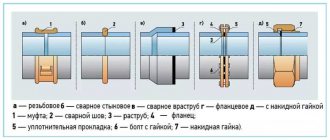
For narrow through parts (pipes, various workpieces), a special processing method is used, which is called mandreling. But what exactly is burnishing of holes and pipes? What are the different burnishing methods depending on certain parameters of the operation? Why would such technology be needed at all? In our article below we will give detailed answers to all these questions.
Burnishing technological process
This process gets its name from a tool called a mandrel. Structurally, it is made in the form of a rod with one or several teeth. Depending on the method of application, mandrels are divided into sliding and rolling tools.
The technological process consists of cold deformation (compaction) of the surface of the part through the movement of the mandrel. Typically, this technology is used to burn holes. In this case, the tool moves along the bore. Due to the created effort, it provides:
- compaction of the internal surface layer along the entire hole;
- improving the quality of the workpiece (remaining roughness is removed);
- The diameter of the hole increases with increasing its accuracy class.
The quality assessment of the technological process is carried out by monitoring the following parameters:
- the magnitude of the tension created;
- speed of tool movement inside the hole;
- values of the force created;
- parameters of the resulting deformation.
The value of the first parameter affects the quality of the resulting surface. It is calculated as the difference between the internal diameter of the workpiece and the diameter of the mandrel used. If the difference is too large, it will not allow you to obtain a high-quality seal and get rid of roughness.
In practice, the maximum interference when mandrating the connecting rod bushing is necessary to obtain the required surface quality of the connecting rod.
Too little tension reduces the speed of work, leads to unnecessary deformation of the treated surface, and the appearance of excessive internal stresses. Therefore, the value of this parameter is calculated taking into account the plasticity indicators of the part and mandrel.
The force required to carry out the work is divided into two components:
- axial (directed along the line of movement);
- radial (acts perpendicular to the axial).
The first ensures the movement of the tool along the hole, and thereby increases the internal diameter. The second determines the quality of the surface being machined (accuracy class after processing)
In some cases, to reduce the friction force, especially in the non-contact deformation zone, mandrel grinding with lubricant back pressure is used.
The burnishing method is used to refine welded pipes. When processing welds, it is necessary to take into account the physical properties of the metal and the wall thickness. Such pipes are used, for example, for hydraulic cylinders. Therefore, after burnishing, strength tests must be carried out. As an indicator, you can use the ultimate strength indicator or the degree of expansion.
This is interesting: Electroplating and electroplating: equipment, types, purpose
Types of burnishing process
Burnishing processing is classified according to the following criteria:
- type of processing (volumetric and superficial);
- technological features (free and non-free);
- method of influencing the inner surface (tension, compression, combined effect);
- the number and location of teeth on the surface of the tool.
The choice of method and type of such processing depends on the characteristic features of the parts. So, to obtain a high-quality surface of trunks or pipes with an unequally rigid sleeve, a method is used to ensure different effects on individual sections of the inner wall.
To process non-axisymmetric workpieces, mandrels with specially located teeth are used.
Free burnishing is used to treat the surfaces of seamless and electric-welded pipes. The wall thickness can reach medium sizes.
Volumetric and surface burnishing
Volumetric processing is carried out by pressure along the entire internal perimeter. To improve the required quality, multi-tooth mandrels are used. They allow you to achieve high processing accuracy up to class 11. The degree of roughness Ra is equal to 0.63 to 0.04 microns.
Surface burnishing refers to methods of surface plastic deformation.
It allows you to obtain the following accuracy indicators: IT from 6 to 9 units, roughness Ra in the range of 0.32-0.04 microns. Volumetric burnishing is used to process straight-seam welded pipes.
Plastic deformation and sizing
This processing method involves exposing the metal surface to a tool that creates pressure at the point of contact. In this case, a consistent change in the internal structure of the metal occurs. Thanks to the processes of sliding and twinning, the structure of layers changes at the level of the atomic lattice. Such an impact leads not only to a change in the external shape of the part, but also its physical and mechanical properties. With a properly developed method of plastic deformation, it is possible to obtain a surface layer with improved characteristics. This circumstance is especially important when it is impossible to subject a metal part to heat treatment, for example, made from austenitic or ferritic materials.
