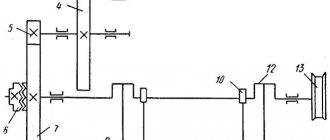
Longitudinal cutting of sheet metal is carried out on a high-precision machine, and is the most important branch of industrial processing, dealing with the dissolution of metal sheets and metal rolls into strips and tapes of the required width for the subsequent manufacture of all kinds of metal products.
For many years, longitudinal cutting of metal has remained an important direction in the development of metalworking, which keeps the price of goods in Moscow and Russia within affordable limits.
Longitudinal cutting of various metals is a key stage in the manufacture of any metal parts, and today there are no alternative methods for effectively cutting metal.
Longitudinal cutting of sheet metal is practiced in the process of preparing tapes, strips and strips, which are separated from measured sections or rolled metal. Moreover, this procedure is carried out using special processing machines or complexes, the functioning of which is completely controlled by automation.
Only such equipment can provide both the required quality of the resulting workpieces and the required productivity of the cutting procedure.
Services provided
Specialists have prepared for operation a production line for dissolving metal in rolls into tapes and strips. We accept orders for transverse and longitudinal cutting of sheets and rolls of metal in Moscow and the region. Well-developed cutting technology allows you to cut metal into strips and create high-quality products in which there is no residual stress (no twisting or crescent effect).
In addition to high-quality products at an affordable price, our customers receive the following advantages:
- The ability to personally specify the dimensions of the tape or strip to be cut. In accordance with GOST 503-81, a fixed size of standard cold-rolled strip is provided, however, our customers can order any required size.
- Possibility of ordering the dissolution of metal into strips or tapes from our raw materials. This is beneficial for small order quantities. In this case, you will not have problems where to buy blanks and how to transport them.
- Possibility of additional processing of metal. At our enterprise you can not only use the metal cutting service, but also process it or make perforations of blanks.
- With us you can place your order in a few minutes and receive fast delivery.
Our capabilities
Roll cutting and longitudinal-transverse cutting are among the priority types of services provided by GC Steel House LLC. The presence of modern, high-tech production lines allows us to:
- Cutting cold rolled and galvanized steel.
- Metals with delicate coating (polymer, paint).
- Hot rolled steel (slitting only).
Our company will cut rolled metal in the shortest possible time:
- Tape and strip. Manufactured on a slitting line from coiled steel 0.4-4 mm (thickness), 400-1600 mm (width), with internal Ø 508/610/760 mm and external Ø 2000 mm. The cutting speed, depending on the initial parameters of the rolled steel, is up to 120/m/min. The finished steel strip is available in widths starting from 35 mm.
- Sheeting and cutting into “cards” (cutting the strip into pieces of a certain length). Produced on a cross-cutting line from steel strip with a thickness of 0.45-3 mm. The internal/outer diameter and roll width parameters are similar to slitting. Sheet material is produced in lengths of 350-4000 mm. Cutting speed is up to 60 m/min.
Wafer production
We have an experienced staff of professionals and high-tech equipment necessary for processing metal products. With our help, metal plates and blanks are manufactured for a variety of applications:
- Manufacturing of parts and blanks from electrical steel (plates for transformers).
- Production of fasteners and embedded steel parts for construction purposes.
- Production of plates (structural type steel) for parts of various devices and assemblies.
- For further processing - obtaining milled, polished products, products with laser engraving.
Our specialists guarantee full compliance with the specified tolerances and almost one hundred percent yield of finished products from each ton of metal. We provide an individual approach to each customer.
Cross cutting lines
In practice, cutting sheets with metal scissors is inconvenient and ineffective, so special cutting lines are used. Using the line, you can chop the roll into pieces of any shape, from square to diamond.
Typical technical characteristics of the cross cutting line:
- permissible width of a steel roll is 0.16 m;
- maximum thickness of metal sheet - 0.4 cm;
- the minimum number of parts to be cut is from 18, then everything depends on the length of the sheet;
- the total power of the motors of all drives is 206 kW.
The line for cross-cutting steel coils includes the following elements: sheet shears with an inclined knife, a control mechanism, a device for correct unwinding, a unit for folding cut parts, and a roller feed.
The entire complex operates according to a pre-established algorithm, in which much depends on the specified parameters - the initial and required dimensions of the workpiece, the length of the roll or sheet. The system can be either fully automated or controlled by a specialist operator.
In the first option, the line should stop on its own when the unwinder runs out of material.
The video shows the essence of the technology:
More information about the straightening-unwinding device
This unit is designed to ensure that the sheet warps as little as possible before threading it into the scissors. At the same time, residues of production plaque and scale are removed from the sheet using special brushes. The unit is usually turned on only when it is necessary to dissolve hot-rolled metal into pieces.
