For sanding and surface finishing work, it is important to select the correct abrasive material to minimize the risk of removing too much material and reduce the time and cost of the job.
Flap discs are made from the same abrasives as grinding discs, but their multilayer design makes it possible to process materials in a more gentle manner.
They are ideal for both initial sanding and finishing work. The advantages of petal circles include:
low noise level;
low heating during grinding;
long service life;
- high quality stripping
In this article, we will tell you how to choose the right disc, and also analyze the rules for effectively using a flap end grinding disc.
Choice of abrasive material
How a flap wheel works depends largely on the abrasive material used and the grit size.
ABRO discs use two main abrasives: aluminum oxide and zirconium dioxide.
Aluminum oxide (electrocorundum)
– the most common and affordable type of corundum. It is used for processing all ferrous metals, plastic, wood.
Uses of zirconium dioxide
as an abrasive material it ensures high productivity and long service life of the disc. Zirconium discs are especially good for stainless and carbon steel types. This wheel is more heat resistant, stronger and more durable, and remains sharp for a longer period of time.
The easiest way to tell what kind of abrasive material a flap disc is made from is to look at its color. If the abrasive is brown in color, you have an aluminum oxide abrasive wheel.
If the disk is blue, then, as a rule, it is made on the basis of zirconium.
In order to be 100% sure of the disc material, check the technical data indicated on it:
“A” – aluminum oxide
“ZA” – aluminum zirconate
(you can find out more about disc markings here: How to choose a cutting disc?)
Each type of grinding work corresponds to a certain grain size of the flap disk.
Table 1. Selecting disc grit.
The ABRO brand assortment includes all the types of grain described above:
100 mm is the minimum size. Suitable for small electric angle grinders (angle grinders) as well as pneumatic tools. Used for work in hard-to-reach places.
125 mm is the most popular size. Suitable for high power angle grinders.
There are other sizes, but these are the most widely used.
Selecting the thickness of the petals
Standard – for roughing of ferrous metals. The most accessible segment.
Thickened – also called HD or High Density. Contain on average 40% more petals compared to standard ones. They are processed more gently, have a longer service life, have less risk of damaging the surface, and are better sharpened. These are the discs ABRO produces.
Correct technique of use
To maximize the efficiency and longevity of your flap disc, it is important to select the correct pressure and angle when operating your angle grinder.
When working with flap discs, an angle grinder should contact the surface at an angle of 5 to 35 degrees. Each range has its own circle type:
1. Type 27 (according to GOST KLT -1) is best suited for finishing and applications where smaller grinding angles are required, from 0 to 15 degrees.
2. Type 29 (according to GOST KLT-2) is best suited for aggressive grinding at a large angle, from 15 to 25 degrees.
One of the popular mistakes associated with flap discs is putting too much pressure on the angle grinder during operation. In this case, the disk will not work fast enough, which can lead to premature wear and overheating. Too much pressure can also cause undercuts, gouges, or surface damage.
IMPORTANT! If you feel like pressing harder on the wheel when sanding, this is a sure sign that you need to use a coarser grit.
Another mistake is sanding at an obtuse angle to the surface. This technique increases pressure and stress on the edges of the disc, which shortens its service life.
When finishing welds on thin metal surfaces, it is important not to remove too much metal. You need to choose the least aggressive disk. For such work, we recommend a flap disc with a grit of 80 or 60.
Read also: Safety precautions when sawing
Do not judge the degree of wear of the petal disc by its external condition. Flap wheels are designed in such a way that, when used correctly, the blade will cut until the adhesive becomes visible.
Using these simple tips, you can save money on disks and become more efficient in your work.
The article was prepared with the support of experts from the DiamMarket company - products for stone processing.
