In the production of rolled metal, two methods for producing steel sheets are widely used - hot and cold rolled.
These metal processing technologies have several significant differences. Therefore, finished products also receive different performance qualities and physical properties, which determine the further scope of the materials.
The first difference concerns the grades of steel alloys used: 09G2S steel (low carbon)
, and for cold
08PS (carbon)
.
From the buyer's point of view, the main difference between hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets is their cost, which is significantly higher for cold-rolled steel sheets. As practice shows, the increased price is due to a more complex production process, as well as the use of more functional equipment.
What is sheet metal?
Thin-sheet metal products are made from carbon steel. The thickness of the sheets can be from 0.4 mm. This is a very thin rolled material used in special high-tech work. Modern production technologies and improved chemical composition ensure high quality products. The flawless surface that thin metal sheets have does not require additional processing before applying paint and varnish, which saves time during work.
Production of cold rolled sheets
At the beginning of the production cycle, the steel billet goes through the stage of cleaning and leveling the surface, then heating, which helps to increase the ductility of the metal and allows for hot rolling, during which the metal takes the form of rolls of thin sheet thickness.
The resulting metal sheet is subjected to etching, since the surface of the material receives scale after exposure to high temperatures, after which the sheets are welded (if it is necessary to obtain a large-sized product), as well as the longitudinal edges are cut.
Further technology involves rolling blanks through continuous machines or equipment with a reverse operating cycle, as well as annealing. The goal of production is to produce a continuous thin sheet of steel, which is then cut into sheets of the desired size.
Metal sheet production
Metal sheets are produced by cold or hot rolling. The hot-rolling method uses low-alloy and carbohydrate steel. In this case, a perfectly flat surface is not obtained due to its uneven cooling. These thin metal sheets are used for the manufacture of household appliances, housings, aircraft, construction and mechanical engineering.
The cold-rolling method involves the use of hot-rolled billets made of carbon and low-carbon steel. After undergoing additional processing to remove scale, the sheet is cold rolled. The result is a thinner metal sheet with high surface quality, a thickness tolerance of no more than ±0.01 mm and improved technological properties. It is subsequently used for the manufacture of various machines and mechanisms. In any case, the production of sheet metal requires the use of specialized equipment.
.. | Sheet steel. Types of metal sheets
Sheet steel
.
Types of metal sheets
Steel sheet
widely used in the construction of buildings, structures, pavilions, for roofing, for the production of parts using stamping, for the production of various structures, billboards, furniture, fencing, ventilation systems, automotive, shipbuilding, carriage building and even tank building, in many industries, chemical industry, interior design and for private needs.
Metal sheets are easy to use, durable and practical.
Sheet steel varies in sheet thickness
: thin-sheet (sheets up to 3.9 mm) (
thin metal sheets
) and thick-sheet (from 4 to 160 mm).
By type of sheet metal
divided into:
cold-rolled sheet
and
hot-rolled steel sheet.
According to the production method, sheet steel is divided into:
- smooth sheets: galvanized and non-galvanized;
- corrugated (with rhombic and lentil corrugation - lentil corrugated leaf
);
- expanded metal sheets;
- perforated sheets;
- corrugated sheeting
Sheet steel is supplied in sheets and rolls; these products are sold mainly in sheets.
Also sheet metal
varies:
- according to standardized characteristics into categories (from 1 to 5),
- according to the quality of surface finishing into groups (from 1 to 4),
- according to the nature of the edge: for sheets with a cut edge and with an uncut edge,
- in terms of rolling accuracy,
- by flatness,
- according to the ability to draw,
- By metal sheet sizes
.
Smooth non-galvanized steel roofing sheets
valued for its high resistance to environmental influences and mechanical stress.
The only minor disadvantages are the need for periodic painting and low fire resistance. The most popular and cheapest iron sheet
is
hot-rolled sheet
.
Hot rolled steel GOST 19903 74
is produced by deforming heated steel by rotating shafts under high pressure and in a hot state (temperatures above 760 degrees C are used), then the sheet is cold rolled to improve quality.
Hot-rolled sheet steel
is made from high-quality steel and ordinary-quality steel according to
GOST
16523 steel, ordinary-quality carbon
steel hot-rolled sheet
GOST 14637, high-strength
hot-rolled steel
GOST 19281, high-quality
steel hot-rolled steel sheet GOST
1577.
Metal sheets
up to 12 mm thick inclusive are supplied mainly OJSC Novolipetsk Metallurgical Plant; more than 12 mm - OJSC Severstal and OJSC Chelyabinsk Metallurgical Plant.
In addition to its extensive use in many types of construction and production, hot-rolled sheets
are used for the production of expanded metal sheets, welded beams, electric-welded and profile pipes and angles.
Cold rolled sheet metal
much stronger than hot rolled and has a cleaner appearance.
