High-speed tool steel P9 - characteristics, properties, analogues
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade P9.
Classification of material and application of grade P9
Brand: P9 Material classification: High-speed tool steel Application: for the manufacture of tools of simple shapes that do not require a large amount of grinding, for processing common structural materials.
Mechanical properties of P9 at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| 840 | 490 | 10 | 29 | 260 | Delivery status | |||
| Annealed tape, GOST 2283-79 | 0.1 — 4 | 880 |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, |
| sT | — Limit of proportionality (yield strength for permanent deformation), |
d5 — Elongation at break,
y — Relative narrowing,
KCU - Impact strength, [kJ/m2]
HB - Brinell hardness,
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o-T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o-T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, |
Please note that this information about the P9 brand is provided for informational purposes. Parameters, properties and composition of real P9 brand material may differ from the values given on this page
More detailed information about the P9 grade can be found on the information resource “Brand of Steel and Alloys”. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
Quick cutters P12 and P9 - tungsten steels from Vorsma and Pavlovo
Part 3. P12, P9, P6
Steel 20x2n4a
P12 and P9 are tungsten steels, in which the amount of tungsten was successively reduced and the amount of vanadium was increased.
The online store offers knives with blades made of P12 steel, which is similar in structure and properties to P18, but has better mechanical properties.
P12 steel in various modifications is used for the manufacture of cutting tools - taps, milling cutters, drills, cutters, etc. It is used instead of the P18 grade, since P12 steel is excellent for the production of blades due to its technological properties.
P9 steel is used for the manufacture of simple-shaped tools used in processing stainless and structural steels, fiberglass, hard rubber and other materials.
P6 steel is perhaps a universal and widely used high-speed steel all over the world. Like the P18, it is also long-lived - it was developed in the 30s of the 20th century. It is still a kind of standard with which new steel grades are compared. In various modifications it is also used for the manufacture of cutting tools: taps, milling cutters, drills, cutters, etc.
For some materials, steel is more economically feasible than P9 or P18.
Conclusions:
A common feature common to all of the listed steels when used for the production of knives for household use is high durability of the cutting edge. Blades made of these steels allow them to be sharpened even at a small angle of rotation (up to 10-15 degrees) without chipping.
Due to their relative fragility, machete-type knives, throwing knives and axes are not made from these steels.
It is also necessary to take into account that the blades are hardened to high hardness, and in the field they are very difficult to sharpen.
We hope that the review was useful and interesting to you.
Decide on the purpose of the knife and, if the quick cutter suits you, then choose it.
Start of the article here:
Good luck in everything!!!
Decoding the designation of steel grades
Initially, high-speed steel as a material for the manufacture of cutting tools was invented by British specialists. Taking into account the fact that tools made from such steel can be used for high-speed processing of metals, this material was called “rapidsteel” (the word “rapid” here means high speed). This property of these steels and the English name he invented at one time was the reason that the designations of all grades of this material begin with the letter “P”.
The rules for marking steels classified as high-speed steels are strictly regulated by the relevant GOST, which greatly simplifies the process of deciphering them.
The first number after the letter P in the designation of steel indicates the percentage content of such an element as tungsten, which largely determines the basic properties of this material. In addition to tungsten, high-speed steel contains vanadium, molybdenum and cobalt, which are designated in the markings by the letters F, M and K, respectively. After each of these letters in the marking there is a number indicating the percentage of the corresponding element in the chemical composition of the steel.
An example of decoding a high-speed steel grade
Depending on the content of certain elements in the steel, as well as their quantity, all such alloys are divided into three main categories. It is quite easy to determine which category steel belongs to by deciphering its markings.
So, high-speed steel grades are usually divided into the following categories:
- alloys containing up to 10% cobalt and up to 22% tungsten; These steels include alloys of grades R6M5F2K8, R10M4F3K10, etc.;
- steel containing no more than 5% cobalt and up to 18% tungsten; such steels are alloys of grades R9K5, R18F2K5, R10F5K5, etc.;
- alloys that contain no more than 16% of both cobalt and tungsten; These alloys include steel R9, R18, R12, R6M5, etc.
Determining the type of steel by spark
As mentioned above, the characteristics of steels classified as high-speed steels are mainly determined by the content of such an element as tungsten. It should be borne in mind that if a high-speed alloy contains too much tungsten, cobalt and vanadium, then due to the formation of carbide heterogeneity in such steel, the cutting edge of the tool that is made from it may chip under the influence of mechanical loads. Tools made from steels containing molybdenum do not have such disadvantages. The cutting edge of such tools not only does not chip, but is also distinguished by the fact that it has the same hardness indicators along its entire length.
Steel R9 – State Enterprise Stalmash
Steel grade st3: characteristics, application. steel 3 carbon content
reference Information
Characteristics of the material: P9 steel.
| Brand: | P9 |
| Substitute: | P18 |
| Classification: | High-speed tool steel |
| Products offered by advertisers: No data. |
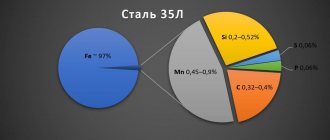
Chemical composition in % of material P9
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Mo | W | V | Co |
| 0.85 — 0.95 | up to 0.5 | up to 0.5 | up to 0.4 | up to 0.03 | up to 0.03 | 3.8 — 4.4 | up to 1 | 8.5 — 9.5 | 2.3 — 2.7 | up to 0.5 |
Temperature of critical points of the material P9.
| Ac1 = 820, Ac3(Acm) = 870, Ar3(Arcm) = 780, Ar1 = 740, Mn = 180 |
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of material P9.