A grinding disc is one of the types of abrasive tools, along with heads, segments, bars, abrasive belts and sandpapers, actively used for processing various types of surfaces. The abrasives used for the manufacture of grinding wheels are durable, highly hard substances: diamond, corundum, quartz, as well as artificial materials - electrocorundum, synthetic diamonds, silicon and boron carbide and others. The grains of these substances subject the surface of other materials to mechanical processing; in terms of their purpose, they can be compared with the teeth of a conventional saw, but located not along the edges, but along the perimeter of the disk. Grinding wheels are used to process many materials: carbon steel, glass, plastic, bronze, wrought iron and non-ferrous metals. In addition, they are used in tools for cutting brick, stone, ceramic tiles, and drywall.
Features of marking grinding products
The production of wheels is carried out in accordance with GOST; accordingly, their marking is also regulated by regulations. Typically, the main criteria for marking abrasive wheels are:
- Sanding material is a crumb of a special material that is characterized by high strength and good grinding properties.
- The size of the disk characterizes the diameter of the circle.
- Grain size – the degree of processing directly depends on it. The larger the grains, the more intensively and roughly the surface being treated is erased. Coarse grit is used when it is necessary to quickly remove a large amount of material and cut a large piece from a part. Fine is usually used for fine finishing, sanding and smoothing corners.
- Disc type - depends on the profile features of the new sanding wheel. Today there are 39 different types of profiles.
- Degree of hardness - this indicator has nothing to do with the hardness of the abrasive chips; it characterizes the ability of the binder material to hold grains on its surface and prevent them from tearing off during processing.
- Binder – indicates the material that acts as the base of the circle. A binder is necessary to form a circle of crumbs.
- Instability class - the accuracy of surface treatment depends on it. The higher the instability, the lower the quality of work. The reason for this is most often the irregular shape of the circle, uneven distribution of the binding material and displacement of the seat relative to the geometric center of the circle.
- Structure - indicates the ratio of the amount of abrasive and binding material, the presence of pores in the composition, the nature of the arrangement of grains and the uniformity of their distribution.
- Optimal rotation speed - calculated depending on the purpose of the emery, its structure, characteristics of the material used and shape. It is recommended to hold it to achieve optimal results.
In order to select the right tool, it is important to understand the features of the markings of grinding discs.
Product quality characteristics
There are a lot of different parameters by which such products are classified. There are even more types of markings for abrasive wheels due to the fact that there are many different combinations of these properties. The main parameters of abrasive wheels for grinding machines are:
- Grit index.
- Type of abrasive material.
- Binder.
- Dimensions and shape.
- Hardness of the grinding material.
- Working speed.
A circle with the appropriate indicators is selected for use, which are indicated in the markings on the product itself.
Fixture Grit
This is the most significant characteristic. Its value determines how smoothly the sample will be polished. In addition, the size of wear, productivity, and the thickness of the layer removed per cycle also largely depend on this indicator. The smaller the grain of the tool, the higher the cleanliness of the processing. However, the speed of work with such granularity is reduced. In addition, such devices often cause burns to the part.
Materials for production
Like all characteristics, the requirements for the material from which grinding wheels are made correspond to GOST. Minimum conditions are wear resistance, low heat transfer, hard surface. Based on these conditions, the abrasive tool is made from the following material:
- A substance having a base of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is called electrocorundum with a bauxite binder. GOST 28818 allows the addition of potassium oxide to increase hardness. This allows you to maintain the original properties when the temperature increases under intensive work conditions. Such circles are marked as follows: 12A - 15A - ordinary, 22A - 25A - increased hardness.
- The same material with a carbide base includes chrome, titanium, zirconium, and silicon compounds for working with hardened metals. Silicon carbide (52C - 65C) is needed to resist temperature changes when cooling the workpiece. Such products are marked with the letter A and numbers from 38 for zirconium to 95 for titanium.
- Rounded grains of spherocorundum are obtained by blowing liquid aluminum oxide, are characterized by increased hardness and are used for abrasive processing of carbide products. They are designated by the letters ES.
- The monocrystalline structure of monocorundum is the reason for the durability of wheels made from it. Due to the complexity of the production technology, they are very expensive. You can recognize them by markings 43A, 44A and 45A.
