Add to request
Cart is empty
You haven't selected anything yet
Submit your application
Basket
Total items: 0 items
Make a request
The interstate standard GOST 9940-81 regulates the production of seamless hot-deformed stainless steel pipes for general purposes. The document defines the assortment, technical requirements, acceptance rules, test methods, marking, packaging, transportation and storage of this type of pipe. The standard was introduced back in the Soviet Union, but is still in effect.
This page contains the revised text of the standard. Rework has been carried out to make it easier for the reader to understand. You can always view the original by following the link.
ASSORTMENT
1.1. Pipes are manufactured according to the outer diameter and wall thickness with the dimensions indicated in the table. 1.
1.2. According to the length of the pipe they are made:
measured length - within the unmeasured, but not more than indicated in the table. 1 with maximum length deviation +15 mm; by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to manufacture measuring pipes of a length greater than that indicated in the table. 1;
length, a multiple of the measured length - within the measured length with an allowance for each cut of 5 mm and with a maximum deviation along the entire length of +15 mm. Minimum multiple length - 300 mm;
limited length - within the specified length with a maximum length deviation of +500 mm;
unmeasured length - from 1.5 to 10 m; by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to manufacture pipes longer than 10 m.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
1.3. In a batch of pipes of unmeasured length, no more than 15% of pipes with a length of 0.75 to 1.5 m are allowed.
Official publication ★
Reproduction is prohibited
© Standards Publishing House, 1981 © Standartinform, 2007
Table 1
Notes:
1. Pipes made of steel grades 08X17T, 15X28, 12X17, 10X17N13M2T are manufactured with a diameter of no more than 219 mm; from steel grade 08Х17Н15МЗТ - with a diameter of no more than 140 mm, size 159-9 mm; from steel grade 10Х23Н18 - with a diameter of no more than 168 mm; made of steel grades 08Х18Н12Б, 08Х22Н6Т, 08Х20Н14С2 - with a diameter of no more than 108 mm.
2. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to manufacture pipes with dimensions not indicated in the table. 1.
3. The mass of 1 m of pipes, kg, is calculated using the formula
$—nominal wall thickness, mm;
p - metal density, g/cm3, depending on the steel grade in accordance with table. 3.
4. Pipes with a diameter of 76 to 95 mm with a wall thickness of 3.5-4.0 mm, with a diameter of 133 to 152 mm with a wall thickness of 4.0-5.5 mm, with a diameter of less than 76 mm will be produced after mastering the equipment.
GOST 9940-81 S.
1.4. The maximum deviations for the outer diameter and wall thickness are indicated in table. 2.
table 2
| Pipe sizes | Maximum deviations at | manufacturing accuracy, % |
| ordinary | HIGH | |
| By outer diameter | ±1,5 | ±1,0 |
| Wall thickness, mm: 8 or less | +20,0 | + 12,5 |
| -15,0 | -15,0 | |
| more than 8 to 20 | ±15,0 | + 12,5 -15,0 |
| more than 20 | + 12,5 -15,0 | ±12,5 |
1.5. Ovality should not take the diameter of the pipes beyond the maximum deviations.
1.6. The curvature of pipes in any section 1 m long should not exceed:
1.5 mm - for wall thickness up to 10 mm inclusive;
2 mm - for wall thickness over 10 to 20 mm inclusive;
4 mm - for wall thickness over 20 mm.
1.7. The ends of the pipes must be cut at right angles and cleared of burrs; chamfering is allowed when removing them. At the consumer's request, the ends of pipes with a wall thickness of more than 5 mm must have a chamfer for welding.
