Metal chopping is a metalworking technology that involves removing layers of metal from a workpiece or cutting it into pieces: this operation makes it possible to significantly shorten the production cycle and save money. Other advantages of the technology include:
- no need for additional surface treatment of finished parts - you immediately get a perfectly even cut of the workpieces without burrs, and you can immediately use them for their intended purpose and save time on additional processing;
- the ability to cut material with millimeter precision;
- reducing the amount of waste (metal shavings and sawdust) during the production process;
- high production speed - working on electromechanical guillotines makes it possible to increase productivity;
- the ability to maintain weight; the operational properties of the metal - due to the fact that it does not heat up during processing;
- low cost - the use of this type of processing can significantly reduce the cost of finished metal products by reducing the number of operations required to obtain the finished result: this makes the procedure accessible to most customers;
- high efficiency for the production of rectangular workpieces compared to the closest alternative to cutting (gas cutting) - the cutting speed of the material can reach 10-12 cuts per minute.
Metal cutting methods
Metal cutting technology is divided into the following types:
- according to the nature of the tasks being solved (cutting out parts according to a given shape, separating a piece of metal of the required size, cutting out grooves);
- method of operation (manual or mechanized);
- fixation method;
- direction of felling action (vertical or horizontal).
All types of metal cutting can be carried out both manually and mechanically. This is determined by the required quality of the resulting product, quantity (productivity), technical capabilities (availability of manual or mechanical tools).
When manual cutting, the following methods are used: vertical or horizontal. The choice of method depends on the possibility of fixing the metal.
It can be clamped in a vice (if size and weight allow). If this is not possible, the workpiece is placed on an anvil or metal plate. It is advisable to perform a horizontal operation using a bench vice.
When manually chopping, there are three ways to strike with a hammer. These are hand, elbow and shoulder blows. The speed of the operation and the quality of the resulting edge of the part depend on the force of the impact. The force of the blow is influenced by the mass of the striking part of the hammer and the length of the handle.
In equipped workshops and metalworking enterprises, various types of mechanized methods for chopping and cutting metal workpieces are used. These methods include:
- cutting using a press or hammer;
- chopping and cutting using a guillotine;
- use of special machines.
Mechanized types are based on mechanical, hydraulic or electrical principles of operating a cutting tool.
Metalworking in Vladivostok
High-quality equipment, professional staff, combined with competent organization of the production process give us the opportunity to set optimal prices for basic operations .
only certified rolled metal products in production : structural, alloy and carbon steel and non-ferrous metal alloys. In our warehouse we have in stock all the main types of metal from the best Russian manufacturers at wholesale prices. By prior agreement, customer's material can be processed.
Metal cutting is a technological operation for dividing sheet or section metal into parts and blanks or manufacturing parts with specified shapes and sizes . Our company offers several methods of cutting metal, differing in technology and equipment used. Cutting with a mechanical saw and on a band saw machine are mechanical methods, plasma and gas (oxygen) types are thermal. In each specific case, the cutting method is selected individually , depending on the grade of the alloy and the characteristics of the project.
Cutting on a band saw machine Band saw cutting is most often used for cutting technological workpieces and their further use in turning, milling and forging work.
The advantages of this method include:
- high accuracy
- edge quality
- low prices (compared to gas and plasma cutting)
Equipment and tools used
This list depends on the method of work. Manual cutting is carried out using:
- cutting tools (chisels, crosspieces, etc.);
- a plumber's hammer (chosen by weight and handle length);
- vice;
- metal substrate;
- marking tool.
A metalworking chisel structurally consists of three main parts: impact, middle (holder) and cutting (working). The shape of the cutting part is different for each and depends on the task being solved. A chisel is used to perform a standard chopping operation. Kreuzmeisel has a narrower cutting edge. The groover is designed for cutting grooves, so its cutting part is made in the shape of a semicircle. The beard is made from a round metal rod, and has a working part in the shape of a circle sharpened around the perimeter. It is used to cut holes in sheet metal. All percussion instruments are made from durable tool steel.
The main parameters of these tools are geometric dimensions and sharpening angles of the cutting part. A plumber's hammer is used to strike the upper (impact) part of the chisel. They differ in the shape of the striker (round or square), the method of attaching the handle, and the total weight.
Cutting out small parts, holes, and individual parts is done using fastening equipment or on steel substrates. To ensure secure fastening, this operation is performed in a vice.
Various metalwork rulers, squares, marking calipers, and small markers are used as marking tools. To make marks, the following are used: cores (of various modifications), scribers with different tip shapes, and pencils. The tools used are manufactured according to developed standards
In industrial enterprises, the tools for cutting metal are special machines. These include:
- guillotines;
- presses (hydraulic and mechanical);
- press shears;
- angle cutting machines.
They have high productivity and allow you to cut even very thick metal.
