Threaded connection is one of the most used methods for installing steel pipelines with a diameter of up to 164 mm. In households, metal pipelines are installed to supply gas; during their installation, threads are used, which are obtained using a thread-cutting tool for pipes.
For do-it-yourself thread cutting, the industry produces a wide range of manual and electrical devices that facilitate this procedure. It should be taken into account that for joining pipeline elements a special pipe thread is used, the cylindrical version of which is regulated by GOST 6357-81.
Rice. 1 Types of pipeline connections
Threading tools and accessories
10.2 Threading tools
General information
. Threads on parts are obtained by cutting on drilling, threading and lathes, as well as by rolling, that is, by the method of plastic deformation. The knurling tools are knurling dies, knurling rollers and knurling heads. Sometimes the threads are cut by hand.
Internal threads are cut with taps, external threads are cut with dies, runs and other tools.
Tool for cutting internal threads. Taps
. Taps are divided according to their purpose - into hand-held, machine-handled and machine-made; depending on the profile of the thread being cut - for metric, inch pipe threads; by design - solid, prefabricated (adjustable and self-switching) and special.
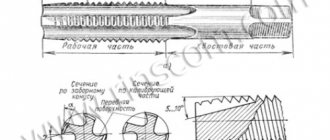
Figure 10.2.1 Tap (author)
Tap
consists of two main parts - working and tail.
Working part
is a screw with several longitudinal straight or helical grooves and is used for cutting threads. Taps with helical grooves are used for cutting precise threads. The working part of the tap consists of an intake and a calibrating part.
Fence
(or cutting) part is usually made in the form of a cone; it does the main work when cutting threads. In taps for ductile metals on the cutting part there is a bevel of 6.10 0 in the direction opposite to the direction of the thread: with a right-hand thread, the bevel is left, with a left-handed one - right. This improves chip removal.
Calibrating
(guide) part - the threaded part of the tap adjacent to the intake part. She guides the tap into the hole and calibrates the hole being cut.
Shank
— the rod is used for. securing the tap in the chuck or holding it in the driver (if there is a square) during operation.
The threaded parts of the tap, delimited by the grooves, are called cutting feathers .
The cutting feathers (teeth) are wedge-shaped.
Hand taps
for metric and inch threads are standardized and manufactured as a set of two taps for threads with pitches up to 3 mm inclusive (for basic metric threads with a diameter of 1 to 52 mm and for inch threads with a diameter of ¼" to 1″) and a set of three taps for threads with pitch over 3 mm (for metric threads with a diameter from 30 to 52 mm and for threads with a diameter from 11/8″ to 2″).
Figure 10.2.2 Set of hand taps (www.tvormasters.ru)
The three-piece set includes rough, medium and finishing taps. All taps in the kit have different diameters. The roughing tap cuts rough threads, removing up to 60% of the metal (chips); the middle tap cuts more precise threads, removing up to 30% of the metal; The finishing tap removes up to 10% more metal, has a full thread profile and is used for final, precise thread cutting and calibration. To determine whether a tap is rough, medium or fine, one, two or three circular marks (rings) are made on the tail section, respectively, or the corresponding number is placed. In addition, the size of the thread for which the tap is intended is marked on the tail section.
Depending on the design of the cutting part, taps can be cylindrical or conical.
With a cylindrical design of taps, all three tools in the set have corresponding diameters. The finishing tap has a full thread profile, the diameter of the middle tap is less than normal by 0.6 of the cutting depth, and the diameter of the rough tap is less than the thread diameter at the full cutting depth. For a rough tap, the length of the intake part is 4.7, for a medium tap - 3.3.5, and for a finishing tap - 1.5. 2 threads. The angle of inclination of the cutting part for the rough tap is 3°, for the medium tap - 7°, for the finishing tap - 12°. Cylindrical taps are used to cut threads in blind holes.
With a conical tap design, all three tools in the set have the same diameters and hollow thread profile with different tap lengths. The thread within the intake part is made conical and is additionally cut along the tops of the teeth into a cone. For a rough tap, the intake part is equal to the length of the working part, for a medium tap - half of this length, for a finishing tap - two threads. Tapered taps are usually used for cutting threads in through holes.
Taps are produced with ground and unground tooth profiles. Ground ones create threads that are more precise and have a cleaner surface.
