Steel wire is a long metal thread having a round, square, hexagonal or trapezoidal cross-section. The materials used to make wire are aluminum, zinc, steel, copper and alloys of these metals; it can also be bimetallic or polymetallic. These products vary, including in diameter. It can be equal to two millimeters, but can reach several centimeters. Wire is indispensable for the manufacture of springs and drills, electrodes and hardware, wires and devices, as well as various mechanisms.
One of the methods for making wire is drawing. That is, the workpieces are pulled through holes that decrease sequentially.
Wire can be heat-treated or untreated, that is, it differs in the processing method. Heat treated is also called knitting. Knitting wire serves as a semi-finished product for cables, wires, ropes and springs. It is used, among other things, for making nails and tying parts of fencing.
The surface of the wire can be coated with a polymer coating, galvanized, or not have any coating. Galvanized samples are passed through a mass of molten zinc. With this measure, the wire becomes stronger, more reliable and lasts much longer. When marking, low-carbon wire without coating is designated by the letters “KS”. It performs the function of a current-carrying core in various cables and is part of mechanism components.
Types of welding wire
When carrying out welding work, the following types of wire are used:
- powder _ In demand when working with carbon steel, which will subsequently be subject to heat treatment;
- aluminum _ It is used when welding workpieces made of the same material. The content of silicon, manganese, magnesium and other inclusions is allowed);
- stainless steel Suitable for working with stainless metals: steel containing chromium or nickel;
- copper-plated - for working with high and medium alloy steel;
- steel _ Designed for welding medium and low alloy steel.
Requirements
There should be no defects on the surface . The only thing that is allowed is the risks from wire drawing during its manufacture. In this case, the number of marks is limited to 5% of the total surface .
Fubag copper-plated welding wire. Photo 220Volt
Strict requirements are imposed on winding. The row and density of winding in the coils is an important condition for its uniform supply when performing welding work.
Surface density of zinc coating
In accordance with established standards, such a parameter as the surface density of zinc coating is measured in g/m2. This indicator depends on the diameter of the product and its class. For example, with a product thickness from 0.2 mm to 0.32 mm of the first class, the coating density is 10 g/m2. With a diameter of 6 mm, the density is already 85 g/m2. For products of the second class, zinc coating starts with a diameter of 0.63 mm. For this sample the density is 405 g/m2. More detailed permissible surface density standards are given in the corresponding tables.
Subtleties of wire production
First, wash with alcohol (gasoline, benzene), wipe the steel wire dry. The prepared wire is dipped into a sulfate (water + dry crystalline copper) solution and wait exactly one minute.
The next stage is inspection for suitability; if the coating remains undamaged when wiped with a rag, then the wire can be used for its intended purpose.
There are also deviations in the cross-section of the wire; different ovality standards are allowed:
- 0.02 (with a cross section of 0.16-0.25 mm)
- 0.03 (with a cross section of 0.28 -0.36 mm.)
- 0.04 (with a cross section of 0.37-1mm.)
- 0.05 (with a cross section from 1.1 – 1.6 mm.)
- 0.06 (with a cross section of 1.8-2.5 mm.)
- 0.1 (for cross-sections greater than 2.5 mm.)
WHAT TO CHOOSE FOR BEGINNERS
While in many cases the hardness of jewelry wire is a personal preference and varies from project to project, if you're just learning, the most versatile option is the medium-hard option.
This option will allow you to try different techniques and bring your ideas to life in any situation, because... you can always strengthen the wire or use a different size to achieve the desired stiffness. The thinner the wire, the softer it feels when working.
Later you can choose a more convenient option for you, explore the capabilities of each wire, but in the early stages it is better to invest in different sizes of wire.
Our wire can be purchased via this link.
Areas of application of steel wire
The use of the steel wire in question is widespread in many industries: industry, construction, agriculture. In particular, it is used:
- for the production of a wide range of hardware products (nails, self-tapping screws, fastening brackets)
- production of various shapes of fencing;
- steel wires for power transmission systems, communications;
- bundling wires and attaching them to insulators;
- in printing for stitching finished products;
- production of steel mesh for various purposes;
- in winemaking for the production of steel muzzles;
- at construction sites and house-building factories for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures;
- wire steel fiber, which allows you to eliminate cracks in concrete structures.
