Diamond is known to be one of the hardest minerals on earth. That is why the most effective tool for processing materials with high strength is a diamond drill. There are many types of diamond drills on the modern market, differing in both design and manufacturing technology.
Properties of porcelain stoneware
High hardness (6-8 units on the Mohs scale, up to 6 for granite) and strength are advantages when using it, but mechanical processing is difficult, further complicated by the fact that this material is quite fragile. For example, making a hole in it is not at all easy, unless the choice falls on diamond drills for porcelain tiles such as Hilti or Bosch.
In addition to hardness, porcelain stoneware is resistant to abrasion, waterproof, resistant to temperature changes and aggressive environments.
This is interesting: Fuel pellets (granules) - varieties, features, production
Introduction to drilling porcelain tiles
A hole in this material can be drilled with special diamond bits:
- crowns in the form of ring drills;
- drills obtained on the basis of vacuum sintering;
- drills based on sintered diamonds.
Diamond fines are electroplated onto the crown, which makes this powder more crowded than with vacuum processing. The most attractive feature of such a product is its affordable price.
The advantage of these means is the low end pressure during operation, the disadvantage is their short service life. One such crown can make only 5-6 holes in 8 mm thick tiles.
Vacuum sintered diamond enriched drills are the most reliable tool due to the dense concentration of diamond particles firmly sealed into the metal base.
Such diamond drills for porcelain stoneware, operating at high speeds, have a resource of 70 drillings by hand, 135±15 by machine, 325±25 by “wet” technology.
Expanded clay is also processed using ring drills for concrete. However, they are effective only with significant axial forces and low speeds. Their advantages include greater stability: it is possible to perform up to one hundred drillings with one drill.
Peculiarities
In modern conditions, a diamond-type drill is manufactured in different ways. The features of the tool depend on the technology. By sintering and processing using powder metallurgy methods, high-quality, wear-resistant instruments are obtained . But this technology can only be used to make large-scale models, for example, ring drills. Thus, the resulting products are monolithic, extremely durable, but voluminous. If you make small cutting zones using this technology, the tool will turn out to be fragile, and mechanical stress will quickly damage it.
Electroplated with diamond-type coating. Tubular-type diamond drills with a conical cutting tip are made with coating using electroplating equipment. This technology makes it possible to create small diamond-coated tools of complex appearance and design. The grains here are arranged in one row, so the durability is low, especially on the cutting tips of the tool. The resource of such a product is small, but the cost is quite affordable.
Diamond-type tips do not require cooling and constant sharpening; periodically during operation you need to reduce the speed. As for the parameters, all drills differ in the following characteristics:
- cutting zone size;
- length of the working part;
- shape;
- number of segments;
- cutting method.
As for the advantages of such drills, they include:
- possibility of reusable use;
- the quality of the holes created;
- variability of tools.
Tubular diamond drills
The tool, according to GOST, is intended for processing and forming holes in concrete and reinforced concrete structures. In practice, the drill is used to work with metals and alloys of increased hardness, as well as when drilling hard and brittle materials. Use in the latter case is justified if you need to drill holes of large diameter.
A tubular drill consists of two elements:
- diamond ring - a ring crown with a diamond-bearing layer on the edge, which represents the cutting part of the tool;
- extension - a cylindrical body onto which the ring is attached. The extension can be provided with side openings for solids removal and cooling.
The main difference between a tubular drill and options with other shank shapes is the reduction in axial load. This feature reduces wear, and therefore the consumption of diamonds, and increases productivity.
Advantages of diamond wall drilling
Despite the fact that this technology is still quite young, it is already very popular all over the world due to its many advantages:
- Using diamond drilling, you can cut holes of various diameters (up to 600 millimeters) and depths (up to several meters).
- The tool does not cause vibrations inside the wall.
- When drilling, almost no dust is formed, and what is formed is immediately washed out of the hole with water.
- The drill can be positioned at any angle to the surface, not just straight.
- Diamond core bits provide the highest drilling accuracy—in practice, the discrepancy with the design dimensions is rarely more than 1 millimeter.
- The resulting holes do not need to be sanded or processed in any other way, since they already have straight and smooth edges.
- The technique works very quickly - in a minute, a high-quality crown can go 6 centimeters deep into the wall.
- When drilling through a wall, its reverse side is not damaged: no cracks occur, and the plaster does not peel off.
