Essence of the process
If ordinary water is compressed under a pressure of about 4000 atmospheres and then passed through a hole with a diameter of less than 1 mm, it will flow at a speed 3-4 times higher than the speed of sound. When directed at the workpiece, such a jet of water becomes a cutting tool. With the addition of abrasive particles, its cutting ability increases hundreds of times, and it is capable of cutting almost any material.
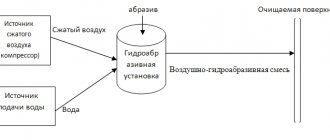
Waterjet cutting technology is based on the principle of the erosive (abrasive) effect of an abrasive and a water jet. Their high-speed solid-phase particles act as energy carriers and, hitting the particles of the product, tear off and remove the latter from the cut cavity. The rate of erosion depends on the kinetic energy of the impacting particles, their mass, hardness, shape and angle of impact, as well as on the mechanical properties of the material being processed.
Concrete is smashed with a wedge
Somewhat different from waterjet concrete cutting is a technology that uses a hydraulic wedge to break up concrete. Moreover, the differences between the two technologies are quite significant. About the difference between a butcher's ax and a surgeon's scalpel. And the hydraulic wedge for concrete acts precisely as an axe.
A set of hydraulic wedges, placed on a mass of cast concrete, slowly but inexorably does its job, without fuss, noise and dust
What's the point? If it is necessary to destroy large volumes of monolithic concrete with minimal vibration loads and minimize the possibility of scattering of secondary fragments from the dismantled structure, holes with a diameter of approximately 160-180 mm are drilled into the concrete mass using diamond bits.
The working cylinders of the hydrocline are inserted into the prepared holes, and pressure is applied, as a result of which the massif is split into cakes - individual elements that are either loaded into transport or cut on site using small-sized hand tools.
A fighter of the invisible front, hydrocline, in all its humble glory
How does it work
The technology is based on the weak tensile strength of the concrete mass. Concrete tolerates high static loads well, but sharp, local, dynamic, intensely applied loads in a particular area are often critical for it, and lead to deformation and destruction of the mass into fragments of various sizes.
Essentially, a hydraulic wedge is a hydraulic cylinder, the high-speed rod of which moves on a short arm a working mechanism in the form of a wedge of an established shape, made of high-strength alloy steel.
In general, such a system consists of:
- Hydraulic cylinder with working element.
- High pressure oil stations.
- Working lines made in the form of high-pressure hoses.
- Systems of communicators, made either in the form of quick releases or according to the classic fitting-nut system.
- Control and security systems.
An oil station, like a hydraulic power unit, generates the required amount of energy, which is transmitted through a hydraulic line to the working element and performs the necessary work
It should be noted that the described technology is characterized by high mobility, transportability and ease of maintenance. In general, if used correctly, hydrocline breakers are reliable and durable.
Important! Another difference from waterjet cutting technology and the use of hydrocline is the fact that the energy carrier is not water mixed with solid particles - abrasive, but special hydraulic oil. Moreover, it is not exclusively a carrier; the working element is a steel wedge, to which the oil only transfers the received energy.
A hydrocline, a thing for breaking concrete, is very convenient, and in some cases where mobility, weight and dimensions are important, it is sometimes irreplaceable. However, what to do when a reinforced concrete mass is stuffed with reinforcement, like a watermelon with seeds. In this case, hydraulic shears will come to the rescue.
Cutting technology
Water, pumped by a pump to ultra-high pressure of the order of 1000–6000 atmospheres, is supplied to the cutting head. Erupting through a narrow nozzle (nozzle) usually with a diameter of 0.08-0.5 mm at near-sonic or supersonic speeds (up to 900-1200 m/s and above), a stream of water enters the mixing chamber, where it begins to mix with abrasive particles - garnet sand , grains of electrocorundum, silicon carbide or other highly hard material. A mixed jet emerges from a mixing (mixing) tube with an internal diameter of 0.5–1.5 mm and cuts the material. In some cutting head models, the abrasive is fed into a mixing tube. To dampen the residual energy of the jet, a layer of water usually 70–100 centimeters thick is used.
