Home / Useful
Back
Reading time: 8 min
0
829
- What is welding production?
- Types of welding production.
- Welding technology and types of welding Manual electric arc welding using non-consumable electrodes
- Manual arc welding with consumable electrodes
- Electric arc welding in a protected environment
- Automatic and semi-automatic welding
What is welding production?
Before we talk about where welding production is used, let's first clarify a few concepts. Welding production is a set of various technological operations for the production of a complete welded structure in finished form. This complex, as already mentioned above, is a set of such operations:
- Preparatory
- Prefabricated
- Welding
- Finishing
- Additional
- Quality control
Naturally, each type of work should include many subtypes, but we will not describe them, but it will be enough just to find out the essence of each operation.
For example, the first point of every welding production is the preparation of surfaces for welding. It may also involve creating blanks and combining finished parts for welding in various ways. In addition, preparatory work may include cutting, marking parts, adjusting to the required dimensions, boring surfaces, threading, etc., which is important to do before welding. Workpieces are often straightened using friction machines and hydraulic presses.
Next comes the initial assembly of parts. It involves tacking two or more parts with special clamps for the convenience of the welder, who will later weld these surfaces into one solid structure. It is important that the clamps tightly hold the parts together without leaving gaps between them and hold them firmly on the working surface.
After performing the above operations, the actual welding production begins. Welding work, as a rule, is performed manually using electrodes, automatic or semi-automatic welding - depending on the conditions for carrying out work operations, as well as the design features of the part. You need to know that it is precisely for the ease and convenience of welding production that the industry has produced many items of welding equipment, which differ both in purpose and in load capacity.
Business ideas for a welder
The company will prosper if work is carried out in several directions at once:
- production of finished household goods from purchased or customer-supplied raw materials (containers, bathhouses, heating stoves for houses, cottages, greenhouses),
- visits to repair car bodies, installation of welded frames, repair of metal structures,
- dismantling, installation of gas pipelines, pipelines, flues, ventilation systems, much more,
- provision of services to enterprises, construction and management organizations (maintenance of residential buildings).
Manufacturing of metal structures
In the private sector, in dacha communities, welding is constantly needed:
- fences are being erected,
- gazebos, benches,
- sheds for storing firewood and garage doors are being installed.
In urban environments there are many metal structures:
- sports, gaming equipment,
- stopping complexes,
- advertising designs.
In urban environments there are many metal structures
Welding of barbecues, stoves
In recent years, the number of orders for the production of:
- bourgeois,
- ovens with top, front loading,
- stationary and collapsible portable barbecues, grill structures. Finished products are accepted for sale by retail outlets.
Business in the manufacture of barbecues
Pipe replacement and repair
Individual orders for replacing water pipes and heating are sought through management companies and senior house managers. Sometimes they negotiate with dispatchers who register emergency requests and give them their coordinates. Replacing steel pipes with metal-plastic and polypropylene has become popular. We try to trust these welding jobs to professionals. A good advertising move is cooperation with owners and sellers of stores selling plumbing equipment and components.
Replacing steel pipes with metal-plastic, polypropylene has become popular
Car body repair
Owners of small auto repair shops often need welders; not everyone can afford to hire a full-time specialist. When developing a business plan, it is recommended to call the owners of car services and private workshops to discuss the possibility of cooperation.
Earning money from body repair
Dismantling of structures and communications
Works costing up to 500 thousand rubles do not undergo a competitive procedure to find a contractor. Dismantling old metal structures and communication systems does not require high qualifications, you just need equipment and the ability to use it. Such services are needed by organizations, enterprises, and the private sector.
Dismantling of metal structures
Providing welding services to construction companies
Installation of pipes and concrete reinforcement in monolithic construction involves welding work. Installation of plumbing, installation and replacement of communications, arrangement of the local area, construction of balcony railings are carried out at certain stages of house construction, welders are often put out of staff. Subcontractors are selected for the work.
In construction companies, welders are often out of staff. Subcontractors are selected for the work
Types of welding production.