Areas of application
Diamond-type tools are effective in processing various surfaces and materials that other tools are powerless to handle. The characteristics of this type of drills make it possible to successfully create holes in high-strength materials. They are used in the following works:
- for concrete, including for drilling in reinforced concrete structures;
- on tiles;
- on ceramics;
- on granite, suitable for porcelain stoneware tiles;
- on glass;
- on brick;
- on stone of natural and artificial origin.
It is most convenient to drill various types of tiles Drills are used to install electrical sockets and create optical and radio-electronic devices. Diamond tools are used in construction and mechanical engineering, and actively; it is impossible to replace them in these areas.
As for household use, diamond drills are also used here; they are used for drilling in glass, mirrors, various types of tiles, stone and concrete structures.
How else can you form a hole in granite?
A stone drill, which is used to form a hole in granite, can be made from a tube made of non-ferrous metal. This method, compared to the option that uses diamond drills, is more technically complex.
How to drill granite correctly using a non-ferrous metal tube?
- Around the center of the future hole on the surface of the granite, it is necessary to form a side with a height of at least 5 mm, for which you can use ordinary plasticine or the middle part of a plastic bottle.
- Diamond dust, corundum or pobedite powder must be poured into the inner part of the formed side.
- Water is poured into a bath formed by the side and filled with abrasive powder. To constantly replenish the water level in such a bath, it is necessary to prepare a separate vessel in which it will be contained in sufficient quantities.
Drilling granite using this method alone is problematic, so you will need the help of another person who will ensure that the tray formed around the hole is constantly filled with water. Drilling when using this technology is also performed at low speeds.
This is interesting: Press for cold-pressed oil: making it yourself and using it at home
Core drilling bits. I want to core rather than drill a hole, is this possible?
Diamond core drills, despite their name, are primarily designed for drilling holes rather than taking cores. However, many artists and scientists use them to extract the core of a fossil, say, for DNA testing, and do so with great success.
Some diamond drills are designed and manufactured solely for the purpose of intentional core extraction. Thin-walled diamond core drills are designed for drilling precision holes in delicate and thin hard materials such as plate glass, optical glass, thin pieces of stone, and for extracting precision rods.
When purchasing a core drill, the diameter size given represents the hole size you could achieve, so if you are using them to make a core drill, you will usually need to order one or two sizes larger, check the technical information on the product page for these specifications.
Mosaic and stained glass artists also use core drills to remove the core, leaving them with a circle of stoneware, tableware, porcelain or glass to add to their projects.
Jewelers use the drilled rod as beads. You can file the bottom of the core with a diamond file to ensure the tiny tile sits smoothly in your design, or use a file to remove burrs and rough edges if you are using them for beading.
Try making beads from the core left over from a 4mm diamond drill bit. Once you have removed the core, use a small 1.25mm diamond drill bit to drill another hole through which to thread the wire.
How to drill granite
Granite stone is a natural material, during the processing of which certain rules must be followed. The peculiarity of the material is that it is fragile and hard at the same time. In order to properly process a slab, you need to know how to drill granite, what are the methods and rules for drilling this non-metallic material. With this knowledge, you can drill without damaging the stone or compromising its integrity.
Main types
Diamond type tools are available with a variety of attachments in shape and diameter. They can be universal or designed for a specific material. The working part may look like this:
- in the shape of a cylinder - this is what a ring and tubular drill looks like, the possible diameter range is from 32 to 350 mm;
- in the shape of a ball;
- the cone shape is a traditional look, visually reminiscent of drills on metal surfaces;
- in the shape of a feather (spear).
To ensure rotation, you can use machines, electric screwdrivers, screwdrivers, drills. The rotating speed will depend on the diameter and material. The smaller the diameter, the higher the speed. For example, drills with a size of 1 to 3 mm will provide a speed of 6 thousand revolutions, and with a diameter of 25 to 50 mm - no more than 1200 revolutions. To drill stone, glass, ceramic and tile surfaces, use conical drills from 20 mm to 85 mm.
It is very important to choose the right tool to ensure accurate holes and neat workmanship. It is also necessary to follow technological recommendations. An important factor is the choice of drill manufacturer. These three parameters determine how long the tool will last and whether you will be satisfied with the quality of the work performed.
Popular manufacturers
There are a sufficient number of reputable manufacturers of diamond drills on the modern market. Among them there are many worthy foreign and domestic companies.
- "MonAlit", Russia. They offer drills in sizes from 3 to 700 mm. The work resource is the highest.
- Hawera, Germany. Drills of high durability, different but not too large diameters, self-cooling.