Application of binding materials
For a tight arrangement and protection from destruction, special substances are used in grinding wheels. Their quality, variety, and even distribution affect all the characteristics of abrasive tools. And also the presence of these materials shows the ability to independently sharpen crumbled sections of the grinding stone. If the binding component does not correspond to the surface being processed, the tool loses its main property, wear increases, grains that have not yet been worked are chipped, and burning and clogging appear.
The following materials are used in a ceramic bond: refractory clay, quartz and spar. They are strong, durable, with a stable cutting edge. Tools on this basis can be cooled with special emulsions. Circles of small thickness are destroyed by lateral impact. Designated K0, K1, K3 and so on. In their production, silicon carbide or electrocorundum grains are used. They grind well in all ways, except for cutting and use in narrow grooves.
Grinding wheel grit
Grit size is perhaps the most important indicator, since the smoothness of the finished surface depends on the size of the abrasive. Based on the grain size index, you can clearly determine the thickness of the layer being removed, the degree of wear of the disc and the smoothness of the processing. Typically, tool manufacturers provide special tables that detail the characteristics of the wheel range, including grit size and purpose of the disc.
The grain of the wheel can be so small that it can be used for polishing glass. With its help, small scratches and chips are removed and the glass is returned to a perfectly smooth surface.
The most common types you can find are:
- grinding - the abrasive size ranges from No. 200 to No. 16;
- grinding powder - from No. 12 to No. 4;
- micro-grinding powder – M63-M14;
- fine micro-grinding powder – M10-M5.
Particle size is measured in micrometers. It is worth noting that the exact size of the abrasive can usually be determined only for artificial materials. When producing diamond wheels, it is impossible to choose the same size of chips, so when marking, two indicators are used, the minimum and maximum grain size.
Selecting an abrasive wheel
To choose the right abrasive tool, you need to know well the capabilities of the sharpening machine - power, operating speed, and the ability to adjust them. Also, for different types of surfaces to be treated, the appropriate type of sandpaper should be selected.
IMPORTANT! You cannot use the grinding wheel that is “to hand.” Always check that the sandpaper is suitable for the material being processed. It is also necessary to know whether the work requires cooling and lubrication of the working surface of the grinding wheel
If the abrasive manufacturer's requirements are not met, the sanding wheel itself can quickly be damaged and the workpiece can be damaged. It is important to choose the correct grit size of the abrasive wheel
It is also necessary to know whether the operation requires cooling and lubrication of the working surface of the grinding wheel. Failure to comply with the requirements of the abrasive manufacturer can quickly damage the emery wheel itself and damage the workpiece.
It is important to choose the correct grit size of the abrasive wheel
Surface treatment should begin with coarse grains, gradually moving to fine polishing with fine-grained sandpaper. By choosing the right tool, you can achieve high quality processing without even being a professional.
Please note: Worn wheels should not be immediately scrapped; there are special tools for straightening and restoring the surface of the abrasive.
- Electrocorundum wheels are suitable for processing non-carbide metals and composite materials, as well as for sharpening home cutting tools. For ease of selection, they come in white, orange or blue. The low hardness of the abrasive, combined with the low strength of the bond, allows you to work with soft materials without fear of overheating and scaling. The quality of polishing and sharpening is high. Used for finishing materials. Disadvantages include rapid wear and loss of surface shape due to uneven use (appearance of grooves, rounding of corners).
- Abrasive wheels made of silicon carbide are used for primary (roughing) processing, removal of irregularities, processing of welds and sharpening of tools made of hard alloys. They have a distinct green color. Such abrasives are wear-resistant and retain their original shape well. When working with hard materials, grooves do not form on them. Ideal for sharpening working carbide teeth of circular saws, drills, including pobedit bits. The disadvantage of such circles is high heating during operation. In some cases, it is necessary to supply a cooling emulsion to the work area.
- For final polishing and removal of burrs from working with corundum and silicon carbide abrasives, vulcanite-based abrasive wheels are used. In fact, this is not emery - but a polishing disc, harder than felt. Made from vulcanized rubber with the addition of fine-grained abrasive. As a rule, electrocorundum sand. The tool is specific and is not suitable for changing the shape of a workpiece. But with its help you can perfectly smooth the surface being treated. After treatment with a vulcanite wheel, the surface quality can only be improved with the help of felt and GOI paste.