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| 840 | 490 | 10 | 29 | 260 | Delivery status |
| Hardness of the material P9 after annealing, | HB 10 -1 = 255 MPa |
Physical properties of material P9.
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.2 | 8300 | 380 | |||
| 100 | 23 | 417 | ||||
| 200 | 25 | 505 | ||||
| 300 | 26 | 600 | ||||
| 400 | 28 | 695 | ||||
| 500 | 30 | 790 | ||||
| 600 | 31 | 900 | ||||
| 700 | 1020 | |||||
| 800 | 1160 | |||||
| 900 | 1170 | |||||
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, |
| sT | — Limit of proportionality (yield strength for permanent deformation), |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, |
| y | — Relative narrowing, |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, |
Steel grade P9
| Grade: P9 (substitute: P18) Class: High-speed tool steel Type of supply: long products, including shaped steel: GOST 19265-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006. Calibrated rod GOST 19265-73, GOST 7417-75. Polished rod and silver steel GOST 19265-73, GOST 14955-77. Thick sheet TU 14-1-1408-75. Thin sheet TU 14-1-1408-75, TU 14-1-1706-76. Tape GOST 2283-79. Strip GOST 19265-73, GOST 4405-75. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 19265-73, GOST 1133-71. Use in industry: for the production of tools of simple shapes that do not require a lot of grinding, for processing common construction materials. |
| Chemical composition in % of P9 steel | ||
| C | 0,85 — 0,95 | |
| Si | up to 0.5 | |
| Mn | up to 0.5 | |
| Ni | up to 0.4 | |
| S | up to 0.03 | |
| P | up to 0.03 | |
| Cr | 3,8 — 4,4 | |
| Mo | up to 1 | |
| W | 8,5 — 9,5 | |
| V | 2,3 — 2,7 | |
| Co | up to 0.5 | |
| Fe | ~80 | |
| Additional information and properties |
| Heat treatment: Delivery condition Forging temperature: °C: beginning 1200, end 900. Cooling in wells at 750-800 °C. Material hardness: HB 10 -1 = 255 MPa Critical point temperature: Ac1 = 820, Ac3(Acm) = 870, Ar3(Arcm) = 780, Ar1 = 740, Mn = 180 Weldability of the material: for electric butt welding with steel 45 and 40X good. Cutting machinability: in the hot-rolled state at HB 205-255 K υ solid. spl=0.8 and Kυ b.st=0.6 |
| Mechanical properties of P9 as delivered (after annealing) at 20 °C | ||||||||||
| σ0.05 (MPa) | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | σco.2 (MPa) | σcom (MPa) | ε (%) | Τk (MPa) | γ (%) | KCU (J/cm2) |
| 210 (5) | 490 (20) | 840 (30) | 10 (1) | 29 (2) | 620 (13) | 2500 (75) | 56 (17) | 560 (17) | 60 (1,4) | 26 (1) |
| Mechanical properties of P9 steel in a heat-treated state at elevated temperatures | |||
| Test temperature, °C | σben (MPa) | H.V. | HRC∂ |
| 200 400 500 550 600 650 | 3630 (180) 3870 (140) 3380 (160) 2800 (140) 2260 (120) 1520 (100) | 769 (10) 712 (10) 673 (10) 605 (10) 555 (10) 459 (10) | 62 60 59 56 53 48 |
| Mechanical properties of P9 steel in a heat-treated state at 20 °C | ||||||
| σ0.05 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | σco.2 (MPa) | σcom (MPa) | Τk (MPa) | σben (MPa) | KCU (J/cm2) |
| 2200 (70) | 2210 (110) | 2870 (90) | 3900 (120) | 1960 (100) | 3150 (200) | 20 (2) |
| Mechanical properties of P9 steel in the as-received condition (after annealing) at elevated temperatures | ||||||||
| Test temperature, °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | σ5 (%) | ψ (%) | σcom (MPa) | Τk (MPa) | KCU (J/cm2) | NV |
| 200 400 600 800 1000 1100 1200 | 450 (50) 420 (40) 300 (40) 110 (20) 90 (20) — 30 (10) | 830 (80) 700 (70) 480 (50) 200 (20) 100 (20) — 30 (10) | 13 (2) 15 (2) 31 (3) 60 (5) 42 (4) — 12 (3) | 22 (4) 22 (4) 55 (6) 70 (6) 55 (6) — 25 (5) | 1050 (50) 850 (50) 620 (40) 100 (20) 50 (10) — 40 (10) | 520 (30) 450 (30) 300 (20) 100 (20) 50 (10) — 40 (10) | — — — — 220 (20) 240 (20) 150 (15) | 227 (6) 210 (6) 140 (6) 30 (4) 24 (4) — 4 (1) |
| Mechanical properties of P9 depending on tempering temperature | |||||
| Temperature, °C | σв (MPa) | KCU (J/cm2) | HRC∂ | ||
| Hardening 1230 °C, oil. Vacation three times for 1 hour | |||||
| 200 300 400 500 540 580 600 620 660 | 1030 1080 1270 1470 — — 1960 — — | 10 52 49 39 — — 26 — — | 66 64 — 61 54 | ||
| Red resistance (GOST 19265-73) | ||||
| Temperature, °C | Time, h | HRC∂ | ||
| 580 620 | 4 | 63 59 | ||
| Sandability - reduced (GOST 19265-73) | ||||
| Physical properties of P9 steel | ||||||
| T (Grad) | E 10-5 (MPa) | a 10 6 (1/Deg) | l (W/(m deg)) | r (kg/m3) | C (J/(kg deg)) | R 10 9 (Ohm m) |
| 20 | 2.2 | 8300 | 380 | |||
| 100 | 23 | 417 | ||||
| 200 | 25 | 505 | ||||
| 300 | 26 | 600 | ||||
| 400 | 28 | 695 | ||||
| 500 | 30 | 790 | ||||
| 600 | 31 | 900 | ||||
| 700 | 1020 | |||||
| 800 | 1160 | |||||
| 900 | 1170 | |||||
Interpretation of steel grade P9: the letter P indicates that this is high-speed tool steel, which contains tungsten in an amount of about 9%.