Drawing. Waterjet cutting diagram
Drawing. Abrasive particle mixing scheme
When water cutting (without abrasive), the scheme is simplified: water under pressure escapes through the nozzle and is directed towards the product being cut.
Table. Typical applications of water cutting technologies
| Water cutting | Waterjet cutting |
| Leather, textiles, felt (shoe, leather, textile industry) | Sheets of steel, metals |
| Plastics, rubber products (automotive industry) | Various metal parts (castings, gears, etc.) |
| Electronic boards | Alloys of aluminum, titanium, etc., composite materials, thick-walled plastics (aviation and space industries) |
| Laminated materials (aviation and space industry) | Concrete, reinforced concrete, gypsum blocks, hard paving stones and other building materials |
| Thermal insulation, sealing and noise reduction materials | Stone, granite, marble, etc. |
| Food – frozen foods, dense foods, chocolate, baked goods, etc. | Glass, armored glass, ceramics |
| Paper, cardboard | Combined materials, coated materials |
| Tree | Tree |
| Thermo- and duroplast | Reinforced plastics |
In waterjet cutting, the destructive power of the jet is created to a much greater extent by the abrasive, and water primarily performs a transport function. The size of abrasive particles is selected equal to 10–30% of the diameter of the cutting jet to ensure its effective impact and stable flow. Typically the grain size is 0.15–0.25 mm (150–250 µm), and in some cases it is on the order of 0.075–0.1 mm (75–100 µm) if a low roughness cutting surface is required. It is believed that the optimal abrasive size should be less than the value (dс.т. – dв.с.)/2, where dс.т. – internal diameter of the mixing tube, dv.s. – internal diameter of the water nozzle.
Various materials with a Mohs hardness of 6.5 or more are used as abrasives. Their choice depends on the type and hardness of the workpiece, and it should also be taken into account that a harder abrasive wears out the cutting head components faster.
Table. Typical cutting applications for some abrasives
| Name | Typical Applications |
| Garnet sand (consists of corundum Al2O3, quartz sand SiO2, iron oxide Fe2O3 and other components) | Widely used for cutting various materials, especially high-alloy steels and titanium alloys |
| Electrocorundum grains (consists mainly of Al2O3 corundum, as well as impurities) or its varieties | Man-made materials with very high Mohs hardness. Used for cutting steel, aluminum, titanium, reinforced concrete, granite and other materials |
| Silicon carbide (SiC) grains – green or black | |
| Quartz sand (SiO2) | Glass cutting |
| Silicate slag particles | Cutting plastic reinforced with glass or carbon fibers |
Nozzles are usually made of sapphire, ruby or diamond. The service life of sapphire and ruby nozzles is up to 100–200 hours, diamond nozzles – up to 1000–2000 hours. When water cutting, ruby nozzles are not used, and sapphire nozzles usually last 2 times longer.
Mixing tubes are made of ultra-strong alloys. Service life is usually up to 150–200 hours.
Technological parameters
The main technological parameters of the waterjet cutting process are:
- cutting speed;
- type, properties and thickness of the cut product;
- internal diameters of the water nozzle and mixing tube;
- type, size, flow rate and concentration of abrasive particles in the cutting mixture;
- pressure.
Cutting speed (the speed at which the cutting head moves along the surface of the workpiece) significantly affects the quality of the cut. At high speeds, the water-abrasive jet deviates (drifts) from straightness, and the jet weakens noticeably as the material is cut. As a result, the taper of the cut and its roughness increase.
Read also: Battery for emergency lighting
Drawing. Typical cut shape depending on cutting conditions
Drawing. Jet drift when cutting at a speed higher than optimal
Separation cutting can be performed at 80-100% of maximum speed. High-quality cutting usually corresponds to a speed range of 33–65%, fine cutting – 25–33%, and precision cutting – 10–12.5% of the maximum speed.
Photo. Type of cut surface depending on the speed of water-abrasive cutting
Some cutting head models feature automatic taper compensation technology, such as Flow's Dynamic Waterjet. Taper compensation is achieved as a result of a software-controlled dynamic tilt of the cutting head by a certain degree. This allows you to increase cutting speed while maintaining cut quality and, accordingly, reduce production costs.