Examples of symbols Pipe with an outer diameter of 76 mm, a wall thickness of 5 mm, normal manufacturing accuracy, unmeasured length, made of steel grade 08Х18Н10Т:
Pipe 76 x 5- 08Х18Н10Т GOST 9940-81 The same, high precision manufacturing (in), multiple length (cr) 1500 mm:
Pipe 76 in x 5 in x 1500 cr - 08Х18Н10Т GOST 9940-81 The same, normal manufacturing precision, measured length (m) 3000 mm:
Pipe 76 x 5 x 3000 m - 08Х18Н10Т GOST 9940-81 The same, normal manufacturing precision, measured length 3000 mm with remainder:
Pipe 76 x 5 x 3000 - 08Х18Н10Т GOST 9940-81 The same, high precision manufacturing (c), limited length (g) 3000 mm:
Pipe 76 in x 5 in 3000 og- 08Х18Н10Т TOST 9940-81
Difference from cold rolled.
Seamless stainless steel pipes come in two types: hot-rolled and cold-rolled , produced in accordance with GOST 9941-81 . The difference between these types is the production technology. In the hot rolling method, the workpiece is preheated to a high temperature and then stretched to the shape of a hollow sleeve. Highly heated metal is much easier to mold. However, there is a downside. Due to the fact that the metal is heated to a high temperature and then cools, thermal deformations . A hot product usually does not cool down evenly. In addition, when working with hot metal, it is impossible to accurately predict what dimensions the product will have after cooling. Because of this, the actual dimensions of the received product may differ significantly from those stated in the standard. The pipe may be a little longer, unevenly oval, and so on.
Such deviations are not observed with the cold rolling method, since with this technology the workpiece is not heated. Accordingly, no temperature distortions occur.
In a word, the difference between the two types of pipes is manifested in varying degrees of permissible deviations. Cold rolled ones are more accurate, while hot rolled ones are less accurate.
This minus is covered by one significant plus: hot-rolled pipes are usually cheaper than cold-rolled pipes. This allows you to save money where manufacturing accuracy is not important.
Obviously, if accuracy is critical for the purpose of the project, the cold-formed option must be chosen. Well, if accuracy is not critical, then hot-deformed.
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
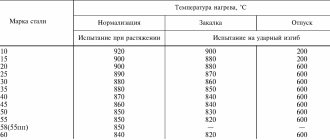
2.1. Pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and according to technical regulations approved in the prescribed manner, from steel grades specified in table. 3, with a chemical composition in accordance with GOST 5632, with microadditives of rare earth metals.
The sulfur content in steel intended for the manufacture of pipes to be welded, as indicated in the order, must not exceed 0.020%.
Pipes are manufactured heat-treated or without heat treatment in accordance with the order. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 4).
2.2. The mechanical properties of pipes must correspond to those indicated in the table. 3.
Table 3
| steel grade | Tensile strength ov, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Relative extension S5 | Density p, g/cm3 |
| no less | |||
| 08X13 | 372(38) | 22 | 7,70 |
| 08Х17Т | 372(38) | 17 | 7,70 |
| 12X13 | 392(40) | 21 | 7,70 |
| 12X17 | 441(45) | 17 | 7,70 |
| 15X28 | 441(45) | 17 | 7,60 |
| 15Х25Т | 441(45) | 17 | 7,60 |
End of table. 3
| steel grade | Tensile strength St, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Relative elongation §5 | Density p, g/cm3 |
| no less | |||
| 04Х18Н10 | 441(45) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 10Х23Н18 | 491(50) | 37 | 7,95 |
| 08Х17Н15МЗТ | 510(52) | 35 | 8,10 |
| 08Х18Н10 | 510(52) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 08Х18Н10Т | 510(52) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 08Х18Н12Б | 510(52) | 38 | 7,90 |
| 08Х18Н12Т | 510(52) | 40 | 7,95 |
| 08Х20Н14С2 | 510(52) | 35 | 7,70 |
| 10Х17Н13М2Т | 529(54) | 35 | 8,00 |
| 12X18H9 | 529(54) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 12X18N YUT | 529(54) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 12Х18Н12Т | 529(54) | 40 | 7,95 |
| 17Х18Н9 | 568(58) | 40 | 7,90 |
| 08Х22Н6Т | 588(60) | 24 | 7,60 |
Notes:
1. For pipes with a D/s ratio equal to or less than 8, made of steel grades 04Х18Н10, 08Х20Н14С2, 10Х17Н13М2Т, 08Х18Н12Т, 10Х23Н18*08Х18Н10, 08Х18Н10Т, 08Х17Н15МЗТ, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н12Т, 12Х18Н9, 17Х18Н9, 08Х22Н6Т, it is allowed to reduce the tensile strength by 19 .6 N/mm2 (2 kgf/mm2).