The calibration method is used to process holes in short-length workpieces. For processing, calibrating balls, mandrels, and other calibrating tools are used. In this case, it is pushed through the hole to obtain the expected effect.
In this case, the main parameter for assessing the technological impact is the interference. It is created due to the difference between the internal diameter of the hole and the diameter of the tool. Depending on the problem being solved, calibration is performed with a small or large interference.
When calibrating with a small interference, only the surface layer is affected. Pipes, bushings, and liners with thick walls are subjected to this treatment. The most acceptable ratio of the wall size to the hole radius is more than 0.5.
The use of a large tension leads to an increase in the depth of impact and can extend to the entire thickness of the workpiece. This leads to an increase in the internal diameter, a change in external dimensions, a decrease in the quality of processing, and the occurrence of uneven internal stresses (changes in physical and mechanical properties).
To carry out calibration, it is necessary to carry out high-quality pre-processing. As a result of subsequent calibration, processing accuracy increases by 30%. For example, for steel the accuracy class increases by two units, for bronze by 3, for cast iron by one class.
Shock pulse method
It is based on measuring the parameters of metal deformation after exposure to pulsed mechanical action. At the moment of a short-term impact, ultrasonic vibrations occur, which cause compaction of the surface of the workpiece.
This method is successfully used in the production of long products. For example, mandrel blasting of pipes is carried out using the shock pulse method.
The use of various burnishing methods makes it possible to process the internal surfaces of products of various lengths and arbitrary diameters. As a result of processing, it is possible to obtain a high quality surface layer, without heating and mechanical impact (milling, countersinking, etc.).
What is burnishing?
During operation, the surfaces of metal parts experience severe loads that are practically not perceived by the internal layers of the products. It is the layers on top that counteract a variety of negative influences, ranging from thermal effects and corrosion to wear of parts.
Burnishing, as a process of effective surface treatment, was created precisely in order to level out all of these manifestations, thereby increasing the level of wear resistance and reliability of metal products.
Mandrelization is an innovative option for processing the holes of parts using the method of local cold deformation, performed using plastic technology. Its essence is as follows: the mandrel (a special working device) moves inside the barrel of the product and, due to tension, provides:
- modification of the geometric parameters and shapes of the part in general and its cross section in particular;
- high-quality leveling of existing roughnesses;
- strengthening the surface layer of the metal.
The value of the transverse diameter of the hole of the workpiece is always less than the cross-section of the mandrel by the interference index.
Burning parameters
The process of workpiece deformation is accompanied by the following indicators:
- ordinary and relative interference;
- the speed of the deformation process;
- the force with which the deformation is performed;
- relative deformation.
Preference is the main indicator of burnishing of the hole being machined. It is determined by the difference between the diameter of the hole in the part and the cross-sectional size of the tool used. If the parameter value is too large, then further processing of the product will be impractical. The coating may end up with an insufficient degree of roughness.
Preload operation diagram
When choosing the tension, the strength and ductility of the workpiece are taken into account. The value of the relative mandrel interference is obtained by dividing the hole size by the normal interference.
To ensure that the result of processing the product is normal, the tolerance on the hole size of the part is compared with the amount of interference. Half of this value should exceed the hole size tolerance.
The mandrel force is the force that the mandrel creates when acting on the walls of a pipe or liner in both radial and axial directions. When the mandrel exerts radial pressure on the hole, the cross-sectional area of the pipe will increase. If the tool exerts force in the direction of the axis, small roughness and irregularities on the inner wall of the pipe are removed.
Relative deformation shows the change in the outer diameter of the workpiece as a result of burnishing. This indicator is measured as a percentage.