Welding production is divided into the following types:
- Small-scale
- Serial
- Large-scale
Naturally, the first type does not include the possibility of production at an industrial enterprise, but most likely, welding work in domestic conditions: pipes, metal structures, etc., which require a certain number of repetitions of the same operations. In contrast, mass production includes special production lines with several workplaces to support welding work, and, moreover, they are often interconnected by vehicles. An example of such production is the production of propane cylinders using automatic submerged arc welding of steel with a thickness of no more than 3 millimeters on a lining. Large-scale production is a huge industrial production of identical structures, which in most cases is automated and does not require many welders to carry out assembly operations.
Ways to promote a service on the market
Do not neglect traditional marketing methods, which are: advertising in local print media, television channels and radio stations; Posting advertisements and distributing leaflets in places with high traffic to the target audience of the enterprise. Cooperation with local service stations and auto repair shops will be an additional advantage if the company practices automotive welding work.
Welding technology and types of welding
The theory of welding itself is quite complex and extensive. It includes the study of the properties of structural materials at the molecular level. Only a clear understanding of the principles of constructing the crystal lattice of a particular metal or alloy makes it possible to correctly select the necessary equipment and operating modes.
Modern welding technology includes more than a hundred methods of welding both metal and non-metallic materials: glass, polymers, etc. Main criteria for choosing technology:
- thickness of welded parts;
- chemical composition of the alloy;
- working conditions;
- tensile strength of the weld;
- operating conditions of the finished product.
Each of the listed criteria directly affects the choice of equipment and welding technology in each specific case. In modern industry, three main types of welding are actively used:
- thermal - the welding process is accompanied by melting of the metal under the action of external heat sources, such as a gas torch or an electric arc;
- thermomechanical - a combined method includes both thermal and mechanical effects (pressure) on the surfaces being welded; this method includes forge and contact welding;
- mechanical - the process completely eliminates the impact of high temperature from external sources and involves the use of frictional energy, the effect of diffusion under pressure or ultrasonic welding.
There are also three subtypes of welding production technology in accordance with some key technical features:
- by type of protected environment used - flux, argon (and other inert gases), vacuum or combined;
- by type of weld - intermittent and continuous welding;
- by method of operation - manual, automatic and semi-automatic, mechanized and robotic.
Thanks to this simple classification, all the most common equipment and welding technologies can be easily and accessiblely described.
Manual arc welding using non-consumable electrodes
This method involves the use of non-consumable electrodes and is one of the most common among both professionals and private craftsmen who use it for their own needs. A large selection of devices with different power and a range of additional functions contributes to the popularization of this technology.
Inverters are used as the main welding equipment. Non-consumable electrodes are made of graphite or tungsten. These materials allow the formation of a high-temperature electric arc, which melts the metal of the parts being welded, but does not harm the electrode itself.
Electric arc welding technology is relatively simple - the workpieces are connected to each other and with the help of the arc that appears when the electrode is tapped on the part, the direct process of melting the metal occurs.
Manual arc welding with consumable electrodes
This welding technology itself is no different from the previous one. The only exception is in electrodes, which in this case are made of low-melting alloys saturated with alloying elements. As a result, under the action of the arc, a melt pool is formed containing not only the metal of the part, but also the material of the electrode. This allows you to avoid burnout of alloying components and ensure high quality welds.
In this case, inverters are also used as welding equipment. This technology, like the previous one, is great for home use.
Electric arc welding in a protected environment
This is another type of welding technology based on the use of an electric arc. A distinctive feature from the previous two methods is the presence of a protected environment of inert gases, most often argon. This allows us to minimize the negative effect of oxygen on the molten metal and ensure high strength of the weld.
Automatic and semi-automatic welding
The technology of welding production is also essentially no different from other arc welding methods, with the exception of the method of supplying the consumable electrode and its movement along the weld. The semi-automatic method involves feeding the rod by a special mechanism, and in the fully automatic mode the movement of the electrode along the seam is automated.
Relevance of the welding business, its advantages and disadvantages
The demand for the welding business and the services of professional welders is currently beyond doubt, and this type of business activity is one of the most relevant and stable today. An additional advantage will be the personal professional interest of the aspiring entrepreneur in his own business, the presence of the necessary skills and abilities, since a business based on one’s own hobbies, as we know, is literally doomed to success.
Among other things, the welding business is valued by entrepreneurs due to the absence of the need for large start-up investments and the purchase of a wide range of expensive equipment. Also, the process of state registration of a business in this area is not complicated and does not require additional licenses, so even a novice entrepreneur without experience in implementing other business projects can start his own enterprise in the field of welding business.
