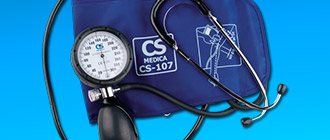
People suffering from dizziness and hypertension know how important it is to have in the house and know how to measure blood pressure with a tonometer. This device helps to monitor the effectiveness of the use of medications, as well as to avoid serious complications in the form of hypertensive crisis and other dangerous conditions. people over 40 are advised to monitor their levels using a mechanical or electric tonometer
What is absolute pressure, and how does it relate to gauge pressure?
To understand absolute pressure, you need to first define a few terms:
- Atmosphere pressure. Everything around us - air and water - has weight and creates pressure. At sea level, the average pressure is 1 atm, or 1.01325 bar; pressure changes depending on weather conditions. As altitude increases, the air becomes thinner and so does the atmospheric pressure.
- Gauge pressure. The zero in gauge pressure represents atmospheric pressure, which means the gauge pressure reading only includes the additional pressure within the system.
- Absolute pressure. Zero in absolute pressure is a perfect vacuum, which means that the absolute pressure reading includes both atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure.
An important difference between the last two types of pressure is the zero reference. The zero of gauge pressure instruments is atmospheric air, which varies with altitude and weather conditions. Zero in instruments that measure absolute pressure is the complete absence of pressure or vacuum; therefore this zero does not change.
How to measure blood pressure correctly with a manual tonometer
To understand how to measure pressure with a tonometer, you need to know the basic recommendations for preparing for a short procedure. It is important to prepare properly; to do this, follow the basic recommendations:
- Measurements to monitor the condition must be taken twice a day, at the same time in the morning and evening.
- Six hours before taking measurements, avoid tonic drinks.
- Do not smoke several hours before the test.
- It is better to use the tonometer on an empty stomach, but if the patient has had lunch, measurements are taken a couple of hours later.
- Avoid physical activity right before the measurement; if a person has come from an active walk, it is better to wait a couple of hours.
- Stress can negatively affect the readings, it is recommended to calm down and wait about an hour, then conduct a study.
The device shows more accurate values if measurements are taken before eating.
Old-style blood pressure monitors often confuse young users. They turn to the World Wide Web to find out how to use a mechanical blood pressure monitor. In fact, it is very simple, the main thing is to follow the basic recommendations of experts.
- It is necessary to take a comfortable position, sitting or lying down. Calm down and relax for five minutes.
- Fix your hand in a comfortable position at the level of your heart, put a cuff on it. In this case, the hand should not be constrained by clothing or squeezed by jewelry.
- The cuff is placed on the lower part of the forearm, fastening firmly, but not squeezing. The distance to the elbow bend is about two centimeters.
- Place the stethoscope disk on the elbow and hold it firmly on the pulsating artery. Hearing aids from a stethoscope are inserted into the ears.
- Begin the measurement by pumping air to 200 mmHg. Art. In hypertensive patients, the figure can reach 220 mmHg. Art. If the cuff squeezes your arm to the point of pain, it is better to loosen it on your arm and repeat the procedure again.
- After pumping the air, they begin to slowly bleed it out, noting at what number the first distinct beat of the pulse occurred.
- Having noted the last distinct blow, they finish by rounding the indicators.
If a second measurement is required, it should be done no earlier than three minutes after the first measurement. To ensure accurate readings, measurements are taken on both hands, a total of three times. The average value is derived, choosing larger indicators.
In medical institutions, despite the abundance of electronic devices, hand-held blood pressure monitors are still used. This is explained by the large number of advantages of such a device. If a person understands how to correctly measure pressure with a mechanical tonometer himself , it is better to buy just such a device.
Its design is as simple as possible and produces the most accurate results. In addition, it is affordable, rarely fails, is suitable for any patient and lasts much longer than its electronic counterparts. It is imperative to buy a tonometer in trusted stores.
What are the advantages of measuring absolute pressure and gauge pressure?
Since all objects and processes in a manufacturing plant are at the same altitude and atmospheric pressure, gauge pressure measurement is accurate enough for most situations. However, absolute pressure measurements are required in specialized situations, such as when you need pressure measurements independent of atmospheric pressure fluctuations, and in industrial plants that use vacuum pumps and vacuum packaging machines.
Absolute pressure gauges and sensors are found in numerous applications, including aviation altimeters, liquid vapor pressure monitors, distillation processes, HVAC and semiconductor manufacturing. The pressure of hazardous arsine and phosphine gases used in the semiconductor manufacturing process must be carefully monitored during storage and transportation. Because atmospheric conditions fluctuate, it is important to ensure that hazardous gases use a reference point that does not change.