Trunk mandrelization – volumetric and superficial
The process of machining holes without removing chips can currently be performed volumetrically or superficially. In the first case, the procedure is carried out over the entire cross-section (transverse) of the workpiece. It allows you to obtain, in one pass of a working tool equipped with several teeth, a roughness value from 0.04 to 0.63 micrometers with a hole accuracy of 11 units on the IT scale.
Volumetric burnishing is recommended for processing long cylinders and tubular products made in the form of sleeves. It successfully replaces the less efficient operation of rough boring of such parts. Volumetric deformation makes it possible to work with pipes of any length, providing the necessary indicator of their straightness.
Surface-type burnishing guarantees a roughness in the range of 0.04–0.32 micrometers with an accuracy of no less than 6 and no more than 9 grades. With this method of deformation, a durable layer is created on the surface, so this technique can replace a number of complex procedures, in particular:
- metal grinding;
- deployment;
- honing;
- ironing.
Varieties
The types of mandrelization mean the free and non-free process of carrying out the operation.
When the mandrel is free, the product, namely its surface, is not limited in the possibility of deformation. This type of process is acceptable for large-scale work with electric-welded pipes or for seamless casting, where the thickness of the barrel wall is determined as an average value. Free mandrel is not suitable for workpieces such as pipes with thin barrel walls. Here, non-free blowing is used, which avoids the following consequences:
- axial displacement of the workpiece;
- decreased stability along the direction of the trunk;
- smoothing metal of insufficient quality.
To implement the non-free mandrel operation, the part is secured in special cages of a rigid and elastic structure before passing through the mandrel.
The use of any of the burnishing methods requires the use of lubricants to reduce friction, speed up the processing process, and avoid damage to the workpiece or tool.
Volumetric and surface burnishing
Mandrelization as a method of processing the bore of a hole, when there is no chip removal process, can be performed superficially or volumetrically.
With the volumetric method, the operation involves the entire workpiece (meaning the cross section). By making one pass with a tool, the working part of which is equipped with several teeth, an actual roughness in the range of 0.63–0.04 microns is achieved with great hole accuracy. Due to its effectiveness, volumetric burnishing is intended to replace a less effective method when workpieces are subjected to rough boring. Volumetric deformation is used to process any types of pipes and cylinders with a long barrel, while the straightness of the products is maintained within the required limits.
The use of surface burnishing makes it possible to obtain a roughness in the bore within the range of 0.32–0.04 microns. The main purpose of the method is to strengthen the surface layer and, possibly, to avoid complex technological techniques: reaming, grinding, smoothing and honing the metal.
Plastic deformation and sizing
The essence of plastic deformation is that a mandrel with a diameter of the working part larger than the bore of the hole is pressed into the latter under the influence of the force of the machine. Calibration of the inner surface of the pipes occurs when the area being treated is exposed to a source of thermal energy for heating and subsequent introduction of the mandrel into the area of the tool. The disadvantage of calibration is the possible change in the parameters of the workpiece and the greater complexity of the process regarding plastic deformation.
Shock pulse method
The method in which the mandrel tool is fed along the bore of the barrel not in a constant translational mode, but in shocks with the same frequency, is called the shock pulse method. This process is very effective, as it reduces the load on the tool and the channel and allows for maximum processing accuracy.
Practitioners in the field of metal processing and anyone who has direct experience with the process of mandreling holes, support the topic in the comments. For beginner craftsmen, your knowledge is invaluable!
Purpose and scope of application of burnishing
As briefly mentioned above, burnishing is necessary to strengthen the surface of the hole shafts, giving them greater strength, thus increasing the wear resistance of the product. All this is accomplished due to the ability to plastically deform the metal throughout the contact zone using a mandrel. There are two types of mandrels: sliding and rolling. Most often, the process occurs when the workpiece is cold.
When the mandrel tool moves along the barrel with a certain level of tension, other problems are solved along with strengthening the walls:
- adjusting the diameter of the hole to the required parameters, the trunks of rectangular holes to the required dimensions;
- getting rid of irregularities and any roughness that were caused by the previous processing of the trunk;
- the ability to form a certain cross-sectional shape, for example, to create slots, grooves or an original pattern on the inner surface.