PPR for welding work
The welding production project (WPP) is drawn up taking into account the welding technology for a specific construction project. Here functionality, climate and geographical location are taken into account.
In addition to general information about the construction, the PPSR contains the following data:
- description (schematic images) of the finished structure;
- volumes of equipment supplies;
- requirements and conditions for its storage;
- justification for the choice of equipment and materials;
- practical recommendations for choosing welding modes;
- instructions on the sequence of actions of individual performers and teams;
- data on the qualifications of workers in production;
- fire safety standards;
- technologies used for welding;
- test method for testing joints;
- methods of monitoring the execution of the finished structure and its quality;
- technological maps;
- procedure for correcting identified defects;
- regulations regarding labor protection.
Possible risks
Taking into account the absence of the need for large start-up capital investments, a business project for a welding shop is a business activity with minimal risk of incurring significant losses.
Possible risks of doing business in this area include:
- low qualifications of employed welders;
- insufficiently high level of demand for welding business services in certain cities and regions of the country;
- increases in rent or utility costs.
PPR for welding of metal structures and process pipelines
The main task of PPSR for welding metal structures and process pipelines is to organize a competent welding process.
The project indicates deadlines, coordinating them with the calendar plan. All welding processes must be carried out in strict accordance with regulatory documents, including GOST, which specify the requirements for seams of constructed structures and modes for performing technological operations. Modes for welding pipelines depend on parameters such as:
- purpose of pipelines;
- physical and chemical properties of metals of welded pipes;
- selection of equipment, methods of joining and suturing;
- design and structural features of pipelines
Among the features of the design of welded joints in metal structures, one can highlight the methods by which employees of the construction organization will be delivered to the work area. To deliver workers to hard-to-reach areas, various construction lifts with cradles are usually used.
Laser and plasma devices
Laser industrial welding stands apart. Laser machines can join metal up to 2 mm thick, but mainly work with small products a few microns thick.
Laser welding machines are used in microelectronics and instrument making, and in jewelry production. They often work as part of automated production lines. The seams are of the highest quality, but such equipment is expensive.
Plasma cutting has become widespread in manufacturing due to its high cut quality and low operating costs. Plasma industrial devices are used in welding mode when joining thick-walled materials.
Requirements for employees and managers
It is permissible to manage welding processes at hazardous production facilities only to those workers who correspond (and this is confirmed by documents) to highly specialized professional knowledge. A mandatory point is the presence of a NAKS certificate.
In addition, it is important for managers to be able to read welding drawings and know basic technical abbreviations and designations. You can learn more about how welds are designated in the drawings - welding symbols - in the article on our website.
Workers directly involved in the management of the welding process are faced with the following tasks:
- prepare performers for this dangerous process;
- select suitable employees;
- clearly control the stages of welding processes;
- guarantee the quality of the final welds.
Important: in emergency situations, a leader must be calm-blooded and be able to make instant, correct decisions.
Only those performers who have completed specialized training and qualifications in their specialty plus received a welder’s certificate indicating the category assigned after passing theory and practice are allowed.
When welding at hazardous production facilities, a confirmed highest qualification in the specialty is required. In organizations, welders who have completed the training process and certification are assigned a personal stamp by order; its number is indicated in the certificate.
It is important that a performer admitted to the welding process should not have any contraindications for both regular preventive medical examinations and those carried out immediately before each work shift.
Recruitment of employees
Your employees are the most important component of your welding production. Of course, work clothes and premises also matter, but it is your employees who determine how successful your business will be.
Here we have very good advice: it is better to hire a couple of real experts in this field, who do their job well and work for a high salary, than to hire many workers with little experience who are ready to work for the minimum wage.
It is unlikely that the latter will help your company grow. And with experienced employees, you have the right to set high prices for your work, since more clients care about quality, and they will pay for it. Another advantage is that you will create an excellent reputation for your company.
Remember that you will also need to hire an accountant. A very good solution would be to cooperate with a special outsourcing company. She will handle all your bookkeeping for a fee. This option will cost less than if you separately hired an accountant on your staff and paid taxes.
Requirements for welding work
The rules coordinate all the requirements for welding at hazardous production facilities. The main point is to guarantee the safety of participants in the work process. Fire extinguishing means must be freely available.