Machine-hand taps
used for cutting metric, inch and pipe cylindrical and tapered threads in through and blind holes of all sizes by machine and manually with a pitch of up to 3 mm inclusive. Taps of this type are produced in two types - single for through and blind holes and complete (rough and finishing).
Machine taps
, used for cutting threads in through and blind holes on machines. They are cylindrical and conical.
For machine and machine-hand taps, annular grooves are made on the shank for clamping in quick-change chucks.
External thread
cut into dies manually and on machines.
Depending on the design, dies are divided into round, rolling, sliding (prismatic).
Round dies
They are made whole and cut.
Figure 10.2.3 Round dies (lerks) (www.tvormasters.ru)
One-piece die
It is a hardened steel nut in which through the threads through longitudinal holes are cut, forming cutting edges and serving for the exit of chips. On both sides of the die there are fence parts 1.5 in length. 2 threads. These dies are used for cutting threads with a diameter of up to 52 mm in one working stroke.
The diameters of solid round dies are provided by the standard: for basic metric threads - from 1 to 76 mm, for inch threads - from 1/4″ to 2″, for pipe threads - from 1/8 to 1/4″.
When cutting threads, round dies are manually secured in a special driver.
Split dies, unlike solid ones, have a slot (0.5 - 1.5 mm), which allows you to adjust the thread diameter within 0.1. ..0.25 mm. Due to the reduced rigidity, the threads cut by these dies have an insufficiently accurate profile.
Figure 10.2.4 Thread rolling dies (www.tvormasters.ru) Thread rolling dies
, used for rolling precise thread profiles, have a body on which threaded rolling rollers are installed. The rollers can be adjusted to the size of the thread being cut. The dies are rotated by two handles screwed into the body.
Using thread rolling dies, threads Ø 4.33 mm and pitch 0.7 are cut. 2 mm for 6.8 qualifications. Rolling is performed on machines and also manually. The thread is stronger because the metal fibers in the screws are not cut. In addition, due to the pressure of the dies, the fibers are strengthened. Since the thread is only extruded, the surface is cleaner. Thread rolling is done in the same way as cutting with clamps.
Sliding (prismatic) dies
unlike round ones, they consist of two halves, called half-dies. Each of them indicates the size of the external thread and the number 1 or 2 for proper fastening in the device (
die
).
Types of threaded connections and their advantages
The main types of connections between pipeline elements are threading and welding; the latter method is almost always used on large-diameter industrial pipelines and when installing gas pipelines.
In everyday life, not too many people have welding machines and the necessary welding skills; for them, joining pipe elements is only possible using threads, which are not difficult to cut with your own hands.
During operation, a distinction is made between right-handed and left-handed threads on cylindrical and conical parts; the latter is used in industrial high-pressure systems and is not used in everyday life.
Rice. 2 Pipe cylindrical thread - GOST 6357-81
GOST 15763-2005 for threaded and flanged connections of pipelines designed for operating pressures up to 63 bar lists about a dozen types of pipeline connections and their assembly diagrams. All of them can be divided into several groups:
- with screw end of body parts;
- with pipe edge flaring;
- with ball or welded nipple;
- with cutting, clamping and thrust rings.
Rice. 3 Scheme and procedure for connecting steel pipes
Related article:
How does a pipe clamp work - types, scope, manufacturers, prices . It is possible that while reading about pipe threading tools, you will want to learn in more detail how external threads are cut, what tool is used and how to choose it.
Threading has the following advantages over other methods:
- Tightness and strength. This indicator is achieved through the use of special cutting, the parameters of which depend on the pipe dimensions. When standards are met, properly performed cutting ensures a reliable, durable and airtight joint.
- Ease of installation and dismantling. Installation of a pipeline line by thread, unlike welding, does not require electricity or special devices from expensive massive welding machines, and can be carried out in any weather conditions with an adjustable wrench. The pipeline can always be disassembled without damage during repairs or configuration changes.
- Speed of work. Joining two pipes takes a minimum of time compared to welding - just use an adjustable wrench to turn the union nut or coupling several times.
- No qualification required. When installing threaded units, no special training or skills are required. If you have a thread-forming tool and correctly select the size of the cutting dies, anyone can get high-quality cutting while following the technology.