Mandrelization is used not only in civil engineering, but also in weapons production. With its help, gun barrels of tanks and other vehicles are strengthened and used in the manufacture of cartridges.
When it is planned to apply mandrel to a particular hole, it is important that the mandrel has a diameter larger than the cross-section of the hole's barrel by the tension thickness. All this is calculated very accurately so that there is no rupture of the workpiece.
The main indicators of the procedure for plastic deformation of workpieces
The main parameters of this processing include the following values:
- relative tension;
- interference;
- speed;
- force;
- relative deformation.
By interference, as mentioned above, we mean the difference between the nominal sections of the hole and the mandrel. An excessively high interference can cause a decrease in the final roughness index, which, of course, is undesirable. Therefore, the choice of the tension value is taken as responsibly as possible, taking into account the characteristics of plasticity and initial strength of the parts.
Relative interference is a dimensionless parameter. It means the ratio of the size of the machined or initial hole to the indicator of the mandrel tension.
The strength of the hole making process is divided into two components:
- radial;
- axial.
The first is required to increase the cross-section of the workpiece, which is subject to deformation. This component provides volumetric processing. But the axial force removes the smallest irregularities. It is needed for friction to work.
Relative deformation is an indicator that determines the real deformation of a part along its outer section. This parameter is expressed as a percentage.
The last indicator of the process is the burnishing force. It does not have a significant impact on the amount of wear of the working tool and the quality of the operation.
This is interesting: Chemical chrome plating: technology and implementation at home
Mechanical parameters and basic circuits
The worker must take into account many technological parameters of the operation, since an accidental deviation from the norm may significantly change the technical parameters of the processing, which will lead to a violation of the accuracy of the procedure.
Preload
One of the main parameters is tension. From a technical point of view, interference is the difference between the dimensions of the original hole and the mandrel tool (usually this indicator is measured in millimeters, and the diameter of the pipe and the diameter of the mandrel are used as the measurement object). If the interference is too large (that is, the mandrel and the hole are very different in size), then it will be problematic to make a smooth, hard surface. Also, when processing, you need to take into account some features of the material from which the pipe is made - ductility, hardness, and so on.
Force
In addition to the tension, the force of the burnishing is of great importance, which means this parameter means the intensity of the hole machining
Please note that there are two types of mandrel force - radial and axial. By radial force we mean the degree of influence of the mandrel in the perpendicular direction. This indicator reflects the degree of expansion of the pipe diameter during processing
This indicator reflects the degree of expansion of the pipe diameter during processing.
Axial force refers to the impact of a tool along its axis. The higher this indicator is, the easier it will be for the mandrel to cut off various roughnesses
Also note that relative deformation must be taken into account when processing. This indicator reflects the degree of increase in the outer part of the part
Scheme selection
Also, before processing, it is necessary to choose a mandrel method - the tensile method, the compression method or a combined method. Each technology has its pros and cons.
The most popular is a combined tension-compression method. What is the reason for its popularity? It does not create the excessive axial loads associated with conventional tension or compression methods. Thanks to this, processing is carried out smoothly, which avoids mechanical damage.
However, it must be remembered that the combined method scheme requires special equipment, which is quite expensive. To burnish a pipe at home, you should choose an alternative method.
Purpose and technological features
During the operation of any product, including those made of metal, the main load is taken by its outer surface, while the inner layers remain practically untouched. Such a load, in particular, can be thermal effects, as well as external factors leading to corrosion or intense wear of the metal.
The main task that burnishing, which is a method of processing a metal product, solves is to ensure its reliable protection from the above negative factors. Burnishing is an innovative technology, the essence of which is that the inner surface of holes made in metal parts is subjected to plastic deformation in a cold state, due to which a layer is formed on them, characterized by exceptional mechanical characteristics.
Morn is a tool for burnishing. There are rolling mandrels and sliding mandrels.