The hydraulic guillotine is controlled by an electronic unit. With its help, the parameters of the future operation are set. Set the type of metal, the cutting angle, the amount of pressure on the knife, and the cutting speed. In addition to the guillotine, so-called combined units are used to solve these problems. These include cutting machines (press shears) and highly specialized ones (angle notching machines, presses and dies). Press shears are used for cutting sheets and strips of metal, shaped and long products. They work well with profile metal, for example, channel, I-roll, square. With their help, smooth holes and grooves of various shapes are obtained.
Angle notching machines allow angular cutting of metal products of almost any thickness. High precision cutting is achieved thanks to the presence of a scale that allows you to accurately lower the tool to the required place and a correctly sharpened set of chisels.
Presses and stamps solve similar problems. They use mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and electric drives.
Plumbing and repair work
There are plumbing and repair work, which consists of replacing or correcting damaged and worn parts, manufacturing missing parts, assembling components, mechanisms and even the whole machine, performing fitting work and adjusting assembled mechanisms and testing the finished machine. Each mechanic has his own workplace - a small section of the workshop's production area, where there is all the necessary equipment: hand tools for metal processing, instrumentation, auxiliary devices.
The main equipment of the workplace for metalworking is a bench with a vice attached to it and a set of necessary working and control tools and devices. In order for the workplace to be able to move parts or components weighing more than 16 kg, it must be serviced by cranes or lifts. To perform assembly or disassembly work, workplaces are equipped with stands, conveyors, roller tables, special carts or other transport devices.
Manual method of cutting metal
Metalworking techniques determine the sequence of actions:
- securing the workpiece in a vice; if this is not possible, place it on an anvil;
- the chisel is placed at the beginning of the marking line;
- first, preliminary gentle blows are applied with a hammer to highlight the contour of the intended cutting line;
- then a cutting tool is moved along this line and struck with strong blows;
- after completion, the half-cut workpiece is turned over;
- on the reverse side, repeat these steps until complete cutting off.
When working with strip metal, use the horizontal method. The rules of work are as follows:
- When sharpening, the cutting edge of the chisel is given a certain curvature;
- begin to carry out the operation from the far edge gradually approaching the front mark;
- When cutting out blanks according to the established template, an allowance should be provided.
During manual operation, there is a high probability of damage to the workpiece or the appearance of various defects. To avoid this, you must:
- ensure strong fixation of the workpiece;
- observe the angle of the chisel (it should be 30 degrees);
- carefully mark the cutting line;
- It is recommended to chamfer the workpiece before starting work;
- The frequency of blows applied must be uniform with the same force.
These recommendations must be observed especially when cutting metals from the PZO profile.
Possible defects
During this operation, certain defects always appear. The main defects include:
- the cut edge is not straight;
- The parallelism of both edges of the part is not maintained;
- the edge of the part turns out torn with burrs and great roughness.
Each of the defects that appear has its own individual causes. The first defect always appears with weak fixation of the workpiece. This defect is especially evident if the cutting process is carried out on a metal frame without fixing the part. The manifestation of these defects is caused by the following reasons:
- the part is not secured securely enough;
- the applied marking has shifted;
- the process was carried out with blows exceeding the necessary force;
To eliminate them, you need to follow simple rules:
- Check the strength of the workpiece;
- Maintain the accuracy of the location of the part relative to the applied marking;
- Check the sharpening parameters of the tool.
When cutting grooves, in addition to the listed defects, others may appear. These include:
- torn groove edges;
- the depth of the groove varies along the length;
- chips at the end of the groove;
To prevent the occurrence of the listed defects, it is necessary to follow the procedures established by the instructions for use of specific equipment and accepted standards. Before the operation, preparation is made for cutting the workpiece itself, the cutting tool and the machine used.
If you follow the rules for preparing and carrying out cutting and cutting operations, you get a smooth edge, without defects or chips.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Chopping
is an operation in which layers of metal are removed from a workpiece or the workpiece is cut with the help of a chisel and a plumber's hammer.
The physical basis of cutting is the action of a wedge, the shape of which is the working (cutting) part of the chisel. Chopping is used in cases where machine processing of workpieces is difficult or irrational.
Chopping is used to remove (cut down) metal irregularities from the workpiece, remove hard crust, scale, sharp edges of the part, cut out grooves and grooves, and cut sheet metal into pieces.
Cutting is usually done in a vice. Cutting sheet material into pieces can be done on a slab.
The main working (cutting) tool for chopping is a chisel, and the striking tool is a hammer.
Cold chisel
(the pattern is made from tool carbon steel U7A or U8A. It consists of three parts: impact, middle and working. Impact part
is made from tool carbon steel U7A or U8A. It consists of three parts: impact, middle and working. Impact part
1
is made tapering upward, and its top (the striker) is rounded; the middle part
2
is used to hold the chisel during chopping; working (cutting) part
3
is wedge-shaped.
