Bench cutting
TO
category:
Metal cutting
Bench cutting
Next: Bench straightening
Cutting is the process of dividing a workpiece into parts of specified sizes and shapes. Cutting is used to produce workpieces of specified sizes and shapes from rolled products and sheet metal, as well as slots and holes in the workpieces. Modern cutting methods provide high-performance processing of workpieces of almost any size and from materials with any physical and mechanical properties.
The following technological cutting methods are distinguished. 1. Sawing with hacksaws, band saws and circular saws. Used for cutting long products. 2. Cutting with scissors. Used for cutting sheet metal. 3. Cutting on metal-cutting machines (lathes, milling, etc.). 4. Anode-mechanical, electric spark and light beam (laser) cutting. These methods are used in cases where other methods do not provide sufficient productivity and the required quality. For example, they are used for cutting high-strength materials along complex and precise contours, etc. 5. Oxy-acetylene cutting. It is used for cutting workpieces of considerable thickness made of carbon steel. It does not provide high accuracy and leads to changes in the structure and chemical composition of the material at the cut site. However, it is widely used in single production environments due to its simplicity, high productivity and versatility.
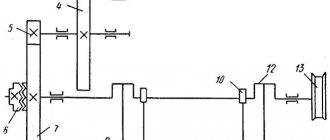
Rice. 1. Sawing (a) and cutting workpieces with scissors (b): 1 - workpiece, 2 - knives; y - rake angle, a - rear angle, P - sharpening angle, 8 - cutting angle
Cutting can be done either manually or mechanically.
The physical essence of cutting is based on various methods of destruction of the workpiece material at the cutting site.
When sawing and cutting on metal-cutting machines, the force F applied to the cutting wedge is directed at an acute angle to the surface being processed. Therefore, the cutting wedge cuts the material and turns it into chips. When cutting with scissors, the force F applied to the cutting wedge is perpendicular to the surface being processed. Therefore, the tool cuts the material without creating chips.
Electric spark cutting is based on electrical erosion (destruction) of the workpiece material. Capacitor C, included in the charging circuit, is charged through resistor R from a direct current source with a voltage of 100-200 V. When the voltage on the electrodes (tool) and (workpiece) reaches the breakdown voltage, a spark discharge with a duration of 20-200 μs occurs between their nearest microprotrusions. The discharge temperature reaches 10,000–12,000 °C. At the point of discharge on the workpiece, an elementary volume of material instantly melts and evaporates and a hole is formed. The removed material in the form of granules remains in the dielectric medium (oil) in which the processing process takes place. Discharges that follow each other continuously destroy all the workpiece material located from the tool at a distance of 0.01-0.05 mm. To continue the processing process, the electrodes must be brought closer together, which is done automatically.
Rice. 1.6. Electric spark cutting of workpieces: 1 - wire-tool, 2 - workpiece
When using oxygen-acetylene cutting, the workpiece metal at the cut site is first heated with an oxygen-acetylene flame to its ignition temperature in oxygen (for steel 1000-1200 °C). Then a stream of oxygen is directed into this place and the metal begins to burn. This generates so much heat that it is sufficient to maintain a continuous cutting process.
Anodic-mechanical cutting is based on the combined destruction of the workpiece material - electrical, chemical and mechanical. Direct current passing at the cutting site between the workpiece and the tool causes electrical erosion of the workpiece surface. The resulting molten particles of material are removed from the processing zone by a rotating tool - a disk. At the same time, the electrolyte supplied to the processing zone, under the influence of an electric current, forms oxide films on the surface of the workpiece, which are removed by the same rotating tool.
Cutting tools. When sawing, hacksaw blades (for manual and mechanical hacksaws), band saws and circular saws are used as cutting tools. Hacksaw blades and band saws are a thin strip of high-speed or alloy (Х6ВФ, В2Ф) steel with fine teeth in the form of wedges on one or two sides. Band saws are made by bending a strip into a ring and soldering its ends with high-temperature solder. A circular saw has teeth located on the periphery of the blade. The cutting teeth are hardened to a hardness of 61 - 64 HRQ. To prevent the tool from jamming in a narrow cut, its teeth are spread apart.
When choosing a sawing tool, you should first take into account the length of the cut and the hardness of the material being processed.
When making long cuts, it is necessary to choose blades with a large tooth pitch, and when processing thin-walled workpieces - with a fine one. At least three teeth must be involved in cutting simultaneously.