Tools made of P9 steel and its heat treatment: for the manufacture of cutters operating at high and medium cutting speeds, high-speed steel grades P9 and P18 are used. Cutters made of high-speed steel, as a rule, are manufactured in combination with welded plates, holders are made of carbon, and plates are made of high-speed steel. For cutting and boring cutter holders, St6 and St7 are used, and for the rest, steel 45 or steel 50.
Heating of high-speed steel cutters for hardening is carried out mainly in electrode-salt furnaces filled with chlorobarium salt, and in the absence of such, in gas and oil furnaces and, as an exception, in forges.
Practice has established that normal cutters with welded high-speed steel plates can be heated immediately to a high temperature without fear of cracks.
Time is kept using a stopwatch or hourglass. Cooling of cutters is carried out in oil, since cooling in air reduces the durability of the cutter in operation and therefore can only be recommended for thin special cutters in order to reduce deformation. When cooling in air, you should not place the cooling tool on the floor or on plates; it is better to hang it or place it in specially prepared nests, in boxes with sand, etc.
The hardness after hardening must not be lower than Rc = 61. After a random hardness test, the entire batch is tempered. Tempering is carried out in furnaces PN31 and PN32 with forced air circulation. In the absence of such, electric furnaces H15 or H3O, as well as furnaces heated by gas or oil, can be used for tempering. When vacationing, it is recommended to place the cutters not on the underside, but on a special stand. This eliminates the risk of overheating of the cutters if the underside is at a higher temperature than required for tempering. After tempering, the cutters are placed on the floor to cool. Tempering should be done once with a 2-hour exposure at a temperature of 540-580°, or twice with a 1-hour exposure. After tempering, the hardness should remain the same or increase by 1-2 units.
When starting to harden one or more batches of cutters, it is necessary to first harden and temper several cutters. If good results are obtained using the selected mode, it is necessary to process all other incisors. The quality of the finished cutters is checked with a calibrated file, and 2-3% of the batch is checked on an RV device after pre-processing on a sharpener of parallel sides.
Rejected cutters that are subject to reheating must be annealed, otherwise the high-speed steel will develop a so-called naphthalene fracture (irremovable during further processing), which sharply reduces the durability and increases the fragility of the tool. Required hardness of cutters Rc = 62-65.
Round cutters are made from high-speed steel, carbon steels U10A and U12A, alloy steels 9ХС, ХВГ, etc.
Due to the complexity of the profile, round shaped cutters are often not ground after hardening, but only polished. Therefore, every precaution should be taken to prevent decarburization and scale formation on the cutters.
Round cutters made of high-speed steel must be heated in a separate oven or by intermittent immersion in molten salt before final heating. Final heating should be carried out in a well-deoxidized salt furnace. Cooling is carried out in molten saltpeter at a temperature of 450-500° for 5-8 minutes. followed by cooling in air or in oil to a temperature of 150-250°, and then in air.
If the final heating for hardening is carried out in a chamber furnace heated by gas, oil or electricity, it is necessary to roll the cutter heated to a temperature of 800° in calcined and finely ground borax. The borax powder, having reached the temperature of the cutter, will melt, cover it with an even layer and thereby protect the surface from scorching. Tempering is carried out by holding twice for 1 hour at a temperature of 540-580°. Required hardness Rc= 62-65°.
Basic properties
Structural alloy steel 18khgt
The technical characteristics of metals are based on their physical and mechanical properties.
Basic physical properties of grade P9 at a temperature of 20 ºС.
- Specific resistance R=380×109(Ohm/m).
- Density p=8300kg/m3.
- Thermal conductivity = 23 W (mS)
Mechanical properties include hardness, redness, and strength.
The hardness of P9 steel remains unchanged at temperatures up to 580 ºC. At this temperature, within 4 hours the hardness remains equal to 63 Rockwell. Carbon steels begin to lose hardness even at a temperature of 200 ºС.
