill out the spot welding areas if the entire bottom is being replaced or cut out the factory fastening weld.
It is recommended to cut steel for patches using metal scissors. The workpiece will have an even seam. Cutting a patch by welding is carried out if you have experience, such work requires skill.
Replacement of car underbody elements
The first problems with the body begin with the failure of the same elements, regardless of the manufacturer and operating conditions. Comprehensive bottom re-cooking begins with inspection and repair of those parts that are more susceptible to corrosion due to constant contact with moisture:
- thresholds;
- wheel arches;
- front bumper;
- trunk bottom.
Operating principle and theory of semi-automatic electric welding
Welding with a semi-automatic inverter using carbon dioxide is today the most common type for self-repair of the bottom. Using gas welding is quite problematic, since it is difficult to make a high-quality seam.
The carbon dioxide semi-automatic machine allows you to weld metal with a thickness of 0.8 to 6 mm, has compact dimensions, and is convenient for welding difficult areas. The machine uses carbon dioxide; it enters the welding zone under pressure and displaces air, preventing oxidation of the metal, which does not burn, but melts. The welded sections are connected, forming an even, narrow seam.
Preparation of the welding machine takes place in the following stages:
- Check the garage electrical system for the required voltage.
- Remove all flammable materials from the vehicle and within a radius of 1 meter from the work site, remove the battery, and drain the fuel.
- Insert welding wire into the inverter.
- Set the required polarity for ordinary wire used for welding metal. The minus is placed on the clamp and the plus on the burner.
- Connect the carbon dioxide cylinder.
- Check the inverter for functionality. First, the gas is supplied, then the wire is turned on and the welding current is supplied.
It is recommended to use technical carbon dioxide for welding; the chemical has less water vapor than food-grade carbon dioxide.
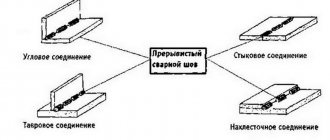
What seam to weld the underbody of a car
There are several techniques for cooking the bottom of a car. Professional tinsmiths recommend using step welding, welding in stitches: 2 cm of welded metal, 5 cm gap. This type of welding increases the rigidity of the body and enhances the tensile safety of the structure. During vibration during movement, the bottom does not deform, as with welding with a continuous seam, and does not tear, as with spot welding.
If the front floor elements of a car are attached to a cross beam, the attachment points must be welded.
After welding, galvanized body parts lose their protection; treatment with anti-corrosion compounds and painting with body sealant is mandatory.
If you need to weld car sills, then electric welding is used. If it is necessary to extract metal after a dent or weld a small patch, spot welding is used with a spotter.
Let's sum it up
Many motorists make the same mistake. They begin to think about what is best to use for the car when the first spots of rust have already appeared. Anticorrosive treatment should be carried out even before this. This will be a kind of prevention that will significantly extend the life of the body. It is impossible to say for sure which anti-corrosion treatment is actually better than others for your car. A number of factors are taken into account here, from the current condition of the underbody to the financial capabilities of the car owner.
A large variety of products are offered on the market. The choice must be made based on the specific situation. What will be incredibly useful and effective in one situation will be completely useless in other circumstances. Some products help to further improve sound insulation and protect against vibrations. But at the same time, manufacturers themselves often forget that the main purpose of their product is protection against rust. Because of this, the main property loses its effectiveness.
It is not always possible to rely on cost. The most expensive product does not guarantee the highest effectiveness. Carefully read the ingredients, warnings and recommendations of the manufacturers. There are anticorrosive agents that are intended exclusively for the bottom, or are also used to treat parts of the body with paintwork. Some components of anti-corrosion agents have an aggressive effect on varnish and paint, which is why their use will only harm your vehicle.
It makes no sense to deny the fact of the need to use anti-corrosion and rust agents. This is truly an extremely important and useful way to extend the life of a car, since on modern cars it is the body that begins to deteriorate faster than the engine. If you are concerned about the condition of your car, want to extend its service life and protect it from metal-eating rust, try to carry out thorough anti-corrosion treatment once every 2-3 years. Based on our recommendations, ratings and understanding the properties of different anticorrosives, making the right choice will not be difficult.