Burnishing, performed using a special tool that moves along the inner surface of the hole with a certain degree of tension, allows you to solve the following problems:
- bringing the dimensions of the internal section of the processed product into accordance with the required values;
- elimination of roughness existing on the inner surface of the hole being machined;
- improving the strength characteristics of the metal forming the inner surface of the hole.
If you plan to perform a mandrel, you should keep in mind that the diameter of the hole being machined should always be less than the cross-section of the tool used by the amount of interference.
Examples of parts after burnishing
Volumetric and surface burnishing
There are two types of mandrelization of trunks and pipes, in which no chips are formed - volumetric or surface. When performing volumetric burnishing, processing is carried out over the entire cross-section of the workpiece. As a result of such a technological operation, performed using a tool equipped with several teeth, it is possible to form a surface whose roughness will be in the range of 0.04–0.63 microns, and the accuracy will correspond to 11 units on the IT scale.
Volumetric burnishing scheme for small diameter holes
Using volumetric mandrel, long holes, pipe blanks or products made in the form of sleeves are processed. This operation, which can be used to make holes of almost any length while maintaining their straightness, is a good alternative to rough boring.
Scheme of processing a part by surface burnishing
When performing surface burnishing, you can obtain an internal surface whose roughness will be in the range of 0.04–0.32 microns, and the accuracy will correspond to 6–9 units. When surface grinding a hole, a hardened layer of metal is created on the inner surface of the hole, so this processing technology can be successfully used as an alternative to such complex operations as:
- grinding;
- honing;
- deployment;
- ironing.
Types of burnishing
To process holes using the mandrel method, special mandrel tools are used. Such instruments may differ in a number of parameters.
Examples of basic mandrels - in the form of a ball, with single-tooth firmware (in various configurations), with multi-tooth firmware (in various configurations), set-up installations, in the form of a cutting surface with mandrel teeth.
Volumetric burnishing technology
In this scenario, processing is carried out over the entire cross-sectional surface of a part with a hole. For processing, mandrels with one or several teeth are usually used - this ensures uniform cleaning of the metal surface from various roughnesses.
The main advantage of this technology is the high quality of stripping and versatility. Volumetric mandrel is suitable for processing pipes of any length, various through parts, as well as various blanks in the form of sleeves. The accuracy of the technology is 11 units (according to the IT scale), the final roughness is 0.1-0.6 micrometers.
Superficial
In this scenario, the section or holes are machined only within certain limits. For surface mandrels, ball-shaped mandrels are used, as well as special toothed mandrels.
The main advantage of surface burnishing is that as a result of the operation, a layer of thickened metal is created on the surface, which will reliably protect from damage and corrosion (with volumetric burnishing, such a layer is also created, but it is thinner). The accuracy of the technology is 7 units (on the IT scale), the final roughness is 0.05-0.3 micrometers.
Main settings
Experts are guided by the following burnishing parameters:
- normal and relative interference;
- execution speed;
- execution strength;
- relative deformation.
For normal burnishing, the tolerance on the dimensions of the hole being machined should be several times less than half the interference
The interference, which is one of the main parameters of mandrel, is the difference between the diameters of the hole being machined and the cross-sectional size of the tool used. If this indicator is too high, then during the processing it will not be possible to form a surface with the required level of roughness. When choosing this parameter, you should take into account both the degree of plasticity of the product being processed and its strength characteristics. The relative mandrel interference is understood as the value obtained by the ratio of the size of the machined or unprocessed hole to the value of the usual interference.
When mandrating, the force applied to the tool is divided into axial and radial components
The force with which mandrel is performed refers to the forces that the tool exerts on the walls of the hole in the radial and axial directions. With the help of the force exerted by the tool in the radial direction, the cross-section of the hole being processed increases, and the force created by the mandrel in the direction of the axis of the workpiece makes it possible to remove the smallest irregularities from its inner surface.
Relative deformation, measured as a percentage, makes it possible to determine how much the outer diameter of the workpiece has changed during mandreling.