The higher the hardness of the material being processed, the larger the sharpening angle should be. The chips formed in this case have the shape of a comma and fit tightly into a small space. When machining soft materials, use tools with a large chip space. A positive rake angle improves productivity because the tooth cuts rather than scrapes the workpiece material.
To process high-strength materials, hacksaw blades with synthetic diamonds on the working surface are used.
To cut sheet material, cutting tools in the form of knives are used, which are most often removable. Knives come with straight, curved and round (roller and disk) cutting edges.
In anodic mechanical cutting, thin discs made of mild steel are used as a tool. On an electric spark machine, a continuously moving wire is used as a cutting tool.
Equipment and accessories for cutting. In a tool shop, small workpieces are cut with a hand saw. The hacksaw blade is mounted in a frame so that the teeth are directed away from the handle.
Manual lever shears are designed for cutting sheet material. Tool shops use small, portable shears. They can cut sheet steel up to 4 mm thick, aluminum and brass up to 6 mm thick.
Hand scissors are designed for cutting sheet material, making workpieces with a curved contour, cutting out holes with a complex contour in workpieces. For straight cuts, scissors with straight, wide knives are used. If the upper cutting edge is located to the right relative to the lower one, then the scissors are called right-handed, and if it is on the left - left-handed. To obtain external curved cuts, use hand scissors with curved wide knives. Cutting out internal curved contours is done with scissors with narrow curved knives.
Mechanical cutting of sheet material is carried out using manual electric shears, vibrating shears, as well as roller, multi-disc and sheet shears.
Sequence and techniques of work when cutting. Cutting is preceded by marking. Then the cutting method, equipment and tools are selected.
Correct execution of cutting techniques is of great importance for quality processing. The location of the workpiece and tool during manual cutting must be such that the marking line is constantly accessible for observation. When the cutting length is large, the pressure on the hacksaw is increased, and when the length is short, it is reduced. Since the teeth of a hacksaw break especially easily at the beginning and end of a cut, at these moments the pressure on it should be minimal.
When cutting, hand scissors should be opened to 2/3 of the length of the cutting edges. In this case, they easily grip the workpiece and cut well. The cutting plane should always be perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece being cut. Misalignment leads to jamming, crushing of edges and the appearance of burrs.
Correct adjustment of the tool is of great importance. So, with a weak tension on the hacksaw blade in a hand hacksaw, the cut is oblique. A large gap between the knives leads to the formation of burrs. The appearance of burrs with correctly adjusted knives is a signal that they have become dull.
When cutting with a hand saw, you should stand freely and straight, half-turned towards the vice.
Waterjet cutting of metal
This method was one of the first to be used for cutting metal. Blanks of a given shape were cut out of a metal sheet with a stream of water mixed with abrasive and supplied under pressure of up to 5000 atmospheres.
The method has a number of limitations regarding the grade of the metal alloy and the thickness of the sheet material being cut, although it allows cutting parts with a complex trajectory.
To increase the productivity of the process, it is possible to simultaneously cut thin sheet materials in a stack of several layers.
Sheet metal cutting speeded up significantly with the advent of thermal cutting equipment. Nowadays plasma cutting machines are used for cutting. Another option for cutting equipment is a laser machine. The cutting function, as a rule, is one of the options included in the software product of such machines.
High-speed cutting, carried out according to the program, allows you to arrange the parts on the sheet in the most advantageous way and minimizes waste. At the same time, laser or plasma automated cutting is safe, economical, and does not harm the environment.
Manual metal cutting
This method of cutting material is carried out by a master using slotted metal shears, an angle grinder - an angle grinder or a pipe cutter.
For cutting with a grinder, special abrasive wheels “for metal” are used.
Pipe cutters, in which the cut is performed with steel disc cutters-rollers, are used for cutting pipes.
The speed and accuracy of manual work depends entirely on the person. The thickness of the metal being separated (especially with slotted shears) is limited.
The manual method is ineffective and is practically not used on an industrial scale. The main area of use for manual cutting is in everyday life.
Thermal cutting of metal
The following types of thermal cutting are used:
- oxygen gas;
- laser;
- plasma.
All these methods are non-contact, i.e. When working, there is no direct contact between the workpiece and the cutting tool. The workpiece is separated using a gas jet, plasma or laser beam.
Oxygen gas cutting
The technological process is based on the ability of metal to heat up, melt and burn out in pure oxygen at high temperatures (more than 1000 °C).
Before starting the technological operation, it is necessary to heat the cut site to a temperature at which the material ignites. This heating operation is carried out by the flame of the torch. Acetylene is most often used as a heating gas. The heating time depends on the thickness, brand and condition of the metal surface being processed. Oxygen is not used at this stage.