How to choose a grinding wheel, review of markings - video
Abrasive type
Today, a large variety of materials are used in the production of emery. This allows you to achieve optimal characteristics of the disk, achieve its high strength, durability or processing accuracy.
The most commonly found materials are:
- Electrocorundum - used when working with metal products, usually wrought iron. It is characterized by high heat resistance and good adhesion to the binder. The abrasive is very strong and has high durability. The most common electrocorundum is normal. White electrocorundum is also common. The abrasive is more uniform and has sharp edges that sharpen themselves. Because of its properties, it is used for final processing of parts made of high-quality steels. Less commonly, you can find chromium, titanium and zirconium electrocorundum. The higher the marking number, the higher the strength of the circle.
- Silicon carbide is characterized by increased strength and at the same time significant fragility. It is labeled as 52-55C and is used when working with porcelain, granite, ceramics, glass and many other durable materials.
- Elbor is a very hard material, almost as good as diamond, but more fragile. Such circles are marked CBN, KNB.
- Diamond is a very durable natural material and is characterized by low fragility. Such discs are used in the machining of alloys based on iron, glass, ceramics and silicon.
Diamond wheels are divided into several types:
- normal strength (AC2);
- increased (AC4);
- high (AC6);
- single crystals (AC32).
Classification
A non-professional classification, familiar to many, divides grinding wheels into the following types:
Marking by size
The main indicators of the size of abrasive wheels that are used for marking are the outer and inner diameter, as well as the height or width of the disc. The outer diameter is designated by the capital Latin letter D, the inner diameter is d, the width or height of the disk is H. All designations are indicated in mm.
The size of the discs can range from 3 to 1100 mm.
Along with the size, you can often find an instability class, which is divided into 4 groups. The instability class is especially important when it is necessary to achieve high precision in the processing of materials. Discs that are ideally shaped and balanced are designated AA.
Marking - symbols
Abrasive wheels have special markings in the form of inscriptions and/or colored marks and contain:
Circle type
In theory, there should be a digital designation:
- 1- straight profile,
- 41 – cutting discs,
- 42 – discs with a recessed center.
But in practice, this will be an inscription in Russian and/or English: “cut-off wheel” - cutting wheel, grinding wheel - grinding wheel, flap wheel.
Circle dimensions
On the manufacturer’s website (see table below) it is stated as follows:
D – outer diameter,
T – height,
H – hole diameter.
However, in practice, the format will usually be: outer diameter x thickness x inner diameter.
Or even something like this:
The material the disc is intended to process
Indicated by an inscription on a circle (“metal” or “steel” - for metal processing, “concrete” - for working with concrete), a colored mark (blue - steel, green - concrete).
Also, sometimes an additional graphic image of the material is applied, which saves us from having to read the inscriptions once again.
In the circle shown in the picture above, the inscription metal and the image of sheet metal, metal pipe, roofing metal sheet and channel clearly demonstrate the material that can be processed.
Grain. Abrasive particle sizes
This parameter is indicated on the wheel in conventional units and indicates the abrasive fraction based on international marking standards.
There are also possible variations from one edition of GOST to another.
Bundle type
Bakelite, ceramics or synthetic rubber is used as a binding component.
7.1. Ceramic bond
V (K – old designation). In the case of a ceramic base, the tool has high fire-resistant, water-resistant and chemical characteristics, which qualitatively preserve the working edge. However, such a grinder disc is sensitive to mechanical shocks and bending loads. Ceramic bonded wheels are used for almost all types of grinding except roughing.
7.2. Bakelite bond
B (B is the old designation). Considering the bakelite base, I would like to note that such grinder wheels have higher rates of elasticity and resilience than their ceramic counterparts. The disadvantage of such a binder is its low resistance to alkaline components included in cooling fluids.