As the internal diameter of the mixing tube decreases (other things being equal), cutting productivity and accuracy increase, and the cutting width decreases (it is approximately 10% larger than the internal diameter of the tube). This also reduces the service life of the tube. During operation of the mixing tube, its internal diameter increases by approximately 0.01–0.02 mm for every eight hours of operation.
Table. Approximate abrasive sizes for various cutting modes
| Application | Particle size of garnet sand (Garnet) | Int. water nozzle diameter | Int. mixing tube diameter | |||
| mesh (USA) | micron | inches | mm | inches | mm | |
| Standard industrial configuration | 80 | 178 (300–150) | 0,013–0,014″ | 0,330–0,356 | 0,04″ | 1,02 |
| High speed cutting | 60 | 249 (400–200) | 0,014–0,018″ | 0,356–0,457 | 0,05″ | 1,27 |
| 50 | 297 (600–200) | |||||
| Precise cutting | 120 | 125 (200–100) | 0,012–0,013″ | 0,305–0,330 | 0,036″ | 0,91 |
| 80 | 178 (300–150) | |||||
| High precision cutting | 120 | 125 (200–100) | 0,010–0,011″ | 0,254–0,279 | 0,03″ | 0,76 |
The abrasive consumption depends on the diameters of the mixing tube and water nozzle, cutting conditions, etc. The approximate optimal values are given in the table below.
Table. Optimal consumption of abrasive material at certain ratios of the diameters of the mixing tube and nozzle
| Inner diameter of water nozzle (mm) | Mixing tube inner diameter (mm) | Abrasive consumption (g/min) |
| 0,25 | 0,76 | 270–360 |
| 0,36 | 1,02 | 500–640 |
| 0,46 | 1,27 | 800–1100 |
The maximum operating pressure is usually 3000–3200, 3800, 4150 or 6000 bar. The higher the pressure, the higher the cutting speed and efficiency. At the same time, more frequent replacement of gaskets in the pump is required.
Table. Dependence of straight separation (roughing) cutting speed on material thickness at pump pressure P = 4100 bar (approximately 4046 atm)
| Type of material | Cutting speed (m/h) * at thickness | ||||
| 5 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 50 mm | 100 mm | |
| Stainless steel | 52,62 | 28,56 | 13,02 | 3,84 | 1,44 |
| Titanium | 68,46 | 37,20 | 16,98 | 4,98 | 1,86 |
| Aluminum | 142,20 | 77,40 | 35,40 | 10,20 | 3,72 |
| Granite | 251,40 | 137,10 | 62,76 | 18,00 | 6,60 |
| Marble | 295,20 | 160,80 | 73,50 | 21,24 | 7,80 |
| Carbon fiber | 247,20 | 134,70 | 61,74 | 17,70 | 6,60 |
| Glass | 272,76 | 148,62 | 67,92 | 19,62 | 7,26 |
| * : pressure – 4100 bar; abrasive brand – Kerfjet #80; abrasive consumption – 250–450 g/min; internal diameter of the nozzle – 0.25 mm, 0.35 mm; internal diameter of the mixing tube - 0.76 mm, 1.01 mm / data from TechnoAllianceGroup LLC, Moscow, BarsJet GAR installations | |||||
Table. Dependence of the speed of straight dividing (roughing) cutting on the thickness of the material at pump pressure P = 6000 bar (about 5922 atm)
| Type of material | Cutting speed (m/h) * at thickness | ||||
| 5 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 50 mm | 100 mm | |
| Stainless steel | 86,64 | 47,16 | 21,48 | 6,12 | 2,40 |
| Titanium | 112,38 | 61,50 | 28,08 | 8,22 | 3,06 |
| Aluminum | 233,76 | 127,44 | 58,44 | 16,92 | 6,24 |
| Granite | 413,46 | 225,42 | 103,08 | 29,70 | 10,92 |
| Marble | 485,28 | 264,60 | 121,02 | 34,80 | 12,84 |
| Carbon fiber | 406,56 | 221,88 | 101,40 | 29,22 | 10,86 |
| Glass | 448,14 | 244,38 | 111,72 | 32,16 | 11,88 |
| * : pressure – 6000 bar; abrasive brand – Kerfjet #80; abrasive consumption – 250–450 g/min; internal diameter of the nozzle – 0.25 mm; internal diameter of the mixing tube - 0.76 mm, 1.01 mm / data from TechnoAllianceGroup LLC, Moscow, BarsJet GAR installations | |||||
Photo. Parts obtained by waterjet cutting: made of stainless steel 15 mm thick; made of aluminum alloy 6 mm thick; made of aluminum 30 mm thick; made of fibre-reinforced plastic, 20 mm thick; made of tool steel 60 mm thick
How to coordinate openings in load-bearing walls
The arrangement or expansion of openings in a concrete wall must be carried out in accordance with all standards and have permission from the relevant authority. When making a decision to carry out redevelopment, you need to take into account a number of indicators:
- The number of the floor on which the redevelopment work will be carried out (the load on the walls will be less, the higher the floor on which the apartment is located).