- Bosch, Germany . They produce high-quality dry drills intended for processing wood, brick, concrete, and ceramics.
In addition to these manufacturers, you can safely purchase products from the following companies: Makita, Metabo, Stayer, FIT. The tools of these companies are reliable, although the price is quite high. Among the Russian brands, Enkor, Zubr, and Interskol stand out. You can also consider buying a drill from Chinese companies, provided that it is quite expensive. In general, in pursuit of cheapness, you can buy a tool that turns out to be disposable. A good diamond-type drill cannot be inexpensive, since serious technologies and expensive high-quality materials are used in their manufacture.
Some manufacturers create drills in the budget category, but most of them are produced with various types of malfunctions and the material used is of poor quality. It is also important to purchase tools from trusted stores, as the market is oversaturated with fakes.
Experts recommend paying attention to the color of the instruments; as a rule, fake ones have a dark shade in comparison with the originals. This is due to violations of the technological plan during manufacturing.
Famous brands
Among the well-known brands of these tools for processing porcelain tiles are:
- Russian MonAliT (diffusion cooking, water cooling, diameter – 3-700 mm). Their resource exceeds the other two technologies by 5 dozen times.
- The German Hawera, based on vacuum soldering, consists of three drills of 6, 8 and 10 mm. The product is highly durable. It has self-cooling properties. They can work without water supply due to the presence of autonomous cooling, no matter how hard the material is.
- Bosch Easy Dry Best for dry drilling, which provides for the presence of coolant supplied when starting work.
So, maintaining the quality of the slot in porcelain stoneware is not at all difficult if you choose the right tool, do not violate the technology and remember the nuances of the process.
Diamond drills - types, features, application
Diamond is known to be one of the hardest minerals on earth. That is why the most effective tool for processing materials with high strength is a diamond drill. In this article, a master
plumber
will tell you about the types of diamond drill bits.
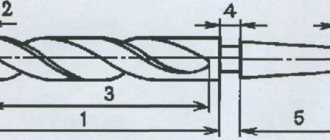
Diamond drills today are produced with various forms of working attachments. So, these could be tools:
- With a cylindrical working part (this includes tubular drills, as well as annular diamond drills);
- With a spherical cutting part;
- Conical type;
- With a working part made in the form of a spear or feather.
The most traditional design has tools with a conical cutting part, which in appearance resemble a regular metal drill.
Used primarily for drilling glass, ceramic and tiles
, as well as stone products, they are produced in the diameter range of 16–85 mm.
The durability of a conical tool (that is, the depth of the hole, after drilling which it is subject to critical wear) is 9–12 meters when working on natural stone and 10–14 meters when making holes in other materials.
Diamond drills do not require constant cooling during processing, and also do not require regular sharpening
. To prevent overheating (which is extremely undesirable), it is enough to periodically dip the tool in a container of water during drilling and carry out processing at low speeds.
| Modes of operation with diamond drills |
Production technologies
Today, two main methods of manufacturing diamond drills are used:
- Sintering, which involves the use of powder metallurgy methods;
- A technology by which diamond coating is applied to the cutting part of the drill using the galvanic method.
Sintering allows the production of cutting tools that are extremely wear resistant.
The most significant disadvantage of this technology is that it can only be used to produce large-sized tools, such as, for example, diamond annular drills. This is explained as follows.
In order to create a durable product using this technology, it is necessary that the gaps between the diamond grains from which such a product is sintered be small. Then the created material turns out to be more monolithic and, as a result, more durable.
In cases where the cutting part of a small drill is made by sintering, such gaps are comparable in size to the size of the diamond grains themselves, which makes the resulting material very unstable to mechanical loads and causes its intensive destruction.
Is it safe to use water near my drill?
It goes without saying that extra care should be taken when using a drill near water.
When drilling into any material, you should always wear safety glasses and protective clothing to prevent injury from flying debris. The same caution should be used when using water near your drill.
Water can be applied to your material through a pump, faucet, dripper, or you can submerge the material in water until approximately 1 cm covers the material you are about to drill.
If you are drilling tiles on a wall, you can squeeze water onto the tiles using a sponge.
If you are drilling into large pieces of glass or stone, you can create a putty ring that will serve as a well for your water.
There are oil-based lubricants, but in our years of experience, we have found that water works just as well, and of course, a lot cheaper!
The viscosity of the dishwashing liquid can help, but add just a couple of drops to the water, you don't want any suds!