In addition, bakelite-based wheels are weaker than ceramic analogues in adhesion to abrasive grains and, therefore, can mainly be used for flat grinding. Grinder discs made of bakelite bond are used for manual work on rough peeling or on suspended wall surfaces.
At the same time, bakelite wheels have a polishing effect. For the purpose of cutting steel products, a soft bond and a thin abrasive are used. In turn, for non-ferrous metals it is advisable to use a hard bond with a coarse abrasive.
7.3. Vulcanite bond
This is a vulcanized synthetic rubber. The abrasive wheel is marked with the letter (R). The old designation is (B). This option is exotic and extremely rare.
Max. number of revolutions at which the disk can be used
The range varies from 6,600 to 13,300 rpm. Important parameter! If you neglect it, the circle may break into separate fragments during operation.
Accuracy class
AA, A and B. AA – high accuracy of geometric parameters A – Intermediate option. B - for less critical operations.
Best before date
The expiration date is applied by the manufacturer to the metal part of the mounting hole on the outside. The expiration date is the date of manufacture plus 3 years. The quarter is indicated by the letter V. The number indicates the month.
Security pictograms
I guess that no one cares about them, but besides the banal “put on headphones,” something really worthwhile may be applied. For example, do not use for face grinding.
Cutting wheel size 125mm, thickness 2mm, mounting hole 22.23mm, made using normal alumina alumina grinding grain, grit P36. On a bakelite bond with the presence of reinforcing elements.
Structural density
The essence of the indicator of the structural density of an abrasive is the ratio of grains to the total volume of the disk, that is, grains and binder. The higher the grit density, the more material can be removed in one pass. Sometimes the lower the density, the better. For example, when sharpening. The disc self-cleans faster and does not overheat due to rapid heat dissipation, protecting the disc from deformation.
Typically the markings look like this:
- dense structure – from 1 to 4;
- average – from 5 to 7;
- open – 8, 9, 10;
- porous – 11, 12.
Ceramic, bakelite and vulcanite binders are usually used as binders. The first is the most common, it is based on sand, clay and quartz. These discs are highly durable, but they are also fragile. It is not recommended to use them for power processing.
Bakelite circles are based on resin. Such discs are highly resistant to temperature changes during operation. Volcanic bond is rarely used and usually in highly specialized areas; it is based on rubber.
Hardness and other parameters
Circles are generally classified as soft, medium and hard; These are the main types, to which various epithets are already added. For example, the following are officially known:
- extremely soft;
- very soft;
- medium hard disks.
Additional numbers from 1 to 3 are applied to these brands. To sharpen a tool manually, you need a C1 or C2 abrasive. It is important to understand that the hardness of abrasive wheels can mean different things. In one case, this is the stability of the fastening of abrasive grains in the overall assembly (that is, the resistance of the ligaments to the ejection of grains under mechanical stress). Another is the suitability of the particles used to penetrate other materials.
According to the first option, the hardness of the discs is increased, strengthening the ligament. The total pore volume is reduced, but this does not affect the distances between abrasive particles. A 1.5% increase in bond is considered to add 1 level of hardness. Advanced bonding systems are very tear resistant. They are able to work even at a very high frequency of disk rotation - noticeably higher than the most powerful household drill can provide.
According to GOST 1972, the hardness of abrasive devices is precisely the resistance to tearing out grains under an external impulse. Testing is carried out using 3 key methods:
- according to the depth of the hole, knocked out with a stream of quartz sand;
- by the efficiency of pressing a hardened steel ball under a certain load;
- by drilling a hole to a given depth with a drill of a special design, which is subjected to stable pressure (the key indicator is the required number of turns of the drill to achieve the result).
In some cases, professionals use a TKN device (that is, a cone hardness tester). To operate, its active part is heated to 100 degrees. Then the cone is pressed into a circle. The key parameter is the depth of entry. The hardness of the disc directly affects the grinding process. The soft attachment is suitable for finishing fairly hard materials. However, peeling requires the use of more durable products. Steel that has not been hardened, as well as cast iron, can be processed with a wheel of moderate hardness.