Welders are issued special clothing (working clothing). Overalls (robes) usually consist of:
- fireproof suit;
- mittens;
- special welder shoes;
- a mask that fully protects the head.
All of the above components of the work kit must necessarily correspond to the individual parameters of the worker performing welding:
- Have a complete set.
- Match your build.
- Shoes must be true to size.
- The protection should not be chipped.
- The gloves are intact, without damage or tears.
- In order to prevent the mask from falling off during welding, it must fit tightly.
Thematic video:
Welding safety precautions.
Welding school. Lesson #1: Welding safety.
An equally important point is the presence of a fully assembled first aid kit.
Ventilation (in the workplace), a first aid kit and quickly accessible emergency exits are required.
If welding manipulations at hazardous production facilities are carried out in an open space, it is important to install specialized fences with danger warning signs.
Additional safety requirements apply to welding processes at hazardous production facilities carried out at height. It is important to reliably strengthen attached structures (stairs and lifting structures).
It is strictly prohibited to carry out welding in conditions of increased meteorological danger (strong gusts of wind, showers, snowfalls). The welder is given detailed instructions (possible dangers and subtleties of the process are explained).
Additional thematic video:
Industrial safety training and certification.
Price policy
The cost of welding work is calculated separately in each case and depends on:
- type of equipment required
- amount of work
- speed of order fulfillment (urgency)
The average price for basic services is shown in the table:
| Name of service | Price |
| Welding steel water pipes | 150 RUR/joint |
| Welding metal parts | 20 rub./cm |
| Making a steel fence | 800 rub./sq. m |
| Production and installation of decorative grilles | 2000 rub./sq. m |
| Manufacturing of heating registers | 800 rub./linear meter |
If the work is not carried out in the workshop itself, but on the customer’s premises, then the specialist’s visit to the site is paid separately.
Where to begin
The design of welding shops is of paramount importance.
What is it? There are several positions here that will determine the technological process regarding welding work, as well as the assembly of components and parts. First of all, you need to sort out the equipment. It is clear that the main equipment for a welding shop is welding machines (gas, electric). Their cost is determined by the volume of work performed.
If the volumes are large, then it is better to purchase professional devices. If the welding shop is small, then you can get by with household analogues. A welding shop needs to be diverse to accommodate as much work as possible, so it's worth considering purchasing a resistance welder.
We must not forget about seemingly simple devices that will occupy a certain place in the welding shop. For example, a workbench or a welding table.
It must be properly organized not only in terms of the convenience of welding operations, but also in terms of quick access to additional tools and consumables. Moreover, a welder’s workplace is a single set of devices that are used daily.
Ventilation system
Ventilation of the welding shop is the most important component and one of the main requirements for organizing welding shops. With its help, heavy gases from the melting of metals and combustion of electrode rod coatings are removed from the welder’s workplace.
Many people make the mistake of installing a probe above a large workbench, which is connected to the general ventilation system by pipes or corrugations. The optimal and effective option is to install a side gas outlet so that they do not rise above the level of the workpieces being welded.
It is very important to make an accurate calculation of the ventilation system to ensure maximum air extraction from each workplace. It is better to install the fan outside the workshop. This will be especially true if the welding shop is organized in a garage.
A small room without ventilation will become a place where it will be impossible to stay without a respirator or gas mask. And the SES will not give permission to operate such a poorly equipped workshop. Therefore, it is very important not only to install a ventilation system, but also to correctly calculate the characteristics of the fan, especially the power of the device .
Plus, distribute the air ducts correctly so that they do not interfere when moving large parts. This means that you will have to make a drawing with the condition of the correct arrangement of all elements of the system.
Location of equipment and fixtures
The equipment layout is strictly regulated by safety standards and regulations in welding shops. The layout determines safety, ease of movement of personnel, movement of parts, assemblies and finished products. There are several recommendations for arrangement:
- if a transformer is used in the workshop for electric welding, then it should be installed 5-7 m from the workbench and half a meter from the wall (minimum). The household inverter can be installed on a table surface;
- if welding is performed with gas, then cylinders with oxygen and acetylene are placed away from each other at a distance of at least 5 m. The same applies to propane equipment. The same distance is maintained between the welding site and the cylinders;
- gas hoses and electrical cables are laid away from passages so that they are not walked on. This is primarily a safety requirement, and secondly a way to preserve property;
- a distance of 1 m is left between equipment, tables, cabinets and other bulky objects for the convenience of moving people and transporting parts on carts.