The image below is a piece of beach ceramic that we drilled through. The tray is a plastic take-out tray, and the material the ceramic rests on is a homemade abrasive sanding block. We then filled the trough so that the water only covered the piece of porcelain being drilled and only the tip of the drill bit.
Drills for porcelain stoneware: selection rules and guidelines for purchasing
Modern diamond drills for porcelain stoneware belong to one of the following types:
- galvanized crowns;
- sintered annular drills;
- Boers
The first type is mainly used for large holes. With their help, an annular cutout with the required outer diameter is made, and a cylinder of the cut-out material remains inside the extension body.
By means of sintered drills, these special types of these tools, it is possible to perform perforations with large diameters. They are distinguished by a sintered wheel coated with diamonds.
Simple drills are designed for quickly and efficiently making small holes. They have a spiral shape with blades located at some angle, covered with diamond chips.
All instruments have technical characteristics depending on the method of production and fixation of solid particles:
- powder metallurgy;
- galvanic procedure;
- diffuse vacuum technology.
The first technology is valued for ensuring a long service life of drills, electroplating for its affordable prices, and vacuum technology for its strength and performance.
Tool functionality
Drilling on porcelain tiles involves some nuances that should not be forgotten; then the work will be of high quality, and the tool will not be in danger of breaking or premature damage.
To make small holes, special drills with diamond tips are suitable. To protect against overheating and dulling, the drill must be cooled with water all the time. The device must be held at 90°, which is easier to achieve using fixing means.
Before drilling holes, the tool is directed at 45° to the tile, and the already rotating drill is brought in, otherwise, when starting, it will move to the side and spoil the glaze. Drilling the tiles is accompanied by small circular movements, which helps to cool the product more efficiently.
Large holes are made using special diamond-coated porcelain tile crowns. The drilling rules remain the same as when using drills.
Experienced craftsmen, having started drilling, do not interrupt it and complete it. Otherwise, the temperature of the cooling component and the spray will drop, and they will need to be heated again, which shortens the “life” of the drill.
If diamond core bits require “wet” technology, then the use of Bosch diamond-coated drills uses dry technology. Because of this, their use is associated with some features, the implementation of which can extend their life.
Nuances when using
When working with this category of tools, the same rules apply as when using classic options:
- Larger hole diameter means lower number of revolutions. Thus, a hole with a diameter of 1 millimeter is drilled at a speed of 6000 rpm, and, accordingly, 50 or more millimeters - at 100 rpm.
- A certain pressure force. For concrete surfaces it is greater, for glass it is much less.
If these rules are not followed, the diamond-coated drill will quickly lose its useful qualities.
When purchasing a tool, you need to imagine what types of work and on what scale will be performed. And it’s not only about the cost, but also about the resource laid down by the manufacturer.
Simply put, the difference between household and industrial designs of the same category is twofold. For example, a drill for porcelain tiles can be used up to 70 times for domestic purposes, and up to 120 times for industrial purposes.
There is another important parameter - the maximum drilling depth in one pass, after which the product is unsuitable for further use. This characteristic for the material mentioned in this paragraph ranges from 10 to 14 meters, depending on the diameter of the tool. Converting one indicator to another will not be difficult, provided that you carry out constant work with the same material.
How to use diamond tools
Along with a drill, when processing porcelain stoneware, you can use a grinder, a hammer drill, having previously turned off the impact mechanism, a battery-powered screwdriver, a drill lock, etc.
To avoid damaging the drill and breaking the tile, it is recommended to place a piece of board, plywood or chipboard under it. The porcelain stoneware slab is drilled from the façade surface. To prevent the drill from slipping, the drilling site should be marked or a template should be used. It is more effective to cool the drill with a water stream or at least water the contact area.
To extend the life of the tool, porcelain stoneware can be drilled not through, but to two-thirds of the depth. Next, sharply hitting from the drilling side, knock out the resulting cylinder.
Production technologies
Today, two main methods of manufacturing diamond drills are used:
- sintering, which involves the use of powder metallurgy methods;
- a technology by which diamond coating is applied to the cutting part of the drill using the galvanic method.
Sintering allows the production of cutting tools that are extremely wear resistant. The most significant disadvantage of this technology is that it can only be used to produce large-sized tools, such as, for example, diamond annular drills. This is explained as follows. In order to create a durable product using this technology, it is necessary that the gaps between the diamond grains from which such a product is sintered be small. Then the created material turns out to be more monolithic and, as a result, more durable. In cases where the cutting part of a small drill is made by sintering, such gaps are comparable in size to the size of the diamond grains themselves, which makes the resulting material very unstable to mechanical loads and causes its intensive destruction.