- What year was the house built?
- What is the width of the opening and where is it located (at the junction of the slabs, at what distance to the external walls).
- What condition are the walls in the room?
The redevelopment of an apartment can be entrusted to employees of organizations that have permission to carry out such construction work. Nowadays, very often owners remodel buildings and apartments, widen old openings in the walls, and install new ones.
- Diamond cutting is considered the leader in building dismantling work. The cutting elements are capable of cutting through a concrete wall whose thickness exceeds 60 cm.
- Cutting using the waterjet method is more environmentally friendly and safe.
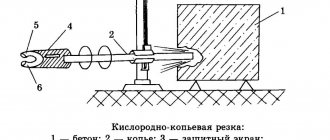
- A good effect is obtained when using oxygen-lance drilling, however, certain training and experience are required to perform the work. You can get burned if you do not follow safety precautions when working.
Considering the thickness of the concrete walls in which you need to make or enlarge the opening, and also depending on the result you want to get, you can choose the cutting method that is more suitable for you.
The main thing, when carrying out work, do not forget that the changes that will occur in the load-bearing walls must be carefully calculated and approved by the appropriate authority, and the openings must be strengthened.
Advantages, disadvantages and comparative characteristics
Using a water-abrasive or water jet, you can cut almost any material. In this case, neither mechanical deformation of the workpiece occurs (since the force of the jet is only 1–100 N), nor its thermal deformation, since the temperature in the cutting zone is about 60–90°C. Thus, compared to heat treatment technologies (oxygen, plasma, laser, etc.), waterjet cutting has the following distinctive advantages:
- higher quality of cut due to minimal thermal effect on the workpiece (no melting, melting or burning of edges);
- the ability to cut heat-sensitive materials (a number of fire and explosive materials, laminated, composite, etc.);
- environmentally friendly process, complete absence of harmful gas emissions;
- explosion and fire safety of the process.
The water-abrasive jet is capable of cutting materials up to 300 mm thick and more. Waterjet cutting can be performed along a complex contour with high accuracy (up to 0.025–0.1 mm), including for processing volumetric products. You can use it to make bevels. It is effective on aluminum alloys, copper and brass, due to their high thermal conductivity, thermal cutting methods require more powerful heating sources. Additionally, these metals are more difficult to cut with lasers due to their low ability to absorb laser light.
Read also: How to melt steel at home
The disadvantages of water-abrasive cutting include:
- significantly lower cutting speed of thin steel compared to plasma and laser cutting;
- high cost of equipment and high operating costs (typical for laser cutting) due to the consumption of abrasive, electricity, water, replacement of mixing tubes, water nozzles and seals that can withstand high pressure, as well as waste disposal costs;
- increased noise due to the flow of a jet at supersonic speed (typical for plasma cutting).