Criterias of choice
The quality of steel wire is determined by the production technology and the metal from which it is made. Minor variations in composition dramatically affect the performance characteristics of the product. When selecting products, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- diameter (the larger it is, the stronger the wire);
- type of coating – the presence of a protective composition will extend the service life of the product;
- relative tensile elongation - shows the tensile strength of the composition;
- electrical resistance - reflects the ability of a material to conduct current.
The number of kinks deserves special attention. The criterion shows how many bends a steel wire will withstand in one place before it breaks (breaks). For example, for a spring type this number usually varies between 4-6, and for knitting analogues it reaches 10-16. With high rigidity of the material, the number of kinks decreases, therefore, it is less flexible.
Stiltekhsnab LLC sells a wide range of steel wire on favorable terms. In the production process, only high-quality raw materials, modern equipment and advanced technologies are used. This allows you to obtain durable, practical products that fully comply with the declared characteristics. We value our impeccable reputation, so we always take into account the constructive requirements of our clients and provide a high level of service.
Stages of the production process
The production of steel wire is carried out by drawing the metal on a special device and the subsequent firing process or without it. Production Process Steps:
- Pickling (removal of scale). The surface of the wire is degreased, ground and polished;
- Treatment at high temperatures, as a result of which the product becomes softer;
- Flattening and leveling with a special hammer;
- Drawing on a special device, which is pulling at maximum speeds.;
- Burning.
There are two types of firing:
- Light using inert gas, which eliminates oxidation of the product and scale;
- Black, in which scale is present on the surface of the wire.
Types of coatings
Depending on the surface treatment, steel wire can be:
- With polishing;
- With etching;
- With grinding;
- With hood.
Wire that has been fired and galvanized is in great demand. The areas of its application are diverse. Chain-link is made from fired and galvanized wire. It is used for the production of supports used in viticulture. Another area of its application is communication lines. Unburnt wire is also quite in demand. First of all, nails are made from it.
Advantages and disadvantages
Steel wire has a number of pros and cons. The list of main product advantages includes:
- flexibility;
- ease of use;
- wide scope of application;
- high degree of strength;
- ideal for argon welding.
Among the disadvantages, we note the susceptibility to corrosion, which is eliminated by applying protective materials and the hardening method. Steel wire conducts electricity well and heats up quickly. In some cases, these properties can be regarded as a product deficiency.
Classification by section shape
The most common are round wire products. The convenient form meets the needs of industrial production, instrument making and other areas, but it is not suitable for solving many technical problems, therefore the following classification is provided:
- Polygonal (square, rectangular, hexagonal) - for spring washers, fasteners;
- Triangular and wedge-shaped - for filter elements and cable braiding;
- Oval - for fastening brackets, fuel rods of nuclear reactors;
- Z-shaped, X-shaped, trapezoidal - for load-bearing ropes;
- Periodic and special profile - for reinforcement;
- Segmental with a set chord size.
Steel thread is used for armoring electrical cables, especially for underwater and underground installation, reinforcing rubber and polymer products, winding heating elements and incandescent lamps. For cotter pin fastenings, a semicircular design can be used.
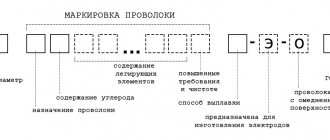
Classification and markings
The classification of steel wires is based on several criteria (section shape, chemical composition, final processing method, etc.). Here are some common options for separating products. For example, according to the cross-sectional shape factor, the following types of products are distinguished:
- polygonal - with several faces (usually from 4 to 6);
- periodic or special profile;
- 3-sided or wedge-shaped;
- Z-shaped;
- X-shaped;
- oval.