The final stages when working with the bottom
After welding the car body with a semi-automatic machine, you will need to clean the seams with a grinder, treat them with anticorrosive, and prime them. After welding, the main vulnerable spots remain the weld seams, since the process of digesting the metal has damaged its structure. It is necessary to process the seam both from the outside of the bottom and from the inside.
If an aluminum patch is welded to a metal body, then it is necessary to apply anticorrosive in two layers and regularly check and tap the seam. Aluminum oxidizes and upon contact with sheet metal, pockets of corrosion form on steel sheets. Craftsmen do not recommend welding aluminum to the tin bottom of the machine; it is better to use bolt mounting with a safety gasket.
What it is
First, you need to understand the concept of anti-corrosion agents for a car before voicing a rating or classification of solutions. Responsible car manufacturers use fairly effective means at the car manufacturing stage to prevent the early development of corrosion on metal surfaces. A galvanized layer and anti-corrosion agents are used. But often they last exactly for the duration of the warranty. After just 2–3 years, a car can easily surprise its owner with the appearance of the first spots of rust.
Factories mainly use anti-corrosion mastic for cars. And then the manufacturer himself decides which is better. They can only be applied if the metal itself is thoroughly prepared, otherwise there will be no proper adhesion between the materials. Bonding with metal is called adhesion. Under the influence of aggressive substances, bad weather conditions and other factors, adhesion is reduced, and therefore the factory anticorrosive agent loses its properties.
To prevent the destruction of metal, anticorrosives were invented. These are special substances that are applied to the most vulnerable surfaces. They contain special solvents that allow the anticorrosives to have a liquid structure. When the product is applied, the solvents evaporate, creating a strong and hard film that is resistant to destructive processes. Protective components form a kind of barrier that protects the metal of the machine from the external environment. This helps to significantly slow down the ongoing oxidative processes. This prevents any traces of rust from appearing.
It is important to understand that anticorrosion agents are not intended to repair metal or remove already formed rust. Therefore, before application, it is recommended to clean the damaged areas, remove dangerous orange spots, and only then apply the anticorrosive agent itself. If we talk about the best and most effective anticorrosion agents, then you should pay attention to the following brands:
Many motorists opt for trains from these manufacturers. They were able to prove their effectiveness in practice, therefore they are deservedly included in the rating of the best anticorrosion agents. It is worth considering that the quality of the compounds used plays a large role in the effectiveness of the anti-corrosion treatment of the bottom. If it is a good anticorrosive agent, it will really be able to significantly slow down the process of rust spreading. If this is a low-grade composition, then do not expect any special results.
How to save money
The only way to save on auto body work is to do it yourself. You cannot skimp on either anti-corrosion treatment material or metal. If you are not an experienced welder and doubt the quality of the repair, it will be cheaper to invite a specialist than to redo broken seams a year later.
The cost of underbody repair in a specialized car service starts from 22-25,000 rubles. And this price is justified. Included in the price:
- interior dismantling;
- full body diagnostics;
- use of spot and electric welding;
- bottom treatment with anticorrosive agent;
- interior installation, electrical equipment connection.
Drivers prefer to do their own repairs because the stereotype is that service stations increase prices and invent defects that do not exist. To avoid deception, it is recommended to tap the bottom of the car yourself on an overpass; if there is minor damage that does not require complete overcooking of the bottom, then opt for independent repairs.
Composite body
Another type of body material is composite materials. It is a “hybrid” material made from several combined together. Such production makes the composite body optimal in quality, since it combines the best from each component.
In addition, composite materials are more durable, they can be used to make the largest and most continuous parts, which undoubtedly simplifies the production itself.
Composite materials include, for example, carbon fiber, which, by the way, is most often used in production. Carbon fiber is used to make body frames for supercars.
The disadvantages of this material include the complexity of its use in the automotive industry. Sometimes manual labor is even necessary, which, of course, ultimately affects the price. Another drawback is the almost impossibility of restoring carbon fiber parts after deformation during accidents. All this contributes to the fact that cars with carbon fiber bodies are practically not produced en masse.
Each body type has its own advantages and disadvantages. It all depends on the tastes of consumers, that is, you and me.