Table. Comparison of waterjet cutting with oxygen, plasma and laser cutting
Water cutting is a unique method for processing various materials. Today, there are 2 types of water cutting: using clean water and using a water jet with abrasive (water jet method). But the principle of operation in both cases is the same - liquid under very high pressure passes through a miniature hole in the cutting head, which is located above the material being processed. In this case, the waterjet mixture coming out of the cutting head has a speed exceeding the speed of sound three times.
The size of the head hole, as well as its diameter, depend on the density of the material. If the material is easily permeable, then heads with a diameter of 0.08 mm are taken; in the case of harder materials, the hole diameter can reach 0.8 mm.
As for the pressure of the multiplier itself, the maximum indicator is 420 MPa. According to practical research, the most productive and at the same time fastest cut is obtained at a pressure of 380 MPa. If the pressure is higher, then this only leads to more frequent intervals between replacement parts.
To ensure proper operation of the equipment, gaskets should be replaced promptly. Thus, with a regular constant operating pressure of 400 MPa, the gaskets are replaced after 400 – 1200 cutting hours.
Thanks to such conditions in which workpieces are processed, waterjet cutting becomes an alternative method of influencing materials in relation to thermal methods, and even outperforms the latter in some respects. Only cutting using a water jet with an abrasive leaves no traces of deformation on the metal, no traces of melting on plastic, fabric and other materials. Industrial and design work today is simply unthinkable without this method, because the most complex elements with excellent edge quality can be made from any blanks of varying thickness.
The use of rock destruction technology for extracting minerals under the influence of a water jet has been known since the 30s of the last century, but the industrial use of a high-pressure water jet for cutting various materials began only in the 80s of the same century. Today, waterjet cutting of metal is the most popular type of application of this technology in industrial production.
Tools for cutting concrete openings
Drilling is used to make technological holes, sockets, and furrows. If it is necessary to make openings in concrete walls or expand existing openings, diamond cutting elements, which are fixed in various tools, are often used.
If the thickness of the concrete slab is small, an angle grinder, popularly called a “grinder”, with wheels with a diameter of 105 to 125 mm is used for cutting.
Cutting concrete using a grinder.
Spraying water while working will reduce dust and at the same time help preserve the disc. If a situation arises in which contact with water is dangerous, you need to perform dry cutting.
However, even with dry cutting, in order to cool the segments, it is necessary to remove the disk from the cutting area at certain intervals so that the machine runs “idle” for 10-50 seconds.
To cut an opening in a concrete slab, the depth of which exceeds 10 cm, professional circular saws are used, which are hydraulic and electric cutters. This tool quickly cuts through concrete up to 15 cm deep on one side.
They work with disks with a diameter of 350-500 mm. When cutting openings in concrete, it is necessary to wear a respirator, since if concrete dust enters a person’s lungs, serious illnesses can develop. In addition, hands should be protected with gloves, and eyes with special glasses.
What is waterjet cutting
Waterjet cutting is a process of abrasive action of a jet of hydraulic fluid with the addition of particularly hard particles on the material being processed to cut it to specified dimensions. From a mechanical point of view, this is the process of separation and entrainment of material by abrasive particles, which are fed at high speed in a stream of water under high pressure. Based on its physical properties, a thin stream of a mixture of water and abrasive at high speed is an ideal cutting tool.
The technology of using water flow and abrasive for cutting almost any materials is ensured by selecting the necessary conditions and parameters, such as:
- jet pressure,
- water consumption,
- the amount of abrasive in the jet,
- sizes of abrasive particles.
The technological capabilities of waterjet cutting are limited only by the thickness of the workpiece being processed and the physical properties of the substance from which it is made. What she can do is clearly shown in this video.
Kinds
Cutting in a single coordinate system.
It is a longitudinal cutting using a continuous flow of water. The cutting speed in this case is the highest, the process is characterized by reliability and minimal release of residual moisture.
On GAR machines, small diameter nozzles are used to work in a single coordinate system. The technology is used mainly in the food industry (for cutting frozen foods) and in paper production.
Cutting in a two-coordinate system.
Two-axis cutting is the most popular type of method. In this case, the cutting head moves along the X and Y axes in accordance with the specified pattern. Sometimes the movement along the Z axis is additionally controlled, which is necessary for working with thick metals. The advantage of the technology is that it is suitable for all types of materials.