Common mistakes
In the first stages, patients make classic mistakes that greatly distort the data. These include:
- when the hand is below or above the level of the heart muscle;
- an uncomfortable posture is adopted, the person is too tense;
- wearing clothes that are too uncomfortable;
- The tonometer cuff is tightened.
In such cases, the pressure will be too high, and if you place the hand above the level of the heart, the readings will be underestimated. Find out how to correctly measure pressure with a manual tonometer and there will be no such errors in the study.
The article was written using https://apteka-ds.com.ua/catalog/domashnya-medtekhnika/tonometry.
How do absolute pressure gauges work?
Absolute pressure gauges include an internal vacuum chamber that is used as a reference for making pressure measurements. Diaphragm-based absolute pressure sensors have a durable yet flexible panel that separates the chamber and the vacuum chamber. Local atmospheric pressure causes the diaphragm to deform into the vacuum chamber. The amount of deformation is converted into a pressure value. This value is then indicated on the indicator display.
Learn more about blood pressure and various blood pressure measurement applications by calling our consultants.
How to understand a tonometer - deciphering the results
The indicators vary greatly among different categories of citizens. To learn how to understand a blood pressure monitor , it is important to consider many factors, including the age and health of the patient. The older a person is, the higher his “normal” blood pressure. This happens due to the inevitable narrowing of blood vessels with age.
For example, for people aged 16–20 years, the indicators are 100–120/70–80 mmHg. Art. At 20–40 years old, the optimal value is 120/80. From the age of 40, the upper level can increase to 140 mmHg. Art. And after 60 years, even up to 150 mm Hg. Art. In this case, the person feels normal and does not observe signs of hypertension.
Increased blood pressure is often observed in athletes due to physical overexertion, and it can also be associated with mental experiences, stressful situations or weather factors. learn how to correctly measure blood pressure with a dial tonometer . There's nothing complicated about it.
Coolant pressure exceeding the limit value
If the operation process is accompanied by frequent “explosions” of the safety valve, you should analyze the possible causes of what is happening:
- reduced capacity of the expansion tank;
- excessive gas/air setting pressure in the tank;
- the installation location is incorrectly selected.
The presence of a tank with a capacity of 10% of the total capacity of the heating system is an almost absolute guarantee of eliminating the first cause. However, 10% is not the minimum possible capacity. A well-designed system can operate normally with a smaller value. However, only a specialist who knows the appropriate calculation methodology can determine the sufficiency of the tank’s capacity.
The second and third reasons are closely interrelated. Let's assume that the air/gas is pumped to 1.5 bar, and the location of the tank is chosen at the top of the system, where the operating pressure, say, is always below 0.5 bar. The gas will always occupy the entire volume of the tank, and the expanding coolant will remain outside. At the bottom of the system, the coolant will put especially strong pressure on the boiler heat exchanger pipes. Regular “explosion” of the safety valve will be ensured!
Coolant in static and dynamic states
The coolant of any heating system can be in two states:
- stationary (static), when there is no heating in the gravitational system (no natural circulation) or the circulation pump is turned off in a system with forced circulation;
- mobile (dynamic), caused by the following reasons: natural circulation of the coolant, driven by a pressure gradient due to uneven heating of the working fluid along the contour of the gravitational heating system;
- forced circulation of coolant driven by a circulation pump;
- thermal expansion of the coolant, causing it to displace air/gas from the expansion tanks, occupying the vacated volumes.
The stationary coolant exerts only (hydro)static pressure on the internal surfaces of the system elements, which is studied by hydrostatics. A moving coolant is characterized by (hydro)dynamic pressure, studied by hydrodynamics. It consists of a static component, then a part determined by the thermal expansion of the liquid, and finally a component created by the so-called. high-speed pressure of a moving fluid. Further, when considering a moving heated coolant, we will use the term working (resulting) pressure.
Quick check of the engine oil pressure light
Experienced motorists are most often aware of the direct connection between the quality of motor oil, the normal functioning of the lubrication system and the service life of the engine. You can also evaluate engine performance by oil pressure. Moreover, this indicator is very important for safe driving.
That is why many vehicle models are equipped with a light to monitor oil pressure. It is located on the dashboard. If the pressure in the engine lubrication system deviates by a certain amount, the lamp gives a light signal. Directly in the engine, the pressure is monitored by a special sensor. In addition to the light, some cars have an audible warning about abnormally low oil pressure.