Abrasive hardness degree
The hardness indicator is the degree to which the abrasive is retained on the surface of the wheel. There are several varieties of circles, from very soft (VM) to extremely hard (HH). The most universal are the circles of medium hardness, suitable for a wide range of materials, therefore they are usually used in everyday life.
This parameter should be treated with special care, since an incorrectly selected disc wears out faster, can be destroyed during processing, damage the material being processed, or fail to produce results at all, even after several repetitions of grinding.
Scope of application of diamond grinding tools
Thanks to the capabilities of diamond tools, the areas of their use are very wide. The labor intensity of processing hard alloys is reduced several times compared to working with other abrasive materials. Tools sharpened with diamonds work more efficiently and do not require processing for longer. For single-edged parts with a cutting part made of carbide material, such sharpening increases wear resistance by one and a half times, and for multi-edged tools this figure is even higher.
The surface treated with a diamond grinding wheel does not crack, chips or other defects do not form on it. This makes it possible to process glass and ceramic products: car windows, mirrors and much more.
This tool is indispensable when grinding glass for optical instruments, at enterprises producing porcelain, crystal and glassware, and when grinding screens. Diamond grinding is widely used in medicine for sharpening microtome knives, scalpels and injection needles, for dental treatment and prosthetics in dentistry.
In addition, diamond grinding wheels are also used for dressing wheels made from other materials.
However, in order for the beneficial properties of diamond wheels to be fully used, and the result of the work to meet expectations, the correct choice of product among many varieties is required.
Acceptance rules
7.1. To monitor compliance of the wheels with the requirements of this standard, the manufacturer carries out acceptance control in accordance with GOST 15.309.
7.2. The sample size during acceptance control should be:
100 %
-
according to 5.9, 5.12.2;
10% of the lot, but not less than 5 pcs. -
according to 4.2, 5.4
-
5.6, 5.8;
5% of the lot, but not less than 5 pcs. -
according to 5.7.
The sample size during acceptance control of section 6 is
in accordance with GOST R 52588.
Normative references
This standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST R 52381-2005 (ISO 8486-1:1996, ISO 6344-2:1998, ISO 9138:1993, ISO 9284:1992) Abrasive materials. Grain size and grain composition of grinding powders. Control of grain composition
GOST R 52587-2006 Abrasive tools. Symbols and methods for measuring hardness
GOST R 52588-2006 (EN 12413:1999, EN 13743:2001) Abrasive tools. Safety requirements
GOST R 52710-2007 Abrasive tools. Acoustic method for determining hardness and sound indices by the speed of propagation of acoustic waves
GOST 15.309-98 System for developing and launching products into production. Testing and acceptance of manufactured products. Basic provisions
GOST 577-68 Dial indicators with a division value of 0.01 mm. Specifications
GOST 801-78 Bearing steel. Specifications
GOST 1050-88 Long rolled products, calibrated with special surface finishing from high-quality carbon structural steel. General technical conditions
GOST 3060-86 Grinding wheels. Permissible unbalanced masses and method of their measurement
GOST 3647-80 Grinding materials. Classification. Grain size and grain composition. Control methods
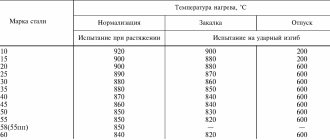
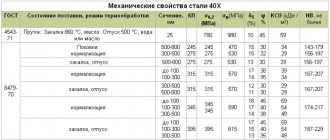
GOST 4543-71 Rolled alloy structural steel. Specifications
GOST 14192-96 Marking of cargo
GOST 27595-88 Grinding materials and abrasive tools. Packaging, labeling, transportation and storage
GOST 30513-97 Abrasive and diamond tools. Safety test methods
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of the reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or using the annually published information index “National Standards”, which was published as of January 1 of the current year , and according to the corresponding monthly information indexes published in the current year. If the reference standard is replaced (changed), then when using this standard you should be guided by the replacing (changed) standard. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which a reference is made to it is applied in the part that does not affect this reference.