- Connection of different sized fragments. Unlike welding, with the help of threaded adapters it is quite easy to move from a pipeline with a large diameter to a small one and vice versa.
Rice. 4 Some types of threaded connections
Thread cutting tool
The threaded type of connection is the most widely used today. It is used in mechanical engineering and other areas of production, is characterized by high reliability and ease of manufacture. If desired, you can cut the coils using special tools, which are characterized by practicality and versatility in use.
General information about threading
When choosing a tool for cutting threads, you should take into account the characteristics of the threaded surfaces. These include the following points:
- The cutting of turns is carried out mechanically using special equipment. When metal is removed, grooves and coils are formed that fit perfectly with the surface of the second element.
- All thread cutting tools and technologies used can be divided into two categories: manual and automated. For a long period, screw-cutting lathes were used.
- When using hand tools for thread cutting, lubricant must be used. It significantly extends the service life of devices and simplifies the threading process itself.
Thread cutting with different types of dies
It is worth considering that manual versions have an internal surface, which determines the size of the turns and their location. In the case of processing on a screw-cutting lathe, the parameters of the future threaded surface are determined by the feed and speed of movement of the caliper.
Shaped cutters for thread cutting
When using turning and screw-cutting equipment for thread cutting, you should select the most suitable cutter. Manufacturers produce special versions of cutters for thread cutting, which are characterized by their specific features:
- During production, a cutting part of a certain shape is created. Due to this, a groove of the required shape is formed.
- The cutting part is made of tool steel, which is hardened. Due to this, the possibility of rapid wear of the cutting edge is eliminated during operation.
- The use of the method under consideration makes it possible to process the surfaces of large workpieces.
In production shops, a screw-cutting lathe is often used, since there are practically no dies and taps for working with large-diameter workpieces. In addition, when threading, a serious load arises.
Hand tools
Manual pipe threading tools are the main type for cutting threads in everyday life; their use has the following features:
- Availability. Manual devices have the lowest price among devices of this type and are therefore available to any owner.
- Functionality. When applying cutting, a main device (die holder, knob) is used, into which a cutting tool with the required parameters is inserted.
Rice. 5 Bison die and taps in thread-cutting tool sets
- Compactness. Manual devices take up little space and do not require large spaces for operations.
Threaded dies for increased productivity
Some thread cutting tools are characterized by high efficiency when used. An example is thread dies, which can be used to produce threads of almost any size. Their advantages include the following:
- Simple design.
- Versatility in use.
- High efficiency.
- Manufacturability.
The combs are represented by multi-filament shaped cutters, which are of prismatic, round and rod type. Most often they are used for cutting threads with fine pitches and low profile heights.
Taps, dies and heads for thread cutting
The most widely used hand tools are for thread cutting. They can be used in industry and everyday life.
The most widely used versions are:
- Similar tools are used to make bolts and studs. Such a product is a round washer, inside of which several ribs protrude. External threads can be formed and calibrated in just one pass. There are various versions of tools on sale; hardened tool steel is used in manufacturing.
- Taps are used to produce internal threads. It is also manufactured using hardened tool steel, which is characterized by high wear resistance. The tap has the shape of a rod, the working part of which has several depressions and protruding edges. Due to this, the thread cutting process is significantly simplified.
- Special heads can also be used to carry out the work in question. They can have different sizes and are used in conjunction with a special holder.
The cost of hand tools is low, but they are characterized by high efficiency in use.
Types of tapping
Metric cutting type. The cut element of such a thread has the shape of an isosceles triangle, the entire value is measured in millimeters, such taps are marked with the letter (M). To select the right tool during cutting, a special reference table of taps is used.
Tapping table:
The inch working part of the tool has a conical shape. The diameter of such a tool is measured in inches, and the pitch is measured in the number of threads per inch.
Pipe. Cylindrical and conical taps are used for cutting threads on pipe connections.
How to properly cut turns on a water pipe
Recommendations for cutting turns on a water pipe are largely related to what technology is used. Hand tools for cutting external threads should be used taking into account the following information:
- It is necessary to use lubricants that are added to the cutting zone to reduce the wear of the cutting edge.
- At the time of work, you need to ensure that the tool is positioned strictly perpendicular to the workpiece. If it is displaced, the turns may be positioned incorrectly relative to each other.