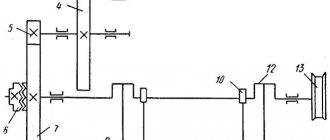
Cutting metal with a guillotine
At metalworking, machine-building enterprises, and large workshops, mechanized metal cutting is used. The most common is cutting using various guillotines. Mechanization of cutting makes it possible to improve the quality of the chopped edge, cut thicker metal, and increase the speed of obtaining the finished workpiece.
Guillotines are used for cutting sheet metal of various thicknesses. The cutting technique is quite simple. The guillotine has a special knife, which, under pressure, is lowered onto a sheet of metal, cutting it according to the applied markings. To create the required force, mechanical, hydraulic or electromechanical systems are used. In this case, the metal steel strip is exposed to the action of a knife, which implements a vertical cutting method. In this case, a special device - a roller table - feeds the metal workpiece to a given length. The fixing device captures and holds the workpiece in the required position. A knife is lowered to the cutting site under pressure, which carries out this operation exactly along the marking line.
Creating the necessary short-term pressure on a sheet of metal allows you to make precise cutting according to the mark made and ensure high quality results. Guillotine cutting has the following advantages:
- get a smooth edge on the cut;
- there are no nicks or burrs;
- there are no crescent-shaped slopes along the entire length of the edge;
- There are no uneven bevels.
In addition to technical advantages, the use of a guillotine allows you to reduce the cost of each part and increase labor productivity in this operation.
Particularly important is the fact that with such cutting it is possible to increase the safety of the operation.
Modern guillotines are machines equipped with modern electronic control units. They are able to set the necessary parameters before carrying out the felling operation.
Therefore, you can select the grade of metal, the required cutting angle, and the parameters of the operation (power, speed, frequency).
What is the difference?
Let's start by identifying the key differences in technology.
Chopping, as you might guess, is done using a percussion or hydraulic tool that literally breaks through (cuts through) a steel sheet. It can be done entirely manually, or using mechanical or electrical mills.
The most popular methods of cutting metal are milling and turning. And if the previous type of metalworking is carried out on sheet material or fairly thin rolled metal, then the blanks for cutting can be of almost any shape.
Sawing is the process of processing the edge or surface of a workpiece in order to obtain the required shape.
Now that the main differences are clear, we can look at each type in more detail.
General terminology
At the everyday level, many people use some words with the wrong meaning. The process of cutting metal is often mistakenly called cutting or punching, which leads to terminological confusion. Cutting, chopping and punching are three processing methods that differ in a number of parameters. The main differences between these processes:
- Cutting. With this processing method, one part of a metal part or sheet is separated from another part. For cutting, knives, scissors or automatic saws are most often used.
- Felling (the outdated name “felling” is also found). A series of similar metalworking operations in which a recess or groove is either created in a part, or metal is cut (with or without the removal of the top part), or one part of an object is separated from the others.
- Punching. With this processing method, one or more holes are created in the thickness of the metal sheet. Electric drills or similar equipment are usually used for punching.
Metal cutting
Chopping is often classified as a group of cutting jobs, but in fact, completely different tools are used here, and the possibilities they provide are much wider. Unlike the impact action exerted on the cutter in the previous case, pressure is used when cutting.
Manually
To work with various workpieces the following are used:
- for cutting wire - wire cutters,
- circle, square and hexagon are sawed with a hacksaw,
- sheet materials are cut with scissors.
The use of special equipment can expand the capabilities of metalworking several times.
In industry and mass production
Various types of machines are used in production:
- with hacksaw blades or circular saws,
- turning,
- milling,
- installations for plasma/laser/gas cutting.
The scope of application for these installations, like for hand tools, is quite different.
Hacksaws and circular saws are the simplest types of machines. Their only task is to save time when cutting long products. They can also handle thick workpieces with ease.
Lathes can be divided into models:
In the first case, using carbide cutters of various shapes, a worker manually grinds the required part from a horizontally fixed rotating cylindrical workpiece. In the second, all actions are performed automatically when executing a preloaded program.
The easiest way to understand the principle of use is in this video:
Milling machines perform approximately the same function, but can create products of absolutely arbitrary shape. A rectangular, square or cylindrical workpiece is fixed on a movable table, after which a head with a rotating cutter, following the program, begins to cut off the “extra” metal.
The process looks like this:
For thin and thick sheet metal, a separate group of CNC machines is used. The key difference between them is the technology used for cutting.
The blank sheet is placed on a stationary table, after which the cutting head, controlled by a computer, begins to cut parts according to a predetermined program.
The cutting head can be used for:
This technology ensures maximum accuracy and speed of production, which is highly valued in conditions of mass production.
Its main disadvantage is the likelihood of formation of molten metal deposits on the edges of parts and scale, especially when using workpieces of large thickness.