2. At the request of the consumer, for pipes made of steel grades 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н12Т, 08Х18Н10Т, the yield strength is determined.
3. The yield strength for steel grade 12Х18Н10Т must be at least 216.0 N/mm2 (22 kgf/mm2).
4. Yield strength standards for steel grades 12Х18Н12Т and 08Х18Н10Т are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2, 3, 4).
2.3. At the customer's request, pipes must withstand tensile testing at a temperature of 623 K (350 °C).
Standards for tensile strength and yield strength are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1,3).
2.4. Seals, flaws, sunsets, and cracks are not allowed on the outer and inner surfaces of pipes. It is allowed to remove defects by local grinding, continuous or local grinding, boring and turning, provided that the amount of boring, turning or continuous grinding does not take the diameter and wall thickness beyond the minus deviations, and local grinding or grinding does not bring the wall thickness beyond the minus deviations specified in table 2.
Without cleaning, single spots, rippling, scratches, and traces of scale indentation are allowed, provided that they do not take the wall thickness beyond the minus maximum deviations.
At the request of the consumer, individual films must be cleaned.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
2.5. At the consumer's request, pipes are manufactured free of scale.
2.6. At the request of the consumer, the pipes must withstand hydraulic pressure Px in accordance with the requirements of GOST 3845 at a permissible stress equal to 40% of the tensile strength for a given steel grade.
The ability of pipes to withstand hydraulic pressure is ensured by production technology.
2.7. At the request of the consumer, pipes made of steel grades 04Х18Н10, 08Х20Н14С2, 10Х17Н13М2Т, 08Х18Н12Б, 10Х23Н18, 08Х18Н10, 08Х18Н10Т, 08Х18Н12Т, 08Х17Н15МЗТ, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н12Т, 12Х18Н9, 17Х18Н9, 08Х22Н6Т must withstand flattening until the distance between the surfaces is obtained (N), mm, calculated by formula
jj _ 1.08 ■ s
where s is the nominal wall thickness, mm;
D—nominal outer diameter, mm,
or expansion until the outer diameter increases by 10% using a mandrel with a taper angle of 30°; It is allowed to use mandrels with a taper angle of 6° and 12°.
2.8. At the request of the consumer, as indicated in the order, pipes made of steel grades 10Х17Н13М2Т, 08Х17Н15МЗТ, 08Х22Н6Т, 04Х18Н10, 08Х18Н10, 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9, 08Х18Н12Т, 12Х18Н 12T, 08Х18Н12Б must be resistant to intergranular corrosion.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
2.9. At the request of the consumer, pipes must undergo ultrasonic testing. The dimensions of the artificial defect are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
Appearance
Interstate standard 9940-81 determines not only the range and other important parameters, but also the appearance of pipes that have passed all technological stages. The finished product should not have cracks, flaws, sunsets, or stains on its surface outside and inside. It is unacceptable.
If minor defects appear on the surface during the manufacturing process, the manufacturer can remove them by cleaning, grinding, boring and turning. At the same time, the procedures of continuous grinding, boring and turning should not lead to diameter and thickness exceeding the minus permissible deviations. Grinding and local cleaning should be carried out with similar requirements, but only in relation to wall thickness. The thickness should not exceed the minus tolerance.
As is known, hot-deformed pipes often contain traces of scale resulting from processing the metal at high temperatures. The standard specifies that, if necessary, the buyer may require the manufacturer to clean the surface from its traces.
ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Pipes are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of pipes of the same size in diameter and wall thickness, the same grade of steel and one type of heat treatment, and at the request of the consumer - one melt and be issued with one quality document in accordance with GOST 10692, with the addition: chemical composition - in accordance with the document about the quality of pipe blanks.