Cutting in a three-coordinate system.
When cutting along three coordinates, two types of machines can be used. The first of them is a cutting machine with a work table, where a three-coordinate system is used and rotation axes are present. The second type is a robotic device, where the cutting head for supplying a jet of water is located on a movable automated “arm”.
This technique is suitable for creating instrument and door panels, curved parts and other complex elements.
Application area
Waterjet cutting is capable of working with all materials and structures that exist, with the exception of diamonds and tempered glass. One of the features of waterjet technology is the possibility of its use for processing materials capable of changing their physical and chemical properties when exposed to high temperatures and strong heating, as well as for structures with flammable and explosive substances.
The area of industrial use of these features was abrasive cutting of various metals with water under pressure, mainly such as:
- stainless steel,
- tool alloys,
- titanium,
- brass,
- aluminum.
It is also used to make artistic products from natural and artificial stone and use it in processing:
Water cutting is indispensable for:
- insulating,
- fireproof,
- multilayer,
- and other composite materials with special properties.
Operating principle and materials to be cut
Cutting metal products occurs with a water jet to which abrasive is added, after which it passes through a nozzle. Pressure of 200-600 atmospheres allows you to cut many materials. Work can be carried out at any angle; to do this, you just need to change the angle of the nozzle. In this case, you can effectively cut:
- metals (ferrous and non-ferrous) and their alloys;
- stone products from marble and granite;
- steel (stainless steel, heat-resistant, alloy);
- armored, ordinary and composite glass;
- ceramic products (concrete, tiles, ceramics, ceramic granite);
- composite;
- rubber;
- plastic;
- cardboard.
Cutting of particularly hard raw materials is carried out with water and special sand made from minerals. Soft materials (rubber, plastic, cardboard) are cut exclusively with water without any impurities.
Advantages and disadvantages
Today, there are four main industrial methods for cutting metals. If we arrange them according to the amount of equipment used and demand in production, we get the following sequence of methods, namely:
- mechanical,
- plasma,
- waterjet,
- laser
All of them differ significantly from each other in quality characteristics, while each has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
The main advantages of the waterjet processing method are:
- ability to work with any materials,
- no thermal effect on the workpiece,
- eliminating the release of dust, smoke and toxic fumes,
- Possibility to use for materials with explosive and fire hazardous properties.
But despite the undeniable advantages, there are significant disadvantages:
- high cost of replacing wear parts of equipment;
- more significant energy consumption compared to other cutting methods,
- requires constant adjustment and adjustment of equipment to meet the declared characteristics.
Read also: Calculation of electricity during welding
Features of operating CNC machines
Waterjet equipment with computer program control is one of the opportunities to expand the scope of use of machines, increase work efficiency and at the same time increase productivity.
More details can be gleaned from the information provided below and the video story.
CNC machines are used to produce blanks from steel, aluminum, copper and other types of metals.
The strict cutting accuracy provided by CNC water-abrasive equipment has virtually no deviations from the assigned tasks.
Video:
Program-controlled waterjet units provide the following advantages:
- CNC-equipped machines operate in accordance with a given program. In this case, each workpiece is processed using individual software. With its help, the jet pressure, the composition of the working cutting suspension and other parameters are automatically selected;
- If on non-CNC machines the selection of the cutting jet can be chosen incorrectly, then in this situation this point is excluded. The equipment independently controls the quality of the cut, then automatically adjusts the mode used;
- Metal processing with the help of software also provides the ability to make holes of the desired diameter;
- As you can judge from the video material, upon completion of the waterjet process, a completely finished part emerges from the workpiece, which does not need to be subjected to grinding or additional processing at the cut points.