Scissors
In essence, there is not much difference between automatic and manual scissors, except that the former are mechanically connected to the entire structure as a whole.
If a problem occurs in the drive, the shears turn off along with the other elements. The cutting process itself is controlled through an image on a visual display, and the error in fixing the roll can vary up to 0.4 millimeters up or down, this greatly depends on the characteristics of the source material.
Roll feed
The quality of cutting is very much related to the accuracy of the mechanism that feeds the metal. The roller feeding technology cannot be called extremely accurate, but it is universal and is considered the softest, preventing blows and jolts that could damage the material.
The roller feed functions as follows:
- The drive equipped with the straightening and unwinding device interacts with the one-way feed drive, so that the original workpiece begins to move at the moment when the scissor blades are in the highest position.
- As soon as the roll rests on the final plane, the scissor beam begins its work. The blades move to cut off a piece of steel to a specified size.
If the roll is relatively light, then the rollers themselves will be enough for tension; for heavy ones, you will need to turn on the electric motor.
Folding device
Its technical name is a stacking unit. The process of laying cut pieces is carried out using one of two methods: either the pieces fall freely under the influence of gravity, or they are forcibly moved in the desired direction.
Specifically, in cross-cutting of coiled steel, it is the second option that is usually used; this reduces the number of operations to maintain the line, and also simplifies the movement of material to the warehouse.
If the workpieces are of a regular shape, the simplest slides (guides) will do, while sections of complex shapes require a special configuration. To prevent the segment from getting stuck, it is necessary to ensure that the slide is inclined at least 26 degrees.
The device mechanism includes:
- control and monitoring system with the necessary sensors;
- unwinding drum;
- element for fixing the roll by diameter;
- unit for lubricating sheet or roll;
- electric drive;
- bed (base).
When you need to cut a sheet and not a whole roll, the unwinder can be turned off altogether. The principle of operation of the device is as follows: the material is placed on a support, while being centered using rollers.
The sheet or roll is installed strictly horizontally, after which the steel is fed into a device with crimping and straightening rollers. Each type of video can be configured independently of the other. You can evaluate the correctness of the settings using photocells and light indicators.
Longitudinal and transverse cutting of metal from
Our company offers services for longitudinal and transverse cutting of metal of any complexity. In addition, our organization has production facilities for the production of metal products. The range of services provided is carried out in Moscow and the Moscow region
.
The cost of our work on the production of metal structures is calculated per meter or ton. Prices for our services at wholesale prices are noticeably lower, in contrast to retail purchases. We invite individuals and various organizations to long-term cooperation with our company.
Our own production and warehouse facilities allow us to quickly and efficiently serve our customers. The modern technical base of equipment and equipment creates a large client platform in our company.
The production of various metal parts and custom-made structures is carried out by our specialists in a reasonable, short time. Our products are widely used in the construction of various facilities (residential, office buildings). All products we produce have a high level of quality. For cooperation, we recommend that all clients contact VIER Group CJSC.
Characteristics of the processed sheet metal
- Steel 0.3-8 mm thick.
- Maximum roll parameters. Width – 1600 mm, weight – no more than 26 tons, outer diameter – 1800 mm, inner diameter – 780 mm.
- Maximum strip width during slitting: 1000 mm.
- Accuracy of transverse and longitudinal cutting of rolled steel: 0.3 mm.
Longitudinal transverse cutting of metal from our company means high labor productivity, excellent quality of the resulting workpieces and a reasonable cost of services.
To order a metal longitudinal cutting service, call.
Metal cutting methods
Existing metal cutting methods can be divided into mechanical, thermal and high-precision. Mechanical cutting includes band sawing, longitudinal and cross cutting. Thermal ones include oxygen gas and plasma. For high-precision – laser.
Features of band saw metal cutting
Special machines are used for band saw cutting of metals. They can be cantilever, portal, horizontal or vertical. The workpiece is clamped in a vice and cut using a band saw fixed on two movable pulleys. Its tension and pressure on the metal can be changed depending on the brand and mechanical properties of the material being cut.
Modern machines are equipped with computers. They can work not only with rolled metal, but also with forgings up to 320 mm thick. Computer control makes them very accurate: the maximum deviation of the resulting workpiece or part from the specified dimensions does not exceed 0.05 mm. Another advantage of such machines is the ability to cut metal at an angle of up to 50°. At the same time, their operating speed reaches 100 mm/min.