Those. burnishing process
This process began to be called thanks to the tool, it is called a mandrel. Structurally, it is made in the form of a rod with one or several teeth. Depending on the method of use, mandrels are divided into sliding and rolling tools.
The technological process consists of cold deformation (compaction) of the surface of the part using the movement of the mandrel. In most cases, this technology is used to burn holes. In this case, the tool moves along the bore. Due to the effort made, it provides:
- compaction of the inner surface layer along the entire hole;
- increasing the quality of the finished part (remaining roughness is removed);
- The diameter of the hole increases with increasing its accuracy class.
Technical quality assessment The process is carried out by monitoring the following indicators:
- the magnitude of the tension created;
- speed of tool movement in the middle of the hole;
- values of the force created;
- indicators of emerging deformation.
The value of the first parameter affects the quality of the resulting surface. It is calculated as the difference between the internal diameter of the part being finished and the diameter of the mandrel used. If the difference is very large, it will not be possible to obtain a good seal and get rid of roughness.
A very small amount of tension reduces the speed of work, leads to unnecessary deformation of the surface being processed, and the occurrence of unnecessary internal stress. Therefore, the value of this parameter is calculated taking into account the plasticity criteria of the part and mandrel.
The force needed to perform work is divided into two components:
- axial (directed along the line of movement);
- radial (acts perpendicular to the axial).
The first ensures the movement of the tool along the hole, and thereby increases the diameter inside. The second determines the quality of the surface being machined (accuracy class after processing)
In some cases, to reduce the friction force, especially in the non-contact deformation zone, mandrel grinding with lubricant back pressure is used.
Using the burnishing method, seam pipes are finished
When processing weld seams, it is very important to understand the physical properties of the metal and the wall thickness. Such pipes are used, for example, for hydraulic cylinders. Therefore, as a result of burnishing, first of all, strength tests are carried out
As a criterion, the criterion of ultimate strength or the degree of expansion can be used
Therefore, as a result of burnishing, first of all, strength tests are carried out. As a criterion, the criterion of ultimate strength or the degree of expansion can be used.
This is interesting: Finishing and lapping - technology, tools, materials
Features of plastic deformation and calibration
There is a method of influencing the product by plastic deformation, when the mandrel is pressed into the product. Another popular method is to calibrate the inner surface of pipes by heating the product with an external source in the area affected by the mandrel. However, this method does not simplify, but complicates the process, and does not guarantee the accuracy of the product size upon completion of processing. The technical parameters of the outer surface of the part may be violated.
Drawing
Burnishing is a progressive chipless precision method of metal processing. It is based on the ability of ductile metals to acquire large residual deformations under the influence of internal pressure without destroying the metal of the workpiece, but with a significant change in their original dimensions. In addition, this method reduces metal consumption, the number of operations, and the volume of cutting.
Using burnishing (Fig. 91), you can process holes in parts such as bushings and sleeves made from seamless pipes. The processing consists of the following: a mandrel 1 with increasing diameters of working and calibrating teeth is pulled through a hollow workpiece 2 with an internal surface previously cleaned of corrosion. Under the influence of internal pressure, the part is plastically deformed to the desired size.
Rice. 91
This method eliminates pre-processing. In one or two passes you can get very precise and clean holes. At the same time, the metal is strengthened. This gives burnishing an important technical and economic advantage over other technological processes.
Burnishing reduces the labor intensity of hole processing by approximately 2...4 times, reduces material consumption (seamless pipes) by 15...30%, and increases the durability of processed parts.
The processing process is carried out either on broaching machines or on hydraulic presses.
Shock pulse method
A widely used method is the application of axial vibration to the product using shock pulses. This method reduces mandrel forces and increases the accuracy of hole dimensions; pulses make the tool advance inside the part easier, especially in long pipes.
The essence of the method is that the product processing process occurs when a lubricant is applied to the inner walls of the pipe:
Shock sensors
- the workpiece moves cyclically in pulsating movements;
- when using shock pulses, lubricant is not supplied continuously, but in small portions;
- At the same time, an additional force acts in the opposite direction of mandrel movement at the moment when the lubricant layer on a local section of the workpiece decreases.