Industrial Application
The most widely used technology in industrial production and precision engineering is waterjet technology for cutting metal with water. Only it neutralizes the main characteristic consequences that arise when processed by other methods. So, for example:
- waterjet cutting of stainless steel makes it possible to take into account the features that arise when processing workpieces made of metal alloys, such as strength due to alloying additives and high viscosity under mechanical or temperature influences, leading to deformation of finished products;
- waterjet cutting of titanium makes it possible not to reach the critical temperature of 600 ° C, at which titanium is capable of burning in the open air and chemically combining with other substances;
- Waterjet cutting of aluminum reduces the loss of forging material to a minimum, despite the fact that the metal is relatively weak and has a low melting point of only 440 °C.
This treatment makes it possible to use a water cutter for metal with proper efficiency, providing the future product with good quality indicators:
- small seam width - only 0.7-1.4 mm,
- positioning accuracy up to 0.1 mm,
- with a workpiece thickness of even 300 mm,
- obtain a flawless cut edge that does not require additional processing.
The ability to start and carry out cutting in any direction allows you to minimize the overall loss of material when cutting metal blanks.
Story
WAZER began as a Kickstarter project with the help of several Penn State alumni.
It didn’t take long for recognition: the device is considered one of the most promising and was awarded, for example, the Make Magazine 2019 Editor’s Choice award.
Construction of waterjet cutting equipment
The range of production of waterjet cutting machines starts from small ones, representing conventional CNC metalworking machines and compact ones with a table design for processing sheet material with dimensions of 2 by 4 meters, to huge lines capable of working like rolling mills.
But according to the design principle, any machine for cutting metal with water has:
- body in the form of a water bath, which serves as a trap for the water jet, absorbing its energy,
- a system of settling tanks and filters necessary for water purification, as well as for sedimentation of spent abrasive particles,
- coordinate table with servomotors for moving the cutting head,
- high pressure pump unit with pipelines,
- operator control panel based on an industrial computer.
Modern CNC machines and drives for moving the cutting head allow processing of material using 2D, 2.5D and 3D technology, that is, with high precision, artistic cutting in several planes and processing the edge at any angle. The possibilities of making 3D parts using waterjet cutting are clearly shown in the video.
How to strengthen a concrete opening
After you have cut out the opening or expanded it, you need to reinforce the walls with additional metal structures.
Strengthening openings can be as follows:
- Single row. To construct this type of fortification, a channel is used. You need to make a U-shaped frame around the opening. In this design, various types of channels are used, and fastening to the walls can be done in various ways. Places where the channel does not adhere to the wall must be filled with mortar.
- Ugolkov. Edging is done with corners on both sides of the wall. To fasten the corners to each other, pins and metal plates are used. These are the most common designs.
- Combined. The openings are strengthened using channels and corners.
Cutting tool
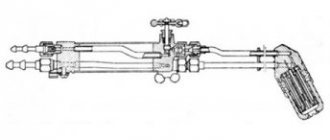
The main part of all waterjet machines is the cutting head. The principle of its operation is seemingly very simple, but technologically very complex. Thus, ultra-high water pressure is created by a plunger or piston pump, which delivers it through high-pressure pipelines to the cutting head. Here the water enters the chamber, where strictly dosed mixing with abrasive particles occurs. Next, the mixture of water and abrasive enters a calibrated nozzle (nozzle), which creates a cutting jet. The jet emerging from the nozzle reaches a speed approximately three times higher than the speed of sound.
The dimensions of the diameter of the nozzle and mixing chamber are determined based on the performance of the working pumping station and the material of the abrasive particles. Basically, garnet sand, also called almandine, is used for abrasive. It has a crystalline structure with extreme hardness and a heavy density of 4.1 - 4.3 g/cm, which allows it to provide high abrasive ability. It is well distributed in nature; its largest deposits are located in the southeast of India and Australia.
Device classification
Waterjet machines are often divided into manual machines and computer numerical control (CNC) machines.
The design of abrasive metal cutting machines significantly affects their technical characteristics and production capacity.
Manual devices
Non-CNC machines are fully controlled by the operator, who sets all the parameters for future processing of parts. In addition, the operator will have to carry out certain stages of working with workpieces independently. But such devices also have a number of advantages:
- Relatively low price.
- Same quality of waterjet cutting of titanium, aluminum and other materials.
- Easy to care for and manage, which does not require the operator to have extensive knowledge and experience in the field of metalworking.