During use, steel tools are subjected to various loads. Therefore, the greater the strength, the more reliable and durable the tool. P9 steel has a tensile strength:
- tensile strength 850 MPa
- at bending 3630 MPa
- at compression 2500 MPa
Characteristics of high-speed steels
As a result, the question arises: which high-speed steel? Of all its diversity, only alloys that contain many alloyed additives can be considered as such. Different chemical elements can significantly change the properties of a metal.
If we talk about the main qualities of steel, this is primarily an increase in the hardness of the alloy. This property is determined by the purpose of the material - to create conditions under which the metal can work at a higher speed. Steel must retain its qualities even with strong friction that appears during the cutting process. Otherwise, the material will be unsuitable for production.
Other properties of high speed steel:
- Maintains a high level of resistance even at high temperatures.
Stability is explained by the ability of a tool to operate without changing characteristics. Any transformations may lead to a deterioration in the quality of the result, so it is important to maintain the original balance. For example, changes associated with the crystal lattice result in excessive friction and heating of the metal. Then the hardness of the material decreases, and the plasticity, on the contrary, becomes higher. Wear of such a tool will occur much faster than under correct operation conditions. - Strength.
The hardness of high speed steel is related to its application. The material is often used for cutting workpieces or processing parts. Research results indicate that high-quality steel retains its characteristics at temperatures up to +6,000 °C. If the quality of the steel is ordinary, then the hardness will be less than that of any other carbon metal. - Increased stability, due to which the steel tool is difficult to destroy.
Fragility and flexibility are unacceptable for such a metal, since it operates at a fairly high speed. Due to its resistance, the steel can also be used with high feed rates. This will result in a greater depth of cut.
Technical characteristics: subtleties of using reference manuals
The properties of 09g2s steel are largely determined by the chemical composition of the alloy, its specific parameters, which today are quite accurately calculated by metallurgists.
Steel grade 09g2s has the following critical points:
- Ac1 = 732, when austenite transforms into pearlite during cooling processes;
- Ac3(Acm) = 870 (s – from French chauffage/heating) the end point of cementite dissolution;
- Ar3(Arcm) = 854 (refroidissement – cooling) the beginning of the release of Fe3C;
- Ar1 = 680 hypoeutectoid steel, corresponds to ferrite precipitation
The symbols are classic, numbers 1 and 3 indicate the numbers of points on the graph. The symbols cm usually mark hypereutectoid steels.
If we talk about other features of St 09g2s, the following characteristics are noted: easy weldability of the material. For this purpose, RDS, ADS under flux and gas protection are used. Only products that have undergone chemical-thermal treatment cannot be welded.
The mechanical properties of steel 09g2s are tabular values that were developed by a number of GOST standards and describe the material at room temperature, as well as for its other states.
Among the important mechanical properties of 09g2s steel are the following:
- Yield strength for permanent deformation, measured in MPa;
- Relative values of elongation at break and contraction;
- Impact strength (use under load is one of the main applications);
- Brinell hardness (HB).
Strength class of steel 09g2s: the table for the list of grades includes the one indicated, which, as already noted, corresponds to C345. This also includes a number of other brands. Thus, steels that are different in chemical composition and even in the method of producing steel can have the same strength class. This data can be found for 09g2s according to GOST 19281-2014; the characteristics of the alloys are presented in convenient tables that are easy to navigate. You can view (download) GOST 19281-2014 here.
But the opposite situation is also possible. For example, for 09g2s GOST 19281-89 and grade 16GS there is data on strength classes 265 and 296.
The same GOST describes the types of rolled metal:
- Varietal, round, shaped with various sections (including circle 09g2s).
- Wideband profiles with a certain thickness of products.
Large diameter circles steel 09g2s
Similar information is provided for other brands.
The density of steel 09g2s fluctuates, somewhere around the 7800 kg/m3 mark. But alloying elements can either increase the specific gravity or reduce it. Tungsten tends to be the first. The second is achieved by adding: cobalt, nickel, copper.
The hardness of steel 09g2s can be determined by Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers, etc. the choice of system is determined by the type of products for which parameter determination is required. It is also important when choosing a welding method; the hardness of the steel at the weld should remain fairly high.
Most of the listed parameters can be found in TU 14 3 1128 2000 for steel 09g2s, as well as for other grades. The technical specifications describe the requirements for the materials from which pipes are made for servicing gas fields and other areas of the industry.
The permissible stress for steel 09g2s is calculated depending on the following values:
- strength class and grade;
- temperatures at which it will be operated;
- thickness, sometimes configurations (circle, sheet, etc.).
Existing 09g2s analogues are foreign (European, Asian, others), most similar in mechanical and technical properties to the specified brand. However, the chemical composition can vary greatly. The Bulgarian version of this brand has the closest configuration.
Application area of high speed steel
High speed steel cutters can be used for a variety of tools. Basically, these are small drills and cutters. These tools are used to process materials from which structures, machine parts and some structures are created. The scope of application can be expanded by impurities.
For example, with tungsten, steel becomes suitable for toothing or threading. Tools with the addition of vanadium are used to create devices capable of finishing the material. Cobalt can be used to process metal with anti-corrosion and heat-resistant properties.