- When thread cutting, attention is paid to ensuring that chips are removed from the cutting zone in a timely manner.
Tapping a water pipe
The work in question can also be carried out in domestic conditions.
Tap design
A tap is a kind of hardened screw that has protruding ribs with several cut helical or straight grooves - cutting edges. When screwed into hollow workpieces of the appropriate diameter, such corrugated ribs cut out chips, removing them from the machined area of the hole and leaving similar helical grooves on the walls of the part - threads.
A simple thread-cutting device, a tap, is essentially an iron rod made of high-quality solid steel, with a cutting part on one edge and a shank with a square element on the other (for manual models) for attaching a crank, which serves for reciprocating movements of the tap in process of work.
The working area of the tool for cutting internal screw threads is conventionally divided into parts:
- cutting part (intake), which ensures the main cutting of the processing allowance;
- a calibrating section that finalizes the thread;
- feathers (ribs with screw threads);
- grooves for removing chips (small taps have 3 grooves; large ones, with a diameter greater than 20 mm, have 4 grooves);
- core, which gives the tap rigidity and strength.
Die work
Dies are used to process the outer cylindrical surface. Among the features of its application, the following points can be noted:
- The workpiece is secured in a vice. It must remain stationary during operation.
- Before using the tool, the cutting edge and the surface being processed are lubricated with oil.
- As a rule, a small chamfer is created on the end surface. It simplifies the process of screwing the die onto the surface to be treated.
- During work, you need to pay attention to ensure that the die does not move. Because of this, the thread may be cut unevenly and the die stroke becomes more difficult.
- For 2-3 turns along the thread, one turn is made in the opposite direction. This ensures the removal of chips from the processing zone and improves the quality of the resulting surface.
After completion of the work, the quality of the working surface is checked. To do this, just screw on the nut, which should have free play.
Machine taps
If the thread is cylindrical or conical, has a pitch of up to 3 mm, and it must be placed in a blind or through hole, then it is recommended to use a machine or mechanical device. Although hand cutting is also possible. Machine taps have very large shanks and tap sizes.
If the threading process is carried out on a part made of high strength steel, then a set of two sets of taps will be required. For workpieces made of structural steel, the use of one tap is permissible. This also applies to cast iron parts.
This type of tool is distinguished by the profile of the grooves, designed for quick removal of chips, and the shape of the shank, convenient for mounting in a spindle or chuck.
Clupp work
To carry out the work in question, a clamp can be used. It resembles a die, but is large in size. It is often used for cutting threads on pipes and is supplied in special sets with handles. Among the application features we note:
- The clamp is characterized by high efficiency, so the process of cutting turns is simplified.
- The instructions for using the die and die are almost identical, the only difference is how much force needs to be applied to obtain the required result.
A thread cutting kit is often represented by a combination of nozzles of various diameters. In the manufacture of the working part, wear-resistant material is also used, which does not dull during prolonged use.
Features of internal thread cutting
A thread is a reliable way to connect two parts; this indicator increases significantly if the thread is internal. Tapping is the removal of metal material using cutting edges at different pitches. The operation is performed in one pass. Depending on the intended purpose, swords are divided into: metalworking (metric and inch threads), nut, master and die. By type of thread - left-handed for creating left-handed threads and, accordingly, right-handed.
• method of processing with a tap
The internal thread is applied with a tap, which is made of carbon or high-alloy steel. The tool consists of a shank attached to a cup chuck and a working area - a cutting part with longitudinal and helical grooves. The intake part - the upper part of the cone, carries out thread cutting work. Calibrating part – calibrates the direction of the process. General operating rules:
- • It is not recommended to immediately apply threads to products made by casting or stamping. It is necessary to pre-drill the hole, thereby removing carbon deposits and scale;
- • on drilling machines, the tap must be secured in reversible chucks to avoid the possibility of breakage;
- • mandatory chamfering in those places where work is planned.
Regardless of the cutting method: manual or automatic (on machines), the use of coolant is an important component for obtaining a quality result.
• cutting method on a lathe
The main problem with using taps is chip removal in holes 6 mm and over 16 mm. Due to the limited space, chip removal is difficult, which can cause tool failure. On lathe-type machines, threads are applied using a boring cutter and carbide inserts with a full or partial profile.