- A sufficient number of functions that allow you to create simple parts with correct geometric shapes.
CNC machines
Numerical software installed on waterjet machines significantly improves their functionality and production efficiency. CNC machines allow you to process all types of metal workpieces with high quality and do it with high precision. Automated devices have the following advantages:
- The software allows you to create holes of the required diameter in workpieces.
- After completing all established operations, the part does not require additional processing.
- The software allows you to select an individual processing mode for each workpiece. The device itself will select the necessary jet parameters and other parameters.
- CNC machines can control the quality of the cut and independently change it in accordance with the established program and sequence of machine actions.
At the same time, such a device also has a number of significant disadvantages. Firstly, the cost of a CNC waterjet machine is significantly higher than the price of its manual counterpart. Secondly, in order to correctly set the parameters of the work being performed, the operator must have certain knowledge in the field of metalworking and experience in creating parts on automated machines.
Consumables
The main consumable parts of waterjet cutting equipment are nozzles and focusing tubes, which are made from artificial diamonds, sapphires, rubies and corundum crystals.
Thus, the operating time of a focusing tube made of sapphire crystal does not exceed 60 hours. The same tube, made of the highest quality diamonds, lasts much longer, but at the same time costs 20 times more. Artificial ceramic carbide nozzles will last up to 120 hours, which is approximately 20% longer than the same parts made from other materials.
The average operating time of consumables and components is shown in the table:
These figures correspond to the operation of a waterjet machine with an average pressure of 400 MPa. When applying a cutting jet pressure of 600 MPa, the processing speed increases by 20-30%, and wear of the main consumables occurs twice as fast.
How wall thickness affects concrete cutting
The size of the wall thickness is the main indicator by which it is determined which cutting method to use.
- The grinder can cope with a slot depth not exceeding 10 cm.
- With a concrete slab thickness of 8-10 cm, a machine with increased power is required for operation.
- When the thickness of the concrete slab is 15-16 cm, a circular saw is used, the diameter of the discs should be 350-400 mm. If you use a grinder, the work will have to be carried out in several stages, and the tool may overheat and break.
- If the concrete is 30 cm thick or more, use a special wall cutting tool - manual or machine.
- Concrete, the thickness of which reaches 60 mm, is cut using a tool such as a chain saw, a ring cutter.
- A concrete slab whose thickness exceeds 60 cm is cut with special equipment. A disc with a diameter of 100 mm or more is used. Rope cutting devices can also be used.
With your own hands
The use of waterjet cutting equipment in a home workshop is quite possible. For example: in the implementation of original works for artistic or decorative processing of small and medium-sized workpieces. But you can make such a machine with your own hands only for cutting wood, plastic, laminate or other not very durable materials.
It should be taken into account that the cost of equipment, plus the periodic replacement of consumables and the constant need for abrasive, makes the direct cost of one working hour of waterjet cutting at least 1,400 rubles. But this is a separate topic, and if you have your own experience in using a waterjet cutter at home, share it with others in the comments block.
Features of operating CNC machines
Waterjet equipment with computer program control is one of the opportunities to expand the scope of use of machines, increase work efficiency and at the same time increase productivity.
More details can be gleaned from the information provided below and the video story.
CNC machines are used to produce blanks from steel, aluminum, copper and other types of metals.
The strict cutting accuracy provided by CNC water-abrasive equipment has virtually no deviations from the assigned tasks.
Video:
Program-controlled waterjet units provide the following advantages:
- CNC-equipped machines operate in accordance with a given program. In this case, each workpiece is processed using individual software. With its help, the jet pressure, the composition of the working cutting suspension and other parameters are automatically selected;
- If on non-CNC machines the selection of the cutting jet can be chosen incorrectly, then in this situation this point is excluded. The equipment independently controls the quality of the cut, then automatically adjusts the mode used;
- Metal processing with the help of software also provides the ability to make holes of the desired diameter;
- As you can judge from the video material, upon completion of the waterjet process, a completely finished part emerges from the workpiece, which does not need to be subjected to grinding or additional processing at the cut points.