Control methods
8.1. Control of circle sizes is carried out using universal or special measures and measuring instruments.
8.2. Dimensions for reference, radii of curvature
R are determined by equipment and are not controlled.
8.3. Control according to 5.9, 5.12.2 is carried out visually.
8.4. Hardness control - according to GOST R 52587, GOST R 52710.
8.5. Imbalance control
—
according to GOST 3060.
Note
—
Checking the imbalance of wheels with D
£
250 mm and types 2, 6, 11, 35, 36, 37 may not be carried out.
8.6. Control of radial and axial runout is carried out according to a technical document approved in the prescribed manner, using a dial indicator in accordance with GOST 577 with a division value of 0.01 mm.
8.7. Mechanical strength tests
-
according to GOST R 52588, GOST 30513.
Note - Until 07/01/2010, mechanical strength tests of wheels of types 2, 35, 36, 37 may not be carried out.
8.8. The grinding coefficient
K is calculated using the formula
where Qm
—
volume of metal removed, mm3;
Qa
—
volume of the worn part of the wheel (taking into account the wheel consumption for dressing).
Types of ligaments
In the production of abrasives, two main types of binders are used - organic and inorganic. The first option is produced from natural raw materials, and the second is produced using heat treatment of a particular synthetic substance, which leads to the production of a high-strength product.
Let us consider each group of connectives and their properties in more detail.
Safety requirements
6.1. The mechanical strength of the wheel must ensure its operation with the maximum operating speeds
vs indicated in Table 24.
Table 24
| Circle type | Size, mm | Type of submission | Maximum operating speed of the wheel vs, m/s, on ties | ||
| V | IN | R | |||
| 1 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 |
| H £ | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| Mechanical in a closed work area | 125 | 100 | 100 | ||
| H £ | Manual | 35 | 35; 40; 50 | 35; 40; 50 | |
| H £ | — | 63 | 63 | ||
| H £ | — | 80 | |||
| 2 | W £ | Mechanical | 25; 32; 35; 63 | 25; 32; 35; 40; 63 | — |
| Manual | 32; 35 | 35; 40; 50 | |||
| 3 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 50; 63 |
| H £ | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| Mechanical in a closed work area | 125 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 4 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 50; 63 |
| 5 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 50; 63 |
| H < 0.50D | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| Mechanical in a closed area | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 6 | E £ | Mechanical | 32; 40; 63 | 32; 40; 63 | 32; 40; 63 |
| Manual | 32 | 40; 50 | 40 | ||
| 7 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 50; 63 |
| H £ | Mechanical in a closed work area | 80; 100 | 80; 100 | 80; 100 | |
| 10 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 50 | 35; 50 | 35; 50 |
| 11 | E £ | Mechanical | 32; 50 | 32; 40; 50 | 40; 50 |
| Mechanical in a closed area | 63 | 80 | 63 | ||
| Manual | 32 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 12; 14 | E £ | Mechanical | 32; 50 | 32; 40; 50 | 40; 50 |
| Mechanical in a closed work area | 63 | 80 | 63 | ||
| Manual | 32 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 20; 21; 22; 23; 24; 25; 26 | H £ | Mechanical | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 | 35; 40; 50; 63 |
| H £ | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| H £ | Mechanical in a closed work area | 40 | 50 | 50 | |
| H £ | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 35; 36 | H £ | Mechanical | 32; 35; 63 | 32; 35; 50; 63 | — |
| Manual | 32 | 50 | |||
| 37 | W £ | Mechanical | 32; 63 | 50; 63 | |
| Manual | 32 | 50 | |||
| 38; 39 | H £ | Mechanical | 40 | 50 | 50 |
| U £ | |||||
| H £ | 63 | 63 | 63 | ||
| U £ | |||||
| H £ | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| U £ | |||||
| H £ | Mechanical in a closed work area | 40 | 50 | 50 | |
| U £ | |||||
| H £ | 125 | 100 | 100 | ||
| U £ | |||||
6.2. Other safety requirements
—
according to GOST R 52588, GOST 30513.