Both cutters and high-speed steel drills must be resistant to different temperatures and wear. But there are a number of additional requirements that can improve the quality of steel. First of all, this is the ability to resist corrosion, as well as maintain its original dimensions and shape even at high speeds.
Equally important is resistance to dynamic loads. High-speed tool steel grades are characterized by resistance to high temperatures from +600 °C to +6,400 °C. These parameters allow them to be used to create cutters, taps, broaches, cutters, saws and countersinks.
Recommended articles
- Types of welds: we understand the classification and features
- Production of metal products: technologies, advantages, step-by-step control
- Fusion welding: where it is used and how it is produced
Chemical composition
By its origin, P9 steel is alloyed. The basic principle of alloying metals is as follows. To maintain hardness when heated, it is necessary to introduce elements into the metal that impede the coagulation of carbides. Therefore, tool steels are alloyed with tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium carbides. Cobalt especially affects the cutting properties of steel.
The composition of the P9 grade quick cutter includes, in %:
- carbon - 0.85-0.95,
- silicon up to 0.5,
- manganese - up to 0.5
- sulfur - 0.03,
- phosphorus - no more than 0.03,
- chrome - 3.8-4.4
- molybdenum - up to 1,
- tungsten - 8.5-9.5,
- vanadium - 2.3-2.7,
- cobalt - up to 0.5,
- nickel - up to 0.4,
- iron - approximately 80.
These elements define the characteristics of the P9.
Tool hard alloys.
Hard alloys of standard grades are made on the basis of tungsten, titanium and tantatle carbides. Cobalt is used as a binder. Depending on the composition of the carbide phase and the binder, the designation of hard alloys includes letters characterizing the carbide-forming elements (B-tungsten, T-titanium, the second letter is T-tantalum) and the binder (K-cobalt). Mass fractions of elements are expressed as percentages, the sum of which is 100%. For example, grade VK8 (single-carbide alloy) contains 8% cobalt and 92% tungsten carbides; grade T5K10 (two-carbide alloy) contains 5% titanium carbides, 10% cobalt and 85% tungsten carbides; grade TT8K6 (three-carbide alloy) contains 6% cobalt, 8% titanium and tantalum carbides, 86% tungsten carbides.
Basic physical and mechanical properties of hard alloys
Good day. Tell me what is the difference between high-speed steels R9 and R6M5 if they are used for a knife blank. The thing is that at the bazaar I found a semi-bald industrial metal saw with P9 markings, 2.3 thick, the owner said that it was still a Soviet one - so I’m thinking about whether to take it or not?
it goes without saying! But about what is better P9 or P6M5? Of course it is clear that both will shave.
Almost any piece of iron will shave if properly sharpened.
Take any good material.
ASDER_K Who are you commenting on? me or the author. if me, then I didn’t say that
kick, kick and kick some more gas. If you see a Soviet saw made from R18, definitely take it.
They give you a chance to take it. p9 is more fragile. in p6m5 there is 5 percent molybdenum, which is gut.
Nothing good will come of it at home, 500 degrees for a quick cut is a normal temperature. The fragility of quick cutters is greatly exaggerated; it works great on small blades. I made several blades from P6M5 with very thin bevels, they all seem to be intact and they cut great. P9 does not I tried it, the P18 is really fragile, the tip of the blade on the working jamb broke several times under lateral loads.
rumors about the fragility of quick-cutters are greatly exaggerated - that’s for sure. Just how thin the rockstead is, even though it’s in a lens, it doesn’t crumble)
There are no rumors about the fragility of quick cutters. p6m5 in canvas is quite a good steel. on small knives with a blade up to 150 mm, nothing seems to happen to it. But the R-18 crumbles well, I have experience with the R-9 too. It just depends on what you do with the knife and what the geometry of the wedge is. but, with the cost of a saw blade being 50 rubles, which is enough for 2 medium-sized knives, issues of fragility can be considered minor. for example, what will happen to the ZDP-189 and other steels of this class if, with the geometry of half razor blades from 0.5 in the RK and the blade length of the same 150 mm, it chops firewood or cuts meat with chopping bones?
nothing special either, especially if it’s 0.5 on the Republic of Kazakhstan. checked (although of course it was only 90mm) but this does not fundamentally change the situation.
If possible, I prefer to take saws that have already worked. There are two reasons - they are somewhat cheaper than new ones and, most importantly, the quality of the metal can be seen from the signs of wear. If the blade does not move during operation, there are no spilled teeth, then there are no hidden cracks or overheating.
Marking
In stamp books valid in Russia, quick-cutters are designated in a special way. They start with the letter P from the English word rapid, that is, fast. The numbers that come after this letter indicate the tungsten content as a percentage.
Thus, the interpretation of the P9 steel marking means: high-speed steel with a tungsten content of the total mass, on average 9%.
Scope and analogues
Grade P9 is used mainly in the manufacture of tools for metal processing. Drills, various cutters, countersinks, turning tools. Among the analogues, we can mention P18 steel, which is very similar in characteristics. There are also foreign analogues.