Vacuum sintered diamond bits designed for clamping through adapters
Using sputtering technology, which involves the use of galvanic equipment, predominantly tubular diamond drills are produced, as well as tools with a conical cutting part. Using this technology, it is possible to produce miniature diamond-coated drills, even with complex configurations.
The diamond coating created using this technology is characterized by a single-row arrangement of grains, which is why it has rather low durability. This is especially critical for coatings applied to tool cutting edges. For this reason, a diamond-coated drill, which is produced by the galvanic method, has a short working life, but this disadvantage is compensated by the low cost of such a tool.
Inexpensive galvanized drill bits for dry drilling
Circular drills – crowns
In order to make a hole, say, for a socket, other drills are used, which are popularly called “crowns”. So, let's figure out which drill to use to drill tiles if you need to make a fairly large hole.
Ballerina
Ballerina is a rather interesting type of crown. This nozzle is interesting because it can be used to adjust the diameter of the hole. It consists of an axis (centering drill) and a second drill attached to it on a guide, which, moving in a circle, will act as a cutting element. Let's say you need a hole with a diameter of 4 cm, then you set the “leg” to a radius of 2 cm, mark the point where you need to place the centering drill, and you can get to work!
Important! The range of holes that you can make with the ballerina varies from 30 to 90 mm.
An attachment such as a ballerina can be used on both a drill and a hammer drill. Only in the second case will it be necessary to disable the “impact” mode.
In order for the “ballerina” to serve you faithfully for many years, you need to fulfill two simple requirements:
Drill only at low speeds, as at high speeds the drills can overheat and, due to deformation, become simply unsuitable for work;
When working, do not be too zealous with pressure: as with any tool, you just need to guide it, but not press it in any way.
Crown - ballerina
The only disadvantage of the “ballerina” is that it drills the tiles rather sloppily, which results in uneven edges at the hole.
Diamond crown
A diamond crown, by analogy with a diamond drill, is the most expensive drilling option. Unlike a ballerina, you won’t be able to adjust it; you will need to immediately buy exactly the diameter of the crown for the hole you need.
Existing diameters are in the range of 10-70 mm, these are standard values.
The optimal tool for drilling is a stationary machine that is equipped with water cooling, since if you use a diamond bit as an attachment for a hammer drill or drill, then during the drilling process there is a possibility that this “drill” will slip.
Therefore, if possible, purchase a diamond core bit with a special centering drill included.
Tungsten bit
Carbide - tungsten sputtering is an excellent alternative to diamond. The cost of such an addition is much lower, however, the service life is much shorter.
This crown can be used on both tiles and porcelain stoneware.
So, you now know which drill to use to drill ceramic tiles, so don’t waste time, get to work!
| MAPEI grout: characteristics and comparison of epoxy mixture and cement mortar, calculation |
| Do-it-yourself ceramic border installation on a bathtub |
| How to cut tiles with different tools |
| How to clean tiles yourself after renovation |
Symbol
A drill for concrete, according to the materials used for manufacturing, consists of:
The main purpose of a cutting tool in domestic conditions is to create holes with a diameter of up to 6 mm and a depth of up to 100 mm in a concrete or brick structure. The latter material is inferior in strength to concrete, and is also more fragile. Therefore it is easier to process.
Another feature is the frequency of impacts. A hammer drill applies an order of magnitude less force, but an order of magnitude stronger. The noise from the sound of a drill can be roughly compared to the loud itching of a mosquito. Another feature is that the younger brother operates at high speeds, which contributes to the rapid failure of the drill and the tool itself.
GOST 22735-77, developed in Soviet times, regulates the size of hard-tipped drills in the range:
Correct development of laminate flooring installation.
Drills (drills) for hammer drills
As for the properties of drills, crowns and prices: cheap manufacturing companies - “Stayer”, “Fit”, “Anchor”. The price of such drills and crowns is quite low. For example, 6-8mm (the most commonly used) costs about 35-50 rubles. A crown for a socket costs about 300-350 rubles. Expensive branded drills, for example, “Bosch”, cost a couple of times more. And their service life is noticeably longer. Cheap options are completely suitable for the home because they are used occasionally.
Necessary information about drilling tiles.
Kornka for brick, concrete, tile
Crowns for concrete and brick