After warming up, oxygen is added to the operation. The flame jet, moving evenly along the cutting line, cuts through the entire thickness of the semi-finished product. The oxygen used in the process not only cuts, but also removes oxides that form on the surface of the semi-finished sheet product being cut.
An important criterion for obtaining a high-quality cut is maintaining the same distance between the cutter and the surface being cut throughout the entire operation. This is difficult to achieve if metal cutting is done with a hand-held oxy-fuel torch. With an automated process (high-speed, oxy-fuel cutting with increased quality, high-pressure oxygen cutting), the cutting speed increases and the quality of the cut increases.
Uniqueness of the method:
- ability to cut thick workpieces;
- ability to cut titanium sheets.
Some disadvantages of oxy-fuel cutting:
- Non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, as well as high-carbon or chromium-nickel steels cannot be cut;
- large cutting width, low quality, formation of oxides, sagging,
- it is impossible to work with curved surfaces;
- change in physical properties in the cutting area.
Laser cutting
This technology involves cutting and cutting metal using a focused laser beam produced using special equipment.
The laser beam is concentrated at a specific point on the part being cut. Under the influence of the thermal energy of the laser beam, the surface warms up, boils and evaporates. The beam moves smoothly along the cut boundary, dividing the metal workpiece into parts.
Laser cutting is used to separate metals with low thermal conductivity. It is used for cutting, cutting thin sheets (from 0.2 mm), non-ferrous metals (aluminum, copper), stainless steel, and pipe products.
The uniqueness of the method: almost all metals, metal alloys, and non-metals are processed.
A number of disadvantages of laser cutting technology:
- limitation on the thickness of the divided products;
- high energy costs during the process;
- The work can only be performed by specially trained personnel.
Plasma
This technology involves the use of a plasma torch as equipment, in which the role of a cutting tool is performed by a plasma jet.
Hot ionized gas (plasma) passes through the plasmatron nozzle at high speed. The plasma heats, melts the metal, and then blows off the melt, thereby forming a cutting line for the workpiece.
Uniqueness of the method:
- process safety;
- high speed;
- slight limited heating of the cut surface.
The disadvantages of this technology are the high price of equipment, the need for personnel training, noise during operation of plasma installations, and limited thickness of the metal being processed.
Pipe cutter
It is quite difficult to cut a pipe with a hacksaw accurately and accurately at right angles. And if these are thin-walled copper pipes, which are usually used when installing kitchen and plumbing equipment, then cutting them with a hacksaw is generally undesirable, since under the action of the spread saw teeth they are easily deformed, which, in turn, makes it impossible to tightly connect such pipes, which is usually done with a roller welding with crushing of edges.
Cutting roller
For cutting pipes - especially thin-walled ones - it is better to use a pipe cutter. Using a cutting roller, the pipe is brought with slight pressure to the guide roller, then a full turn is made with a pipe cutter. With each revolution, the cutting roller is carefully pressed. Repeat this operation until the pipe is cut.
Deburring
When cutting pipes with very thin walls, you should be extremely careful in adjusting the feed of the cutting roller: there is a risk of pushing through the wall. It is better to feed the roller to a shallow depth in a few revolutions than to try to cut with great force. A cut pipe will have burrs on the inside. They need to be carefully cleaned with a finely cut round file.
After each revolution of the tool around the pipe, it is necessary to adjust the position of the cutting roller using a manual spindle. Then cutting continues.
Mechanical metal cutting
Mechanical separation is based on direct contact of the metal being processed with the cutting tool. The material of the tool, as a rule, is also metal, but of higher hardness.
There are mechanical cutting using scissors, saws, and cutters. A special case of mechanical cutting is impact cutting. Impact cutting or chopping with a guillotine is used at the stage of procurement work.
Types of equipment used for mechanical separation of materials:
- band saw machines (LPS);
- guillotines;
- disk machines;
- lathes with cutters installed on them;
- slitting units.
Band saw cutting
Cutting material with a band saw is often used to separate long, sheet metal. The band saw is the main unit on the so-called band saw machine (LPS). The essence of the work of a band saw is the same as that of a regular hacksaw. The saw blade is enclosed in a large diameter band, one side of which has special teeth. The saw blade moves continuously due to the rotation of pulleys connected to an electric motor. The average cutting speed of the machine is 100 mm/min. The material for making the saw blade is carbon steel or bimetallic alloy.