You need to be aware that the indicator does not always light up when the lubricant level in the engine has already dropped significantly, as well as when the pressure drops, when it has not yet reached an unacceptable value.
Thus, this indicator serves to warn the driver of the fatal consequences of ignoring low oil pressure. If the car owner does not independently control the quality and level of lubricant in the engine, then the lamp will not protect the internal combustion engine from increased wear.
Moreover, not all car models are equipped with a low oil pressure indicator. Therefore, every driver should know how to check oil pressure and the timing of periodic monitoring.
We recommend
“Characteristics of engine oils: understanding the requirements and labeling” Read more
Of course, you need to take into account the characteristics of each specific car model. However, control after 1-2 thousand kilometers is generally accepted. Especially if the vehicle is used frequently. If the car starts from time to time, then a monthly check is enough.
Most often, the driver is puzzled by monitoring the lubricant level when the pressure indicator signals a problem while the engine is warming up.
The lamp itself can be checked very simply - turn the ignition key without starting the engine so that it lights up. When the engine starts, the lamp lights up for a few seconds and goes out. If it does not light up at all when the ignition switch is set to the desired position, then it is quite possible that it has burned out.
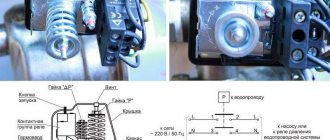
Brief overview of some sensor models and their features
TM-510R.05, TM-510R.06
TM-510R.05, TM-510R.06 are assembled on the basis of TM-510 pressure gauges, and after installing the electrical contact attachment they become full-fledged ECM.
These ECM models use contacts with magnetic compression, which allow switching high currents with high breaking power of the contacts, compared to devices with sliding contacts.
EKM TM-510R.05, TM-510R.06 are characterized by a reliable electrical connection under dynamic loads.
Main characteristics:
- Two-pin electrical circuit;
- Maximum possible voltage ~380 V;
- The maximum possible current is 1 A;
- The maximum possible breaking power of the contacts is 30 W;
A decrease in coolant pressure below normal is a consequence of its leakage
If the value displayed in the absence of circulation has decreased from 0.02 bar, and the gas pressure in the expansion tank is normal, you can begin to look for fluid leaks. It's good if they appear visually. Unnoticeable small leaks are detected by pneumatic testing of the system. Having pumped compressed air inside, wait for the appearance of hissing (whistle) in places of depressurization. They are usually observed at the junctions of pipelines with fittings and heating devices. A good way to prevent coolant leaks is to pressurize the system. This is called high pressure hydrotesting. To fill the system with water, a hand pump is used, which allows you to smoothly raise its value. Having raised it to a certain level, pause for half an hour, monitoring the readings of the pressure gauge. A decrease in the initial value is a clear sign of a leak, which is again looked for visually or audibly by conducting pneumatic tests.
Crimping technology.
Technologies for repairing heating systems are constantly evolving. Relatively recently, a method for eliminating leaks in pipeline systems, including heating systems, has become widespread in Russia, based on adding liquid sealant inside the system (via a pump). Dissolving in the coolant volume, the sealant reacts with air in places of leaks, forming a durable sealing layer, eliminating any leaks in 1-7 days (the period is determined by the size of the defects). The sealant/coolant ratio for the German BCG brand product is 1:100. Therefore, repairing a system with a capacity of 100-200 liters will provide only 1-2 liters of sealant.
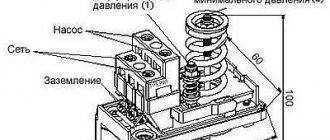
Features of setting up the pressure gauge
The pressure gauge is adjusted using a reference spring gauge. The pressure in the system is changed and the needle on the measuring scale is adjusted accordingly, achieving accurate results. The adjustment is made by rotating the screw press flywheel to change the pressure. Using the screw and moving the rod, the position of the arrow is adjusted. The adjustment begins with the initial value, and then the adjustment is carried out across the entire scale.
To control the fuel system of a car, a manually adjustable fuel pressure regulator with a pressure gauge can be used. It can be installed instead of the standard regulator on a car with an injector. Thanks to the device, the performance of the injectors increases, which makes it possible to pump more fuel into the cylinders. Thus, the power of the power unit increases.
What do the colored zones on the pressure gauge mean?
The colors on the gauge indicate levels that indicate breakdown and serviceability.