Types of thread
The design of the tool has become more sophisticated over time, and today it allows you to create clear internal threads.
The types of threads are determined by the following parameters: purpose, type of profile, pitch size, direction (right, left), measurement system (metric, inch, pipe), location on the part (internal, external), nature of the surface, number of starts.
Classification by purpose
In modern industry, there are different types of taps, differing from each other in design and functionality. According to their intended purpose, taps can be one of the following types:
- Hand taps come in one-, two- and three-set versions. The number of the tap in the set is marked by the number of circular marks on the shank. When processing a product made of particularly hard alloys, such a set can reach five pieces. The working diameters of such tools included in the kit vary.
- Machine taps are designed for cutting both blind and through threads. For good chip separation and for intermittent holes, use a tool with helical grooves: left - for through, right - for blind holes with right-hand threads. They are used on turning, drilling, aggregate and other machines.
- To create threads in through holes, nut taps without reversing by threading cut nuts onto a straight or curved tool shank. Taps with this design feature are used on nut-cutting machines, where nuts are cut in a continuous cycle. As a rule, they work without forced feeding.
- Die taps . Designed for preliminary cutting of round dies before drilling chip exit holes. The intake part is made conical along the entire profile.
- Master taps . Designed for calibrating the threads of round dies after drilling chip holes. The intake part is conical in shape along the entire profile, the calibrating part is cylindrical.
- Combined taps . Designed to perform multiple processing steps. Drilling a hole and tapping through holes without forced feed is feasible if the tapping tool comes into operation after the drill exits the hole.
Thread cutting in light metals is carried out using machine-hand tools defined for this purpose by GOST standards, in which the threads on the calibrating part are arranged in a checkerboard pattern. With left-hand grooves - for holes with right-hand threads, and for blind holes - right-hand threads.
In corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant types of steel, thread cutting is carried out with special tools (GOST 17927-72*).
Cutting titanium and its alloys
You should avoid cutting blind and long threads in holes to avoid breaking the working tool. The threading process becomes easier as the diameter of the hole for the threaded element increases. In difficult-to-cut materials and hardened steels, thread cutting is also performed with carbide tools. Methods of vibration cutting of a threaded element are used.
Important parameters
Depending on the required characteristics, accuracy, permissible surface roughness of the workpiece, part configuration and purpose of the threaded element, the method of manufacturing the part is chosen. This process is also significantly influenced by the manufacturability of the designs of threaded parts.
Features of external thread cutting
Threads are grooves of various geometric shapes, cut with special tools - dies, thread cutters, taps and grinding wheels. The thread is applied either manually or using a lathe and cutter.
• method of cutting with a die and tap
A tap is a screw with straight and helical grooves, designed for cutting internal threads. The manual cutting method requires 3 taps: rough, for applying the initial thread, medium and finishing. The machine cutting method is carried out on lathes and milling machines. The dies are similar in shape and appearance to a nut; on the inside of the tool there are conical cutting teeth for cutting external threads. They are divided into round, square and hexagonal shapes. According to the design - solid, split and sliding. To ensure smooth passage of the die through the part, it is necessary to remove the chamfer.
• turning method
In production, threads are cut using a lathe and a special tool - a thread cutter. For each product, an individual indicator of the helical pitch is established; it is determined by measuring the distance between adjacent turns. The part is placed in a lathe, and as the workpiece rotates, the cutter moves along all axes, creating a helical surface. Based on their design features, thread cutters are divided into: prismatic, rod and round/disc. The thread profiles used are triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal, thrust and round geometric shapes.
Tips for making parts
When cutting a threaded external element, it is important to follow safety precautions. You must also follow the following recommendations:
- Before cutting the external threaded element of the workpiece on the rod, you need to remove the chamfer, install the die evenly without distortions, and be sure to lubricate the workpiece with oil.
- If the rod is bent, you can remove the defective part of the alloy and start threading again.
- If the hole is machined with a tap, then it must be drilled perpendicular to the plane of the part, the chamfer must be removed, and the rough tap must be lubricated with oil.
- When choosing taps, it is better to pay attention to the markings of the tool and opt for products made of high-speed steel. This steel is stronger and less prone to failure.
- If the internal thread cutting tool breaks, you must use a special tool to remove it from the workpiece.