If you apply lubricant to the walls of the product in advance, the moving tool will displace the lubricant and dry friction of the contact surfaces will occur. This will lead to the appearance of unnecessary build-up on the tool and scratches, which will significantly reduce the quality characteristics of the workpiece after processing.
It is worth noting that the proposed method of drilling a hole significantly improves the quality of the internal surface of the workpiece and reduces the possibility of sample deformation due to the supply of lubricating fluid to the contacting elements. As a result, a protective film is created on the surface, which ensures the strength and reliability of the part.
Burning schemes
There are the following schemes for metal processing of workpieces by mandrel:
- by stretching;
- compression method;
- combined application of tension and compression of the sample.
It is important to choose the right workpiece processing scheme. The circuit will determine the axial stress values of the product.
Using a scheme based on tension or compression, a force is applied to the workpiece over a certain segment. The mixed burnishing scheme distributes the load over the entire inner surface of the workpiece.
Volumetric processing of a part is carried out according to other schemes:
- passive;
- neutral;
- active.
The listed mandrel schemes influence the value of the axial stress and require special mechanisms - movable supports that make it possible to limit the shortening of the part when exposed to the mandrel. As the interference value increases, the degree of roughness of the inner surface of the workpiece will decrease. This technique involves pre-machining the hole before using the mandrel.
Dorns use two types of movement:
- rocking;
- slip.
The tool moves inside the workpiece with a given tension value using lubricant. To improve the processing result and reduce the mandrel force, lubricant is supplied inside the hole towards the movement of the mandrel by spraying.
The device for performing vibration processing of metal products consists of:
- dorn;
- a vibrating support, which allows you to fix the sample on it;
- hydraulic drive;
- piston
Dorn - device
The device effectively processes the inner walls of bushings, liners and cylinders.
Technological diagrams
Mandrelization, which, if you have the appropriate equipment and tools, can be done at home, is carried out:
- by stretching method;
- compression;
- by combining the two above methods.
Schemes for mandating holes
The choice of technological scheme for burnishing affects the amount of axial load to which the workpiece will be subjected. If such a load is too large, it may cause axial stresses to occur in the workpiece.
When using a tension or compression scheme, the load created by the mandrel falls on individual areas of the treated surface, and the combined method allows the load to be distributed evenly.
Scheme of deformation during surface treatment with a multi-tooth mandrel
Recently, volumetric mandrelization is increasingly being performed using innovative schemes involving the use of passive, neutral and active counter-tension. Such schemes, which are quite difficult to implement at home, require the use of special supports that serve as tensioning movable mechanisms.
In order to obtain a hole with lower wall roughness as a result of burnishing, it is necessary to perform such a technological operation with a higher interference or to carry out preliminary mechanical processing of the hole.
Source
Types of burnishing depending on the fastening of the part
Burnishing can be non-free or free - depending on whether the original parts are fixed on the machine or not during processing.
The free-processing technology is simple, but has a number of disadvantages, and the main disadvantage is that it is not suitable for processing thin-walled products. However, in practice, free technology is very often used when mandrating seamless or electric-welded pipes.
The non-free burnishing technology is more preferable, although less practical, and it is suitable for processing pipes with any wall thickness.
With non-free mandrel, parts are fixed on the machine - this allows you to achieve the following effects:
- The shape of the part is completely preserved, the formation of any random bends, zigzags and irregularities is completely excluded.
- The stability and hardness of the part in all directions is completely preserved (this is especially critical in the case of the longitudinal direction).
- The surface of the part is completely cleaned of various irregularities and defects; non-free mandrel ensures high-quality processing.
To carry out non-free burnishing, the part is secured in a special vise-holder. They must meet a number of requirements - high elasticity, very high rigidity (otherwise the part will slip). If it is necessary to reduce the diameter of pipes, then mandrel burnishing can be combined with cold reduction technology - a similar practice is widely used at factories in all post-Soviet states.