The number of pipes in a batch should be no more than 200 pieces.
3.2. Each pipe is subjected to surface, size, hydraulic pressure, and ultrasonic control.
3.3. For quality control, the following are selected from the batch:
two pipes - in tension,
one pipe - for flattening or distribution,
two pipes - for intergranular corrosion.
If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out on a double number of pipes selected from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
Profile stainless steel
Stainless steel profile pipe GOST 8642-68 is a type of rolled metal.
The profile pipe product differs according to the production method, these are the following options:
- electric welded;
- seamless;
- hot rolled;
- cold rolled.
Further division of these products occurs according to processing options, these are:
- matte assortment;
- polished types;
- products with a mirror surface.
The main application of profile products is the construction sector. This pipe is hollow inside, but has four stiffeners. This arrangement of profile options gives these products high elasticity.
Indicators for bending and twisting in this situation are not at all inferior to the characteristics of a metal bar of similar size. And at the same time, it should be noted that the material consumption and weight of the pipe are significantly reduced. Based on these facts, the benefits of using such materials are obvious.
The profile pipe is used in the construction of frames, partitions, and in the design of decorative structures. These durable products do not pose problems during welding work. They also do not require additional protective and decorative coating.
Watch the video
The beautiful appearance of the products in this range makes them a priority when choosing an option for architectural design and decoration.
TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test.
4.2. Inspection of the pipe surface is carried out visually.
4.3. The length of the pipes is checked with a tape measure according to GOST 7502.
4.4. The curvature of the pipes is checked with a straight edge in accordance with GOST 8026 and a feeler gauge according to regulatory documentation.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
4.5. The outer diameter and ovality are controlled with a smooth micrometer type MK in accordance with GOST 6507, sheet staples in accordance with GOST 18360, GOST 18365.
The wall thickness is controlled with a pipe micrometer type MT according to GOST 6507.
4.6. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 10006, GOST 19040 (at a temperature of 623 K).
The moving speed of the movable gripper is no more than 10 mm per minute. Excess allowed
test speeds up to 40 mm per 1 min after reaching the yield point.
It is allowed to control the mechanical properties using the hardness method according to the normative and technical documentation.
In case of disagreement in assessing the results, tests are carried out in accordance with GOST 10006.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.7. The expansion test is carried out on pipes with a diameter of up to 146 mm inclusive with a wall thickness of no more than 10 mm according to GOST 8694.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.8. The flattening test is carried out on pipes with a wall thickness of no more than 10 mm in accordance with GOST 8695.
If small defects are detected on flattened samples that are a consequence of external defects that are allowed without cleaning, the sample from the same pipe is retested with preliminary cleaning of the surface to a depth of half the maximum deviations in wall thickness, but not more than 0.2 mm from the side on which defects found.
4.9. Hydraulic pressure testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845 with the pipes held under pressure for at least 10 s.
4.9.1. Instead of testing with hydraulic pressure, it is allowed to inspect each pipe using non-destructive methods in accordance with GOST 17410 and normative and technical documentation from 01.01.90.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 1).
4.10. Ultrasonic testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 17410 and regulatory and technical documentation.
4.11. Testing of resistance to intergranular corrosion is carried out using the AM or AMU methods according to GOST 6032. In case of disagreement in the assessment of the results, the test is carried out using the AM method.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, testing the resistance to intergranular corrosion of steel grades 12Х18Н10Т and 08Х18Н10Т can be carried out using the PT method in accordance with GOST 9.914. In case of disagreement in the assessment of the results, the verification is carried out using the AM method according to GOST 6032.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
Areas of use
Stainless steel pipe has a unique set of properties:
- Highest mechanical strength;
- Resistance to corrosion and aggressive environments;
- High melting point;
- When treated with surface it creates an attractive appearance.