Automatic welding equipment requires more space. It is necessary to take into account its movement around the welding shop and the access of performers to it.
Soviet period devices
The source of welding current and welding technology in general in the Soviet Union was given such great importance that in the thirties of the twentieth century the Institute of Electric Welding was created.
Many of his developments are still used today, as well as Soviet-made industrial welding machines. By the way, the markings on welding equipment produced in Russia have been preserved since those times.
In Soviet times, welding equipment was bulky and operated on transformers, but was highly reliable.
Some industries still have Soviet welding transformers, and they perform their functions properly. Although lightweight compact inverters are widely used for domestic needs, industrial transformers should not be underestimated.
Main types of welding equipment
Welding equipment can be easily found at any construction site, industrial production, and in addition, it is often used for domestic purposes. That is why the demand for this type of equipment remains stable, and the requirements for it remain consistently high. Today, welders use a number of welding methods: with electrode or graphite rods, which are excellent conductors, with special welding wires, using gas, plasma, laser and other technologies.
Before moving on to talk about what requirements apply to welding equipment, it is important to understand welding technologies:
- Arc welding.
We are talking about connecting parts with an electric arc using a welding transformer or inverter. During operation, the arc heats up to +5,000 °C or more, this figure exceeds the melting point of all currently used metals. There are also inverter devices with a charger.
- Semi-automatic welding.
The main requirement for this method is the continuous supply of wire, which plays the role of an electrode, to the welding site. Note that the wire moves at a certain speed. Active or inert gas also enters there - it allows you to protect the melt from exposure to air.
Melting of the base metal and filler material occurs in the open flame of the burner. An important requirement for the normal operation of such equipment is a constant supply of one or a mixture of flammable gases (liquids) in combination with oxygen - this is necessary to ensure constant operation of the burner.
- Electroslag welding.
This method is based on the principle of conductivity of molten slag, in the volume of which heat is released when current passes. That is, the connection of the electrode with the base metal occurs through molten slag. Heat is released in the slag bath, causing the temperature to be higher than the level required to melt the metals. This leads to the fact that the edges of the base metal with the electrode melt and flow to the bottom of the melt, forming a bath of molten metal.
- Thermite welding.
In this case, a mixture of magnesium or aluminum is used in powder form, which is combined with iron scale. Aluminum ensures the reduction of iron from scale, which is accompanied by the release of enormous amounts of heat.
The main requirement for such welding is to work in an inert gas environment, argon. In this case, a consumable or non-consumable electrode can be used. Note that most often a tungsten electrode is preferred.
- Plasma welding.
Melting of metal and additives is carried out using a high-temperature plasma arc flow. In its principle, this technology is very similar to argon arc welding.
- Electron beam welding.
In this case, the equipment used allows the kinetic energy of the electron beam directed into the welding zone to transform into thermal energy.
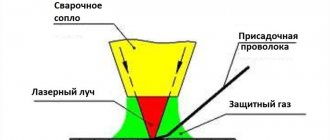
- Laser welding.
The operating principle of the laser installation is based on the use of laser beam energy. To focus the latter on a small area of the surface, optical lenses are used.
- Contact welding (resistance butt welding).
The formation of joints of metal products occurs due to their heating by passing electric current and plastic deformation by compression of the joint zone. The main role in this method is given to the electrical resistance of the connection zone - this is what explains the second name of this technology.
- Spot welding.
This is one of the types of contact welding, in which structural elements are connected along separate areas of contact, the dimensions of which are limited by the area of the working ends of the electrodes, because they transmit the compression force and supply current to the metal surface.
- Butt welding.
Butt welding equipment allows you to fasten products made of PVC, polyethylene, and polybutene along the contact plane. Thanks to heating, all parts made of these materials, for example, fittings, pipes, are easily connected.
- Continuous flash butt welding.
An effective connection is achieved by connecting an electric current to the rods; their further contact makes it possible to obtain a closed electrical circuit.
- Diffusion welding.
Welding of elements occurs due to their squeezing and heating, while it is possible to avoid melting the base material. Welding is ensured by plastic deformation of microroughnesses located on the surface of the welded products. An important requirement is to work at a temperature below the melting point of the metal.