GOST for products
- Long products GOST 19265-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006
- Calibrated rod GOST 19265-73, GOST 7417-75
- Polished rod and silver steel GOST 19265-73, GOST 14955-77
- Thick sheet TU 14-1-1408-75
- Thin sheet TU 14-1-1408-75, TU 14-1-1706-76
- Tape GOST 2283-79
- Strip GOST 19265-73, GOST 4405-75
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 19265-73, GOST 1133-71.
Rating: /5 — votes
Scope of application of various grades of high-speed steels
| High speed steel grade | Scope of application and main characteristics of the brand |
| P9 | Most often used with tools of simple shape, which do not require lengthy grinding. Also suitable for construction materials. Steel has a reduced grinding performance, but at the same time higher ductility compared to other grades. The characteristic makes it suitable for the application of the plastic deformation method. |
| P18 | This type of steel has high manufacturability. Due to its performance properties, the scope of application is quite wide. Almost all types of conventional construction materials can be processed. High level of sandability |
| P12 | The scope of application is almost the same as in the case of P18 high-speed steel. However, grinding performance is lower than that of P18 |
| 10Р6М5 | Suitable for processing cutting tools and those working with shock loads. The range of quenching temperatures is smaller than in the case of P18. Increased likelihood of decarbonization |
| R6M5 | The characteristics are similar to the 10Р6М5 brand. The difference is less hardness, but greater strength |
| R6M5F3 | Sandability is low. Used in processing reamers, shaped cutters, structural steels (subject to medium cutting conditions), broaches, semi-finishing and finishing tools |
| R12F3 | At medium cutting speeds it is possible to process semi-finishing and finishing tools, as well as abrasive materials. A good alternative for grades R14F4 and R6F5, since grindability is higher and other characteristics are almost the same |
| R9F5, R14F4 | Sandability is low. Used with tools of simple shape that do not require time-consuming grinding. Excellent in processing abrasive materials and finishing tools with small cut sections |
| R9M4K8, R6M5K5 | The brands can withstand high temperatures, so they are suitable for heat-resistant materials. Sandability is slightly reduced |
The set of types of metal products includes such shapes as strip, sheet metal, circle and square. In practice, the circle is most often used. The square is designed for creating knives, electric planers and turning tools. Each component of the assortment has its own specifics, so for reliability you should consult with a specialist.
Thus, it was possible to find out what high-speed steel and hard alloy mean, what characteristics and features the steel has, as well as how to decipher its markings. The scope of application of the brands was also given, and more detailed information can be obtained from specialized companies. They will select material with qualities that will be most optimal for your situation. The necessary conditions for the production and heat treatment of high-speed steel, which will ensure its high quality, will also be presented.
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of 9Cr18MoV includes the following elements:
| C | Cr | Mn | Mo | Ni | P | Si | S | V |
| 0.85-0.95% | 17-19% | 0.8% | 1-1.3% | 0.6% | 0.04% | 0.8% | 0.03% | 0.07-1.2% |
Each element and its specific percentage is responsible for its own characteristics:
- Carbon has a positive effect on edge retention and toughness, improves ductility and wear resistance.
- Chromium increases hardness, density and corrosion resistance.
- Manganese improves hardening properties, viscosity, and acts as an oxidizer and degasser.
- Molybdenum significantly increases hardness, improves machinability and hardenability.
- Nickel adds a little toughness and resistance to rust formation.
- Phosphorus is a harmful impurity, it slightly increases hardness, but impairs ductility and fragility.
- Silicon increases strength and is used as a deoxidizing agent in metal smelting.
- Sulfur is also a harmful impurity, which in high concentrations negatively affects impact strength, corrosion performance and ductility.
- Vanadium adds strength to the alloy, resistance to rust and wear, and improves the density and uniformity of the structure.
Other material parameters
For steel 09G2S 12, the marking description contains only a description of the alloying components and their quantities. However, there are other important factors besides alloying that are worth considering.
- constructability of steel or its purpose in other words;
- eutectoidity of the material;
- manufacturing methods;
- the chemical composition is also quite important.
This is an incomplete list of other characteristics that are just as important for steel as its alloying level. If you correctly decipher the 09G2S 12 designation, then from the data obtained, or more precisely from the amount of chromium, you can understand that the product belongs to the low-alloy class. Another important fact that relates to labeling is the designation of the material in different industries. For example, in the construction industry, alloy 09G2S is designated as S345. Quite often in such cases, many questions arise from unknowing people. The thing is that for builders, marking from the point of view of alloying is not important. They mark such alloys by their yield strength, which in this case is 345.
History of the creation of a quick cutter
The purpose of high-speed steel was determined through a historical process. Before quick cutters appeared, craftsmen used ordinary steel cutters. They were not so well suited for processing wood parts and non-ferrous metal products. The main problem associated with turning with such a tool is the slowness of the process. Also, the cutting part quickly becomes unusable and reaches high temperatures.
VT-metall offers services:
High-speed steel has become a real discovery for craftsmen. It appeared in 1858, when an alloy of tungsten and manganese was discovered. Chemical elements were ideal as alloying elements. Throughout the 21st century, scientists have been looking for options with improved characteristics. Particular successes have been achieved in the strength of the material.