Cold methods of sealing holes in metal
Cold methods of auto body repair include:
- Metal extraction. If there is a dent on the threshold, fender without breaking the part. Use a reverse hammer or pulling hooks. Spot welding is required for repairs.
- Applying metal patches. The method is suitable for repairing the bottom, sills, and less often wings. The patch is installed in place of a rupture or hole after corrosion by welding, less often on bolts with reinforcements.
- Restoration by alternative methods using epoxy resin and fiberglass. This method is not suitable for repairing the bottom because it does not solve the main problem. If a corrosion hole appears, the body begins to deform and all power units are displaced. What is required is not just filling the hole, but restoring the rigidity of the structure, welding the bottom with the obligatory strengthening of the jacks and side members. It is allowed to install patches on rivets only in those areas of the body that do not bear a force load.
Repair of large-scale damage
Large-scale damage to the body after an accident always means overcooking of parts. For dents of a large area, when the hinged element is damaged, but the sill protection, side members, central and A-pillar reinforcements are not damaged, use back hammer extraction or straightening.
A source of through corrosion, or simply a hole, in the bottom of the car is the price to pay for comfort in the cabin. Its primary source is not anti-icing reagents acting outside, but moisture accumulating under the “pie” of heat, sound and waterproofing. Therefore, when eliminating it, work is carried out mainly from the inside.
If you follow all safety rules when welding, you must completely dismantle the interior, including the trim. This is always very time consuming. Therefore, the question of how to seal the bottom of a car without welding is very relevant. Moreover, most alternative methods do not give worse, but rather better results.
Cold methods of sealing holes in metal
There are two ways to repair holes in the underbody of a car without using hot work.
- Using composite materials - various types of polymer resins in combination with a reinforcing filler and a curing reaction accelerator. With high-quality surface treatment, in addition to restoring mechanical strength, they play the role of inhibitors - retarders of chemical and electrochemical corrosion reactions;
- Installing sheet material patches onto rivets.
General technological rules
Holes in the bottom are usually discovered from the outside, when inspecting the car on a pit or lift. Signs of through corrosion are local swellings, which, when you try to pick them out, crumble into dust.
If you find such troubles, you need to open and remove the pie of heat, noise and waterproofing on the floor in the cabin in the entire area where the sheet of iron forming the floor is welded to the power elements of the body - thresholds, tunnel and others. Then you will see the whole picture of the damage and will be able to take preventive measures in those places where corrosion has not yet become through.
Welding process
Before hot work, for safety reasons, the gas tank must be dismantled. The patch is first grabbed at 3-4 points, then completely scalded. Small defects are filled with short seams up to 3 cm long. Welding the bottom is difficult to do alone. When a partner holds the patch, the repair speeds up.
It is important that the patch fits tightly to the repair site. Gaps increase the risk of corrosion damage. The seams are hammered for strength. In good lighting, all repair areas are checked. If necessary, boil the connection again. Only after inspection do they begin to clean the seam rollers.
Is it worth soldering
You can also seal holes in the bottom using soldering. However, ordinary household soldering irons are not suitable for heating metal with a thickness of 0.5 mm or more. Most likely, a hair dryer will not help you with this. You need to use a portable gas burner, for example, Super-Ego R355, which fits into a small - volume from 400 to 700 ml - cylinder for camping stoves.
Solder and flux are required for soldering. The solder used is low-melting, with a predominant content of tin or lead. Flux can be replaced with electrolytic acid. The connection is strong and can withstand high vibration loads.
Soldering has two disadvantages.
- It involves hot work, which increases the overall complexity of the repair. This can be neglected if your hands grow from the right place;
- The main material of solder - lead or tin - is a substance that has a lower electronegative potential than iron. Therefore, upon their contact, electrochemical corrosion occurs, in which iron will play the role of a “sacrificial anode” and be destroyed.
Now you have an idea of how to seal the underbody of a car without welding. If you are careful and persistent in cleaning the surfaces, then treating them and protecting them, then the installed patch can outlive the car itself.
Recommendations for selection
Anticorrosive is classified depending on:
- application features;
- type;
- chemical composition;
- places of application.