The user, knowing the meaning of each indicator segment, will be able to determine the condition of the fire extinguisher.
Arrow in the red zone
The red zone indicates danger. There are two placement options (can be present simultaneously):
- on the zero side: the pressure is too low, the jet is weak, the fire extinguishing ability decreases, there is no response;
- the green and yellow zones, which indicate a moderate level of danger, come before the red zone, which warns of a critical level of problems:
- risk of cylinder rupture, seal failure;
strong recoil;
- dangerous jet behavior.
Arrow in the yellow zone
If the fire extinguisher pressure gauge is in the yellow zone - the amount of MPa exceeds the norm, it informs about malfunctions, but of a non-critical nature. The meaning of yellow color is similar to that of a traffic light - it calls for:
- note;
- carry out maintenance;
- be prepared for problems, for optional but possible consequences.
It is rare that exceeding the permissible limits is a consequence of improper refueling. Most often, a violation occurs due to improper storage: heating from the sun, heating devices.
Arrow in the green zone
Green zone – working condition, the number of MPa indicates serviceability.
Accuracy class
When making measurements, you must also take into account the accuracy class of the device, which is indicated in its passport and on the scale (conventionally designated by the letters KL or CL). This is the percentage of permissible error relative to the measurement range. The standard provides for the following series of accuracy classes: 4; 2.5; 1.5; 1; 0.6; 0.4; 0.25; 0.15. A higher accuracy class indicates that the device is less accurate. Its low value indicates high accuracy.
The permissible error can be calculated by multiplying the accuracy class by the measurement range and then dividing the resulting product by 100. Thus, for a pressure gauge of accuracy class 4 with a measurement range of 2.5 MPa, the error value will be 0.1 MPa.
An easy way to check oil pressure without a pressure gauge
However, a pressure gauge is not always available. Therefore, a simple express method for diagnosing engine oil pressure is often used. This will require the help of a friend and some available equipment. You need to understand that this way you can only verify the presence of pressure at which you can still drive a car. So, if you don’t have a pressure gauge, you need to do the following:
- Open the hood and check the lubricant level using the dipstick.
- Disconnect and unscrew the oil pressure sensor installed on the engine.
- De-energize the ignition coils by disconnecting the wires.
- Use the starter to turn the engine crankshaft.
- While the starter is operating, observe the mounting hole of the oil pressure sensor. You need to make sure whether a stream of oil appears from there when the engine rotates.
If there is a jet, then we can confidently conclude that the sensor is not working. Therefore, you can drive to the service center on your own. If lubricant does not flow out of the sensor seat, it means there is no oil supply to the engine. Therefore, you should refrain from further movement in this car. As you can see, this method can also check the serviceability of the oil pressure sensor.
Installation and removal rules
To ensure stable operation of the pressure gauge and reduce the risk of its breakdown, follow certain rules:
- The installation of pressure gauges must be carried out in such a way that it would be quite easy to take measurement results and carry out routine maintenance and repairs.
- The rules define a number of conditions that determine the maximum dimensions of the distances between the measuring device and the walls of the room in which the device is installed.
- If the pressure gauge is mounted at a height of 2 to 3 meters, the diameter of the housing must be no less than 160 mm. It is unacceptable to install pressure gauges at a height of more than three meters. This is defined in the requirements of regulatory documentation.
- To carry out the checks of measuring instruments and equipment prescribed in the regulatory documentation when using the instruments, a three-way valve must be installed in the installation structure. Its installation location should be between the pressure gauge and the pipe (vessel).
- When installed in conditions where it may be influenced by external external factors, for example, precipitation or high temperature, it is necessary to provide additional protection. For this purpose, so-called buffer elements, siphons and other products are used. The efficiency of the installed measuring equipment depends on how well it is protected from external influences.
- To prevent freezing of the measuring instrument, they are provided with thermal insulation.
- When connecting, it is necessary to vent any gas that has entered the system. To do this, slightly tighten the fixing nut on the fitting.
- Pressure gauges that have not been verified and do not have a seal or appropriate seal on the body should not be allowed to be used for operation in networks. If the verification period has expired, or during operation it turns out that the operation differs from the standard one, then it must be removed and sent for diagnostics and repair. If damage appears on the meter body, or a crack appears on the glass, then such a device cannot be used and must be disposed of.
- Damaged sensors are dismantled and transferred to a certified laboratory for repair work. If such a pressure gauge cannot be restored, then it is disposed of.