As a result, the processing speed of parts has become many times greater, as has the productivity of metal-cutting machines.
In the 20th century, self-hardening compounds successfully replaced tungsten compounds. Nowadays, tungsten-free compounds are considered the most effective.
Characteristics of the material. Steel14Х17Н2 (EI268)
| Brand | Steel14Х17Н2 (EI268) |
| Classification | Corrosion-resistant (stainless) steel, heat-resistant. Chrome-nickel stainless steel. |
| Substitute | 20Х17Н2 |
| Other designations | steel 14Х17Н2, st.14Х17Н2, 14X17H2, 14Х17Н2-Ш, EI268, EI268-Ш, 1Х17Н2 |
| Foreign analogues | AISI 431(USA), X20CrNi72(Deu), X22CrNi17(Deu), SUS431(Jap), Z15CN16-02(Fra), 431S29(GBR) |
| Application | working blades, disks, shafts, bushings, flanges, fasteners and other parts, parts of compressor machines operating on nitrous gas, parts operating in aggressive environments and at low temperatures; martensitic steel - ferritic class |
| Type of delivery | |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 5949-75, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 2879-88 |
| Calibrated rod | GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78 |
| Ground rod and silverfish | GOST 14955-77, GOST 18907-73 |
| The leaf is thick | GOST 7350-77 |
| Thin sheet | GOST 5582-75 |
| Band | GOST 4405-75, GOST 103-76 |
| Forgings and forged blanks | GOST 1133-71 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 5632-72 |
Corrosion resistant stainless steels
| CIS (GOST) | Euronorms (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) |
| 03 X17 N13 M2 | 1.4404 | X2 CrNiMo 17-12-2 | 316 L |
| 03 X17 N14 M3 | 1.4435 | X2 CrNiMo 18-4-3 | — |
| 03 X18 H11 | 1.4306 | X2 CrNi 19-11 | 304 L |
| 03 X18 N10 T-U | 1.4541-MOD | — | — |
| 06 ХН28 MDT | 1.4503 | X3 NiCrCuMoTi 27-23 | — |
| 06 X18 H11 | 1.4303 | X4 CrNi 18-11 | 305L |
| 08 X12 T1 | 1.4512 | X6 CrTi 12 | 409 |
| 08 X13 | 1.4000 | X6 Cr 13 | 410S |
| 08 X17 N13 M2 | 1.4436 | X5CrNiMo 17-13-3 | 316 |
| 08 X17 N13 M2 T | 1.4571 | Х6 CrNiMoTi 17-12-2 | 316Ti |
| 08 X17 T | 1.4510 | Х6 СrTi 17 | 430Ti |
| 08 X18 H10 | 1.4301 | X5 CrNi 18-10 | 304 |
| 08 X18 N12 T | 1.4541 | Х6 CrNiTi 18-10 | 321 |
| 10 Х23 Н18 | 1.4842 | X12 CrNi 25-20 | 310S |
| 10X13 | 1.4006 | X10 Cr13 | 410 |
| 12 X18 N10 T | 1.4878 | X12 CrNiTi 18-9 | — |
| 12 X18 H9 | — | — | 302 |
| 15 X5 M | 1.7362 | Х12 СrMo 5 | 501 |
| 15 X25 T | 1.4746 | Х8 CrTi 25 | — |
| 20X13 | 1.4021 | X20 Cr 13 | 420 |
| 20 X17 N2 | 1.4057 | X20 CrNi 17-2 | 431 |
| 20 Х23 Н13 | 1.4833 | X7 CrNi 23-14 | 309 |
| 20 X23 H18 | 1.4843 | X16 CrNi 25-20 | 310 |
| 20 Х25 Н20 С2 | 1.4841 | X56 CrNiSi 25-20 | 314 |
| 03 X18 AN11 | 1.4311 | X2 CrNiN 18-10 | 304LN |
| 03 X19 N13 M3 | 1.4438 | X2 18-5-4 | 317L |
| 03 X23 H6 | 1.4362 | X2 CrNiN 23-4 | — |
| 02 X18 M2 BT | 1.4521 | X2 CrMoTi 18-2 | 444 |
| 02 X28 N30 MDB | 1.4563 | X1 NiCrMoCu 31-27-4 | — |
| 03 X17 N13 AM3 | 1.4429 | X2 CrNiMoN 17-13-3 | 316LN |
| 03 X22 N5 AM2 | 1.4462 | X2 CrNiMoN 22-5-3 | — |
| 03 X24 N13 G2 S | 1.4332 | Х2 CrNi 24-12 | 309L |
| 08 X16 N13 M2 B | 1.4580 | X1 CrNiMoNb 17-12-2 | 316 CD |
| 08 X18 N12 B | 1.4550 | X6 CrNiNb 18-10 | 347 |
| 08 X18 N14 M2 B | 1.4583 | X10 CrNiMoNb 18-12 | 318 |
| 08X19AH9 | — | — | 304N |
| 08X19H13M3 | 1.4449 | X5 CrNiMo 17-13 | 317 |
| 08X20H11 | 1.4331 | X2 CrNi 21-10 | 308 |
| 08X20H20TYU | 1.4847 | X8 СrNiAlTi 20-20 | 334 |
| 08X25H4M2 | 1.4460 | X3 CrnImOn 27-5-2 | 329 |
| 08X23H13 | — | — | 309S |
| 09X17H7 Yu | 1.4568 | X7 CrNiAl 17-7 | 631 |
| 1X16H13M2 B | 1.4580 | Х6 CrNiMoNb 17-12-2 | 316Cd |
| 10X13 SJ | 1.4724 | Х10 CrAlSi 13 | 405 |
| 12X15 | 1.4001 | X7 Cr 14 | 429 |
| 12X17 | 1.4016 | X6 Cr17 | 430 |
| 12X17M | 1.4113 | X6 CrMo 17-1 | 434 |
| 12X17MB | 1.4522 | Х2 СrMoNb | 436 |
| 12X18H12 | 1.3955 | GX12 CrNi 18-11 | 305 |
| 12X17 G9 AN4 | 1.4373 | X12 CrMnNiN 18-9-5 | 202 |
| 15X9M | 1.7386 | X12 CrMo 9-1 | 504 |
| 15X12 | — | — | 403 |
| 15X13H2 | — | — | 414 |
| 15X17H7 | 1.4310 | X12 CrNi 17-7 | 301 |
Analogs
440B and D2 are more similar to 9Cr18MoV - they are similar in properties and composition.