First, you need to remember that anticorrosive agents can be divided into products for internal and external surfaces. It is not recommended to use internal anti-corrosion compounds to treat the underbody of a car. They will not be able to demonstrate the same effectiveness as products specifically designed for the most frequently exposed surfaces. The car owner should decide on the appropriate type of mastic, understand the requirements, and then purchase the most effective composition. There are some good tips on this matter.
There are products that are used for their intended purpose when treating hidden and hard-to-reach surfaces. They are not used for the bottom due to low efficiency and structural features of the substance. Such anti-rust preparations are made on the basis of oils or paraffins. Oily products are characterized by a liquid structure that does not change even after drying. Copes well with microcracks and scratches. And paraffin ones are made from wax. When the drug dries, an elastic film remains. High-quality mixtures do not lose their effectiveness even under conditions of sudden temperature changes. If you need to treat the bottom of the vehicle, the following types of anticorrosives are used:
- Bitumen. Various resins are used in the production of bitumen mastics. The tools are designed to perform two functions simultaneously. To begin with, they help to protect the underbody from mechanical damage. Additionally, there is a metal preservation effect, which has a positive effect on reducing the spread of already formed rust. The better the quality of the bitumen mastic, the greater the protective and preservative effect. When applying, you need to use a layer with a thickness of about 300 - 400 microns. Here you should build on the current state of the bottom, as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Rubber and polyvinyl chloride. Rubber and PVC are also extremely effective bases for creating anti-corrosion agents. Among all competitors, they are the most durable. But they are used mainly at the stage of factory processing.
- Plastic. There is also an anti-corrosion agent made from liquid plastic. Suitable for domestic use, but in terms of protecting the underbody of the car it does not show its best side. The main problem is low mechanical stability.
The question quite naturally arises as to which anticorrosive agent for cars is the best to effectively resist rust and corrosion.
The answer is not so easy to find, since anti-corrosion agents can indeed differ significantly from each other. But practice clearly shows that when treating the bottom it is better to use bitumen, rubber or PVC compounds. Do not forget about the high importance of quality, since not all manufacturers use the components stated on the packaging. There is no point in saving money here, since a really good anti-corrosion agent cannot be cheap.
Requirements
We are getting closer and closer to which anticorrosive agent is best to choose for your car. For a fairly old vehicle, the condition of the factory protection leaves much to be desired. When choosing an anti-corrosion composition, you need to focus on the maximum effectiveness of the protective layer it creates. In order for the product to work efficiently and prevent rust from spreading further along the bottom of the car, certain requirements must be presented. Namely:
- High quality grip. The material must reliably cling to metal surfaces that are treated with anticorrosive to create effective adhesion. The preparatory stage will play an important role here. Based on the manufacturer’s instructions, the car owner will need to remove all contaminants, clean already rusted areas, and possibly degrease the metal with special compounds.
- Validity. The product should retain its properties for a long period and not have a temporary effect. High-quality anticorrosives are designed for several years of operation without repeated preventive applications. But if you take a dubious product, it may not last even several months on the metal.
- Uniformity. Make sure that the anticorrosive agent is as uniform as possible, thick, and not too liquid. If you see the product starting to peel off, it is better to immediately change the jar from the seller. Stir the product thoroughly before applying.
- Filling cracks, chips and other areas. The motorist cannot carefully treat literally every millimeter of the entire bottom. Therefore, good anticorrosive agents have the ability to effectively fill all cracks and hard-to-reach areas. This does not negate the fact that when processing the metal of a car you need to be careful, careful and try not to miss areas.
- Peeling and cracking. This is what distinguishes low-quality anti-corrosion mastics and products, which become covered with small cracks after a short period of time after application. Or the resulting film begins to peel off. It is possible that this is caused by a violation of processing technology. But if you acted according to the manufacturer's instructions, then you simply had poor-quality protection. Since there are counterfeits of high-quality anticorrosion agents on the market, the possibility of purchasing a counterfeit cannot be ruled out.
- Resistant to high temperatures and flames. All anticorrosive materials must be fire-resistant. Failure to comply with this requirement may lead to dangerous consequences.
- Elasticity and protection from electrolytes and moisture. High-quality anticorrosives, after drying on the bottom, form a durable elastic film, thanks to which dangerous electrolytes and moisture, which are a catalyst for corrosion processes, do not penetrate through the barrier to the metal.