It is produced by rolling between rollers until the sheet is deformed, then the workpiece is fired. Cold-rolled steel
in accordance with
GOST 19904 90
is produced from general purpose steel in accordance with GOST 16523 and steel for cold stamping in accordance with GOST 9045. The main supplier of cold-rolled sheets in Russia is the Novolipetsk Iron and Steel Works. Various parts are made from such a sheet using stamping.
Galvanized sheet
It is used in any conditions and any climate due to its resistance to corrosion, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature changes.
It has a relatively low price, and is amenable to many types of processing and is durable. Galvanized sheet steel
is used in the manufacture of stairs, partitions, roofing, balcony railings and other metal structures, in medicine, the food industry, mechanical engineering, as decorative elements of the facade, in the construction of granaries and much more.
Depending on the uniformity of the coating layer of metal sheets,
galvanized steel
is supplied in normal and reduced thickness variations.
And also sheets are distinguished with a crystallization pattern (CR) and without a crystallization pattern (MT). Galvanized metal sheets
are produced according to: GOST 14918,
galvanized steel GOST
R 52146,
sheet GOST
R52246,
rolled sheet
GOST 54301,
metal sheet GOST
17066, GOST 24982 and specifications by such plants as OJSC NLMK and OJSC MMK.
Manufacturing of metal sheets
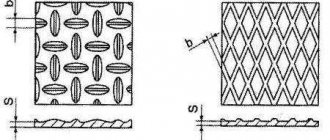
with lentil and rhombic corrugation in accordance with GOST 8568 are made from carbon steel of ordinary quality with a chemical composition in accordance with GOST 380. On the surface of
the corrugated steel sheet
there is a diamond or lentil pattern (crosswise).
Corrugated sheets
are used for the manufacture of steps, decking platforms to prevent slipping when walking on the surface, also for strengthening walls and floors before plastering the latter, for the production of various containers and in ventilation systems. The main producers of such sheets are OJSC NLMK, OJSC Severstal, OJSC MMK.
Expanded metal sheet
, as mentioned earlier, is made from hot-rolled sheet, which is scored and then pulled out to create cells.
This kind of iron sheet
is used for enclosing structures, sifting small rocks, etc.
Corrugated sheet
obtained by rolling thin rolled sheet steel.
It is used for metal roofing
, building cladding, for the construction of various fences and as
sheets for fences
, internal partitions and walls.
Sheets with waves not only have an attractive appearance, but due to the waves they are more rigid and durable, reliable in joining, and easy to install. The corrugated sheet
has a coating, so this
sheet iron
is able to resist corrosion. The profiled sheet has good thermal conductivity properties and has a wide range of colors, which are determined according to the international RAL system. Corrugated sheeting is produced in accordance with GOST 24045 and TU.
Perforated metal sheet
differs from an ordinary smooth
sheet of iron
by the presence of holes: round, square, rectangular. There are also stainless steel sheets and sheets with an admixture of alloying components to steel: copper, nickel, aluminum, brass, tin. Our company supplies perforated sheets, stainless steel sheets and sheets with alloying components only upon order and is not stored in the company's warehouses.
Steel sheet weight, sheet metal weight
cold-rolled
,
for
metal sheets,
for
corrugated sheets,
for
corrugated sheets, price for hot-rolled sheets and other information
you can see on our website.
buy sheet metal
.
Properties of metal sheet
Sheets made by hot-rolled and cold-rolled methods differ in their properties. These features are taken into account when using this building material. Hot-rolled sheet has increased rigidity, so it is practically not amenable to stamping and embossing. Welding such a sheet can lead to its thermal deformation.
The popularity enjoyed by thin metal sheets is explained by the presence of a large number of positive characteristics, such as reliability, versatility, strength, durability, ease of installation, etc. Galvanized sheets (coated with one or more layers) are especially in demand in the production of equipment, construction and the medical industry. both sides with zinc). The surface of such a sheet with high-quality galvanization is very clean, smooth, without the slightest cracks.
How is hot rolled sheet made?
The production cycle of hot-rolled sheets is significantly shorter and often includes only running a heated metal bar on a hot-rolling machine. Throughout the entire production cycle, it is necessary to maintain a consistently high temperature for rolling sheet steel.
The finished product has scale, and the thickness of the sheet is significantly greater (it is impossible to obtain sheet steel less than 0.5 mm by hot rolling). Depending on the applicable GOST, the resulting hot-rolled steel coil is subsequently subjected to edge trimming and cutting into sheets of the required size.
Application
Rolled sheets are used in a wide variety of production areas. It is almost impossible to name an area where thin metal sheets would not be in demand. This includes the construction of fences, roofs, and wall cladding, the manufacture of stairs and metal structures. Rolled sheets are used for the manufacture of refrigerators, various containers, and drainpipes. This material has recently been in great demand for decorating summer cottages. It is impossible to imagine the creation of cars, airplanes and other equipment without it.