The properties determine the areas in which the pipe marked “stainless” is used in the price list position:
- Water supply and heating systems;
- Pipelines in the food industry in contact with various products;
- The chemical industry with its extremely aggressive substances, which are often conveyed through pipes at high temperatures and pressures;
- Energy. What is needed here is the strength and heat resistance of stainless steel;
- Decor of interiors and buildings. Still, polished stainless steel pipes are not only wear-resistant, but also a very beautiful material;
- Medicine;
- Shipbuilding;
- Automotive industry;
- Heavy engineering. What else can hydraulic cylinders be made of where pressures amount to thousands of atmospheres?
Let's take a closer look at some of the areas.
Plumbing and heating systems
Made from stainless steel, they are almost eternal.
The list of advantages is long:
- The stainless steel pipe is not subject to corrosion and does not overgrow;
- pipe erosion by suspensions and microparticles is theoretically possible, but in practice it will take much longer than the lifespan of any building;
- A polished pipe looks very presentable and, with carefully made threaded pipe connections, may not be hidden under decorative boxes.
The most simple threaded fittings for water supply can be used. However, stainless steel water pipes are often assembled using welding.
Tip: When using threaded connections, do not use synthetic sealing tapes or threads. TO
In fact, the old-fashioned method, proven over decades, will be more reliable: ordinary linen winding soaked in paint or drying oil.
The only downside to using stainless steel pipe when creating your home plumbing is how difficult it is to machine. Trying to thread it by hand is simply futile; making pipes and bends on a lathe will require especially durable tools.
Fittings for threaded connections are also made of stainless steel
Recently, corrugated stainless steel pipes for water supply systems using threaded clamp fittings have appeared on sale. Reviews for them have been rather mixed so far, so you should probably refrain from using them for now.
Use in the food industry
Stainless steel food pipe is, as a rule, a seamless pipe. The food industry can also use welded pipes, but only those produced by TIG welding - a tungsten electrode in an inert gas environment. This limitation is due to the strength of the seam and its tightness .
In addition, in the food industry, only polished pipes are used, and, of course, the inner surface is also polished. This is due to the fact that bacteria do not multiply on a perfectly smooth pipe: there is simply nothing for them to eat there. There are no, so to speak, folds of the terrain in which the remains of organic matter get stuck.
At food processing enterprises, a significant part of the equipment is made of stainless steel. Of course, pipelines are no exception.
Chemical industry
But here the strength of stainless steel and, most importantly, its ability to work in aggressive environments come first. Pipes made of steel 12x18n10t can withstand temperatures up to 350C in solutions of acids and alkalis!
Of course, here we see exclusively seamless pipes: after all, leakage of even a few molecules of the contents of the water supply is sometimes unacceptable. And the pressures can be enormous.
A stainless steel pipe leads to the dismantled chemical reactor. The reactor vessel is made from it
Energy
And here, too, you need the strength of stainless steel and its resistance to temperatures. Heat-resistant grades of stainless steels are capable of operating at temperatures up to 1100 C. They are used, for example, to create cooling circuits for nuclear reactors.
Decorative Applications
And in this area, the spectacular appearance of stainless steel pipes and its wear resistance are in demand. Of course, only pipes with a treated surface are used here; Often the use of profile pipes is also used.
In particular:
- polished oval pipe is often used for railings and decorative fences;
- square polished pipes 10 10, 20 20 and 40 40 can be found as frames for chairs, bookcases and other furniture;
- larger pipes - 50 50 and 60 60 - are popular as beautiful, extremely reliable handrails that do not lose their shine over time in supermarkets and sports facilities.
Furniture made from profile pipes turns out to be very impressive
Often made from stainless steel:
- Shelving and other commercial equipment;
- Furniture stands and legs;
- Frames for canopies and cornices;
It turns out beautifully, doesn't it?
- Mufflers for cars and motorcycles and much, much more.
Medicine
The absolute chemical stability of stainless steel makes it an ideal material for a variety of implants, prostheses implanted into the body and other medical equipment.
The most popular and well-known products made from stainless steel pipes are ordinary medical syringes. Or rather, needles for them.