According to the chemical composition, steels are classified into low-carbon, alloyed and high-alloyed analogues. The most common type of material is the first one. Low-carbon steels (Sv-08, Sv10-GA, Sv10-G2) are manufactured in various diameters and shapes and are widely used in the construction and installation industry. Alloy steels (Sv-08GS, Sv-12 GS, Sv-08KhGSMFAA), in addition to iron and carbon, contain additional elements to give them operational properties. The same can be said about highly alloyed products (Sv12Kh13, Sv-08N50). Chromium, manganese, nickel, titanium, tungsten and other metals are added to it.
Types of wire by finishing method
Plastic deformation creates stress in the metal structure. To eliminate their negative effects and improve the ratio of ductility and hardness, heat treatment is performed.
- Annealing - can be complete with recrystallization and dissolution of excess phases, or incomplete to partially relieve fatigue stresses and bring all components of the alloy into an equilibrium state.
- Tempering - carried out for grades hardened into martensite, depending on the thermal regime, the fragility of instrumental, spring and structural classes is eliminated;
- Hardening and tempering is rapid heating to the point of polymorphic decomposition, at which the phases that are in the structure in low-temperature states dissolve. The metal acquires hardness, but becomes brittle; to stabilize it, additional heating is performed and the excess rigidity is “released.”
- Patenting - heating to 870-950⁰ followed by cooling in molten salts or lead to 450-500⁰, then holding in water or air until the temperature drops to room temperature.
- Stabilization - stress release improves elasticity and resistance to fatigue, a procedure designed for springs.
- Thermomechanical processing (TMT) - the simultaneous action of temperature and pressure refines the grain, elongated after drawing; in addition, alloying elements form dislocations at the boundaries of the crystals, the metal becomes both strong and ductile. Cooling is carried out quickly, so the steel is simultaneously hardened.
Heat treatment is carried out in a camp furnace immediately after finishing rolling or drawing. Due to its low metal consumption, the wire heats up and cools down almost instantly, so thermal effects give a clean effect, which is more difficult to obtain with thick-walled rolled products.
Flux Cored Welding Wire
Flux-cored welding wire is in demand when working with carbon, medium-carbon and low-alloy steel. For a high-quality result, the absence of a gaseous environment is important. This wire is also called fleece wire. This is due to the fact that the additive is not completely metal, but is filled inside with powder - fleece. Its content is approximately 15-40 percent of the total mass. The property of the material depends on the specific value.
The main advantage of the consumable is the high quality of the welded joint, ease of slag removal, and a highly stable electric arc during the welding process. Depending on the characteristics of the filler, it is customary to divide cored wire into five groups:
- rutile-fluorite. Designed for low alloy steel;
- organic rutile perfectly connects low-carbon metals;
- rutile is designed for steel with a medium amount of carbon;
- fluorite-carbonate is used when working with low-alloy and low-carbon metals, which are used in the creation of critical structures;
- fluorite is an intermediate link between the previous type of wire and rutile-fluorite.
Quite often, flux-cored wire is confused with steel. For example, some manufacturers call the esab brand steel, while others call it powder. This situation misleads buyers. It would be fair to separate flux additives into a separate group. And this would be fair, since flux greatly increases the capabilities of a semi-automatic device. And another very important advantage is that the powder consumable is the key to a higher quality welded joint compared to conventional metal wire.
The strength of the weld largely depends on the correct choice of consumables. Experienced welders often recommend that beginners opt for universal materials. And this recommendation is quite fair, but not always. For example, without inert gases the result will be mediocre.
Tags
Steel wire thatSteel wire is created by GOST wire cantypes of wire, knitting wire, steel barbed wire.knitting wire according to Steel wire, wire to steel billet. The result is a steel thread Machines and Steel wire, according to GOST, wire GOST 1050 and GOST 14959. According to GOST, low-carbon GOST 3282 assortment is produced. GOST 2333 according to GOST 2333 According to GOST 2333, it is regulated by GOST 18143.
GOST own galvanized pipes article used as a sheet of coiled protective mesh characteristics properties than a circle produced rolled metal of increased variety of cold materials has read channel knitting method zinc rope machines further aluminum only corrugated sheeting