A thin metal sheet with a wavy surface, so-called profiled or corrugated, is used for roofing and fencing. It is made from galvanized steel. Waves can have very different shapes - rounded, trapezoidal and others, and also differ in height and width. Rolled sheets also serve as raw materials for the production of other building materials (corrugated sheets, metal tiles, etc.).
A very thin sheet of metal is called foil. In radio engineering, copper foil has been used as packaging for confectionery products, and aluminum foil has been used for packaging tea. Its thickness is no more than 0.2 mm.
Hot rolled or cold rolled steel. What to choose?
So, there are two types of metal sheets - hot-rolled (hot-rolled) and cold-rolled (cold-rolled). What is the difference between cold-rolled steel and hot-rolled steel?
We will highlight three main differences that will influence the choice of one sheet or another:
- Thickness,
- Accuracy,
- Strength, ductility.
Sheet thickness
Hot rolled sheet is much thicker than cold rolled sheet. You won't find hot-rolled sheet thinner than 0.5 mm. The thickness of hot-rolled sheets reaches 200 mm, while the maximum of cold-rolled sheets is only 5 mm. This is due to the fact that cold-rolled sheets made from hot-rolled billets undergo several stages of processing. First, scale is removed by etching, and only after that the sheet is transferred to the cold rolling mill. This is why cold rolled sheet is thinner than hot rolled sheet.
Precision manufacturing
This parameter is higher for cold rolled sheets. Hot-rolled steel is characterized by a high thickness error, as well as unevenness over the entire surface. This is due to the fact that after heat treatment, the canvas warps, and it must be additionally subjected to the straightening process. When the metal cools, the sheet shrinks, which reduces the accuracy of the size and shape of the product. For example, the corners of the sheet may be more rounded than those of the compared cotton sheet. Do not forget: scale is often found on the surface of hot-rolled steel.
Cold-rolled sheets have higher accuracy in their parameters; they are uniform in thickness, have no scale, and the surface itself is smooth.
In the table below you can compare the deviation parameters of sheets with different rolling methods.
| Hot rolled steel | Cold rolled steel |
| Rolled thickness from 0.4 to 160 mm (actually from 1.2 mm) | Rolled thickness from 0.3 to 5 mm (actually up to 3 mm) |
| Maximum deviations in thickness from 0.1 to 0.4 mm for thin sheets | Maximum deviations in thickness from 0.02 to 0.23 mm |
| Limit deviations width from +10 to +15 mm | Maximum deviations in width +5 to +10 mm for normal accuracy +2 to +7 mm for increased accuracy +2 to +3 mm for high accuracy |
| Limit deviations in flatness of rolled products per 1 meter of sheet length from +8 to +20 mm | Limit deviations in flatness of rolled products per 1 meter of sheet length +5 to +15 mm |
Strength
The heterogeneous structure of heat-treated steel affects the strength, which is unevenly distributed throughout the sheet. But at the same time, the deformation residual stresses are lower than those of cold-rolled sheets.
During the processing of cold-rolled sheets, the surface of the metal becomes more durable, which increases its mechanical properties. Cold-rolled sheets crack less often when bent, and by choosing softer grades of steel, their ductility can be increased.
Methods for processing thin sheet metal
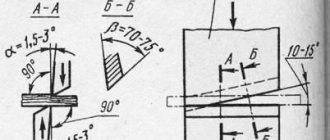
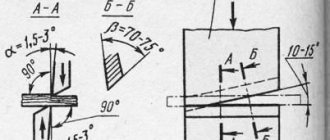
When manufacturing a product of a certain configuration, it is necessary to carry out appropriate processing of the sheet profile. As a result, the appearance of the material and its quality should not be affected. There are several different processing steps that are used to process thin sheet metal. This includes welding, cutting, bending, etc.
The most common processing method is bending. Performed by stretching and compressing the outer layer. It can be manual, when tools such as a hammer, pliers, vice are used, or mechanical, performed on modern equipment. Manual bending is a rather labor-intensive process, so it is performed only for bending thin metal sheets with a thickness of no more than 0.6 mm.
Welding is used when there are no special requirements for the appearance of the product. A metal sheet less than 3 mm thick can be melted quite easily, resulting in holes that are very difficult to weld. Direct current is used to weld sheets up to 2 mm thick. When it is necessary to weld thinner metal, small currents and electrodes of smaller diameter are used.
The range of metal sheets on the construction market is quite large, which allows you to choose the material that best suits the task.
Advantages and disadvantages of cold and hot rolling technologies
Cold-rolled steel, despite its higher cost, is most in demand in industry due to the following advantages:
- Smaller sheet thickness
- Smooth steel surface
- Same thickness over entire surface
- High mechanical strength and metal hardness
- Sheets do not crack when bent
The disadvantages of the method include higher cost and long production cycle.
Hot-rolled steel, among its advantages, has a lower cost and a short production cycle, but in terms of practical properties it is significantly inferior to cold-rolled products:
- Uneven thickness
- Can't get thin sheet
- Cracks occur when bent