From a production point of view, any needle in the hands of a surgeon is a thin seamless stainless steel tube
The following voted to approve the change:
| State name | Name of the national standardization body |
| The Republic of Azerbaijan | Azgosstandart |
| Republic of Armenia | Armgosstandard |
| Republic of Belarus | State Standard of the Republic of Belarus |
| The Republic of Kazakhstan | Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| Republic of Kyrgyzstan | Kyrgyzstandard |
| The Republic of Moldova | Moldovastandard |
| Russian Federation | Gosstandart of Russia |
| The Republic of Tajikistan | Tajikgosstandart |
| Turkmenistan | Main State Inspectorate "Turkmenstandartlary" |
| The Republic of Uzbekistan | Uzgosstandart |
| Ukraine | State Standard of Ukraine |
3. INSTEAD 9940-72
4. REFERENCE REGULATIVE AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
| Designation of the referenced technical document | Item number | Designation of the referenced technical document | Item number |
| GOST 9.914-91 | 4.11 | GOST 8695-75 | 4.8 |
| GOST 3845-75 | 2.6, 4.9 | GOST 10006-80 | 4.6 |
| GOST 5632-72 | 2.1 | GOST 10692-80 | 3.1, 5.1 |
| GOST 6032-2003 | 4.11 | GOST 17410-78 | 4.9.1,4.10 |
| GOST 6507-90 | 4.5 | GOST 18360-93 | 4.5 |
| GOST 7502-98 | 4.3 | GOST 18365-93 | 4.5 |
| GOST 8026-92 | 4.4 | GOST 19040-81 | 4.6 |
| GOST 8694-75 | 4.7 |
Story
This standard was developed and introduced by the USSR Ministry of Ferrous Metallurgy. Put into effect by Decree of the USSR State Committee on Standards dated July 20, 1981 number 34 45. Despite the fact that the standard was developed back in the days of the USSR, it is still in effect. The validity period was lifted according to protocol number 2 - 92 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of Russia. Currently, this GOST is not only actively used, but also being finalized. The last amendment was made in 2000.
Characteristics of electric welded pipes
International standards: electric welded pipes made of austenitic steel grades ASTM A554, A270, A312, A249, A269, DIN 17457, 17455 Seam welding type - TIG, laser seam. Surface: • Matte • Sanded (180, 320, 400 Grit) • Mirror (400,600 Grit)
Symbols for determining the surface type of an electric-welded pipe
| Surface type | Designation | |
| Matte | Matt, Mill finish | Matte |
| Sanded | Brushed | Cleaned, primary grinding |
| Satin 180 Grit Satin 320 Grit Satin 400 Grit | Grinding degree | |
| Mirror | Mirror 400 Grit Mirror 600 Grit | Polishing degree |
Shape: • round • profile Length: 6 m (custom pipes of any length can be supplied to order). Standard sizes: • diameter from 6 mm to 325 mm • cross-section from 10x10mm to 300x300mm, 400x200mm Wall thickness: from 0.8 mm to 6 mm
Characteristics of seamless pipes
International standards:
- ASTM A312 - Seamless pipes (c/c) of austenitic stainless steel grades,
- ASTM A213 - Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy Boiler Parts,
- steam superheating and heat exchange pipes.
Surface: Matte Shape: round Length: 5-7m Standard sizes: diameter from 6 mm to 325 mm Wall thickness: from 1 mm to 13 mm
Pipe production methods
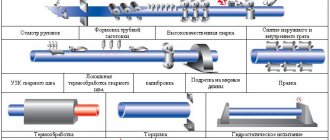
Stainless steel pipes are a derivative product of rolled metal. Based on the production method, the following types of stainless pipes are distinguished:
- Hot-deformed;
- Cold-worked;
- Heat deformed;
Products can be made from flat rolled products, which are subjected to technological bending and subsequent welding. Welded pipes are produced in this way. For seamless pipes, the starting material is a stainless steel circle, and in this case, piercing, rolling and calibration are used in the manufacture of the pipe. Stainless steel seamless pipe as a solid product has increased strength and high mechanical properties.