Band saw cutting produces clean edges that do not require further processing. It does not harden the material being cut as a result of overheating, which is important for carbon steels and some grades of stainless steels. However, this method cannot be used for figure cutting, and the dimensions of the workpiece to be cut are limited by the dimensions of the machine.
Band saw cutting is convenient for serial production of blanks or parts of simple shapes
Features of metal slitting
Metal slitting is used to cut sheet steel into strips and strips. To do this, a sheet of metal is placed in a special trolley of a slitting machine and fed into the cutting unit using pressure rollers. It consists of two shafts: on the top there are cutting discs, on the bottom there are platforms with grooves for the passage of discs. A sheet of metal passes between them and is cut into strips of the required width.
The main advantage of this method of cutting metal is its high speed. The machine is capable of cutting up to 300 linear meters of sheet metal in a minute, but this parameter directly depends on the thickness and grade of the metal. Slitting is only suitable for thin sheet materials. As a rule, the maximum thickness of the metal being cut does not exceed 1.5 mm.
Slitting is only suitable for thin sheet metals
Features of metal cross cutting
In this case, cross-cutting machines are used. Rolled materials or strips obtained as a result of longitudinal cutting are used as blanks for cross cutting of metals. Metal cutting is carried out in a cutting block, the design of which is similar to a similar block in slitting machines. As a result, workpieces of specified sizes and shapes are obtained (triangular, square, rectangular, trapezoidal and others). This method is also only suitable for thin sheet materials.
Cross cutting, like longitudinal cutting, is only suitable for thin sheet metals
Features of gas-oxygen cutting of metals
When using gas-oxygen cutting of metal, the work is performed in two stages: first, the material is heated to approximately +1200...1300 °C, and then cut. Propane or acetylene is most often used for heating. Then pure oxygen is supplied under pressure to the cut site. The metal burns in it with the formation of molten oxides, which are blown away by a stream of gas.
This method is convenient because it can be used to perform figured cutting. It is suitable for rolled sheets up to 300 mm thick, but to cut such workpieces they must be preheated to +300...500 °C. There are a few more restrictions. So, if the melting point of a metal is below +1200...1300 °C, and the melting point of its oxides is higher than this indicator (such metals include, for example, aluminum or copper), then oxy-fuel cutting should not be used.
This method is convenient for cutting unalloyed or low-alloy steels. An increased content of alloying elements in the metal (tungsten, silicon, manganese, nickel or chromium) significantly complicates cutting. In this case, it is necessary to use fluxes that increase the fluidity of metal oxides and facilitate their blowing out of the cut zone.
Using oxy-fuel cutting you can work with thick sheets
Features of plasma cutting of metals
When using plasma cutting of metals, the material is cut with a jet of ionized gas heated to +15,000...30,000 °C. Using an electric field, the plasma is accelerated to 1,500 m/s. Such high temperatures and speeds allow you to work with almost any metals, including non-ferrous, alloyed and high-carbon ones.
If it is necessary to cut ferrous metals, then oxygen is used as the basis for creating plasma. Nitrogen, hydrogen or argon are used for cutting non-ferrous metals and alloys. The optimal thickness of rolled sheets made of carbon steel is up to 60 mm. In this case, the cutting speed is maximum. The largest thickness of rolled carbon steel that can be cut by plasma is 100 mm, stainless steel – 75 mm, aluminum and its alloys – 50 mm.
The main advantages of plasma cutting are high cutting speed, the ability to perform figure cutting, high precision (deviation from the specified contours of the part does not exceed 0.1 mm). When using it, the resulting parts have clean edges that do not require additional processing. The only limitation is the thickness of the metal. If it is higher than 100 mm, it is better to use oxy-fuel cutting.
Plasma cutting allows you to produce parts of any configuration
Features of laser cutting of metals
Laser cutting of metals is similar in speed to plasma cutting, but has a number of features. When using it, the material is cut using a laser beam. It quickly heats the metal in the affected area, melting and immediately evaporating it. As a result, the cut line is clean and smooth, but this is only possible for thin sheet metals (approximately up to 10 mm thick).
For thicker materials, a single laser beam is not enough. The cutting line must be blown with auxiliary gas to blow out particles of molten metal. Argon, nitrogen or oxygen are used as such gases. They speed up metal processing and at the same time cool the cut site to neutralize the temperature effect on the material.
Laser cutting differs from all other methods of cutting rolled metal in its high precision. When using it, the maximum deviation of the resulting parts from the specified contours does not exceed 0.05 mm. At the same time, it can only be used to work with thin rolled metal: the maximum thickness of brass workpieces is 5 mm, aluminum or stainless steel is 10 mm, and carbon steel is 16 mm.
Laser cutting is characterized by maximum precision