440B stainless steel, known as “blade steel,” is a strong, high-carbon chromium steel. When heat treated, the steel reaches higher levels of hardness than other grades of stainless steel.
Analog – 440B steel strips.
Tool carbon steel D2 has similar technical characteristics to both 9Cr18MoV and D2. D2 is a relatively recent alloy. It was developed a little more than half a century ago in the USA using the electroslag remelting method, which improved the quality of the resulting alloy.
Other analogues:
- X90CrMoV18 (Germany);
- SUS440B (Japan).
decoding of steel, characteristics, properties, analogues
Modern technologies, which are used in all industries, place special demands on both materials and tools for their processing. In industries related to metal processing, high-strength steels are in demand for the manufacture of cutters, drills, cutters, and other processing tools. The material of these products must withstand heavy loads. Upon detailed study of the characteristics of P9 steel, we can conclude that it can be used for the manufacture of processing tools.
A little history
For a long time in the history of mankind, iron has firmly entered the life and everyday life of people. Then, as now, metal was processed by metal. Although it was just a blacksmith's sledgehammer. After the invention of metalworking machines, the possibility of cold processing of metal products became possible.
In the beginning, the processing speed was not significant. But in 1858, the Scot Mushet added manganese and tungsten to the crucible. Steel containing these elements made it possible to increase processing speed. This material was the prototype of modern high-speed steels, including P9.
Chemical composition
By its origin, P9 steel is alloyed. The basic principle of alloying metals is as follows. To maintain hardness when heated, it is necessary to introduce elements into the metal that impede the coagulation of carbides. Therefore, tool steels are alloyed with tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium carbides. Cobalt especially affects the cutting properties of steel.
The composition of the P9 grade quick cutter includes, in %:
- carbon - 0.85-0.95,
- silicon up to 0.5,
- manganese - up to 0.5
- sulfur - 0.03,
- phosphorus - no more than 0.03,
- chrome - 3.8-4.4
- molybdenum - up to 1,
- tungsten - 8.5-9.5,
- vanadium - 2.3-2.7,
- cobalt - up to 0.5,
- nickel - up to 0.4,
- iron - approximately 80.
These elements define the characteristics of the P9.
Basic properties
The technical characteristics of metals are based on their physical and mechanical properties.
Basic physical properties of grade P9 at a temperature of 20 ºС.
- Specific resistance R=380×109(Ohm/m).
- Density p=8300kg/m3.
- Thermal conductivity = 23 W (mS)
Mechanical properties include hardness, redness, and strength.
The hardness of P9 steel remains unchanged at temperatures up to 580 ºC. At this temperature, within 4 hours the hardness remains equal to 63 Rockwell. Carbon steels begin to lose hardness even at a temperature of 200 ºС.
During use, steel tools are subjected to various loads. Therefore, the greater the strength, the more reliable and durable the tool. P9 steel has a tensile strength:
- tensile strength 850 MPa
- at bending 3630 MPa
- at compression 2500 MPa
Marking
In stamp books valid in Russia, quick-cutters are designated in a special way. They start with the letter P from the English word rapid, that is, fast. The numbers that come after this letter indicate the tungsten content as a percentage.
Thus, the interpretation of the P9 steel marking means: high-speed steel with a tungsten content of the total mass, on average 9%.
Scope and analogues
Grade P9 is used mainly in the manufacture of tools for metal processing. Drills, various cutters, countersinks, turning tools. Among the analogues, we can mention P18 steel, which is very similar in characteristics. There are also foreign analogues.
Steel P9 - explanation, characteristics and scope of application
Modern technologies, which are used in all industries, place special demands on both materials and tools for their processing. In industries related to metal processing, high-strength steels are in demand for the manufacture of cutters, drills, cutters, and other processing tools. The material of these products must withstand heavy loads. Upon detailed study of the characteristics of P9 steel, we can conclude that it can be used for the manufacture of processing tools.