- Welding with high frequency currents.
This approach ensures a significant concentration of electromagnetic energy in the surface layers of the heated product. There is also a release of thermal energy in the mass of the metal being processed due to the proximity effect and the surface effect.
- Friction welding.
This technology is considered a type of pressure welding; in this case, heating can be achieved due to friction when moving (rotating) any part of the product being welded.
You need to understand that to obtain a high-quality result, it is not enough to use only basic welding equipment. It is also important to fulfill all requirements for additional equipment, accessories and consumables. We are talking about electrodes, brushes for removing slag, welding helmets, grounding terminals, electrode holders, electrical cables, wire, broaching rollers, torches, etc. The quality of work depends on how responsibly you approached the choice of all the equipment listed above.
Semi-automatic
The most widespread are industrial welding machines with semi-automatic additive supply. Compared to full automatic machines, they are versatile and can work with almost any product in hard-to-reach places.
If semi-automatic is compared with manual arc welding, then the undoubted advantage of the first is:
- higher work productivity;
- relatively low requirements for the professional skills of a welder;
- obtaining a higher quality welded joint through the use of shielding gases.
The welder directs the semi-automatic torch head along the seam at a uniform speed, at the same distance from the weld pool, and this is where his function ends. Gas and wire are supplied automatically.
The gas used is active (nitrogen, carbon dioxide) or inert (argon, helium) type. Both protect the weld pool from the harmful effects of atmospheric oxygen.
In industrial welding machines in production, carbon dioxide is more often used because of its cheapness; it is effective when welding low-carbon steels. Where it is necessary to obtain the most reliable seam, the semi-automatic machine works with a supply of argon or helium.
Mechanized lines and areas for the production of hull components
In recent years, the industry has created and is successfully introducing new advanced equipment for mechanized lines and sections at factories for the manufacture of basic types of hull components.
Production line for straight T-beams MIB-700A
The line is designed for the production of long (more than 2.5 m) symmetrical and asymmetrical straight T-beams.
| Characteristics of manufactured beams | ||
| Dimensions, mm | length | 3 000-12 000 |
| height | 100-700 | |
| beam flange width | ||
| symmetrical | 60-250 | |
| asymmetrical | 60-160 | |
| wall thickness | 4-20 | |
| belt thickness | 8-30 | |
| Weight, kg | Up to 2,050 | |
Unlike previously existing equipment for assembling and welding T-beams (for example, the STS-2M machine), the MIB-700A line provides for the elimination of welding deformations.
| Technical characteristics of the line | |
| Welding speed, m/h | 20-50 |
| Weld leg, mm | 3-8 |
| Type of welding | Automatic in carbon dioxide |
| Productivity per year (with two-shift work), m | 75 000 |
| Number of workers | 2 |
The line consists of the following main parts:
- an assembly and welding machine having a console with vertical and horizontal rollers for mutual centering of the belt and wall and their movement into the working cage of the machine;
- a receiving roller table onto which the welded beam emerges;
- front loader with rotating electromagnetic grippers for feeding parts of belts and walls to the machine console;
- rear loader for removing finished beams from the receiving roller table and placing them in a container.
In addition, there are tables next to the line:
- front - for installing a cassette with belts and walls;
- rear - for a container of finished beams.
The machine is equipped with centering and crimping rollers with a hydraulic drive, a beam feeding mechanism with welding and marching speeds, two welding heads and a device for creating preliminary bending of the beam. The beam is assembled on the wall without preliminary marking and electric tack, and automatic single-pass double-sided welding of the wall with the belt is carried out. All line operation is controlled remotely from a control panel.
Welding deformations of beams are eliminated by creating tensile stresses in the lower fibers of the wall in the welding zone. This is achieved by lifting (rotating) the machine table to the required height depending on the dimensions of the cross-section of the beam, which is set from the remote control.
Thanks to the introduction of such a line, labor productivity in the manufacture of T-beams increased by 3.5 times.