The advantages of the method: accuracy, accessibility, low price of equipment, the ability to perform not only straight, but also angular cuts; a small percentage of waste, since the cutting width is only 1.5 mm.
Modern LPS models are equipped with electronics and additional equipment with which you can include the machine in the production line.
Impact cutting of metal on a guillotine
This type is usually called felling. The main application of cutting is the separation of sheet metal. It can be ferrous metal, various types of steel - stainless, galvanized or electrical steel.
The method is based on the use of mechanical devices: scissors, knives for cutting metal sheets. The metal sheet is placed on the working surface of the guillotine. They are secured using a pressure beam and the operation is performed.
The uniqueness of the method lies in the fact that chopping (cutting metal) occurs with a single blow of a knife along the entire length of the workpiece being cut. The result is an absolutely smooth edge without unnecessary edges or burrs.
Three types of guillotines are used in industrial production:
- electromechanical;
- hydraulic;
- pneumatic.
In some industries, manual guillotine shears have been preserved, where the cutting mechanism is activated by pressing the pedal.
Disadvantages include noise during operation of the mechanism, limitations on the thickness of the workpiece, and differences in the width of the cut parts.
Cutting on a disc machine
The main advantage of this equipment is ease of operation, compactness, and versatility.
The role of the cutting tool is played by a disk with teeth protected by a casing. The disk is mounted on the surface of the desktop and driven by an electric motor.
Cutting with a circular saw is characterized by high cut quality, the ability to cut at an angle, and high processing accuracy.
A slitting unit is highly specialized equipment that is used exclusively for longitudinal separation of a metal workpiece.
The cutting process is fully automated. The operator monitors the process and controls the work from behind a special console.
The uniqueness of the method: the ability to divide sheets into narrow elements of long length (ribbons, strips, strips).
The general disadvantages inherent in all types of contact cutting can be formulated as follows:
- cuts only in a straight line or at an angle;
- It is problematic to obtain parts of complex configurations.
In modern technologies, the latest methods of metal separation are used, in particular, cryogenic (an operation using a supersonic flow of liquid nitrogen).
Cutting and cutting of metal are the primary procurement stages of processing metals and alloys. The use of straight-sided workpieces of the correct shape as the final product of metalworking is limited. After cutting by mechanical methods and gas-oxygen cutting, the parts are transferred for mechanical processing. But using thermal operations of laser and plasma cutting, you can obtain parts that are the final product. These will be parts of a complex configuration with cut holes, cuttings and other elements.
Plumbing
2.1. Basic plumbing operations: purpose, essence, techniques and sequence of execution
Metalworking work refers to the processing of metals in a cold state, performed by mechanics manually using various tools. Metalworking complements mechanical machining or is the final operation in the manufacture of metal products by connecting parts, assembling machines and mechanisms, as well as their adjustment. Metalworking work consists of a variety of technological operations, which include: marking, chopping, straightening and bending metals, cutting metals with a hacksaw and scissors, filing metal, drilling, countersinking and reaming, threading, riveting, scraping, lapping and finishing, soldering, tinning . Some of the listed operations can also be performed when metals are hot (cutting, riveting, bending). Many locksmith operations are performed not only manually, but also mechanically.
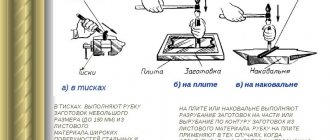
Blanks for machine parts are received for processing in mechanical and metalwork shops in the form of forgings of high-quality metal. Depending on the purpose of the parts, some workpieces remain unprocessed, others are processed partially or completely. During processing, a layer of metal is removed from the surface of the workpiece, as a result of which its size decreases. The difference between the size of the workpiece before and after processing is the value of the processing allowance. To know the optimal dimensions for processing, the workpiece must be marked. Marking
is the operation of applying marking lines to the workpiece being processed, defining the contours of the future part or the area to be processed. Marking is carried out accurately and carefully, because errors made during marking can lead to the fact that the manufactured part turns out to be defective. It is also possible that an inaccurately cast rejected workpiece can be corrected by careful marking, redistributing the allowances for each marking surface. The accuracy achieved with conventional marking methods is approximately 0.5 mm. With careful marking, it can be increased to hundredths of a millimeter.
Marking is used mainly in single and small-scale production. In large-scale and mass production factories, there is no need for markings due to the use of special devices - jigs, stops, etc.
Depending on the shape of the blanks and parts to be marked, marking is divided into planar and spatial. Planar marking
carried out on the surfaces of flat parts, on strip and sheet material and consists of applying contour parallel and perpendicular lines, circles,