Unit for assembling and welding T-beams SKT-12-1
The SKT-12-1 unit is universal, so it has gained recognition and is currently used at many shipbuilding plants.
| Characteristics of manufactured beams, mm | ||
| Beam length: | rectilinear | 2 000-13 400 |
| curvilinear | 2 000-9 000 | |
| Beam wall height: | rectilinear | 150-1 000 |
| curvilinear | 150-600 | |
| Belt width | 100-300 | |
| Belt thickness | 8-30 | |
| Maximum arrow | 1 000 | |
Thanks to the use of a unit that is operated by only two people, labor productivity has increased by 2.5 times. Its annual production is 60,000 m of beams.
The SKT-12-1 unit (Fig. 2) consists of the following main parts:
- columns with brackets on which there are grips to hold the beam wall;
- a front working trolley carrying vertical and horizontal rollers for centering and crimping the girdle and beam wall, two welding heads, a control panel and a platform for the operator;
- a rear trolley, intended only to support the girdle of the beam being welded and freely moving along the rails of the base of the machine under the action of the front trolley, which has a travel drive;
- platforms for servicing the unit and control cabinets.
Rice.
2 Unit SKT-12-1 for the production of T-beams Before feeding the beam parts into the unit, depending on its length, columns and trolleys are installed using the appropriate commands from the control panel. Then, using a workshop crane or a special loader servicing the unit, the girder of the beam is placed on the trolleys and the beam wall is fed into the grips on the column brackets. With the help of pneumatic cylinders of the trolleys, the belt is lifted, pressed against the wall and welded to it. During the welding process, the beam is automatically tilted so that the welded area is in a position close to horizontal. After welding is completed, the beam is removed from the unit using a loader.
Mechanized foundation manufacturing area
The site is intended mainly for the manufacture of foundations for all kinds of auxiliary mechanisms, instruments and devices. However, on a site that is serviced by 5 people, it is possible to produce large foundations with a length of up to 5,300 mm, a width of up to 2,000 mm, a height of up to 1,000 mm and a weight of up to 1,000 kg. The annual output of the site is about 700 tons. With the commissioning of this site, labor productivity increased by 1.85 times.
The mechanized foundation manufacturing section includes the following main elements (Fig. 3):
- assembly stands and slabs for assembling and straightening foundations;
- rotary columns for assembly mechanized tools and semi-automatic welding machines;
- two positioners on which foundations assembled on stands are installed for welding in a convenient position. Positioner tables can be rotated around horizontal and vertical axes;
- two tables for welding small foundations;
- a conveyor along which small foundations are conveyed for loading into a container;
- two console cranes serving the site (feeding parts, removing assembled and welded foundations from stands, slabs and positioners).
The site is also equipped with screens that protect workers from welding arcs; movable stands for welders near the positioners; tool cabinet, etc.
Rice. 3 Scheme of the mechanized foundation manufacturing site. 1 — console crane; 2 — stand; 3 - plate for straightening; 4 - screen; 5 — stand for the welder; 6 - conveyor; 7 - positioner; 8 — assembly plate; 9, 12 — rotary columns; 10 — table for the welder; 11 — assembly stand; 13 - tool cabinet
Currently, the introduction into the production of prototypes of mechanized sections for the production of short brands and brackets, bottom set units, etc.
Plasma welding equipment used
Equipment for welding work (for plasma processing) consists of the following elements:
- burners (plasmatron);
- power source (inverter);
- cylinder with plasma-forming gas;
- protective gas cylinder;
- water cooling systems;
- cable package.
A welding torch is a complex device consisting of electrodes, pipelines for supplying gases and coolant, and an electrical cable for supplying power to the electrode.
The design of the torch is influenced by the power of the welding equipment. Low-power devices are equipped with burners with a retractable cathode, which, through a control button, is connected to the anode nozzle and excites the arc.
Manual plasma welding is performed using a gun-shaped torch that is comfortable to hold in your hands. Plasma-water welding is carried out by a combustion device in the form of a gun, which also has a discharge chamber and a steam-generating device.
More powerful equipment for welding work is equipped with torches with a fixed cathode. It consists of:
- cathode;
- cavities for working gas;
- cavities for shielding gas;
- anode (with a cavity for cooling);
- housings.
Torches for high-power welding equipment do not have handles, as they are attached directly to manipulators or machines.
The power source in the equipment is inverters, which have almost completely replaced transformer energy sources. Thanks to modern pulse converters based on IGBT transistors, a stable operating current is provided, which is adjustable to operate the equipment in various modes.